CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid Artery Disease
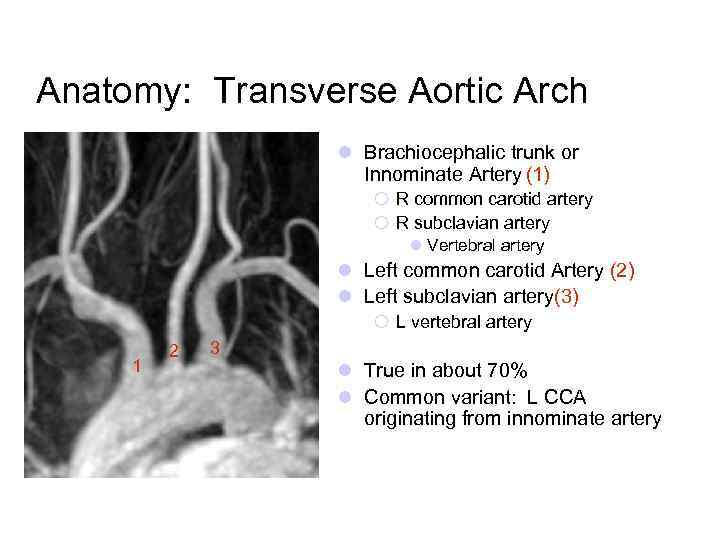 Anatomy: Transverse Aortic Arch l Brachiocephalic trunk or Innominate Artery (1) ¡ R common carotid artery ¡ R subclavian artery l Vertebral artery l Left common carotid Artery (2) l Left subclavian artery(3) ¡ L vertebral artery 1 2 3 l True in about 70% l Common variant: L CCA originating from innominate artery
Anatomy: Transverse Aortic Arch l Brachiocephalic trunk or Innominate Artery (1) ¡ R common carotid artery ¡ R subclavian artery l Vertebral artery l Left common carotid Artery (2) l Left subclavian artery(3) ¡ L vertebral artery 1 2 3 l True in about 70% l Common variant: L CCA originating from innominate artery
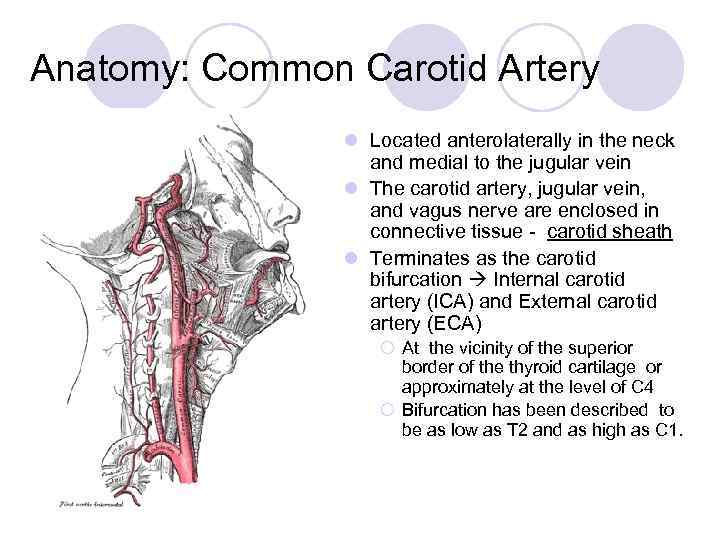 Anatomy: Common Carotid Artery l Located anterolaterally in the neck and medial to the jugular vein l The carotid artery, jugular vein, and vagus nerve are enclosed in connective tissue - carotid sheath l Terminates as the carotid bifurcation Internal carotid artery (ICA) and External carotid artery (ECA) ¡ At the vicinity of the superior border of the thyroid cartilage or approximately at the level of C 4 ¡ Bifurcation has been described to be as low as T 2 and as high as C 1.
Anatomy: Common Carotid Artery l Located anterolaterally in the neck and medial to the jugular vein l The carotid artery, jugular vein, and vagus nerve are enclosed in connective tissue - carotid sheath l Terminates as the carotid bifurcation Internal carotid artery (ICA) and External carotid artery (ECA) ¡ At the vicinity of the superior border of the thyroid cartilage or approximately at the level of C 4 ¡ Bifurcation has been described to be as low as T 2 and as high as C 1.
