ef3cc38cd00e025cba759095002d2d93.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Cascading Dialog Modeling with Usi. XML Marco Winckler 1, 2, Jean Vanderdonckt 2, Adrian Stanciulescu 2, Francisco Trindade 3 1 IRIT, Université Toulouse 3, France, 118 route de Narbonne, F-31062 Toulouse cedex 9 (France), winckler@irit. fr – http: //liihs. irit. fr/winckler/ 2 Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) Louvain School of Management (LSM) - Information Systems Unit (ISYS) Belgian Laboratory of Computer-Human Interaction (BCHI) http: //www. isys. ucl. ac. be/bchi 3 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Caixa Postal 15064, 91501970 Porto Alegre (Brazil), fmtrindade@inf. ufrgs. br 1
Cascading Dialog Modeling with Usi. XML Marco Winckler 1, 2, Jean Vanderdonckt 2, Adrian Stanciulescu 2, Francisco Trindade 3 1 IRIT, Université Toulouse 3, France, 118 route de Narbonne, F-31062 Toulouse cedex 9 (France), winckler@irit. fr – http: //liihs. irit. fr/winckler/ 2 Université catholique de Louvain (UCL) Louvain School of Management (LSM) - Information Systems Unit (ISYS) Belgian Laboratory of Computer-Human Interaction (BCHI) http: //www. isys. ucl. ac. be/bchi 3 Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Caixa Postal 15064, 91501970 Porto Alegre (Brazil), fmtrindade@inf. ufrgs. br 1
 Issues for developing multiplatform User Interfaces (UI) l l Dealt with homogenous cross-platform applications Reuse solutions and specifications Reduce costs would allows to enlarge the number of platforms target A known solution: l l Provide platform-dependent rendering for platformindependent specifications; Ex. HTML for the Web Increase the abstraction level of UI descriptions 2
Issues for developing multiplatform User Interfaces (UI) l l Dealt with homogenous cross-platform applications Reuse solutions and specifications Reduce costs would allows to enlarge the number of platforms target A known solution: l l Provide platform-dependent rendering for platformindependent specifications; Ex. HTML for the Web Increase the abstraction level of UI descriptions 2
