c26a14fc521692085a43bd78bc5ae5a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Care of ST-Segment Elevation Patients: Insights From NRMI C. Michael Gibson, MS, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, TIMI Data Coordinating Center Brigham and Women’s Hospital Associate Chief of Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, Massachusetts
Care of ST-Segment Elevation Patients: Insights From NRMI C. Michael Gibson, MS, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, TIMI Data Coordinating Center Brigham and Women’s Hospital Associate Chief of Cardiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston, Massachusetts
 NRMI: A Historical Overview • Since 1990: 1600 hospitals, over 2. 2 million patients • Model registry for CQI: data reporting, trend analysis, and benchmarking • Accepted performance measurement system for JCAHO ORYX non-core and core measures; CMS Qnet clinical data warehouse • Over 70 published manuscripts and over 120 abstracts presented at ACC, AHA, ACEP, and outcomes research meetings • Referenced in AHA/ACC AMI Management Guidelines • Data used to generate and test hypotheses for future research
NRMI: A Historical Overview • Since 1990: 1600 hospitals, over 2. 2 million patients • Model registry for CQI: data reporting, trend analysis, and benchmarking • Accepted performance measurement system for JCAHO ORYX non-core and core measures; CMS Qnet clinical data warehouse • Over 70 published manuscripts and over 120 abstracts presented at ACC, AHA, ACEP, and outcomes research meetings • Referenced in AHA/ACC AMI Management Guidelines • Data used to generate and test hypotheses for future research