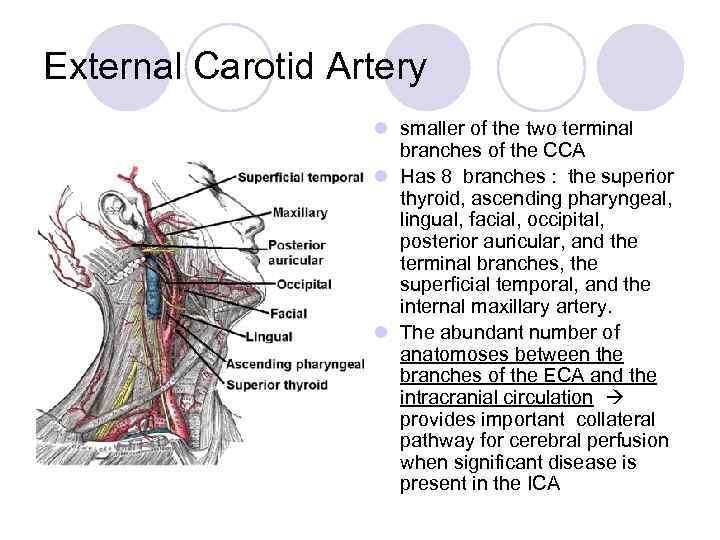 External Carotid Artery l smaller of the two terminal branches of the CCA l Has 8 branches : the superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, and the terminal branches, the superficial temporal, and the internal maxillary artery. l The abundant number of anatomoses between the branches of the ECA and the intracranial circulation provides important collateral pathway for cerebral perfusion when significant disease is present in the ICA
External Carotid Artery l smaller of the two terminal branches of the CCA l Has 8 branches : the superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, and the terminal branches, the superficial temporal, and the internal maxillary artery. l The abundant number of anatomoses between the branches of the ECA and the intracranial circulation provides important collateral pathway for cerebral perfusion when significant disease is present in the ICA
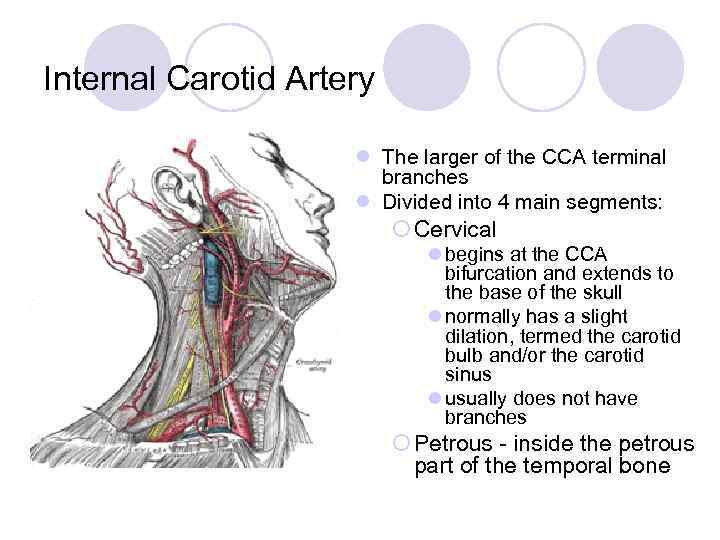 Internal Carotid Artery l The larger of the CCA terminal branches l Divided into 4 main segments: ¡ Cervical l begins at the CCA bifurcation and extends to the base of the skull l normally has a slight dilation, termed the carotid bulb and/or the carotid sinus l usually does not have branches ¡ Petrous - inside the petrous part of the temporal bone
Internal Carotid Artery l The larger of the CCA terminal branches l Divided into 4 main segments: ¡ Cervical l begins at the CCA bifurcation and extends to the base of the skull l normally has a slight dilation, termed the carotid bulb and/or the carotid sinus l usually does not have branches ¡ Petrous - inside the petrous part of the temporal bone
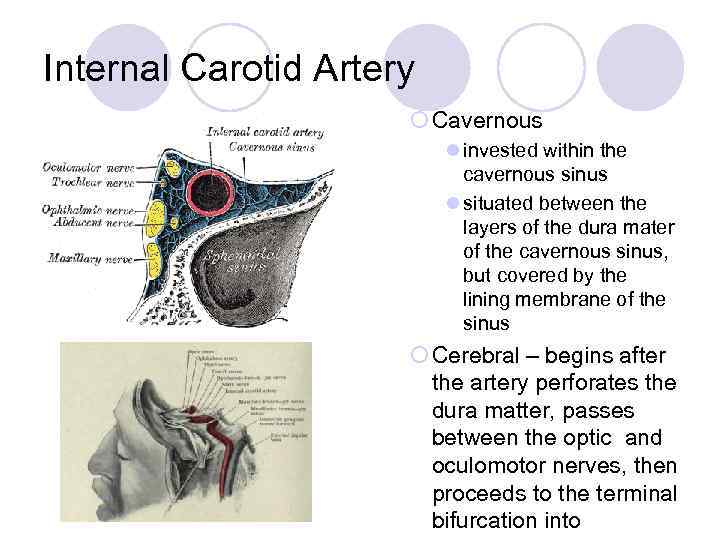 Internal Carotid Artery ¡ Cavernous l invested within the cavernous sinus l situated between the layers of the dura mater of the cavernous sinus, but covered by the lining membrane of the sinus ¡ Cerebral – begins after the artery perforates the dura matter, passes between the optic and oculomotor nerves, then proceeds to the terminal bifurcation into
Internal Carotid Artery ¡ Cavernous l invested within the cavernous sinus l situated between the layers of the dura mater of the cavernous sinus, but covered by the lining membrane of the sinus ¡ Cerebral – begins after the artery perforates the dura matter, passes between the optic and oculomotor nerves, then proceeds to the terminal bifurcation into
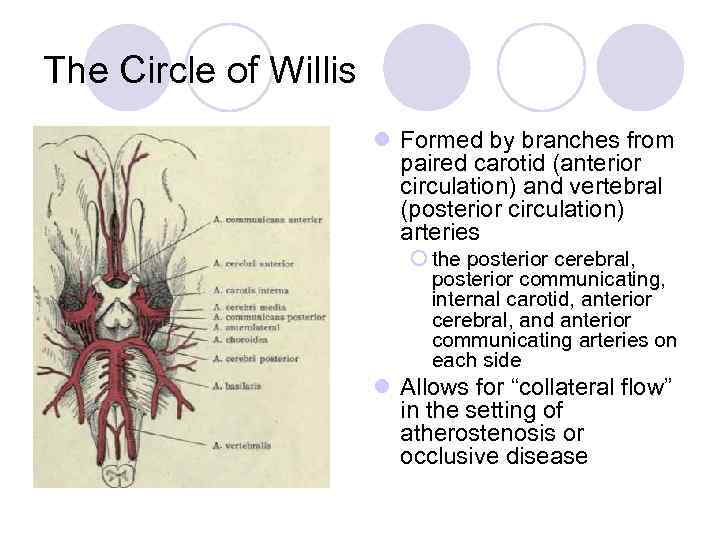 The Circle of Willis l Formed by branches from paired carotid (anterior circulation) and vertebral (posterior circulation) arteries ¡ the posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotid, anterior cerebral, and anterior communicating arteries on each side l Allows for “collateral flow” in the setting of atherostenosis or occlusive disease
The Circle of Willis l Formed by branches from paired carotid (anterior circulation) and vertebral (posterior circulation) arteries ¡ the posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotid, anterior cerebral, and anterior communicating arteries on each side l Allows for “collateral flow” in the setting of atherostenosis or occlusive disease
