38b3387d199a2df30f3bf3ce26576949.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

CARE OF NSTEMI PATIENTS LATEST GUIDELINES Rick Barney MD FACEP Emergency Medicine Beloit Memorial and University of Wisconsin

New NSTEMI Guidelines by ACC/AHA Released August 6 th 2007 www. americanheart. org

NSTEMI Protocols not followed well n STEMI- straight forward and well followed n NSTEMI- no hospital agreement, under use of available treatment, no agreement even amongst cardiologists
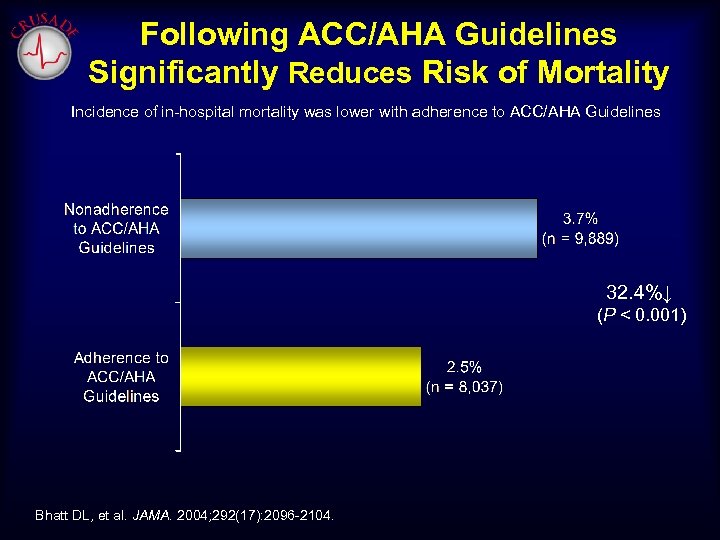
Following ACC/AHA Guidelines Significantly Reduces Risk of Mortality Incidence of in-hospital mortality was lower with adherence to ACC/AHA Guidelines 32. 4%↓ (P < 0. 001) Bhatt DL, et al. JAMA. 2004; 292(17): 2096 -2104.

NSTEMI- Definition Coronary symptoms with ST segment depression, or T wave inversions (new) and/or elevated biomarkers (Troponin preferred)

Nitro Recommendation n If new angina pattern, call 911 if one single nitro has not helped. Take 2 nd and 3 rd dose while waiting for EMS arrival n If typical stable angina pattern, still recommend call for help if three nitro doses 5 minutes apart does not help.

Aspirin and Pre-Hospital 12 lead ECG n Aspirin should be given immediately to all patients who may have a coronary Syndrome. Only reason to not give is a true allergy. n Strong recommendation for pre-hospital 12 lead analysis

Positive Biomarkers are critical to ED Care Latest studies show patients with positive Troponins do best with early invasive management, Clopidogrel, anticoagulation, and glycoprotien II b III a inhibition.
USE OF BETA BLOCKERS COMMIT Trial shows some risk in using IV Metoprolol. For NSTEMI-use IV if hyperdynamic, otherwise PO within 24 hours of arrival

Morphine results in higher mortality for NSTEMI patients Due to blocking pain, yet ischemia still present Due to hypotension Due to decreased myocardial perfusion Many now use Fentanyl instead

Early Invasive Management Improves Outcomes NSTEMI- thus high risk patients in general do better if treated aggressively in ED, then to cath lab in 4 -24 hours. 18% death or MI reduction. Even studies on stabilization and later treatment are predicated on aggressive ED treatment In general, this includes Clopidogrel, anticoagulant, and Glycoprotein II B III A Inhibition

2007 Anti-platelet Guidelines Nothing new on Aspirin- continue to use Recommend Clopidogrel or II B III A OR Use both Clopidogrel and II B III A Using both makes more scientific sense as drugs work differently. Some patients are partial or non-responders to Clopidogrel.