 NRMI As A CQI and Academic Success Story: Improvement in Time to Treatment over 10 Years NRMI Delayed Door to Drug Times Associated with Mortality Science Delayed Door to Balloon Times Associated with Mortality NRMI Data Hospital Door to Drug Times Prolonged Indentifies Problem Door to Balloon Times Prolonged NRMI Data Indentifies Potential Sources of Problem NRMI Data Provides Ongoing Feedback to Centers Door to Data, Data to EKG, EKG to Decision, Decision to Drug; Transfer Times Door to Drug Times Decrease by ½ Door to Balloon Times Decrease Among Transfer Pts
NRMI As A CQI and Academic Success Story: Improvement in Time to Treatment over 10 Years NRMI Delayed Door to Drug Times Associated with Mortality Science Delayed Door to Balloon Times Associated with Mortality NRMI Data Hospital Door to Drug Times Prolonged Indentifies Problem Door to Balloon Times Prolonged NRMI Data Indentifies Potential Sources of Problem NRMI Data Provides Ongoing Feedback to Centers Door to Data, Data to EKG, EKG to Decision, Decision to Drug; Transfer Times Door to Drug Times Decrease by ½ Door to Balloon Times Decrease Among Transfer Pts
 MV Adjusted Odds of Death NRMI 2: Primary PCI Door-to-Balloon Time vs. Mortality P=0. 01 n = 2, 230 5, 734 6, 616 4, 461 P=0. 0007 P=0. 0003 2, 627 Door-to-Balloon Time (minutes) 5, 412
MV Adjusted Odds of Death NRMI 2: Primary PCI Door-to-Balloon Time vs. Mortality P=0. 01 n = 2, 230 5, 734 6, 616 4, 461 P=0. 0007 P=0. 0003 2, 627 Door-to-Balloon Time (minutes) 5, 412
 Primary PCI for STEMI Time to Reperfusion and 30 Day Mortality CADILLAC Zwolle N= 2002 N= 1791 1994 -2001 % Mortality 9. 6 P=0. 04 (< 3 h v > 3 h) 2. 3 P < 0. 001 5. 6 2. 2 3. 1 0. 9 Cox ACC ‘ 03 Abst 827 -1 Time to Reperfusion (h) 2. 5 De. Luca ACC ‘ 03 Abst 827 -3