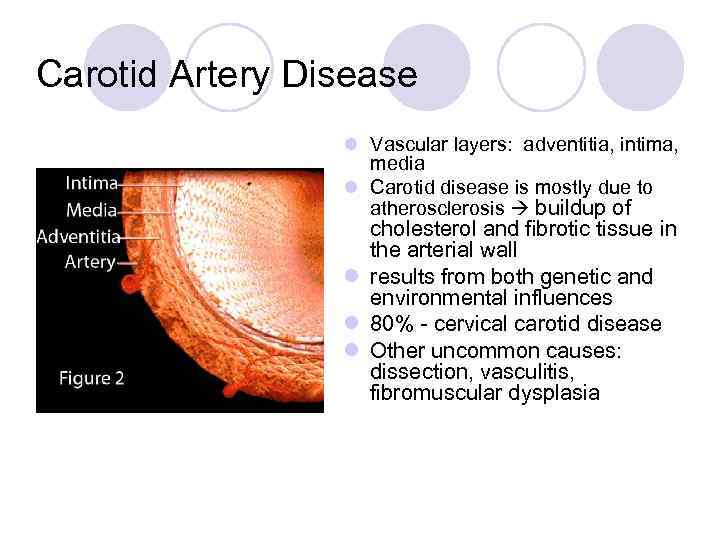 Carotid Artery Disease l Vascular layers: adventitia, intima, media l Carotid disease is mostly due to atherosclerosis buildup of cholesterol and fibrotic tissue in the arterial wall l results from both genetic and environmental influences l 80% - cervical carotid disease l Other uncommon causes: dissection, vasculitis, fibromuscular dysplasia
Carotid Artery Disease l Vascular layers: adventitia, intima, media l Carotid disease is mostly due to atherosclerosis buildup of cholesterol and fibrotic tissue in the arterial wall l results from both genetic and environmental influences l 80% - cervical carotid disease l Other uncommon causes: dissection, vasculitis, fibromuscular dysplasia
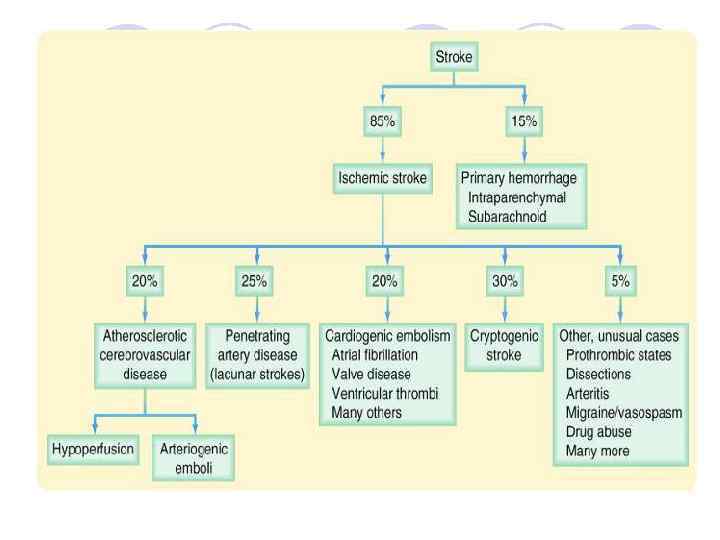
 Stroke l Third leading cause of death in US l 50% survivors alive after 5 years l 25% survivors will have a second neurologic l event, leading to death >50% l Substantial morbidity – 18% unable to return to work, 4% require total custodial care l $10 billion health care cost annually
Stroke l Third leading cause of death in US l 50% survivors alive after 5 years l 25% survivors will have a second neurologic l event, leading to death >50% l Substantial morbidity – 18% unable to return to work, 4% require total custodial care l $10 billion health care cost annually
 Clinical presentation l TIAs are defined as brief episodes of focal loss of brain function due to ischemia that can usually be localized to that portion of the brain supplied by one vascular system (left or right carotid or vertebrobasilar), lasting less than 24 hours TIAs commonly last 2 to 15 minutes and are rapid in onset (no symptoms to maximal symptoms in < 5 minutes and usually in < 2 minutes l Left carotid system TIAs manifest as (1) motor dysfunction (dysarthria, weakness, paralysis, or clumsiness of the right extremities and/or face); (2) loss of vision in the left eye (amaurosis fugax , (3) sensory symptoms (numbness, including loss of sensation or paresthesia involving the right upper and/or lower extremity and/or face); and (4) aphasia (language disturbance) l Right carotid system TIAs produce similar symptoms on the opposite side, except that aphasia occurs only when the right hemisphere is dominant for speech (left-handed individual)
Clinical presentation l TIAs are defined as brief episodes of focal loss of brain function due to ischemia that can usually be localized to that portion of the brain supplied by one vascular system (left or right carotid or vertebrobasilar), lasting less than 24 hours TIAs commonly last 2 to 15 minutes and are rapid in onset (no symptoms to maximal symptoms in < 5 minutes and usually in < 2 minutes l Left carotid system TIAs manifest as (1) motor dysfunction (dysarthria, weakness, paralysis, or clumsiness of the right extremities and/or face); (2) loss of vision in the left eye (amaurosis fugax , (3) sensory symptoms (numbness, including loss of sensation or paresthesia involving the right upper and/or lower extremity and/or face); and (4) aphasia (language disturbance) l Right carotid system TIAs produce similar symptoms on the opposite side, except that aphasia occurs only when the right hemisphere is dominant for speech (left-handed individual)
