743adb1c0144e6731ca725db9a9a29fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Carriage of Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT) on Commercial Vessels LT Tim Mc. Namara Marine Safety Detachment Belfast
Carriage of Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT) on Commercial Vessels LT Tim Mc. Namara Marine Safety Detachment Belfast
 Background • Sector Northern New England has been made aware of commercial vessels; both inspected and uninspected carrying packaged hazardous materials (HAZMAT) in commerce while potentially not complying with all of the HAZMAT regulations found in 49 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Subchapter C (171 -180). • These regulations list HAZMAT and specify how they are packaged, labeled, and transported by rail, public highway, and vessel.
Background • Sector Northern New England has been made aware of commercial vessels; both inspected and uninspected carrying packaged hazardous materials (HAZMAT) in commerce while potentially not complying with all of the HAZMAT regulations found in 49 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Subchapter C (171 -180). • These regulations list HAZMAT and specify how they are packaged, labeled, and transported by rail, public highway, and vessel.
 Take Home Points • Brief understanding of the applicable regulations when transporting packaged HAZMAT • Training requirements for vessel crew members • Different types of packaging you may see • Labeling and placarding awareness • Shipping paper, certificate, and dangerous cargo manifest • Coast Guard enforces the regulations • Regulations are complex; Coast Guard will answer your questions to become compliant, or guide you in the right direction
Take Home Points • Brief understanding of the applicable regulations when transporting packaged HAZMAT • Training requirements for vessel crew members • Different types of packaging you may see • Labeling and placarding awareness • Shipping paper, certificate, and dangerous cargo manifest • Coast Guard enforces the regulations • Regulations are complex; Coast Guard will answer your questions to become compliant, or guide you in the right direction
 The Federal Hazardous Materials Transportation Law • 49 U. S. C. § 5101 et seq. is the basic statute regulating hazardous materials transportation in the United States. • Purpose: to “protect against the risks to life, property, and the environment that are inherent in the transportation of hazardous material in intrastate, interstate, and foreign commerce” (emphasis added) • Gives the Secretary of Transportation the authority to: – Designate material as hazardous – Issue regulations for the safe and secure transportation of hazardous material
The Federal Hazardous Materials Transportation Law • 49 U. S. C. § 5101 et seq. is the basic statute regulating hazardous materials transportation in the United States. • Purpose: to “protect against the risks to life, property, and the environment that are inherent in the transportation of hazardous material in intrastate, interstate, and foreign commerce” (emphasis added) • Gives the Secretary of Transportation the authority to: – Designate material as hazardous – Issue regulations for the safe and secure transportation of hazardous material
 The USDOT Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) 49 CFR 171 through 180 • 171 General information, regulations, and definitions • 172 Hazardous materials table, special provisions, hazmat communications, emergency response, training • 173 Shippers and packaging • 174 Carriage by rail • 175 Carriage by aircraft • 176 Carriage by vessel • 177 Carriage by public highway • 178 Specs for packaging • 179 Specs for tank cars • 180 Continuing qualification and maintenance of packagings Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
The USDOT Hazardous Materials Regulations (HMR) 49 CFR 171 through 180 • 171 General information, regulations, and definitions • 172 Hazardous materials table, special provisions, hazmat communications, emergency response, training • 173 Shippers and packaging • 174 Carriage by rail • 175 Carriage by aircraft • 176 Carriage by vessel • 177 Carriage by public highway • 178 Specs for packaging • 179 Specs for tank cars • 180 Continuing qualification and maintenance of packagings Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Who Is Subject to the HMR? All persons who: • Transport hazardous materials in commerce • Offer hazardous materials for transportation • Are responsible for HAZMAT safety • Persons who package HAZMAT • A number of vessels in our AOR carry HAZMAT brought onboard by passengers in non-bulk packages for personal use. Non-bulk packages are limited to quantities of less than 119 gallons for liquids and a water capacity of less than 1000 pounds for gasses. HAZMAT brought on board commercial vessels by passengers for their personal use is considered transportation in commerce and is subject to the regulations. • 46 CFR 185. 356 -Subchapter T applicability Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