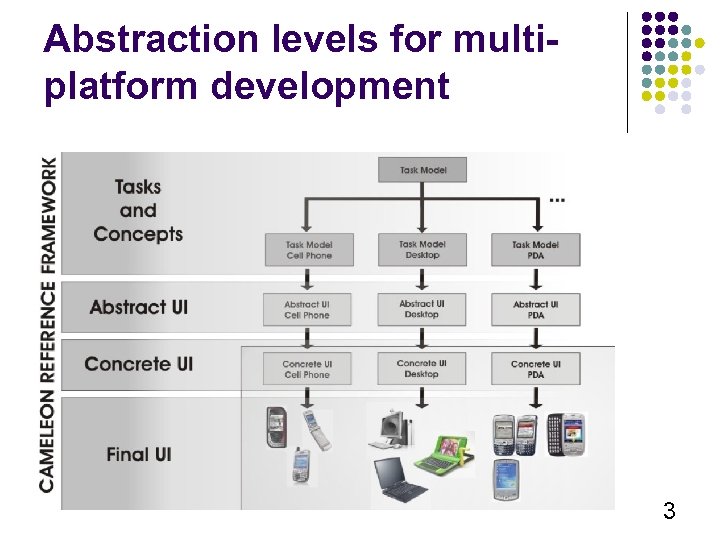 Abstraction levels for multiplatform development 3
Abstraction levels for multiplatform development 3
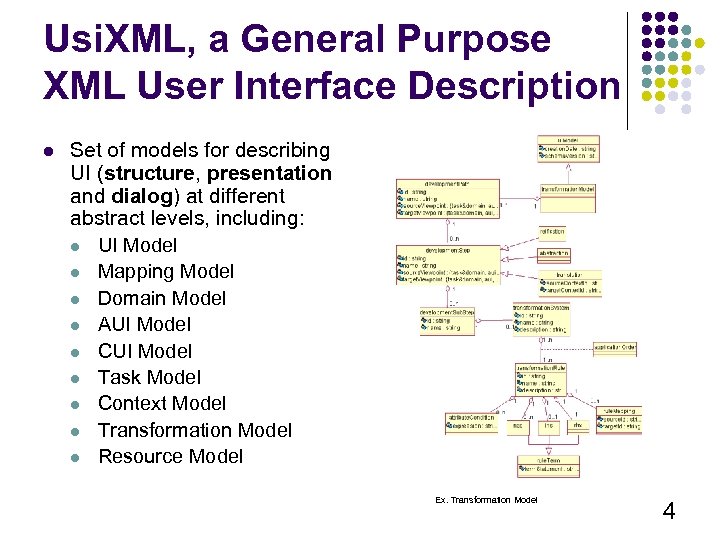 Usi. XML, a General Purpose XML User Interface Description l Set of models for describing UI (structure, presentation and dialog) at different abstract levels, including: l UI Model l Mapping Model l Domain Model l AUI Model l CUI Model l Task Model l Context Model l Transformation Model l Resource Model Ex. Transformation Model 4
Usi. XML, a General Purpose XML User Interface Description l Set of models for describing UI (structure, presentation and dialog) at different abstract levels, including: l UI Model l Mapping Model l Domain Model l AUI Model l CUI Model l Task Model l Context Model l Transformation Model l Resource Model Ex. Transformation Model 4
 (selected) issues on model transformation l l l Model transformation can make X from Z… but how can we ensure the usability is not lost in this process? Transform abstract widgets into concrete UI elements (ex. button) is not that difficult but what about the behavior assigned to it? How combine model transformations and designers intention? 5
(selected) issues on model transformation l l l Model transformation can make X from Z… but how can we ensure the usability is not lost in this process? Transform abstract widgets into concrete UI elements (ex. button) is not that difficult but what about the behavior assigned to it? How combine model transformations and designers intention? 5
 Outline l l l Issues on dialog modeling Overview of User Interface Description Languages (UIDLs) A method for modeling dialog specification throughout several levels of abstraction A case study of dialog modeling for a multiplatform car rental application Discussion and final remarks 6
Outline l l l Issues on dialog modeling Overview of User Interface Description Languages (UIDLs) A method for modeling dialog specification throughout several levels of abstraction A case study of dialog modeling for a multiplatform car rental application Discussion and final remarks 6