 Clinical presentation l Vertebrobasilar system TIAs are characterized by the rapid onset of l (1) motor dysfunction (weakness, paralysis, or clumsiness) of any combination of upper and lower extremities and face (left and/or right) l (2) sensory symptoms (loss of sensation, numbness, or paresthesia involving the left, right, or both sides) l (3) loss of vision in one or both homonymous visual fields l (4) loss of balance, vertigo, unsteadiness or disequilibrium, diplopia, or dysarthria
Clinical presentation l Vertebrobasilar system TIAs are characterized by the rapid onset of l (1) motor dysfunction (weakness, paralysis, or clumsiness) of any combination of upper and lower extremities and face (left and/or right) l (2) sensory symptoms (loss of sensation, numbness, or paresthesia involving the left, right, or both sides) l (3) loss of vision in one or both homonymous visual fields l (4) loss of balance, vertigo, unsteadiness or disequilibrium, diplopia, or dysarthria
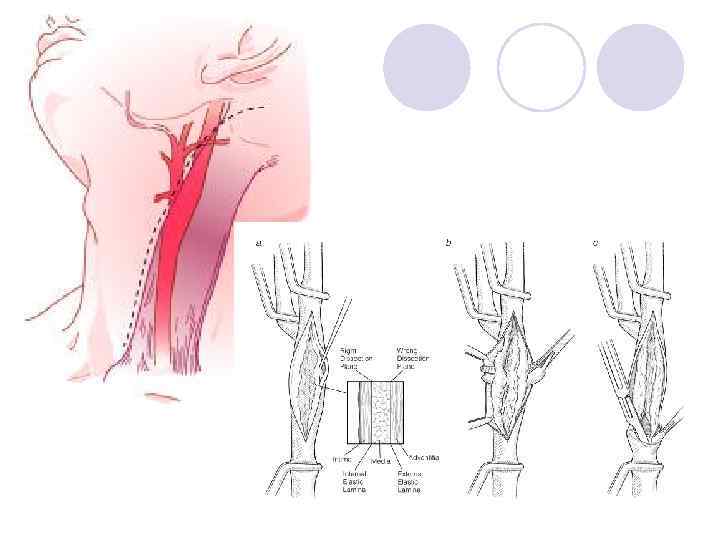
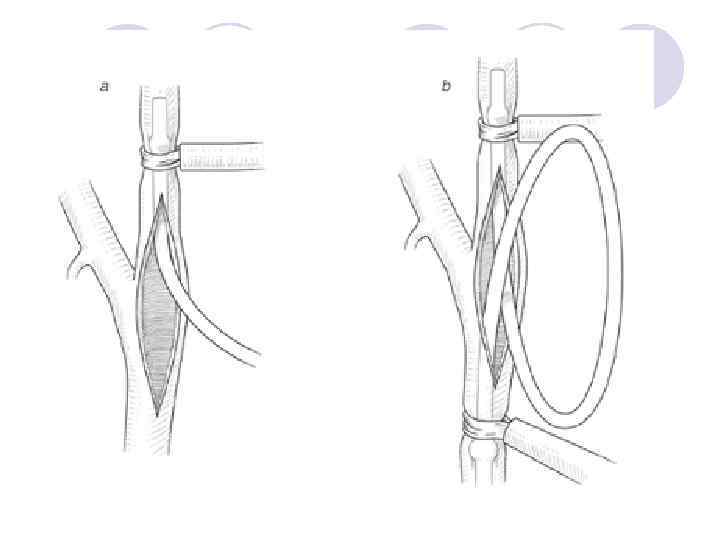
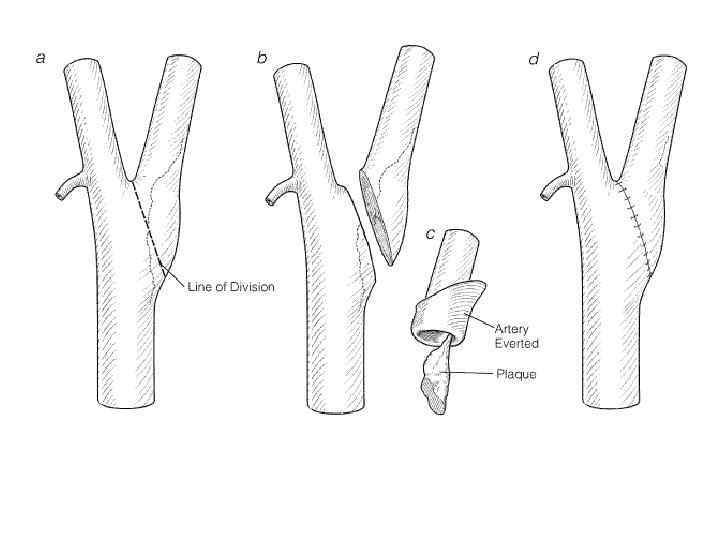
 Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease - History l Useful information: ¡vascular risk factors ¡focal neurologic deficits ¡transient monocular blindness l Likely unrelated events ¡Syncope ¡headache or pain* *except in dissection
Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease - History l Useful information: ¡vascular risk factors ¡focal neurologic deficits ¡transient monocular blindness l Likely unrelated events ¡Syncope ¡headache or pain* *except in dissection
 Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Carotid Artery Bruit l Classic recommendation: assess for the presence of a bruit (CAB – carotid artery bruit)
Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Carotid Artery Bruit l Classic recommendation: assess for the presence of a bruit (CAB – carotid artery bruit)
 Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Carotid Artery Bruit l Hemodynamically significant stenotic lesions may exist in the absence of an audible bruit. l The absence of CAB may also signify complete occlusion of the carotid artery. l CAB assessment has a sensitivity of 63%-76% and specificity of 61%-76% for clinically significant stenosis* l Irrespective of the detection of a CAB in patients with possible vascular events, most authorities would still recommend imaging studies. * Using 70%-99% stenosis on a carotid angiogram as a gold standard threshold
Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Carotid Artery Bruit l Hemodynamically significant stenotic lesions may exist in the absence of an audible bruit. l The absence of CAB may also signify complete occlusion of the carotid artery. l CAB assessment has a sensitivity of 63%-76% and specificity of 61%-76% for clinically significant stenosis* l Irrespective of the detection of a CAB in patients with possible vascular events, most authorities would still recommend imaging studies. * Using 70%-99% stenosis on a carotid angiogram as a gold standard threshold
 Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Imaging Studies l Available Options ¡ Carotid duplex US l Non invasive, virtually without complications l Readily available and quick to do l Sensitivity ~70% when compared with angiography ¡ CT angiogram – CT with IV contrast, very thin sections l Good resolution but requires expertise for interpretation l Readily available and quick to do l Complications associated with IV dye l MR angiogram ¡ Good resolution but requires expertise for interpretation ¡ Readily available and relatively quick to do ¡ Claustrophobia-inducing machine patient required to lie still for about 20 -30 minutes l Digital subtraction angiography ¡ gold standard ¡ Invasive ¡ Complications related to IV dye ¡ 1% stroke risk associated with the procedure
Evaluation of Patients with Carotid Disease – Imaging Studies l Available Options ¡ Carotid duplex US l Non invasive, virtually without complications l Readily available and quick to do l Sensitivity ~70% when compared with angiography ¡ CT angiogram – CT with IV contrast, very thin sections l Good resolution but requires expertise for interpretation l Readily available and quick to do l Complications associated with IV dye l MR angiogram ¡ Good resolution but requires expertise for interpretation ¡ Readily available and relatively quick to do ¡ Claustrophobia-inducing machine patient required to lie still for about 20 -30 minutes l Digital subtraction angiography ¡ gold standard ¡ Invasive ¡ Complications related to IV dye ¡ 1% stroke risk associated with the procedure
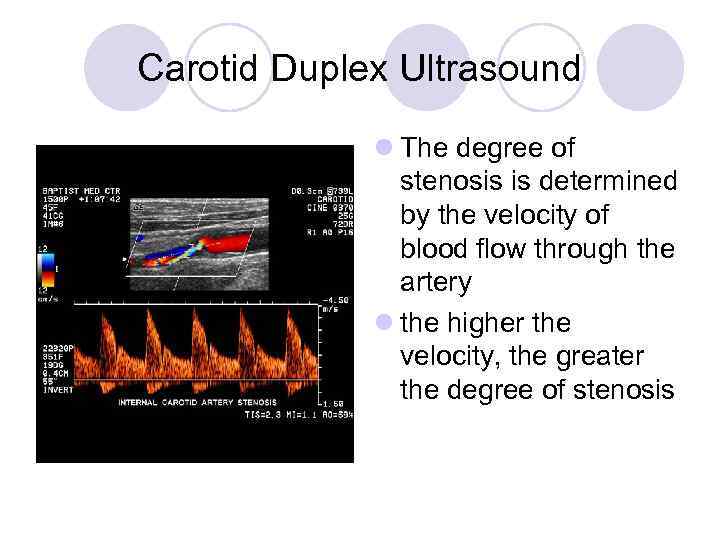 Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l The degree of stenosis is determined by the velocity of blood flow through the artery l the higher the velocity, the greater the degree of stenosis
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l The degree of stenosis is determined by the velocity of blood flow through the artery l the higher the velocity, the greater the degree of stenosis
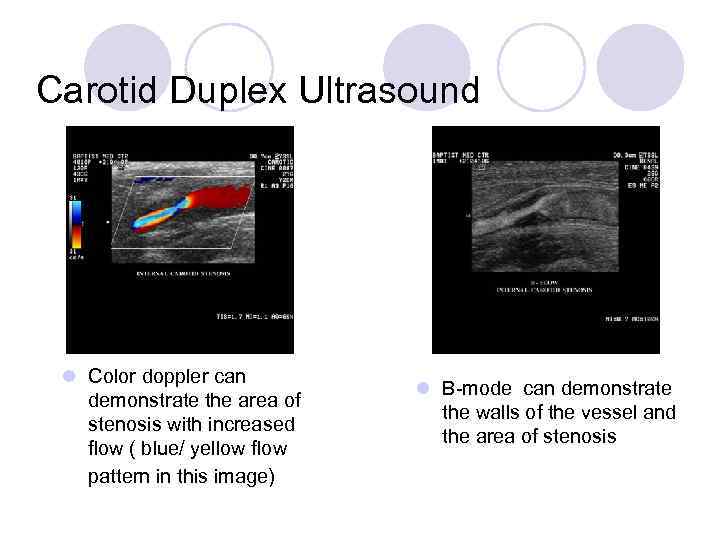 Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l Color doppler can demonstrate the area of stenosis with increased flow ( blue/ yellow flow pattern in this image) l B-mode can demonstrate the walls of the vessel and the area of stenosis
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l Color doppler can demonstrate the area of stenosis with increased flow ( blue/ yellow flow pattern in this image) l B-mode can demonstrate the walls of the vessel and the area of stenosis
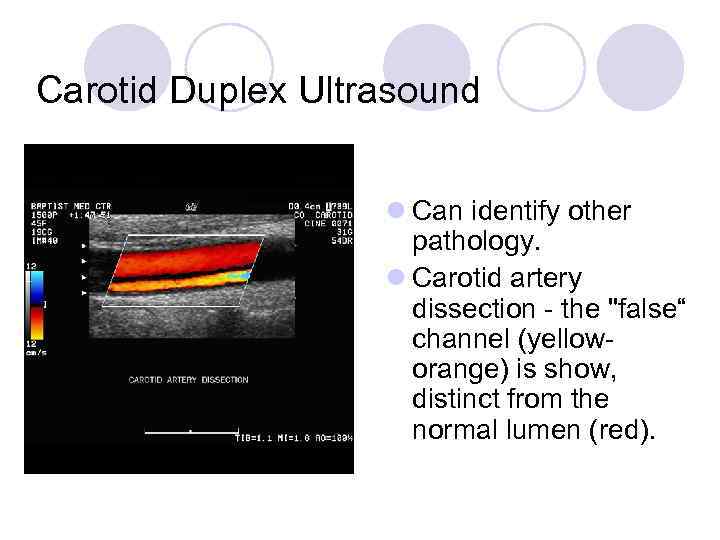 Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l Can identify other pathology. l Carotid artery dissection - the "false“ channel (yelloworange) is show, distinct from the normal lumen (red).