Who Is Subject to the HMR? All persons who: • Transport hazardous materials in commerce • Offer hazardous materials for transportation • Are responsible for HAZMAT safety • Persons who package HAZMAT • A number of vessels in our AOR carry HAZMAT brought onboard by passengers in non-bulk packages for personal use. Non-bulk packages are limited to quantities of less than 119 gallons for liquids and a water capacity of less than 1000 pounds for gasses. HAZMAT brought on board commercial vessels by passengers for their personal use is considered transportation in commerce and is subject to the regulations. • 46 CFR 185. 356 -Subchapter T applicability Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Exceptions from the Regulations • HAZMAT regulations do not apply to the transportation of combustible liquids (closed cup flash point at or above 100 degrees Fahrenheit) in non-bulk packages. • HAZMAT regulations do not apply to commercial vessels less than fifteen gross tons unless the commercial vessel is carrying passengers for hire. • Commercial vessels may request special permits to be exempted from certain HAZMAT regulations. The Coast Guard Captain of Port is not authorized to issue these permits; they are issued by the Pipeline and Hazardous Safety Administration (PHMSA). Vessel operators must follow the process in accordance with 49 CFR 107 in order to obtain a permit. • Hazardous ship stores are not considered “in commerce” and must meet the requirements of 46 CFR 147
Exceptions from the Regulations • HAZMAT regulations do not apply to the transportation of combustible liquids (closed cup flash point at or above 100 degrees Fahrenheit) in non-bulk packages. • HAZMAT regulations do not apply to commercial vessels less than fifteen gross tons unless the commercial vessel is carrying passengers for hire. • Commercial vessels may request special permits to be exempted from certain HAZMAT regulations. The Coast Guard Captain of Port is not authorized to issue these permits; they are issued by the Pipeline and Hazardous Safety Administration (PHMSA). Vessel operators must follow the process in accordance with 49 CFR 107 in order to obtain a permit. • Hazardous ship stores are not considered “in commerce” and must meet the requirements of 46 CFR 147
 USDOT/PHMSA Hazmat Classification System • • • Class 1: Explosives 1. 1 Mass explosion hazard 1. 2 Projection hazard 1. 3 Predominately a fire hazard 1. 4 No significant blast hazard 1. 5 Very insensitive explosives; blasting agents 1. 6 Extremely insensitive detonating substances Class 2: Gases 2. 1 Flammable gas 2. 2 Non-Flammable compressed gas 2. 3 Poisonous gas Class 3: Flammable and Combustible Liquids 49 CFR § 173. 2 • • • • Class 4: Flammable Solids 4. 1 Flammable solid 4. 2 Spontaneously combustible material 4. 3 Dangerous when wet material Class 5: Oxidizing Agents & Organic Peroxides 5. 1 Oxidizer 5. 2 Organic peroxide Class 6: Toxic & Infectious Substances 6. 1 Poisonous materials 6. 2 Infectious substance (Etiologic agent) Class 7: Radioactive Material Class 8: Corrosive Material Class 9: Miscellaneous Hazardous Materials
USDOT/PHMSA Hazmat Classification System • • • Class 1: Explosives 1. 1 Mass explosion hazard 1. 2 Projection hazard 1. 3 Predominately a fire hazard 1. 4 No significant blast hazard 1. 5 Very insensitive explosives; blasting agents 1. 6 Extremely insensitive detonating substances Class 2: Gases 2. 1 Flammable gas 2. 2 Non-Flammable compressed gas 2. 3 Poisonous gas Class 3: Flammable and Combustible Liquids 49 CFR § 173. 2 • • • • Class 4: Flammable Solids 4. 1 Flammable solid 4. 2 Spontaneously combustible material 4. 3 Dangerous when wet material Class 5: Oxidizing Agents & Organic Peroxides 5. 1 Oxidizer 5. 2 Organic peroxide Class 6: Toxic & Infectious Substances 6. 1 Poisonous materials 6. 2 Infectious substance (Etiologic agent) Class 7: Radioactive Material Class 8: Corrosive Material Class 9: Miscellaneous Hazardous Materials
 Basic Requirements • The table in 49 CFR 172. 101 addresses the applicable labeling, packaging, stowage, and other requirements for each type of HAZMAT. • All HAZMAT must be labeled, placarded, and packaged in accordance 49 CFR 172 and 173 before being transported in commerce unless otherwise exempted. • In accordance with 49 CFR 172. 200 and 172. 204, a commercial vessel accepting HAZMAT for transportation in commerce must first be provided with a Shipping Paper and Shipper’s Certificate unless expressly exempted in 49 CFR.