Anti-Platelet Therapy n Clopidogrel is irreversible. Will delay CABG 3 -5 days. n Integrelin is reversible once infusion is shut off. n Anti-platelet therapy is critical to success and is under- utilized n Coordinated, standard approach at your institution is desirable. n ISAR-REACT 2 study shows adding Glycoprotein IIBIIIA

The Central Role of the Platelet in NSTE ACS
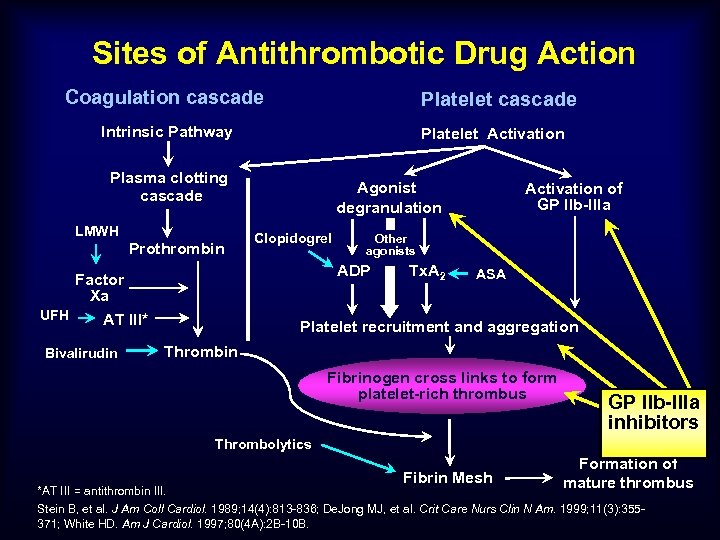
Sites of Antithrombotic Drug Action Coagulation cascade Platelet cascade Intrinsic Pathway Platelet Activation Plasma clotting cascade LMWH Prothrombin Clopidogrel Activation of GP IIb-IIIa Other agonists ADP Factor Xa UFH AT III* Bivalirudin Agonist degranulation Tx. A 2 ASA Platelet recruitment and aggregation Thrombin Fibrinogen cross links to form platelet-rich thrombus GP IIb-IIIa inhibitors Thrombolytics Fibrin Mesh Formation of mature thrombus *AT III = antithrombin III. Stein B, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989; 14(4): 813 -836; De. Jong MJ, et al. Crit Care Nurs Clin N Am. 1999; 11(3): 355371; White HD. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 80(4 A): 2 B-10 B.
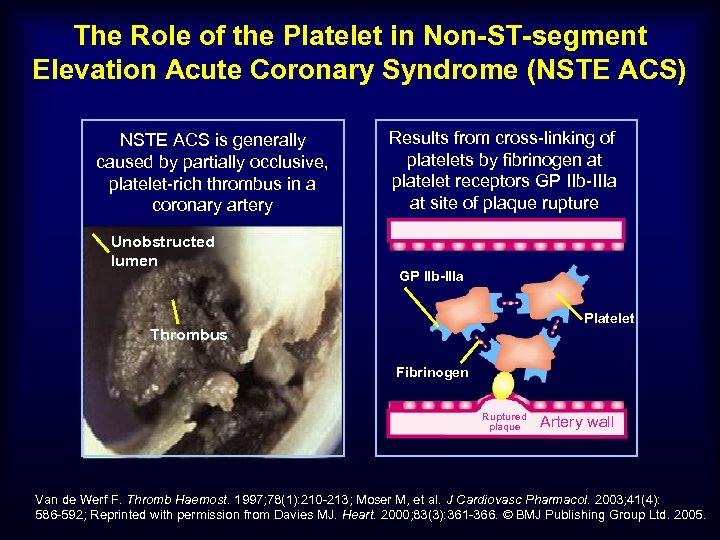
The Role of the Platelet in Non-ST-segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome (NSTE ACS) NSTE ACS is generally caused by partially occlusive, platelet-rich thrombus in a coronary artery Unobstructed lumen Results from cross-linking of platelets by fibrinogen at platelet receptors GP IIb-IIIa at site of plaque rupture GP IIb-IIIa Platelet Thrombus Fibrinogen Ruptured plaque Artery wall Van de Werf F. Thromb Haemost. 