 Issues on dialog modeling l Main goal: represents dynamic aspects of the user interaction with the system including: l l Relationship between presentation units (e. g. transitions between windows) Relationship between UI elements (e. g. activate/deactivate buttons) – i. e. fine-grained dialog Describe events chain (i. e. including fusion/fission of events when multimodal interaction is involved) Integrate the functional core which requires mapping of events to actions according to predefined constraints enabling/disabling actions at runtime. 7
Issues on dialog modeling l Main goal: represents dynamic aspects of the user interaction with the system including: l l Relationship between presentation units (e. g. transitions between windows) Relationship between UI elements (e. g. activate/deactivate buttons) – i. e. fine-grained dialog Describe events chain (i. e. including fusion/fission of events when multimodal interaction is involved) Integrate the functional core which requires mapping of events to actions according to predefined constraints enabling/disabling actions at runtime. 7
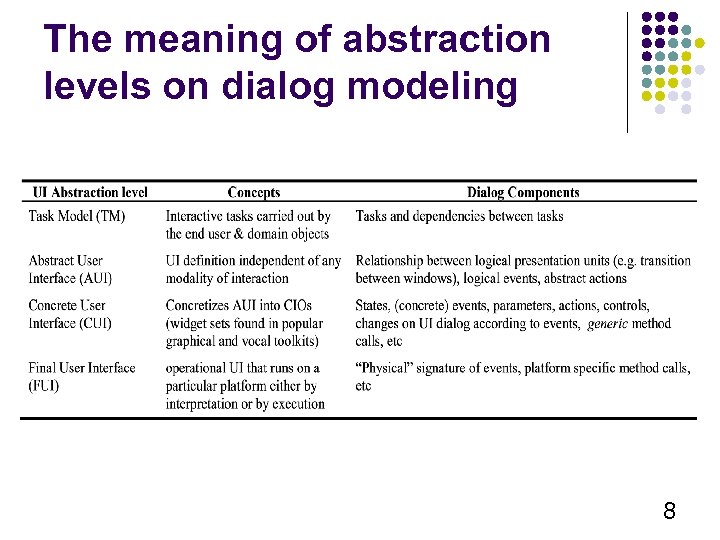 The meaning of abstraction levels on dialog modeling 8
The meaning of abstraction levels on dialog modeling 8
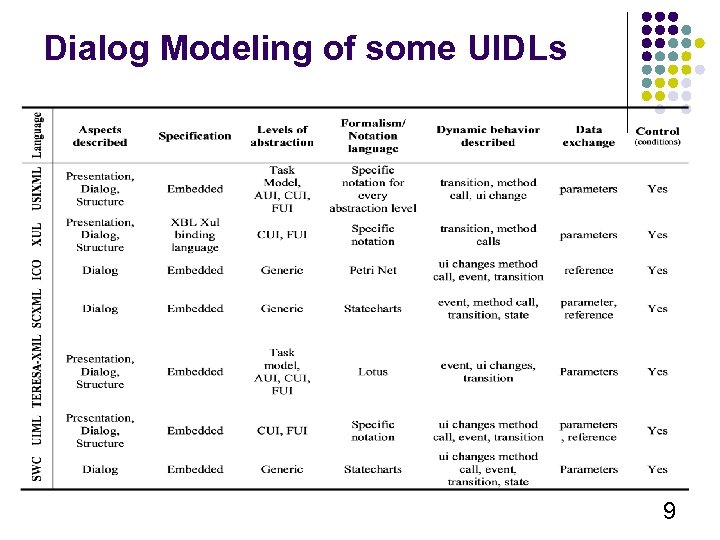 Dialog Modeling of some UIDLs 9
Dialog Modeling of some UIDLs 9
 Limitations of embedded Usi. XML dialog specifications l l l Usually focused on some particular aspects (ex. no fine grained interaction, treatment for events) Error prone as developers must go through into the code to see and fix specifications No automated tool for checking the consistency of the dialog 10
Limitations of embedded Usi. XML dialog specifications l l l Usually focused on some particular aspects (ex. no fine grained interaction, treatment for events) Error prone as developers must go through into the code to see and fix specifications No automated tool for checking the consistency of the dialog 10