Primary PCI for STEMI Time to Reperfusion and 30 Day Mortality CADILLAC Zwolle N= 2002 N= 1791 1994 -2001 % Mortality 9. 6 P=0. 04 (< 3 h v > 3 h) 2. 3 P < 0. 001 5. 6 2. 2 3. 1 0. 9 Cox ACC ‘ 03 Abst 827 -1 Time to Reperfusion (h) 2. 5 De. Luca ACC ‘ 03 Abst 827 -3
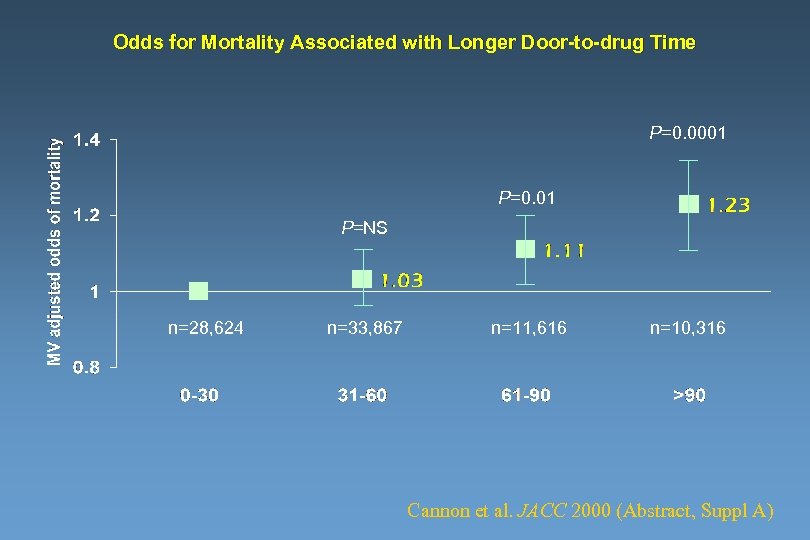 Odds for Mortality Associated with Longer Door-to-drug Time P=0. 0001 P=0. 01 P=NS n=28, 624 n=33, 867 n=11, 616 n=10, 316 Cannon et al. JACC 2000 (Abstract, Suppl A)
Odds for Mortality Associated with Longer Door-to-drug Time P=0. 0001 P=0. 01 P=NS n=28, 624 n=33, 867 n=11, 616 n=10, 316 Cannon et al. JACC 2000 (Abstract, Suppl A)
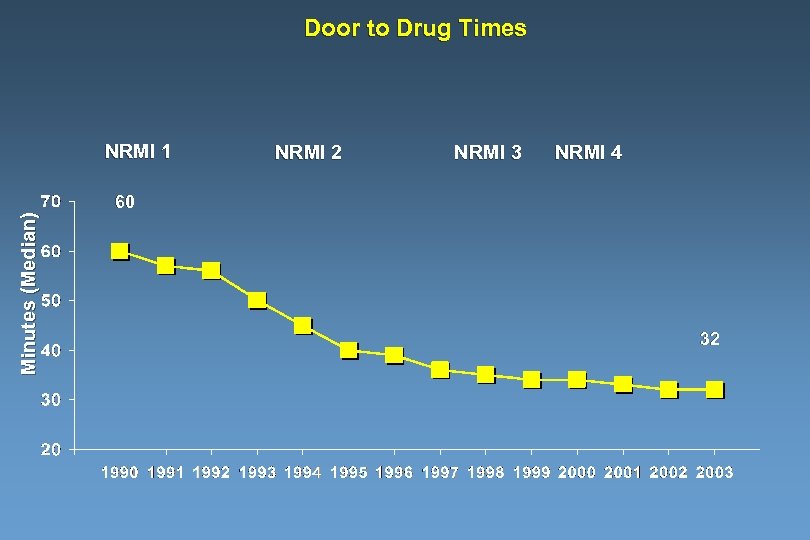 Door to Drug Times Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 60 32
Door to Drug Times Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 60 32
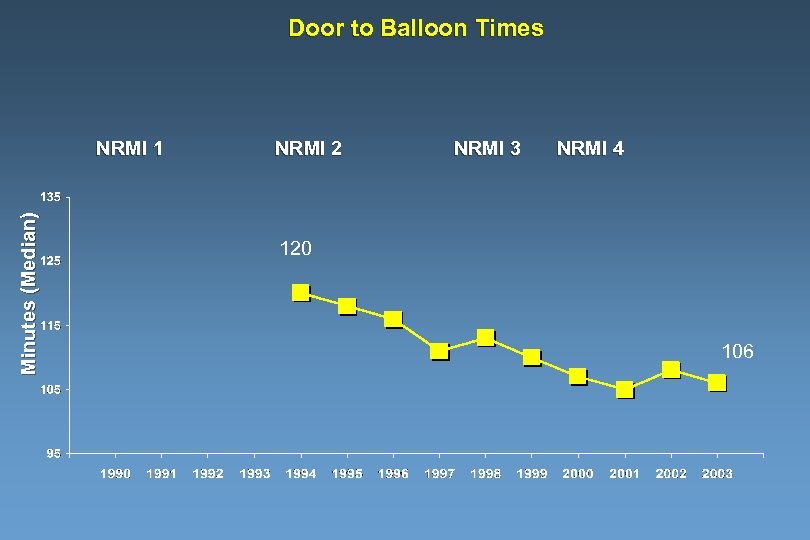 Door to Balloon Times Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 120 106
Door to Balloon Times Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 120 106
 Door to Balloon Times By Subgroup 1994 -2003; NRMI 2, 3, 4 131 Minutes (Median) 127 128 Off Hours 118 114 65+ Years Females 111 103 < 65 Years Males 114 108 On Hours 90
Door to Balloon Times By Subgroup 1994 -2003; NRMI 2, 3, 4 131 Minutes (Median) 127 128 Off Hours 118 114 65+ Years Females 111 103 < 65 Years Males 114 108 On Hours 90
 DANAMI-2: Primary Results Combined Transfer Sites P=0. 0003 Primary PCI Death / MI / Stroke (%) P=0. 048 P=0. 002 RRR 40% RRR 45% Lytic Non-Transfer Sites Lytic Primary PCI RRR 45% Lytic Primary PCI