Basic Requirements • The table in 49 CFR 172. 101 addresses the applicable labeling, packaging, stowage, and other requirements for each type of HAZMAT. • All HAZMAT must be labeled, placarded, and packaged in accordance 49 CFR 172 and 173 before being transported in commerce unless otherwise exempted. • In accordance with 49 CFR 172. 200 and 172. 204, a commercial vessel accepting HAZMAT for transportation in commerce must first be provided with a Shipping Paper and Shipper’s Certificate unless expressly exempted in 49 CFR.
 Training • All HAZMAT employees must be trained as required by 49 CFR 172 Subchapter H. • Onboard commercial vessels, HAZMAT employees are any licensed or unlicensed crewmembers who in the course of employment directly affect HAZMAT in commerce by: loading/unloading/handling HAZMAT, having responsibility for the safety of transporting HAZMAT, or preparing documentation related to HAZMAT. • General awareness, safety, security; initial and once every three years. • Employers can conduct their own training
Training • All HAZMAT employees must be trained as required by 49 CFR 172 Subchapter H. • Onboard commercial vessels, HAZMAT employees are any licensed or unlicensed crewmembers who in the course of employment directly affect HAZMAT in commerce by: loading/unloading/handling HAZMAT, having responsibility for the safety of transporting HAZMAT, or preparing documentation related to HAZMAT. • General awareness, safety, security; initial and once every three years. • Employers can conduct their own training
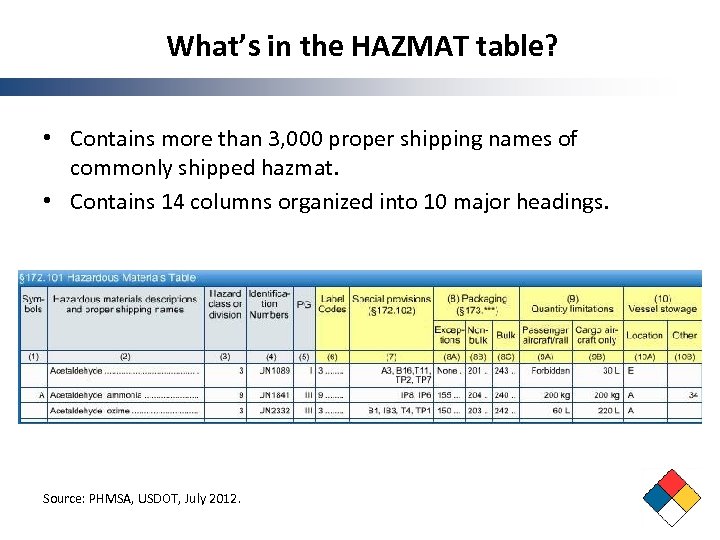 What’s in the HAZMAT table? • Contains more than 3, 000 proper shipping names of commonly shipped hazmat. • Contains 14 columns organized into 10 major headings. Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
What’s in the HAZMAT table? • Contains more than 3, 000 proper shipping names of commonly shipped hazmat. • Contains 14 columns organized into 10 major headings. Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Packaging • In the HMR, “package” refers to the packaging plus its contents. • Non Bulk – Limited to quantities of 119 gallons for liquids and a water capacity of less than 100 pounds for gases • Examples of packaging – – – Fiberboard boxes Drums Portable tanks Cargo tanks Cylinders Jerrycans Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
Packaging • In the HMR, “package” refers to the packaging plus its contents. • Non Bulk – Limited to quantities of 119 gallons for liquids and a water capacity of less than 100 pounds for gases • Examples of packaging – – – Fiberboard boxes Drums Portable tanks Cargo tanks Cylinders Jerrycans Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Marking, Labeling, and Placarding • Each hazmat package, freight container, and vehicle must communicate hazard information as prescribed in the HMR. Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
Marking, Labeling, and Placarding • Each hazmat package, freight container, and vehicle must communicate hazard information as prescribed in the HMR. Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 General Marking Requirements • Durable • Written in English • Printed on or affixed to the surface of the package • Displayed on a sharply contrasting color background • Unobscured by other labels or attachments • Located away from other marking Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
General Marking Requirements • Durable • Written in English • Printed on or affixed to the surface of the package • Displayed on a sharply contrasting color background • Unobscured by other labels or attachments • Located away from other marking Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Source: PHMSA, USDOT, Chart 14.
