9849161b5e09189c4d589add4076d485.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67

Cardiovascular Disease Prof. Mohamed Sobhy, MD, FACC Professor of Cardiology, Alex. University Fellow of American College of Cardiology

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Guidelines: Aim to present all the relevant evidence on a particular issue in order to help physicians to weigh the benefits and risks of a particular diagnostic or therapeutic procedure. They should be helpful in everyday clinical decision-making.

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Prevention programs. Public health Challenges and Community programs.

The Rationale for an active approach to the prevention of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) is firmly based on five observations: CVD is the major cause of premature death in most populations; it is an important source of disability and contributes in large part to the escalating costs of health care the underlying pathology is usually atherosclerosis, which develops insidiously over many years and is usually advanced by the time symptoms occur death, myocardial infarction and stroke nevertheless frequently occur suddenly and before medical care is available, and many therapeutic interventions are therefore inapplicable or palliative the mass occurrence of CVD relates strongly to lifestyles and modifiable physiological factors risk factor modifications have been unequivocally shown to reduce mortality and morbidity, especially in people with either unrecognized or recognized CVD.

Objectives of Cardiovascular Prevention To reduce the incidence of first or recurrent clinical events due to coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke and peripheral artery disease. The focus is prevention of disability and early death. Lifestyle changes, management of major CV factors, use of different prophylactic drug therapies. Intermediate end-points… subclinical organ damage [LVH, CA plaque, ED,

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice

Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice

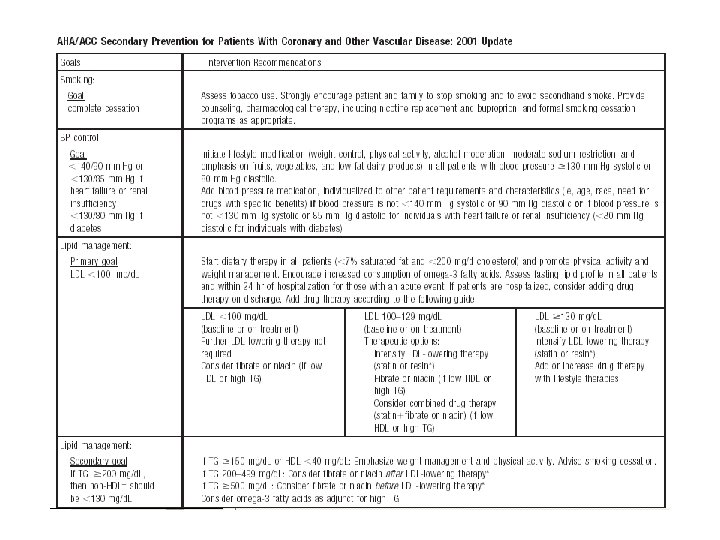

Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice




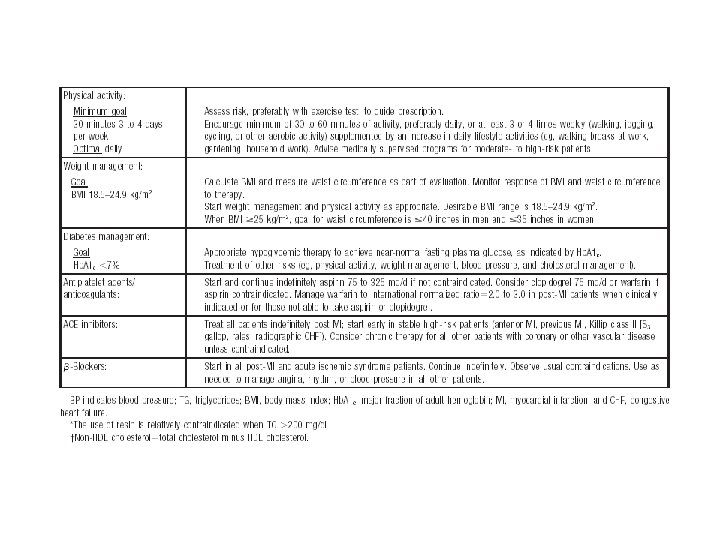
Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice

Canadian Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus Conference On The Prevention Of Cardiovascular Diseases: The Role Of The cardiovascular Specialist

Recommendations for assessment with fasting lipid profile (total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride and low density lipoprotein levels) in various patient groups Clinical judgement should be used for patients with multiple risk factors who are approaching these target ages. Note that the translation of number of risk factors into risk levels is incorrect outside of these age ranges. CAD Coronary artery disease

Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice


Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice

Editorial New British recommendations for prevention of coronary heart disease in clinical practice Heart 1999; 81: 335 (April)

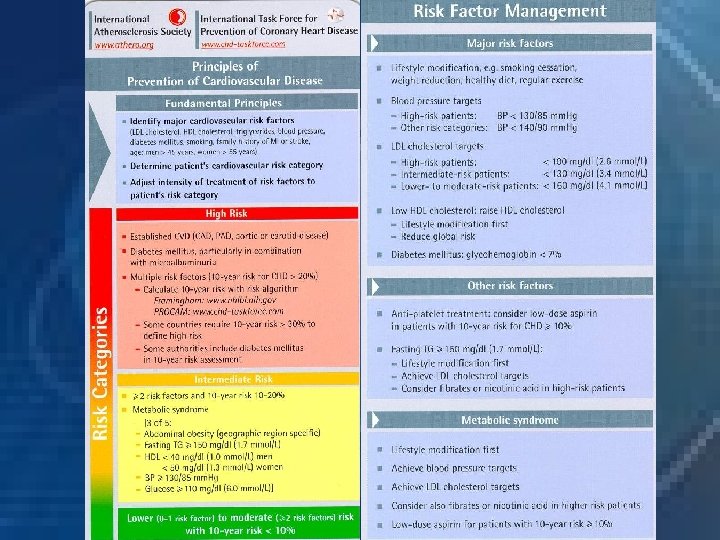
Priorities for CHD prevention in clinical Practice 1. A. Patients with established CHD. B. Patients with other major atherosclerotic disease. 2. Patients with HTN, dyslipidemia, DM, FH of premature CHD or combination.
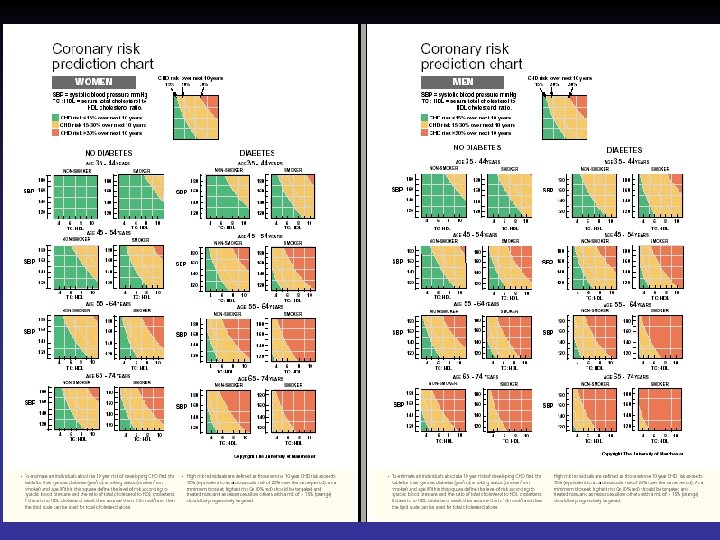
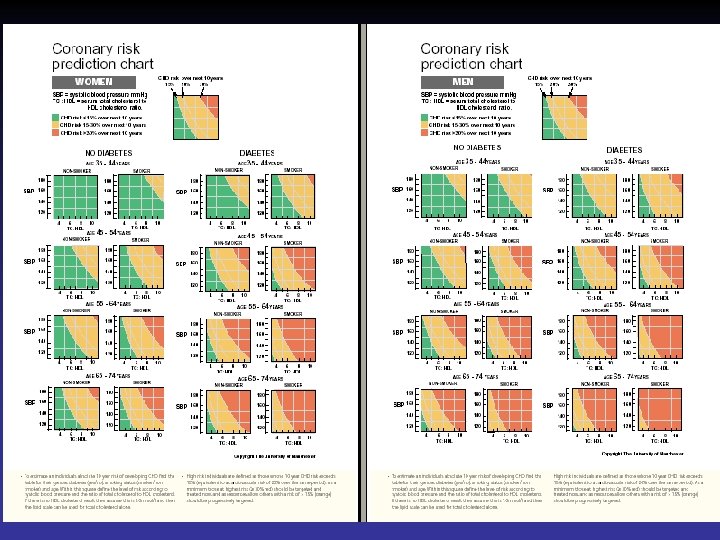
Using the coronary risk prediction chart for primary prevention Charts are not appropriate for: Coronary Heart Disease or other major atherosclerotic disease. Familial hypercholeserolemia or other inherited dyslipidemia Established hypertension (Systolic >160 mm. Hg or diastolic > 100 mm. Hg or associated TOD) DM with associated TOD Renal dysfunction