DANAMI-2: Primary Results Combined Transfer Sites P=0. 0003 Primary PCI Death / MI / Stroke (%) P=0. 048 P=0. 002 RRR 40% RRR 45% Lytic Non-Transfer Sites Lytic Primary PCI RRR 45% Lytic Primary PCI
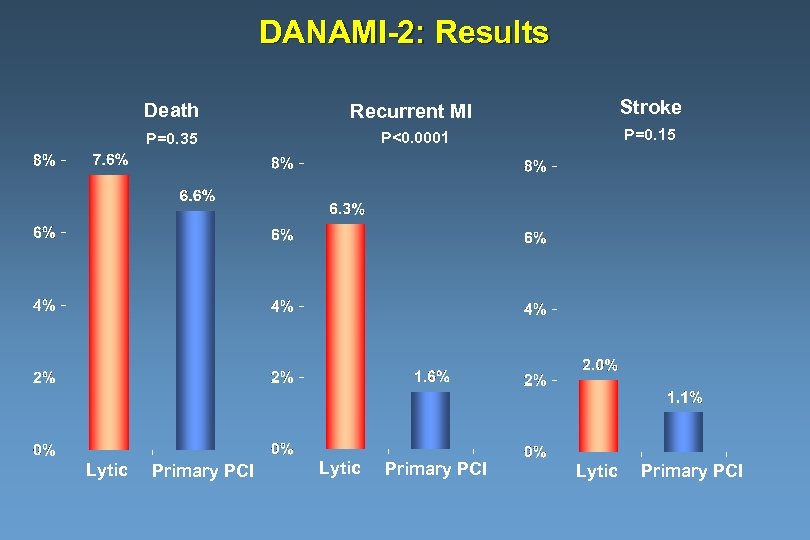 DANAMI-2: Results Death Stroke P=0. 35 Lytic Recurrent MI P<0. 0001 P=0. 15 Primary PCI Lytic Primary PCI
DANAMI-2: Results Death Stroke P=0. 35 Lytic Recurrent MI P<0. 0001 P=0. 15 Primary PCI Lytic Primary PCI
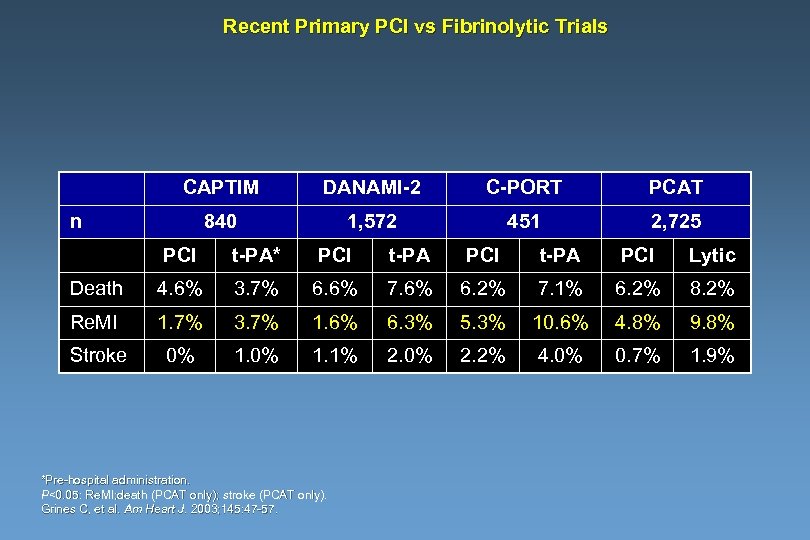 Recent Primary PCI vs Fibrinolytic Trials CAPTIM DANAMI-2 C-PORT PCAT 840 1, 572 451 2, 725 n PCI t-PA* PCI t-PA PCI Lytic Death 4. 6% 3. 7% 6. 6% 7. 6% 6. 2% 7. 1% 6. 2% 8. 2% Re. MI 1. 7% 3. 7% 1. 6% 6. 3% 5. 3% 10. 6% 4. 8% 9. 8% Stroke 0% 1. 1% 2. 0% 2. 2% 4. 0% 0. 7% 1. 9% *Pre-hospital administration. P<0. 05: Re. MI; death (PCAT only); stroke (PCAT only). Grines C, et al. Am Heart J. 2003; 145: 47 -57.
Recent Primary PCI vs Fibrinolytic Trials CAPTIM DANAMI-2 C-PORT PCAT 840 1, 572 451 2, 725 n PCI t-PA* PCI t-PA PCI Lytic Death 4. 6% 3. 7% 6. 6% 7. 6% 6. 2% 7. 1% 6. 2% 8. 2% Re. MI 1. 7% 3. 7% 1. 6% 6. 3% 5. 3% 10. 6% 4. 8% 9. 8% Stroke 0% 1. 1% 2. 0% 2. 2% 4. 0% 0. 7% 1. 9% *Pre-hospital administration. P<0. 05: Re. MI; death (PCAT only); stroke (PCAT only). Grines C, et al. Am Heart J. 2003; 145: 47 -57.
 Recurrent MI During Index Hospitalization is Associated with Higher Mortality at 2 Years Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, by early reinfarction 1 No early reinfarction 10. 1%, n=19, 265 Early reinfarction 19. 6%, n=836 0. 75 Log-rank p<0. 0001 0. 5 0 0. 5 1 Years 1. 5 2 Gibson CM et al, JACC 2003