1997; 78(1): 210 -213; Moser M, et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2003; 41(4): 586 -592; Reprinted with permission from Davies MJ. Heart. 2000; 83(3): 361 -366. © BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. 2005.
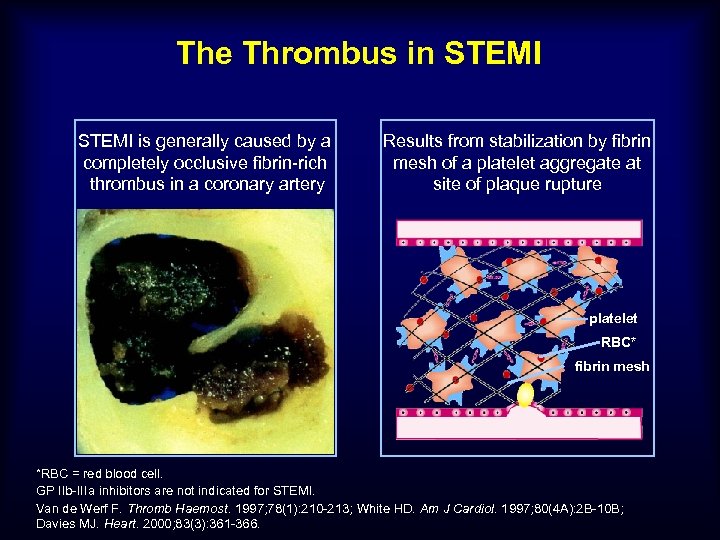
The Thrombus in STEMI is generally caused by a completely occlusive fibrin-rich thrombus in a coronary artery Results from stabilization by fibrin mesh of a platelet aggregate at site of plaque rupture platelet RBC* fibrin mesh *RBC = red blood cell. GP IIb-IIIa inhibitors are not indicated for STEMI. Van de Werf F. Thromb Haemost. 1997; 78(1): 210 -213; White HD. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 80(4 A): 2 B-10 B; Davies MJ. Heart. 2000; 83(3): 361 -366.
Microembolization in Unstable Angina Courtesy of C. Michael Gibson, MS, MD, Director TIMI Data Coordinating Center, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Associate Chief of Cardiology, Interventional Cardiologist, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School.
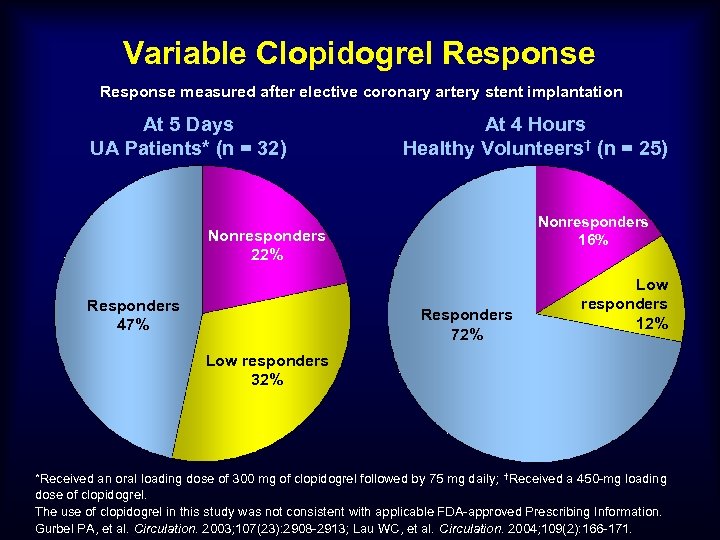
Variable Clopidogrel Response measured after elective coronary artery stent implantation At 5 Days UA Patients* (n = 32) At 4 Hours Healthy Volunteers† (n = 25) Nonresponders 16% Nonresponders 22% Responders 47% Responders 72% Low responders 12% Low responders 32% *Received an