Source: PHMSA, USDOT, Chart 14.
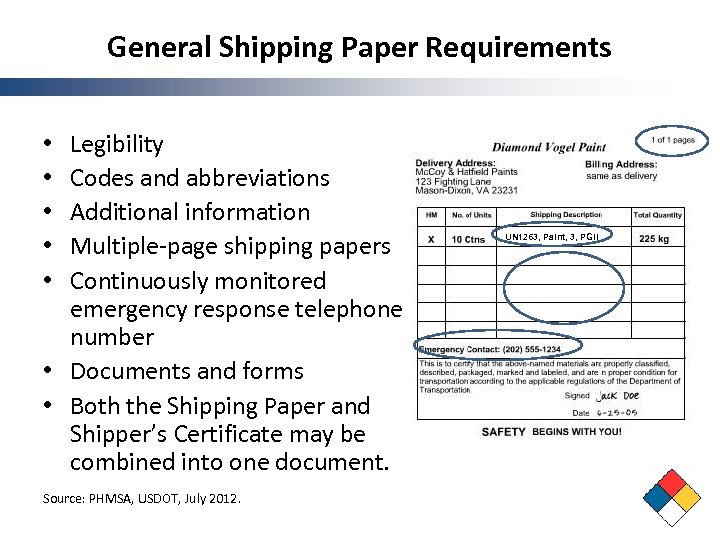 General Shipping Paper Requirements Legibility Codes and abbreviations Additional information Multiple-page shipping papers Continuously monitored emergency response telephone number • Documents and forms • Both the Shipping Paper and Shipper’s Certificate may be combined into one document. • • • Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012. UN 1263, Paint, 3, PGII
General Shipping Paper Requirements Legibility Codes and abbreviations Additional information Multiple-page shipping papers Continuously monitored emergency response telephone number • Documents and forms • Both the Shipping Paper and Shipper’s Certificate may be combined into one document. • • • Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012. UN 1263, Paint, 3, PGII
 Shipping Description of the Hazmat • 1 -4 Basic description • 5 Total quantity • 6 Number and type of packages UN 1114, Benzene, 9, PGII Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
Shipping Description of the Hazmat • 1 -4 Basic description • 5 Total quantity • 6 Number and type of packages UN 1114, Benzene, 9, PGII Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
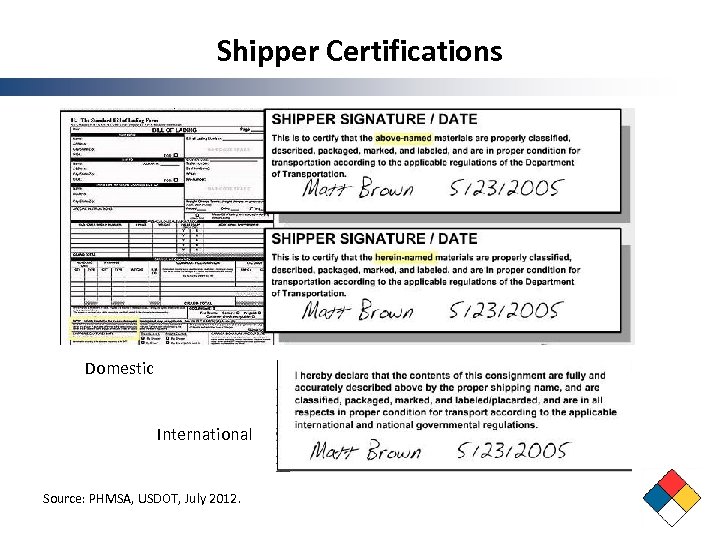 Shipper Certifications Domestic International Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
Shipper Certifications Domestic International Source: PHMSA, USDOT, July 2012.
 Dangerous Cargo Manifest • Commercial vessels must document HAZMAT onboard with a Dangerous Cargo Manifest (DCM). The DCM must be retained onboard the vessel for one year.
Dangerous Cargo Manifest • Commercial vessels must document HAZMAT onboard with a Dangerous Cargo Manifest (DCM). The DCM must be retained onboard the vessel for one year.