Recurrent MI During Index Hospitalization is Associated with Higher Mortality at 2 Years Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, by early reinfarction 1 No early reinfarction 10. 1%, n=19, 265 Early reinfarction 19. 6%, n=836 0. 75 Log-rank p<0. 0001 0. 5 0 0. 5 1 Years 1. 5 2 Gibson CM et al, JACC 2003
 Risk of Recurrent MI Following Thrombolysis in 20, 101 Patients Risk of Recurrent MI (%) 5 4 3 2 1. 6 1 0 No PCI Gibson CM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. In press. Cardiol. PCI
Risk of Recurrent MI Following Thrombolysis in 20, 101 Patients Risk of Recurrent MI (%) 5 4 3 2 1. 6 1 0 No PCI Gibson CM, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. In press. Cardiol. PCI
 Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, by PCI in 20, 101 Patients 1 PCI Survival 0. 9 No PCI Log rank p<0. 0001 0. 8 0. 7 0 0. 5 1 Years 1. 5 2 Gibson CM et al, JACC 2003
Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, by PCI in 20, 101 Patients 1 PCI Survival 0. 9 No PCI Log rank p<0. 0001 0. 8 0. 7 0 0. 5 1 Years 1. 5 2 Gibson CM et al, JACC 2003
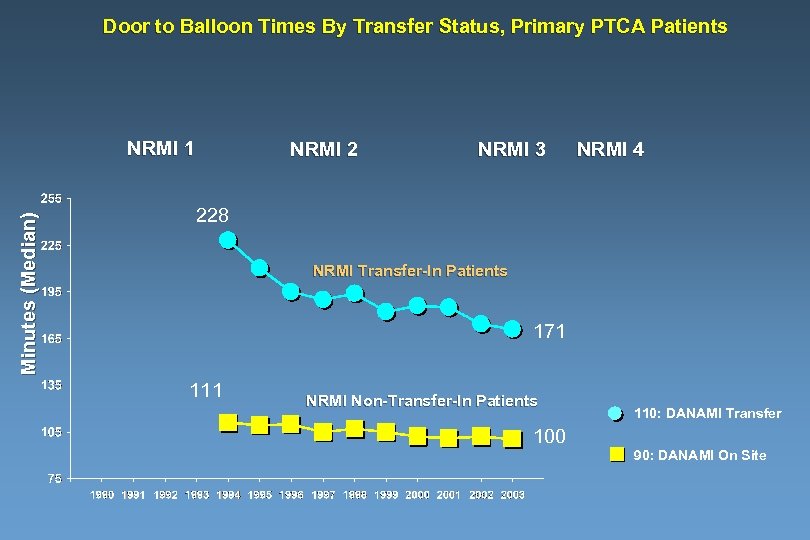 Door to Balloon Times By Transfer Status, Primary PTCA Patients Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 228 NRMI Transfer-In Patients 171 111 NRMI Non-Transfer-In Patients 110: DANAMI Transfer 100 90: DANAMI On Site
Door to Balloon Times By Transfer Status, Primary PTCA Patients Minutes (Median) NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 228 NRMI Transfer-In Patients 171 111 NRMI Non-Transfer-In Patients 110: DANAMI Transfer 100 90: DANAMI On Site
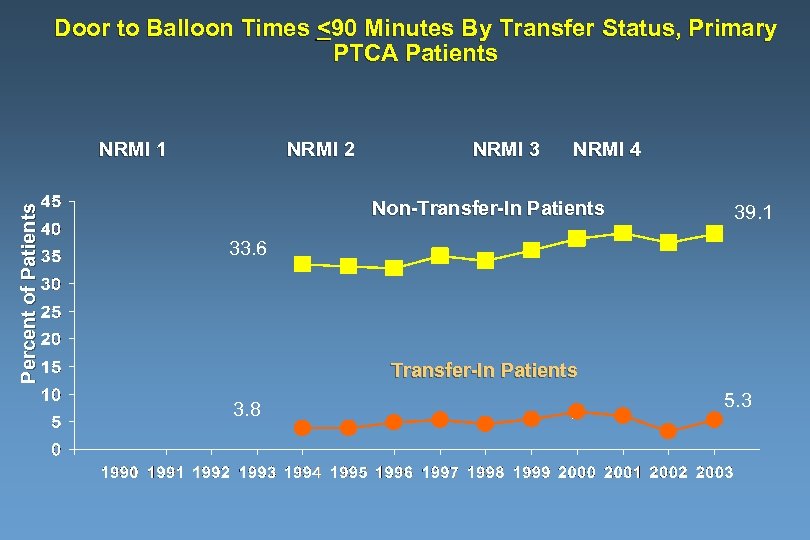 Door to Balloon Times <90 Minutes By Transfer Status, Primary PTCA Patients Percent of Patients NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 Non-Transfer-In Patients 39. 1 33. 6 Transfer-In Patients 3. 8 5. 3