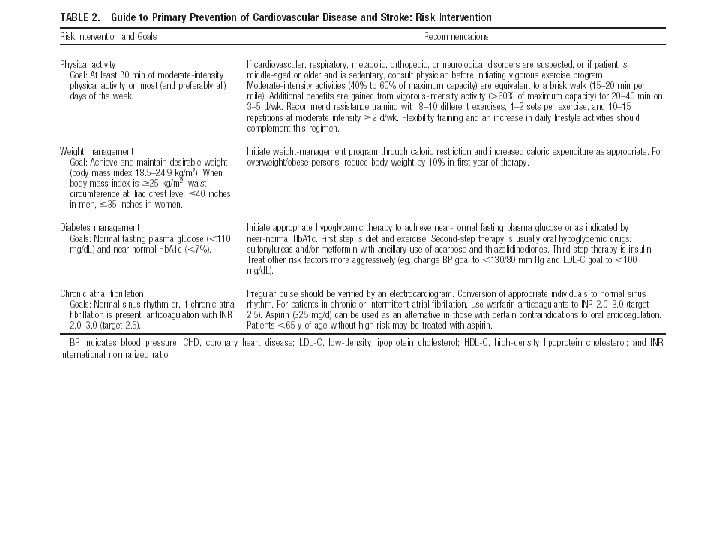
People at high risk without clinically overt CHD or other major atherosclerotic disease Patients with HTN, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, FH of premature CHD or combination are at high risk of developing CHD Patients with DM are at particularly high risk Individuals at high multifactorial risk of developing CHD or other atherosclerotic disease As absolute risk of coronary heart disease increases, so lifestyle intervention should

New British recommendations for prevention of coronary heart disease in clinical practice The joint British recommendations on prevention of coronary heart disease in clinical practice closely mirror the European guidelines. The difference reflect intelligent adaptations to national conditions and concerns The recommendations concerning primary prevention are based on the assessment of risk, in absolute terms of developing clinical coronary disease within the next