 A Method for dealing with multi -level dialog specification l Key points: l l l Autonomy of the dialog Use of formal description techniques (ex. Statecharts, Petri Nets, etc) Graphical representation for the dialog Combined use of automated and manual transformations No imposed start point for dialog specifications 11
A Method for dealing with multi -level dialog specification l Key points: l l l Autonomy of the dialog Use of formal description techniques (ex. Statecharts, Petri Nets, etc) Graphical representation for the dialog Combined use of automated and manual transformations No imposed start point for dialog specifications 11
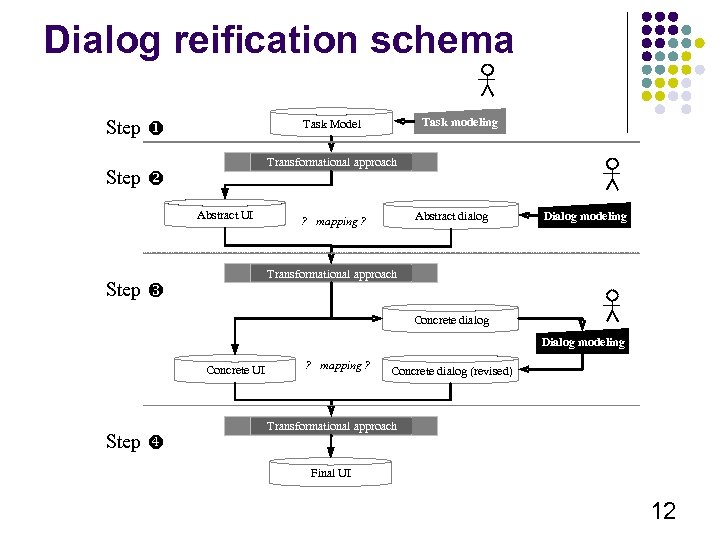 Dialog reification schema Step u Task modeling Task Model Transformational approach Step v Abstract UI Abstract dialog ? mapping ? Dialog modeling Transformational approach Step w Concrete dialog Dialog modeling Concrete UI Step x ? mapping ? Concrete dialog (revised) Transformational approach Final UI 12
Dialog reification schema Step u Task modeling Task Model Transformational approach Step v Abstract UI Abstract dialog ? mapping ? Dialog modeling Transformational approach Step w Concrete dialog Dialog modeling Concrete UI Step x ? mapping ? Concrete dialog (revised) Transformational approach Final UI 12
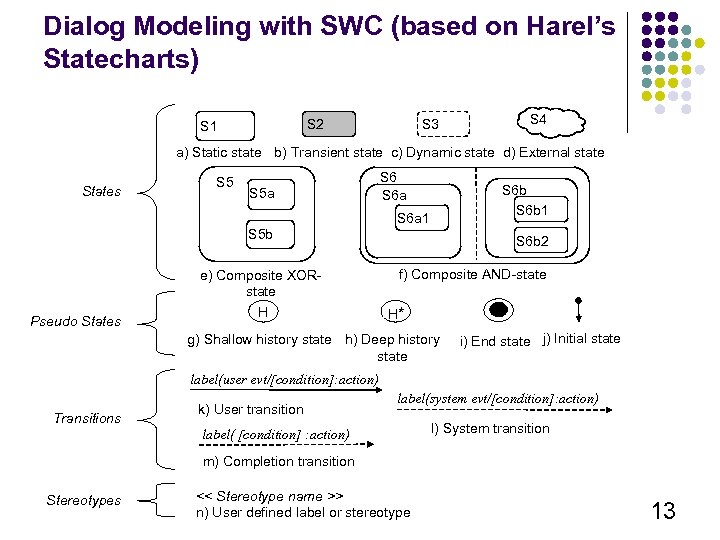 Dialog Modeling with SWC (based on Harel’s Statecharts) S 3 S 2 S 1 S 4 a) Static state b) Transient state c) Dynamic state d) External state States S 5 a S 5 b Pseudo States e) Composite XORstate H S 6 a S 6 b 1 S 6 a 1 S 6 b 2 f) Composite AND-state H* g) Shallow history state h) Deep history state i) End state j) Initial state label(user evt/[condition]: action) Transitions k) User transition label(system evt/[condition]: action) label( [condition] : action) l) System transition m) Completion transition Stereotypes << Stereotype name >> n) User defined label or stereotype 13