Door to Balloon Times <90 Minutes By Transfer Status, Primary PTCA Patients Percent of Patients NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 Non-Transfer-In Patients 39. 1 33. 6 Transfer-In Patients 3. 8 5. 3
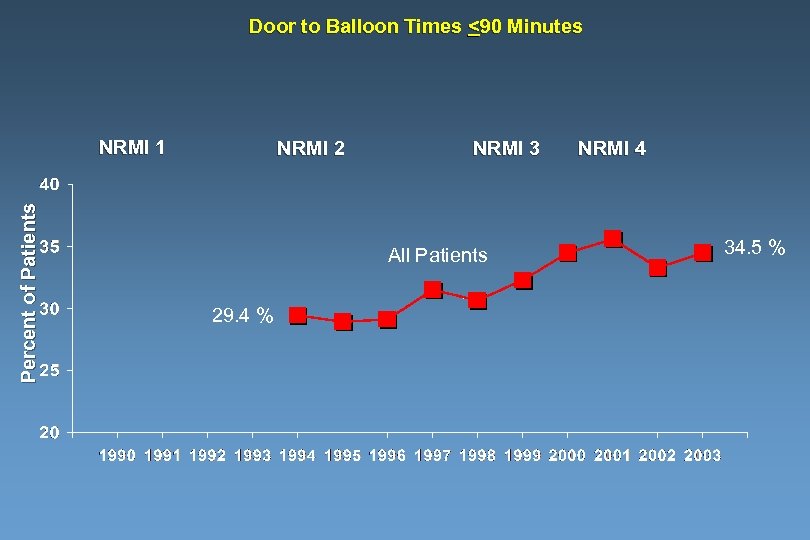 Door to Balloon Times <90 Minutes Percent of Patients NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 All Patients 29. 4 % NRMI 4 34. 5 %
Door to Balloon Times <90 Minutes Percent of Patients NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 All Patients 29. 4 % NRMI 4 34. 5 %
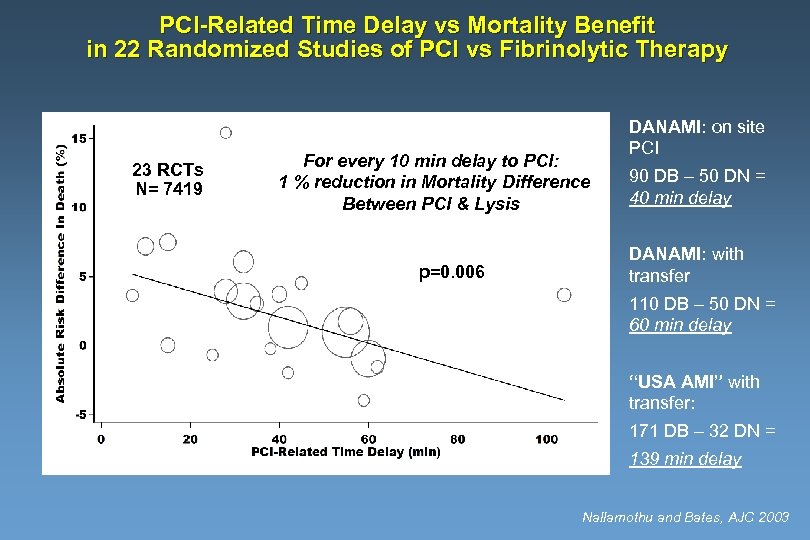 PCI-Related Time Delay vs Mortality Benefit in 22 Randomized Studies of PCI vs Fibrinolytic Therapy 23 RCTs N= 7419 For every 10 min delay to PCI: 1 % reduction in Mortality Difference Between PCI & Lysis p=0. 006 DANAMI: on site PCI 90 DB – 50 DN = 40 min delay DANAMI: with transfer 110 DB – 50 DN = 60 min delay “USA AMI” with transfer: 171 DB – 32 DN = 139 min delay Nallamothu and Bates, AJC 2003
PCI-Related Time Delay vs Mortality Benefit in 22 Randomized Studies of PCI vs Fibrinolytic Therapy 23 RCTs N= 7419 For every 10 min delay to PCI: 1 % reduction in Mortality Difference Between PCI & Lysis p=0. 006 DANAMI: on site PCI 90 DB – 50 DN = 40 min delay DANAMI: with transfer 110 DB – 50 DN = 60 min delay “USA AMI” with transfer: 171 DB – 32 DN = 139 min delay Nallamothu and Bates, AJC 2003
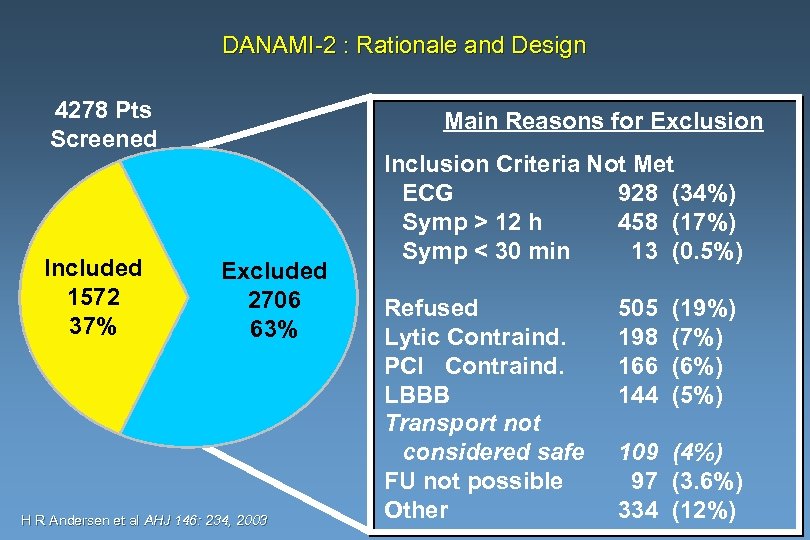 DANAMI-2 : Rationale and Design 4278 Pts Screened Included 1572 37% Main Reasons for Exclusion Excluded 2706 63% H R Andersen et al AHJ 146: 234, 2003 Inclusion Criteria Not Met ECG 928 (34%) Symp > 12 h 458 (17%) Symp < 30 min 13 (0. 5%) Refused Lytic Contraind. PCI Contraind. LBBB Transport not considered safe FU not possible Other 505 198 166 144 (19%) (7%) (6%) (5%) 109 (4%) 97 (3. 6%) 334 (12%)