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound l Can identify other pathology. l Carotid artery dissection - the "false“ channel (yelloworange) is show, distinct from the normal lumen (red).
 Carotid Duplex Ultrasound: Interpretation
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound: Interpretation
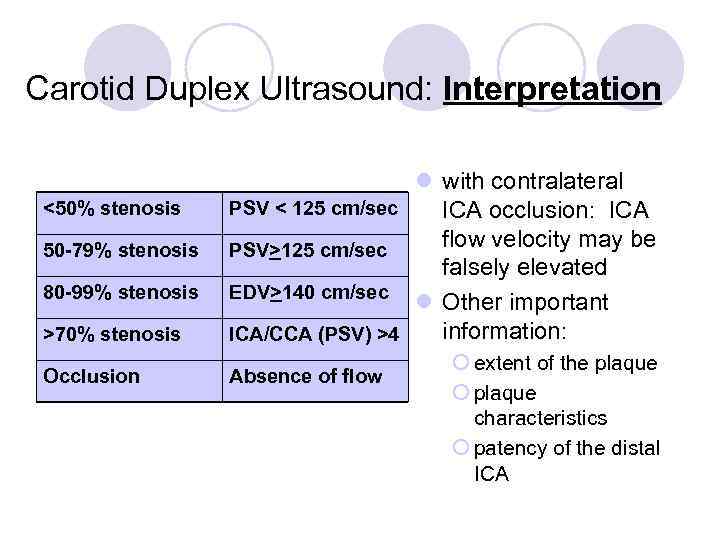 Carotid Duplex Ultrasound: Interpretation >70% stenosis l with contralateral PSV < 125 cm/sec ICA occlusion: ICA flow velocity may be PSV>125 cm/sec falsely elevated EDV>140 cm/sec l Other important information: ICA/CCA (PSV) >4 Occlusion Absence of flow <50% stenosis 50 -79% stenosis 80 -99% stenosis ¡ extent of the plaque ¡ plaque characteristics ¡ patency of the distal ICA
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound: Interpretation >70% stenosis l with contralateral PSV < 125 cm/sec ICA occlusion: ICA flow velocity may be PSV>125 cm/sec falsely elevated EDV>140 cm/sec l Other important information: ICA/CCA (PSV) >4 Occlusion Absence of flow <50% stenosis 50 -79% stenosis 80 -99% stenosis ¡ extent of the plaque ¡ plaque characteristics ¡ patency of the distal ICA
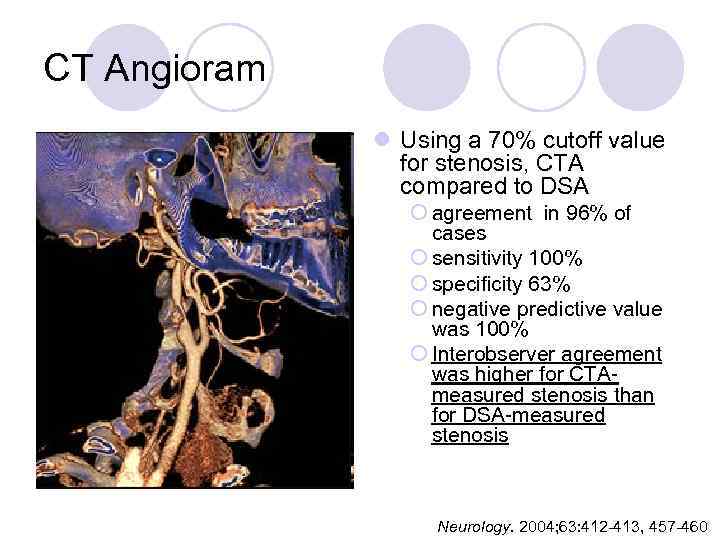 CT Angioram l Using a 70% cutoff value for stenosis, CTA compared to DSA ¡ agreement in 96% of cases ¡ sensitivity 100% ¡ specificity 63% ¡ negative predictive value was 100% ¡ Interobserver agreement was higher for CTAmeasured stenosis than for DSA-measured stenosis Neurology. 2004; 63: 412 -413, 457 -460
CT Angioram l Using a 70% cutoff value for stenosis, CTA compared to DSA ¡ agreement in 96% of cases ¡ sensitivity 100% ¡ specificity 63% ¡ negative predictive value was 100% ¡ Interobserver agreement was higher for CTAmeasured stenosis than for DSA-measured stenosis Neurology. 2004; 63: 412 -413, 457 -460
 CT Angioram
CT Angioram
 MR Angiogram l 70% to 99% ICA stenoses ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 91. 2% Specificity 88. 3% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 94. 6% Specificity 91. 9% l ICA occlusion ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 94. 5% Specificity 99. 3% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 99. 4% Specificity 99. 6% l Moderate (50 to 69%) stenoses ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 37. 9% Specificity 92. 1% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 65. 9% Stroke. 2008; 39: 2237 -2248 Specificity 93. 5%