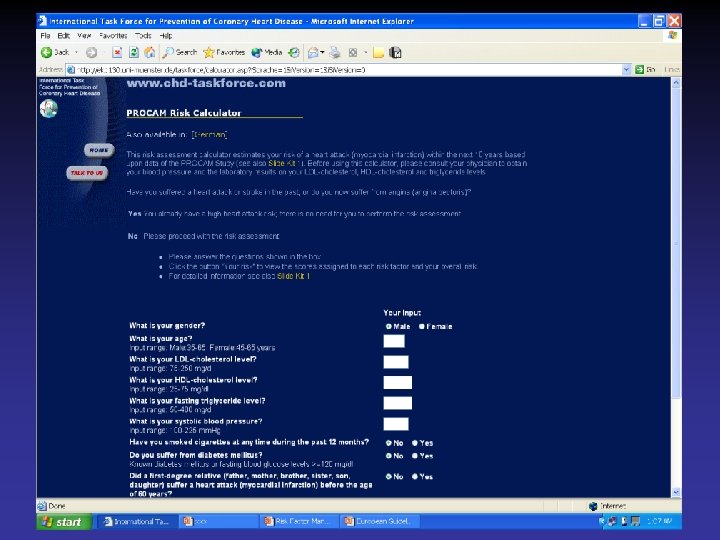
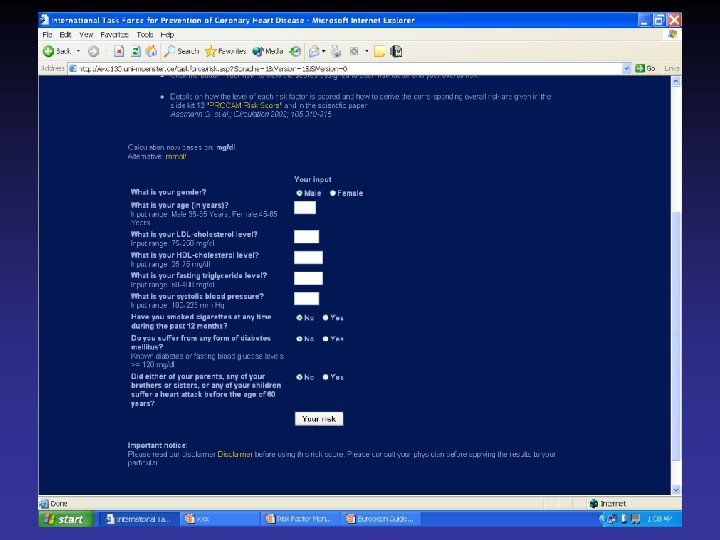
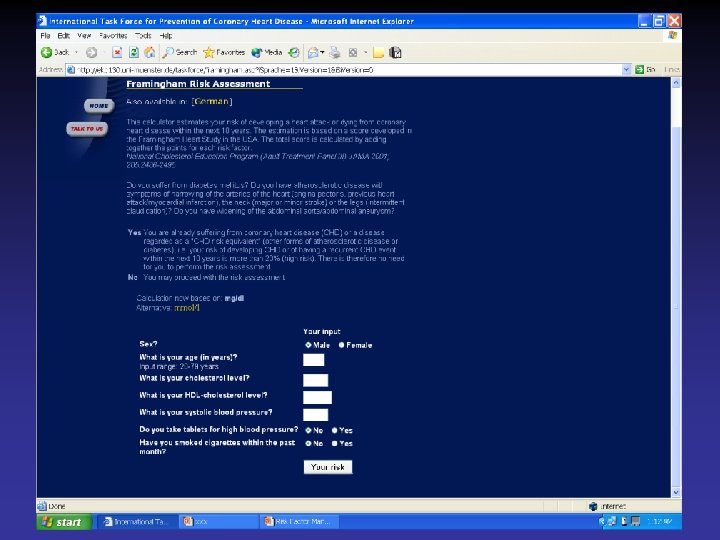
The assessment is based on Framingham risk function (age, sex, smoking status, SBP, lipids measurements) British recommend ratio of total HDL Level of risk at which to intervene in primary prevention European recommends 10 year risk of CHD 20% British a staged approach High risk Low risk >30% 15%

BP …. Based on BP alone rather than BP in the context of absolute CV risk. British recommendations: BP>160/110 mm. Hg should be lowered irrespective of other factors because of established benefit in reducing the cerebrovascular component of CV risk 15% risk of CHD corresponds to 20% overall CV risk. In persons of BP 140 -160/90 -100 mm. Hg. British Society starts treatment when risk of