DANAMI-2 : Rationale and Design 4278 Pts Screened Included 1572 37% Main Reasons for Exclusion Excluded 2706 63% H R Andersen et al AHJ 146: 234, 2003 Inclusion Criteria Not Met ECG 928 (34%) Symp > 12 h 458 (17%) Symp < 30 min 13 (0. 5%) Refused Lytic Contraind. PCI Contraind. LBBB Transport not considered safe FU not possible Other 505 198 166 144 (19%) (7%) (6%) (5%) 109 (4%) 97 (3. 6%) 334 (12%)
 Medications Received Within First 24 Hours All Eligible Patients NRMI 1 – NRMI 4
Medications Received Within First 24 Hours All Eligible Patients NRMI 1 – NRMI 4
 Newer Classes of Medications Received Within First 24 Hours All Eligible Patients NRMI 3 – NRMI 4
Newer Classes of Medications Received Within First 24 Hours All Eligible Patients NRMI 3 – NRMI 4
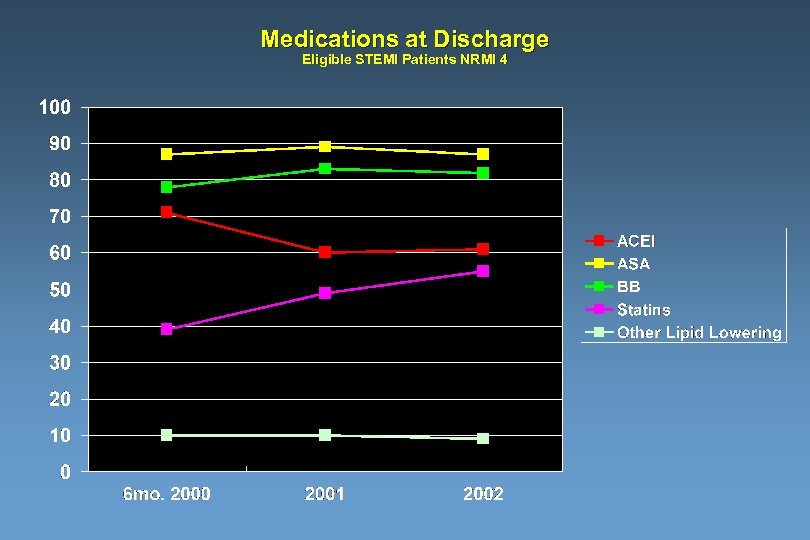 Medications at Discharge Eligible STEMI Patients NRMI 4
Medications at Discharge Eligible STEMI Patients NRMI 4
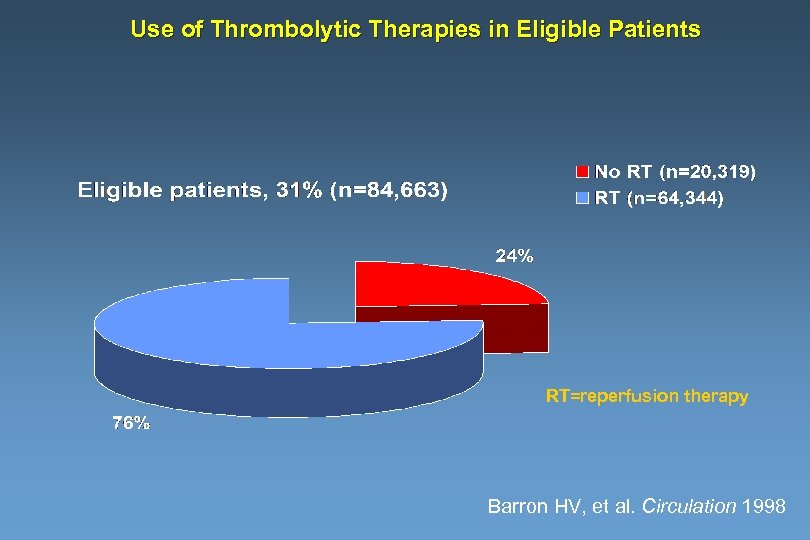 Use of Thrombolytic Therapies in Eligible Patients RT=reperfusion therapy Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
Use of Thrombolytic Therapies in Eligible Patients RT=reperfusion therapy Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
 Use of Reperfusion Therapy RT less likely LBBB No chest pain Age >75 Prior CHF Prior MI Killip III Women Caucasian Smoker Pre-hospital ECG Sx <3 hrs RT more likely RT=reperfusion therapy 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1. 0 1. 2 1. 4 1. 6 Adapted from Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