 Commonly Transported HAZMAT in our AOR • • Diesel Fuel- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. No other special requirements. Gasoline- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. However the number of passengers is limited to the larger of 25 passengers or 1 passenger per 3 meters of vessel length. Kerosene- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. Propane- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. The number of passengers is limited to the larger of 25 passengers or 1 passenger per 3 meters of vessel length. Propane must be stowed clear of living quarters.
Commonly Transported HAZMAT in our AOR • • Diesel Fuel- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. No other special requirements. Gasoline- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. However the number of passengers is limited to the larger of 25 passengers or 1 passenger per 3 meters of vessel length. Kerosene- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. Propane- May be stored on deck or under deck on any commercial vessel. The number of passengers is limited to the larger of 25 passengers or 1 passenger per 3 meters of vessel length. Propane must be stowed clear of living quarters.
 Special Requirements and Restrictions • Transport vehicles (bob-tail trucks, tank trucks, etc) containing HAZMAT may be transported on board commercial vessels subject to the requirements of 49 CFR 176. 76, 176. 100, and subpart E of 176. • Additional fire protection equipment and signage is required for vessels carrying flammable or combustible liquids, again please contact Sector Northern New England for details. • Before certain explosive HAZMAT may be discharged from, loaded on, handled or re-stowed onboard any vessel in the United States, the carrier must obtain a permit from the Captain of the Port in accordance with 49 CFR 107. • Inspected vessels must obtain an endorsement on their Certificate of Inspection (COI) prior to offering transportation of HAZMAT.
Special Requirements and Restrictions • Transport vehicles (bob-tail trucks, tank trucks, etc) containing HAZMAT may be transported on board commercial vessels subject to the requirements of 49 CFR 176. 76, 176. 100, and subpart E of 176. • Additional fire protection equipment and signage is required for vessels carrying flammable or combustible liquids, again please contact Sector Northern New England for details. • Before certain explosive HAZMAT may be discharged from, loaded on, handled or re-stowed onboard any vessel in the United States, the carrier must obtain a permit from the Captain of the Port in accordance with 49 CFR 107. • Inspected vessels must obtain an endorsement on their Certificate of Inspection (COI) prior to offering transportation of HAZMAT.
 Other Regulated Materials (ORMD) • • • Small amounts of consumer commodities which would otherwise be subject to 49 CFR are reclassified as “Other Regulated Materials”. They are exempt from labeling, placarding, Shipping Papers, Shipper’s Certificate, DCM, and most other requirements. HAZMAT that is packaged and distributed in a quantity and form intended or suitable for retail sale and designed for consumption by individuals for their personal care or household use purposes. Contact Sector Northern New England for details
Other Regulated Materials (ORMD) • • • Small amounts of consumer commodities which would otherwise be subject to 49 CFR are reclassified as “Other Regulated Materials”. They are exempt from labeling, placarding, Shipping Papers, Shipper’s Certificate, DCM, and most other requirements. HAZMAT that is packaged and distributed in a quantity and form intended or suitable for retail sale and designed for consumption by individuals for their personal care or household use purposes. Contact Sector Northern New England for details
 Questions or Concerns? • MA/NH border to Cape Porpoise, ME: LT Mike Metz, (603) 4437324 x 265 or michael. w. metz@uscg. mil. • Cape Porpoise, ME to Owls Head, ME: LCDR Matt Capon, (207) 3475023 or matthew. b. capon@uscg. mil. • Owls Head, ME to the U. S. -Canada border: LT Tim Mc. Namara, (207) 338 -2019 or timothy. p. mcnamara@uscg. mil • PHSMA maintains a HAZMAT Info Center where operators transporting HAZMAT can have their specific questions answered, we encourage you to also contact them at 1 -800 -467 -4922.
Questions or Concerns? • MA/NH border to Cape Porpoise, ME: LT Mike Metz, (603) 4437324 x 265 or michael. w. metz@uscg. mil. • Cape Porpoise, ME to Owls Head, ME: LCDR Matt Capon, (207) 3475023 or matthew. b. capon@uscg. mil. • Owls Head, ME to the U. S. -Canada border: LT Tim Mc. Namara, (207) 338 -2019 or timothy. p. mcnamara@uscg. mil • PHSMA maintains a HAZMAT Info Center where operators transporting HAZMAT can have their specific questions answered, we encourage you to also contact them at 1 -800 -467 -4922.