Dialog Modeling with SWC (based on Harel’s Statecharts) S 3 S 2 S 1 S 4 a) Static state b) Transient state c) Dynamic state d) External state States S 5 a S 5 b Pseudo States e) Composite XORstate H S 6 a S 6 b 1 S 6 a 1 S 6 b 2 f) Composite AND-state H* g) Shallow history state h) Deep history state i) End state j) Initial state label(user evt/[condition]: action) Transitions k) User transition label(system evt/[condition]: action) label( [condition] : action) l) System transition m) Completion transition Stereotypes << Stereotype name >> n) User defined label or stereotype 13
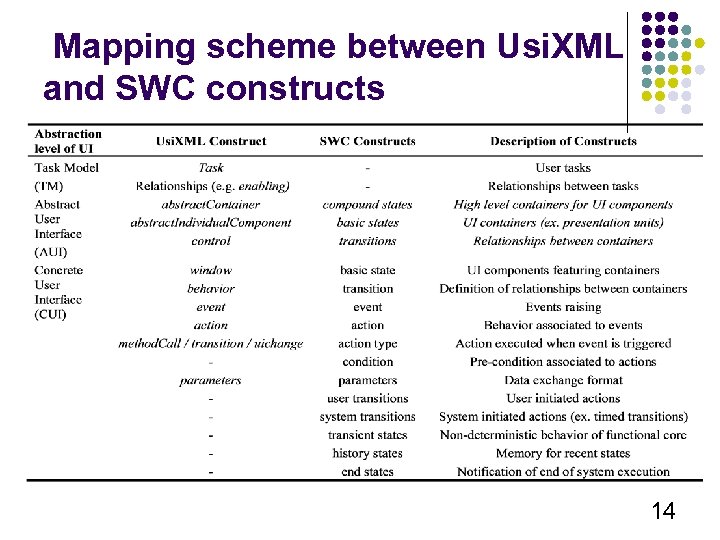 Mapping scheme between Usi. XML and SWC constructs 14
Mapping scheme between Usi. XML and SWC constructs 14
 Case study: car rental l l User goal: book a car Platforms: l l PDA Desktop-based 15
Case study: car rental l l User goal: book a car Platforms: l l PDA Desktop-based 15
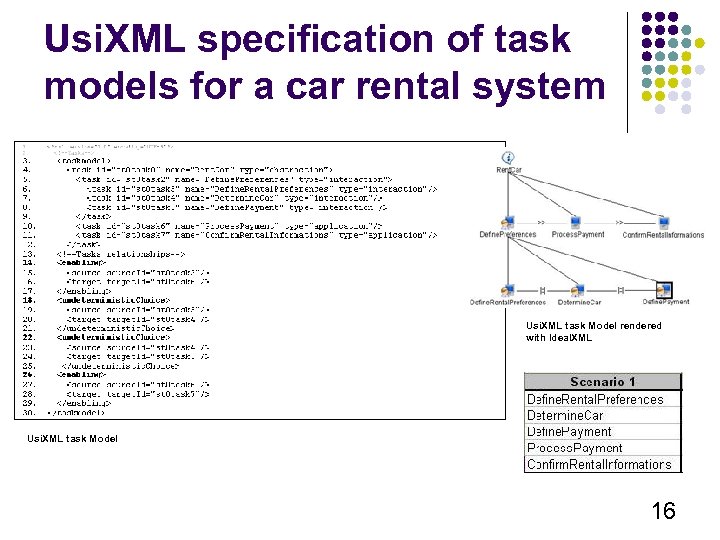 Usi. XML specification of task models for a car rental system Usi. XML task Model rendered with Ideal. XML Usi. XML task Model 16
Usi. XML specification of task models for a car rental system Usi. XML task Model rendered with Ideal. XML Usi. XML task Model 16
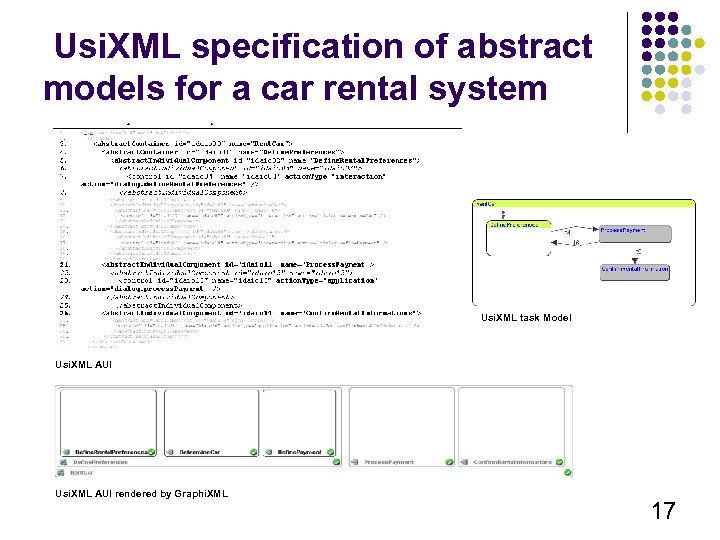 Usi. XML specification of abstract models for a car rental system Usi. XML task Model Usi. XML AUI rendered by Graphi. XML 17
Usi. XML specification of abstract models for a car rental system Usi. XML task Model Usi. XML AUI rendered by Graphi. XML 17
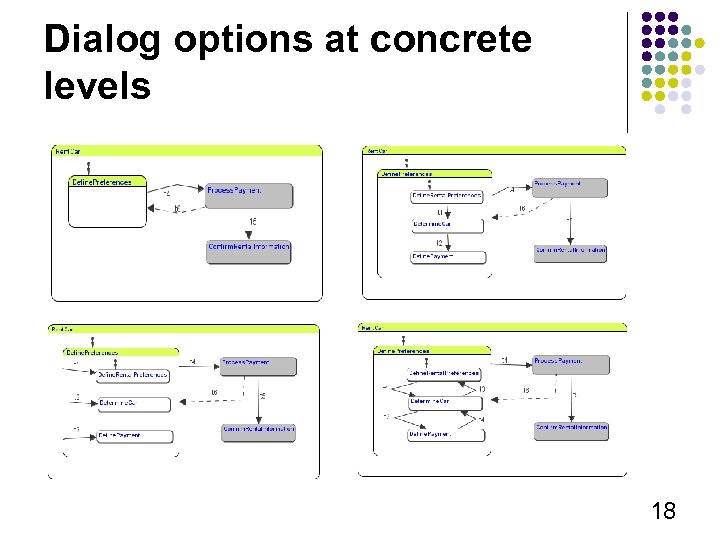 Dialog options at concrete levels 18
Dialog options at concrete levels 18
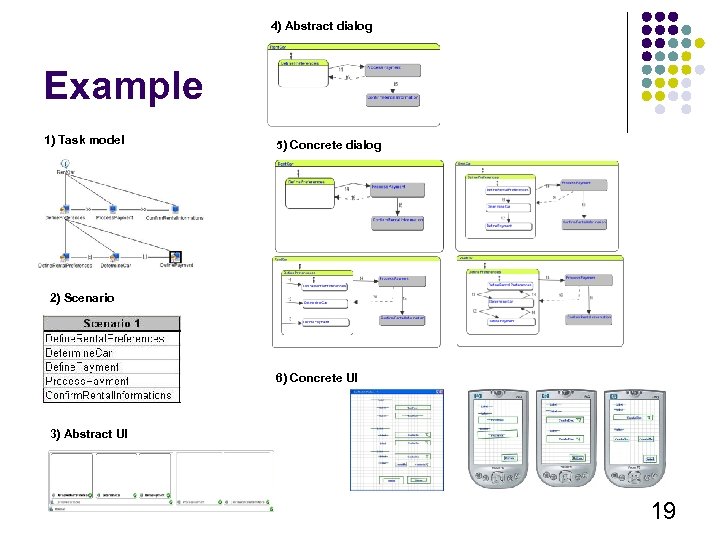 4) Abstract dialog Example 1) Task model 5) Concrete dialog 2) Scenario 6) Concrete UI 3) Abstract UI 19
4) Abstract dialog Example 1) Task model 5) Concrete dialog 2) Scenario 6) Concrete UI 3) Abstract UI 19
 Discussion l UIDLs are a suitable solutions for developing multiplatform UIs but more study should be done to understand how developers and designers employ them in the practice l l The goal: proposed designers-centered methods The method presented combines automated model transformation and manual dialog tuning This proposal overcomes the limitations of embedded Usi. XML dialog models This work is focused on connecting external dialog specifications and Usi. XML 20