Use of Reperfusion Therapy RT less likely LBBB No chest pain Age >75 Prior CHF Prior MI Killip III Women Caucasian Smoker Pre-hospital ECG Sx <3 hrs RT more likely RT=reperfusion therapy 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1. 0 1. 2 1. 4 1. 6 Adapted from Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
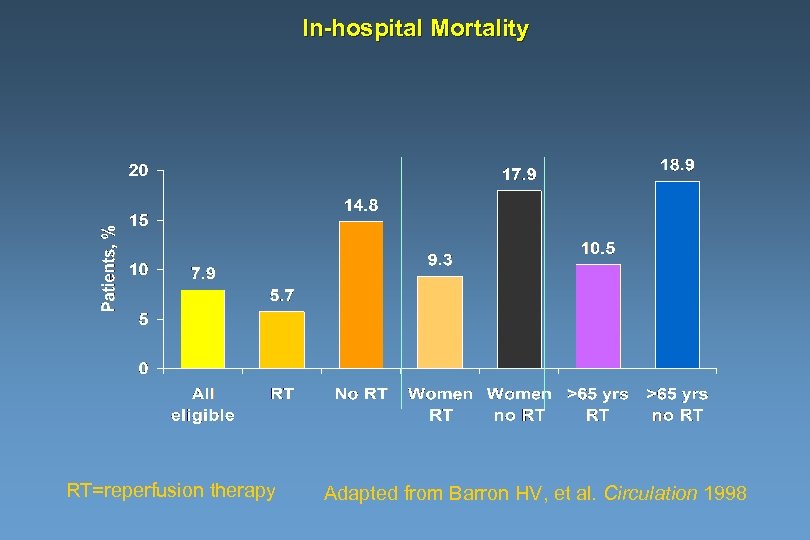 In-hospital Mortality RT=reperfusion therapy Adapted from Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
In-hospital Mortality RT=reperfusion therapy Adapted from Barron HV, et al. Circulation 1998
 Hospital Mortality: Reperfusion Therapy NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 7. 8 % Percent PPCI 5. 2 % IV Lytic 4. 4 % 4. 3 %
Hospital Mortality: Reperfusion Therapy NRMI 1 NRMI 2 NRMI 3 NRMI 4 7. 8 % Percent PPCI 5. 2 % IV Lytic 4. 4 % 4. 3 %
 What’s Coming Up in NRMI? • Cr • TIMI Flow Grades • Coated / non coated stents • Vasodilators in primary PCI • Defibrillator implantation and EFs • ARBs • Clopidogrel administration
What’s Coming Up in NRMI? • Cr • TIMI Flow Grades • Coated / non coated stents • Vasodilators in primary PCI • Defibrillator implantation and EFs • ARBs • Clopidogrel administration
 Room For Improvement • Improve door to balloon times • Improve utilization of reperfusion therapy among appropriate candidates • Improve rates of beta blocker, ACE, lipid lowering and smoking cessation strategies
Room For Improvement • Improve door to balloon times • Improve utilization of reperfusion therapy among appropriate candidates • Improve rates of beta blocker, ACE, lipid lowering and smoking cessation strategies