oral loading dose of 300 mg of clopidogrel followed by 75 mg daily; †Received a 450 -mg loading dose of clopidogrel. The use of clopidogrel in this study was not consistent with applicable FDA-approved Prescribing Information. Gurbel PA, et al. Circulation. 2003; 107(23): 2908 -2913; Lau WC, et al. Circulation. 2004; 109(2): 166 -171.
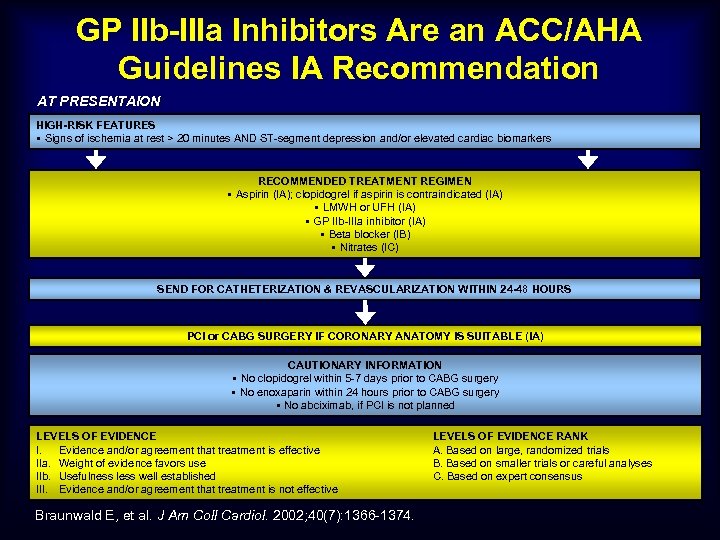
GP IIb-IIIa Inhibitors Are an ACC/AHA Guidelines IA Recommendation AT PRESENTAION HIGH-RISK FEATURES § Signs of ischemia at rest > 20 minutes AND ST-segment depression and/or elevated cardiac biomarkers RECOMMENDED TREATMENT REGIMEN § Aspirin (IA); clopidogrel if aspirin is contraindicated (IA) § LMWH or UFH (IA) § GP IIb-IIIa inhibitor (IA) § Beta blocker (IB) § Nitrates (IC) SEND FOR CATHETERIZATION & REVASCULARIZATION WITHIN 24 -48 HOURS PCI or CABG SURGERY IF CORONARY ANATOMY IS SUITABLE (IA) CAUTIONARY INFORMATION § No clopidogrel within 5 -7 days prior to CABG surgery § No enoxaparin within 24 hours prior to CABG surgery § No abciximab, if PCI is not planned LEVELS OF EVIDENCE I. Evidence and/or agreement that treatment is effective IIa. Weight of evidence favors use IIb. Usefulness less well established III. Evidence and/or agreement that treatment is not effective Braunwald E, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002; 40(7): 1366 -1374. LEVELS OF EVIDENCE RANK A. Based on large, randomized trials B. Based on smaller trials or careful analyses C. Based on expert consensus