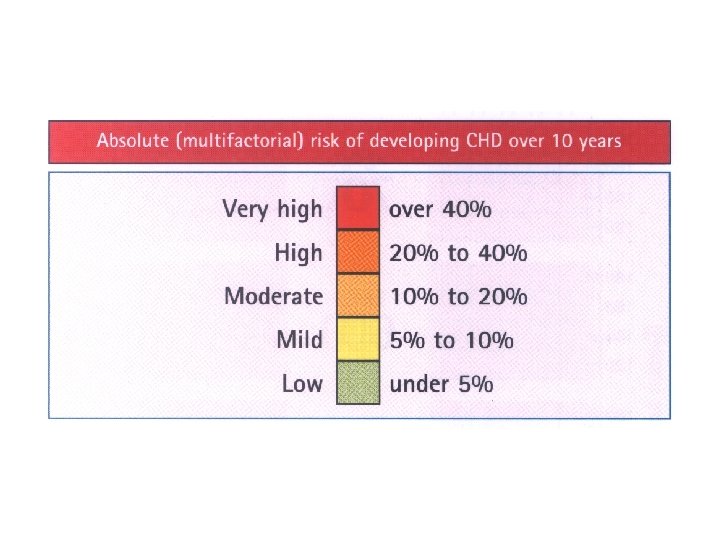
Introducing drug treatment for raised BP or lipid concentration should be strongly determined by the absolute risk of developing disease. An absolute risk of coronary heart disease >15% (equivalent to a CV risk of 20%) over 10 years is sufficiently high to justify drug treatment.

Exceptions to treatment based on absolute risk are: Hypertension (SBP>160 mm. Hg or diastolic BP>100 mm. Hg) or HTN with associated target organ damage. Familial hypercholestrolemia or other inherited dyslipidemia. Diabetes Mellitus with associated target organ damage. Drug treatment is required for all these patients to reduce the risk of CHD (and CV risk).

A staged approach to managing patients at high risk is advised. As a minimum, those with absolute CHD risk >30% should be targeted and treated now. As resources allow individuals with a risk >15% should be progressively targeted For all high risk patients every effort should be made to achieve the lifestyle, risk factor and therapeutic targets.

Recent international guidelines American College of Cardiology (ACC) 2001 update American Heart Association (AHA) 2002 update CANADIAN Cardiovascular Society 1998 Consensus. International Task Force for prevention of Coronary heart disease Joint British recommendation for prevention of CHD 2002 European guidelines on CVD prevention in clinical practice