MR Angiogram l 70% to 99% ICA stenoses ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 91. 2% Specificity 88. 3% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 94. 6% Specificity 91. 9% l ICA occlusion ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 94. 5% Specificity 99. 3% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 99. 4% Specificity 99. 6% l Moderate (50 to 69%) stenoses ¡ Time-of-flight MRA Sensitivity 37. 9% Specificity 92. 1% ¡ Contrast-enhanced MRA Sensitivity 65. 9% Stroke. 2008; 39: 2237 -2248 Specificity 93. 5%
 MR Angiogram R L
MR Angiogram R L
 Digital Subtraction Angiogram
Digital Subtraction Angiogram
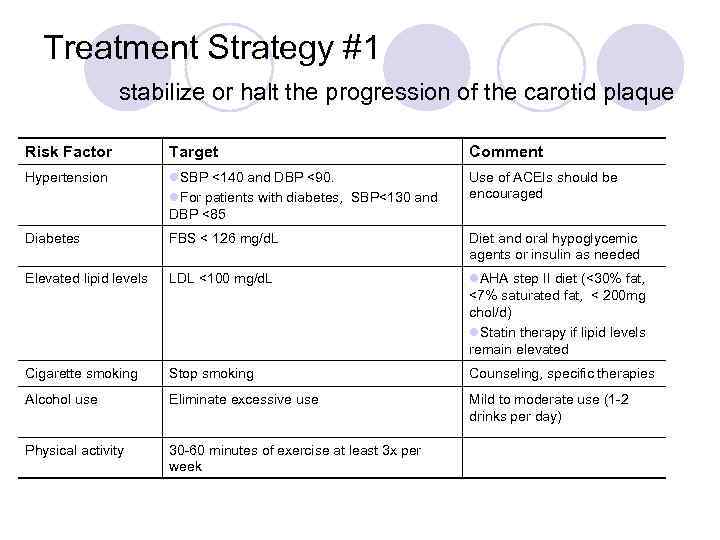 Treatment Strategy #1 stabilize or halt the progression of the carotid plaque Risk Factor Target Comment Hypertension l. SBP <140 and DBP <90. l. For patients with diabetes, SBP<130 and DBP <85 Use of ACEIs should be encouraged Diabetes FBS < 126 mg/d. L Diet and oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin as needed Elevated lipid levels LDL <100 mg/d. L l. AHA step II diet (<30% fat, <7% saturated fat, < 200 mg chol/d) l. Statin therapy if lipid levels remain elevated Cigarette smoking Stop smoking Counseling, specific therapies Alcohol use Eliminate excessive use Mild to moderate use (1 -2 drinks per day) Physical activity 30 -60 minutes of exercise at least 3 x per week
Treatment Strategy #1 stabilize or halt the progression of the carotid plaque Risk Factor Target Comment Hypertension l. SBP <140 and DBP <90. l. For patients with diabetes, SBP<130 and DBP <85 Use of ACEIs should be encouraged Diabetes FBS < 126 mg/d. L Diet and oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin as needed Elevated lipid levels LDL <100 mg/d. L l. AHA step II diet (<30% fat, <7% saturated fat, < 200 mg chol/d) l. Statin therapy if lipid levels remain elevated Cigarette smoking Stop smoking Counseling, specific therapies Alcohol use Eliminate excessive use Mild to moderate use (1 -2 drinks per day) Physical activity 30 -60 minutes of exercise at least 3 x per week
 Treatment Strategy #2 eliminate or reduce carotid stenosis
Treatment Strategy #2 eliminate or reduce carotid stenosis
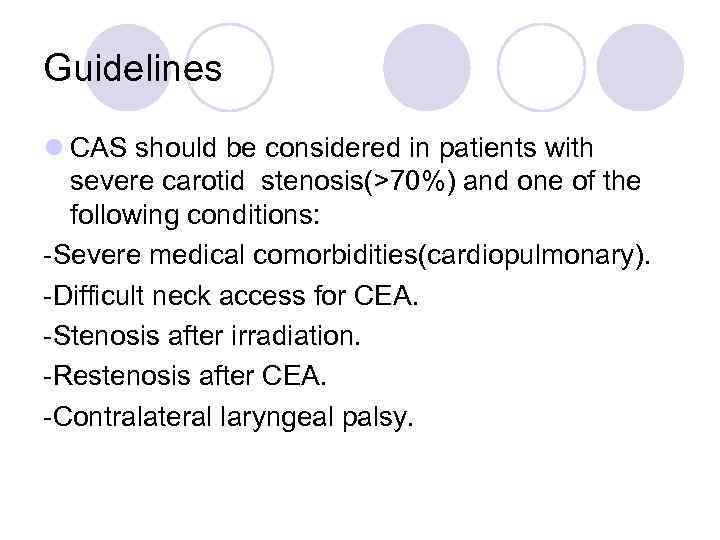 Guidelines l CAS should be considered in patients with severe carotid stenosis(>70%) and one of the following conditions: -Severe medical comorbidities(cardiopulmonary). -Difficult neck access for CEA. -Stenosis after irradiation. -Restenosis after CEA. -Contralateral laryngeal palsy.
Guidelines l CAS should be considered in patients with severe carotid stenosis(>70%) and one of the following conditions: -Severe medical comorbidities(cardiopulmonary). -Difficult neck access for CEA. -Stenosis after irradiation. -Restenosis after CEA. -Contralateral laryngeal palsy.