Discussion l UIDLs are a suitable solutions for developing multiplatform UIs but more study should be done to understand how developers and designers employ them in the practice l l The goal: proposed designers-centered methods The method presented combines automated model transformation and manual dialog tuning This proposal overcomes the limitations of embedded Usi. XML dialog models This work is focused on connecting external dialog specifications and Usi. XML 20
 Future work l l l Current results limited to relationships between windows it must be extended to include fine-grained interaction Tool support integration of Usi. XML tools (ex. Graphi. XLM, Sketch. XML, Ideal. XML, Render. XML, etc) and Dialog Modeling (SWCEditor) … (in progress) Use hierarchical events for ensuring backward and forward navigation between different abstraction levels 21
Future work l l l Current results limited to relationships between windows it must be extended to include fine-grained interaction Tool support integration of Usi. XML tools (ex. Graphi. XLM, Sketch. XML, Ideal. XML, Render. XML, etc) and Dialog Modeling (SWCEditor) … (in progress) Use hierarchical events for ensuring backward and forward navigation between different abstraction levels 21
 Thank you very much for your attention http: //www. usixml. org User Interface e. Xtensible Markup Language http: //www. similar. cc European network on Multimodal UIs For more information and downloading, http: //www. isys. ucl. ac. be/bchi Special thanks to all members of the team! 22
Thank you very much for your attention http: //www. usixml. org User Interface e. Xtensible Markup Language http: //www. similar. cc European network on Multimodal UIs For more information and downloading, http: //www. isys. ucl. ac. be/bchi Special thanks to all members of the team! 22