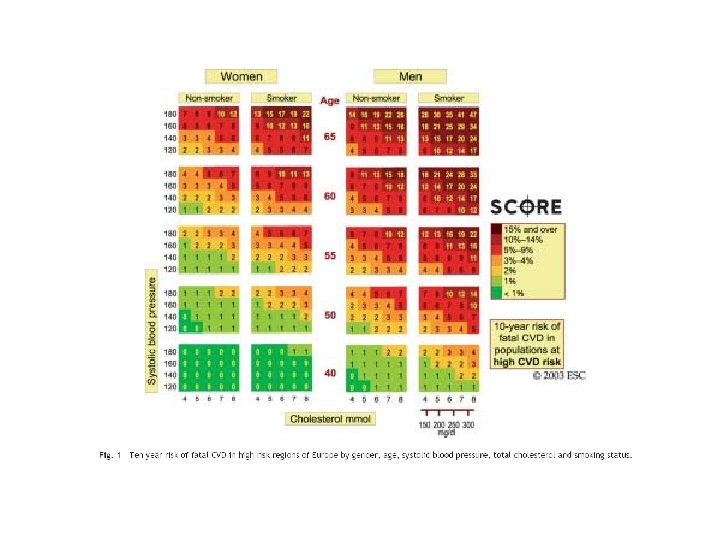
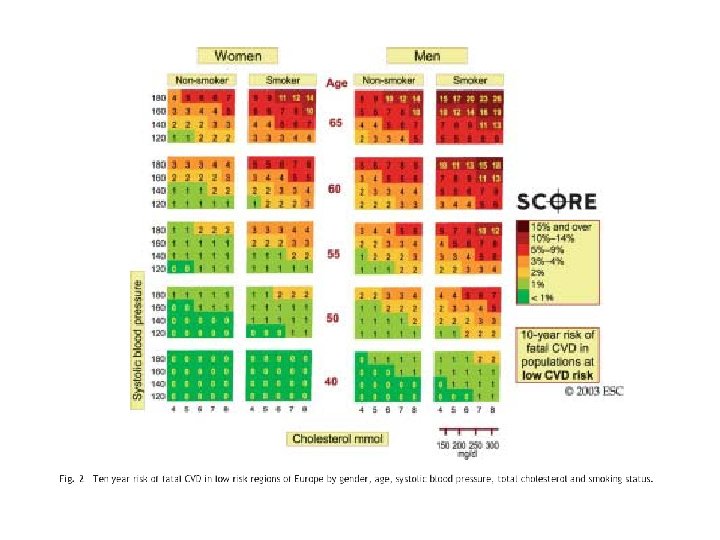
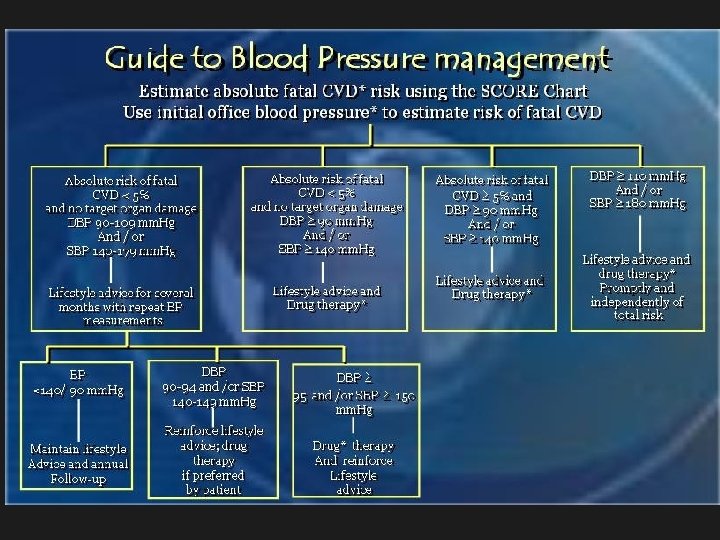


International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.