 Treatment Strategy #2 eliminate or reduce carotid stenosis l Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) – treatment of choice l Other procedures ¡ EC-IC bypass: not beneficial (1980’s) l Currently being revisited - Carotid Occlusion Surgery Study (COSS) • aims to identify a subgroup of patients with carotid occlusion that may benefit from EC-IC bypass • ipsilateral increased oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) measured by positron emission tomography (PET) ¡ Carotid angioplasty and stenting l trials and case series have shown that the outcomes of stenting are worse than or no different from those of carotid endarterectomy l Current use limited to patients with high surgical risk preventing the performance of CEA
Treatment Strategy #2 eliminate or reduce carotid stenosis l Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) – treatment of choice l Other procedures ¡ EC-IC bypass: not beneficial (1980’s) l Currently being revisited - Carotid Occlusion Surgery Study (COSS) • aims to identify a subgroup of patients with carotid occlusion that may benefit from EC-IC bypass • ipsilateral increased oxygen extraction fraction (OEF) measured by positron emission tomography (PET) ¡ Carotid angioplasty and stenting l trials and case series have shown that the outcomes of stenting are worse than or no different from those of carotid endarterectomy l Current use limited to patients with high surgical risk preventing the performance of CEA
 Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l >70% stenosis ¡ 2 rate of ipsilateral stroke: 26% in the medical group and 9%in the surgical group* ¡Relative risk reduction 65%* ¡Absolute risk reduction 17%* ¡NNT 7 -8 (# patients who would need to undergo endarterectomy to prevent one stroke in a 5 -year period)** *, **North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), the **European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST), and the trial by the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Program
Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l >70% stenosis ¡ 2 rate of ipsilateral stroke: 26% in the medical group and 9%in the surgical group* ¡Relative risk reduction 65%* ¡Absolute risk reduction 17%* ¡NNT 7 -8 (# patients who would need to undergo endarterectomy to prevent one stroke in a 5 -year period)** *, **North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), the **European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST), and the trial by the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Program
 Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l <50% stenosis ¡trials showed that there was no significant benefit of surgery. ¡in NASCET, there was no significant difference in the risk of ipsilateral stroke between those who were treated with endarterectomy and those who were treated medically North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST), and the trial by the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Program
Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l <50% stenosis ¡trials showed that there was no significant benefit of surgery. ¡in NASCET, there was no significant difference in the risk of ipsilateral stroke between those who were treated with endarterectomy and those who were treated medically North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST), and the trial by the Veterans Affairs Cooperative Studies Program
 Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l Moderate stenosis, 50 to 69% ¡In ECST, there was no significant benefit of surgery for those with moderate stenosis. ¡In NASCET, the 5 -year risk of fatal or nonfatal ipsilateral stroke among patients was 22. 2% in the medical group and 15. 7% in the surgical group ¡Absolute risk reduction 6. 5% ¡NNT 15 North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST)
Symptomatic Carotid Stenosis l Moderate stenosis, 50 to 69% ¡In ECST, there was no significant benefit of surgery for those with moderate stenosis. ¡In NASCET, the 5 -year risk of fatal or nonfatal ipsilateral stroke among patients was 22. 2% in the medical group and 15. 7% in the surgical group ¡Absolute risk reduction 6. 5% ¡NNT 15 North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET), and the European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST)
 Patients with symptomatic moderate grade stenosis with greatest benefit from CEA ¡ more severe stenosis ¡ 75 years of age and older ¡ men ¡ patients with a recent (within 3 months) history of stroke (rather than transient ischemic attacks) as the qualifying event ¡ patients with hemispheric TIAs rather than transient monocular blindness ¡ radiographic factors: the presence of intracranial stenosis, the absence of microvascular ischemia, and the presence of collateral vessels ¡ operative risk ¡ experience of the surgeon
Patients with symptomatic moderate grade stenosis with greatest benefit from CEA ¡ more severe stenosis ¡ 75 years of age and older ¡ men ¡ patients with a recent (within 3 months) history of stroke (rather than transient ischemic attacks) as the qualifying event ¡ patients with hemispheric TIAs rather than transient monocular blindness ¡ radiographic factors: the presence of intracranial stenosis, the absence of microvascular ischemia, and the presence of collateral vessels ¡ operative risk ¡ experience of the surgeon
 Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis l the risk of stroke is lower than that associated with symptomatic disease l In observational studies, the rate of ipsilateral stroke was 1 to 3% per year among patients with asymptomatic stenosis of greater than 50% l the risk in NASCET was 3. 2% per year for asymptomatic stenosis of 60 to 99%
Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis l the risk of stroke is lower than that associated with symptomatic disease l In observational studies, the rate of ipsilateral stroke was 1 to 3% per year among patients with asymptomatic stenosis of greater than 50% l the risk in NASCET was 3. 2% per year for asymptomatic stenosis of 60 to 99%
 Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study (ACAS) - >60% stenosis l The risk of ipsilateral stroke or any perioperative stroke or death was 5% during 5 years of follow-up in surgically treated patients and 11% in medically treated patients. ¡ Absolute risk reduction (ARR) 6% ¡ NNT 17 l Because of the lower ARR, a rate of perioperative complications (stroke or death) of more than 3% would eliminate the potential benefit of the operation l The benefit of surgery was greater for men than women (reduction in risk, 66% vs. 17%) l The rate of perioperative complications was higher among women than men (3. 6% vs. 1. 7%).
Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study (ACAS) - >60% stenosis l The risk of ipsilateral stroke or any perioperative stroke or death was 5% during 5 years of follow-up in surgically treated patients and 11% in medically treated patients. ¡ Absolute risk reduction (ARR) 6% ¡ NNT 17 l Because of the lower ARR, a rate of perioperative complications (stroke or death) of more than 3% would eliminate the potential benefit of the operation l The benefit of surgery was greater for men than women (reduction in risk, 66% vs. 17%) l The rate of perioperative complications was higher among women than men (3. 6% vs. 1. 7%).