Changes in Cardiac Arrest Management

Pharmacology n No improvements evident based on science with drugs to improve outcome n Epinephrine every 5 minutes n No added benefit to Vasopressin n Amiodarone and Lidocaine equal effectiveness

Defibrillation n Primary treatment for V-fib at 3 minutes and under n Should be delayed until good CPR for 2 minutes if down time over 3 minutes n Biphasic should be used n AED’s good in 3 minutes, bad after n One shock only with no pulse checks after

Vascular Access n Avoid ET drugs whenever possible n Peripheral IV’s OK n Central IV’s slightly better, but compression interruption frequent with placement n Interosseous recommended when peripheral IV’s not obtainable
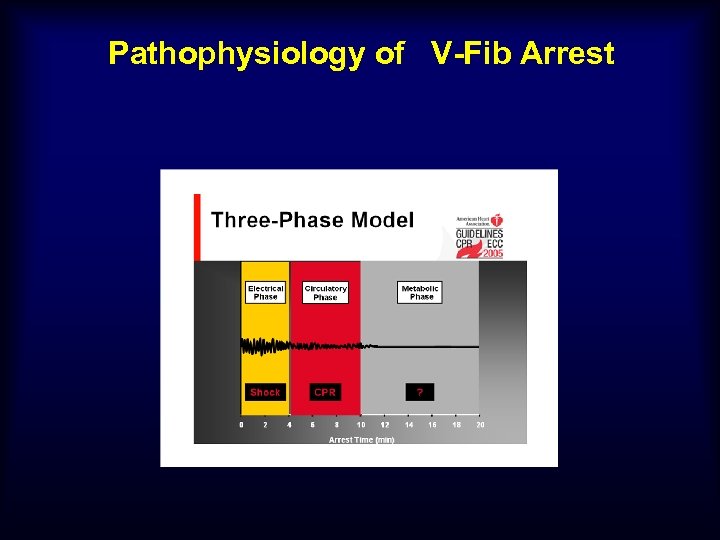
Pathophysiology of V-Fib Arrest




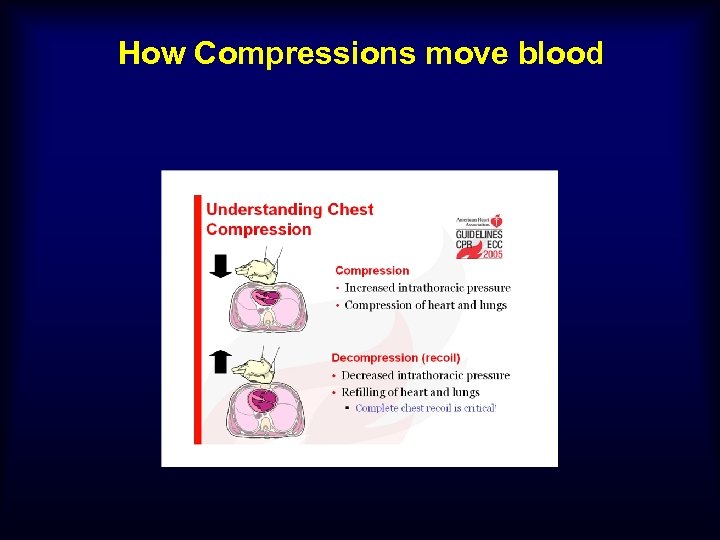
How Compressions move blood




What about AED’s? n Great in first 3 minutes. Must be in community. n Deadly after this as delay to shock is over 30 seconds. Manual defib required after 3 minutes.

Defibrillation n No more stacked shocks n Takes too long n All shocks maximum energy. n EMS probably should not use AED’s n Biphasic increases efficacy

Pulse Checks n Deadly!! n Only check pulses when rhythm appears to have converted thru CPR on ECG or signs of life n ECC says check before shock delivered after 5 cycles of 30: 2 CPR

What about intubation? In first 6 minutes, not a priority (V-fib) ASAP in PEA and Asystole. Understand that positive pressure breaths decrease cardiac output. Some air exchange from CPR plus gasping. Once intubated, 1 second breaths, six per minute. NO MORE.

Airway Combitube or ET equivalent RSA Mentality-view and see cords place ET, otherwise immediate Combitube first try.

Protocol n Dispatch instructs CCC n If good CPR on EMS arrival, shock max X 1 n If no or poor CPR, immediate compressions

Protocol n OP airway n Non-rebreather face mask @ 90+% n 200 compressions n IV access n Epinephrine 1 mg IVP n Vasopressin 40 units IVP ASAP n One shock, 3 -5 seconds, no pulse checks.

Protocol n Begin second round of 200 compressions n Amiodarone 300 mg IVP n Shock X 1 at max joules n No pulse checks, not off chest more than 5 seconds.

Protocol n Begin 3 rd round of compressions n Epinephrine 1 mg IVP n Shock X 1 after 200 compressions

Protocol During 4 th round of compressions place definitive airway without halting compressions on first attempt.

Protocol 200 compressions alternating epinephrine with antidysrhythmic drug and shock X 1. Remain on scene and work until pulse or nonshockable rhythm.

48% Neuro-intact survivors!! 10% before new protocol

QUESTIONS? ?
38b3387d199a2df30f3bf3ce26576949.ppt