International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

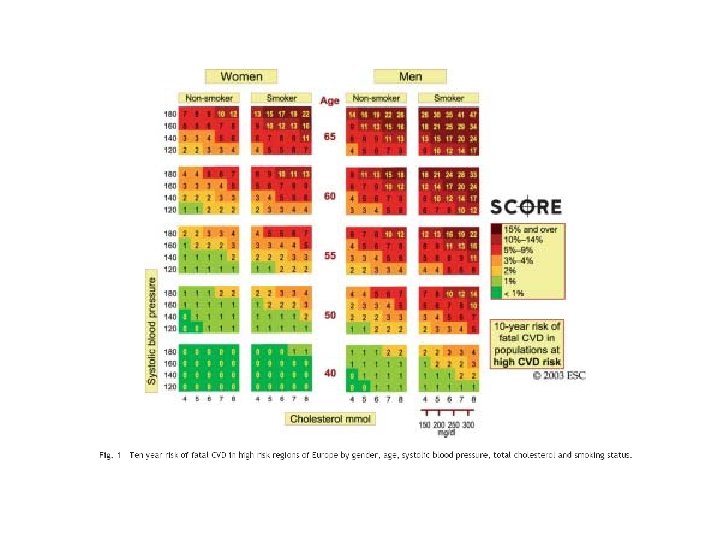
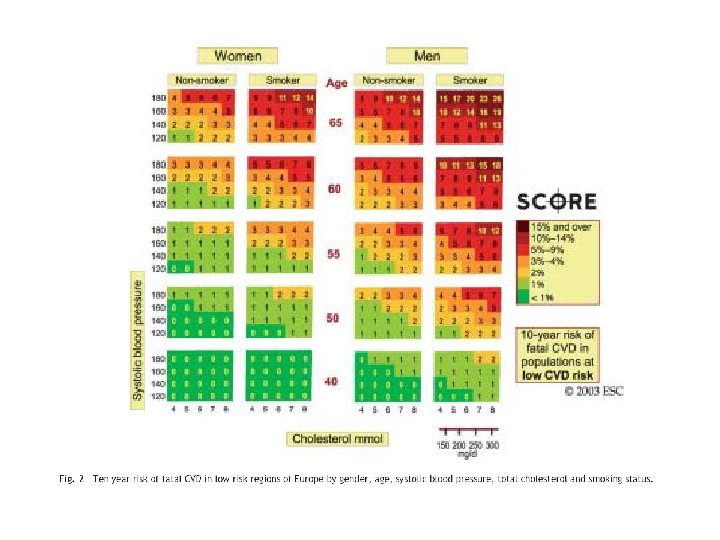
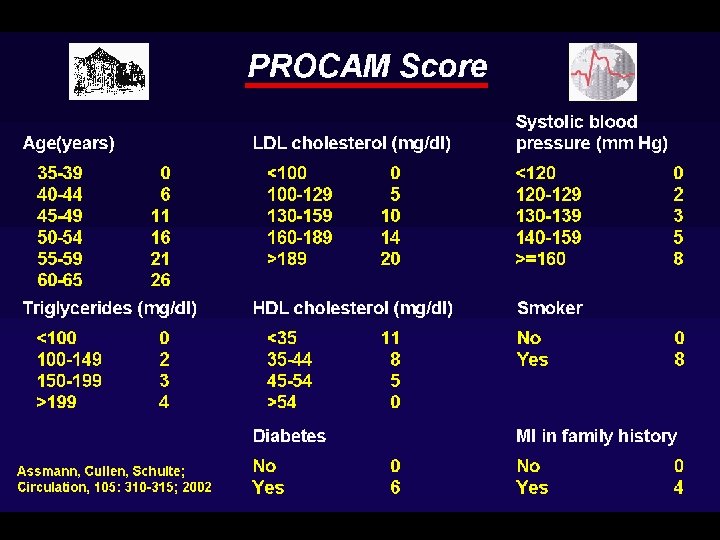
Definition of high total risk for developing fatal cardiovascular event. Patients with established cardiovascular disease. Asymptomatic subjects who have 2 -1 Multiple risk factors resulting in a 10 year risk ≥ 5% now or if extrapolated to age 60. 2 -2 Markedly raised levels of single risk factors: total cholesterol(320 mg/dl), LDL (240 mg/dl), BP ≥ 180/140 mm. Hg 2 -3 Diabetes type 2 and diabetes type 1 with microalbuminuria.
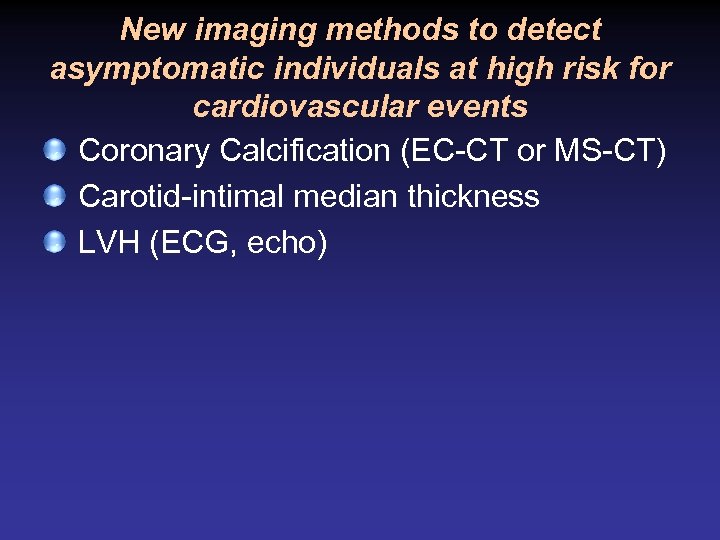
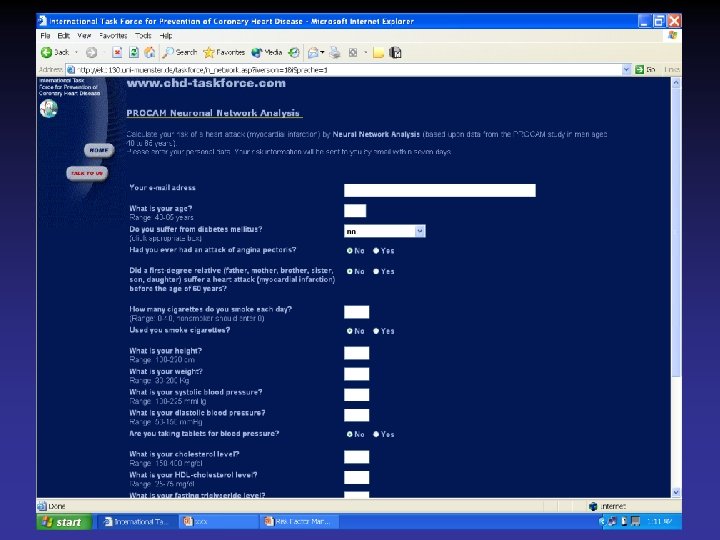
New imaging methods to detect asymptomatic individuals at high risk for cardiovascular events Coronary Calcification (EC-CT or MS-CT) Carotid-intimal median thickness LVH (ECG, echo)

Management of CVD risk in clinical practice: Behavioral risk factors Stop smoking tobacco Make healthy food choices Increase physical activity Management of other risk factors: Overweight and obesity Blood pressure Plasma lipids Diabetes Screening close relatives

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

Why Egyptian Guidelines are mandatory? Religion Habits Cost-benefit ratio Role of university Role of physicians Role of Ministry of Health

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.

When public intervention strategies address the diversity of racial, ethnic, cultural, linguistic, religions, and social factors in the delivery of their services, the like hood of their acceptance by community increases.

Public health approach can provide an attractive opportunity to interrupt and prevent the continuing costly of cycle preventing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and its complications.

Public health challenge and community programs Public health approaches, such as reducing calories, saturated fat and salt in processed food Increasing community and school opportunities for physical activity can achieve a downward shift in the distribution of population’s BP, reduce morbidity, mortality and the lifetime risk of an individual becoming hypertensive. Food manufactures and restaurants should reduce sodium in food supply by 50% during the next decade

International Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Definition of guidelines. Rationale and objectives of guidelines. What are the international guidelines for prevention of atherosclerotic CVD Total CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies. Management of CV risk as a guide to preventive strategies Importance of Egyptian guidelines. Public health Challenges and Community programs. Prevention programs.


Prevention programs Current programs Bridge the gap (clinical trials application) E Quit, computers soft ware Strengths Nationally and internationally recognized physician researchers A medical clinic staffed by registered nurses and certified medical technician Project managers and site monitors experienced with managing and running clinical trials A data coordinating center to collect, input and analyze data generated from prevention research Affiliation with some of the major medical research and healthcare providers. Make a contribution, Foundations and individuals
9849161b5e09189c4d589add4076d485.ppt