33845882bc0a3c673a8c929d1918a80d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Cardiometabolic Syndrome 1 SUSAN YOUNG, MSN, RN NURSE CONSULTANT DIABETES PROGRAM, DSHS

Learning Objectives 2 List at least 3 risk factors for cardiometabolic syndrome Identify 3 preventive strategies for persons with cardiometabolic syndrome Discuss 3 -5 worksite initiatives to address cardiometabolic syndrome, obesity, & type 2 diabetes

Question of the Day 3 In what 2 settings can you influence your health significantly?
What is Cardiometabolic Syndrome? 4 Cardiometabolic syndrome is defined as the presence of 3 of the following clinical markers: Insulin resistance Abdominal adiposity Elevated blood pressure Elevated fasting glucose Elevated triglycerides Low HDL levels

What contributes to these clinical markers? A diet high in saturated fat Minimal to no physical activity

Insulin Resistance 6 Body produces insulin, but it is either not enough, or body does not use properly Presence of abnormal fat distribution, even though one may not be obese

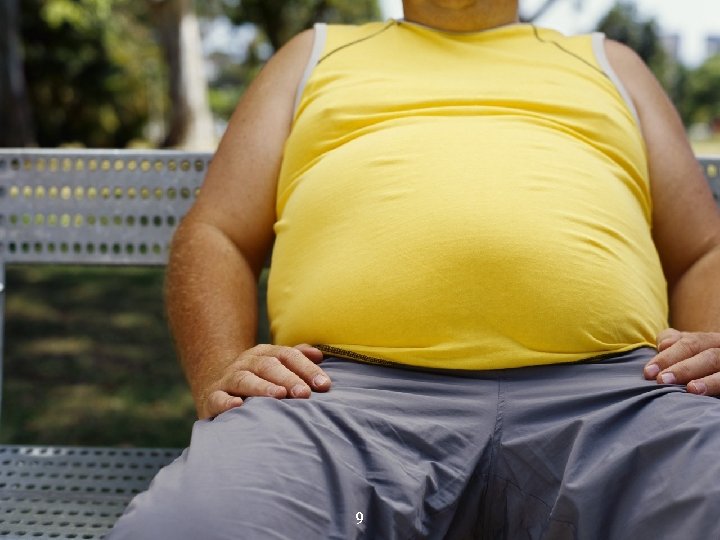
Abdominal adiposity 7 Waist circumference > 40 inches in men > 35 inches in women
8

9

10
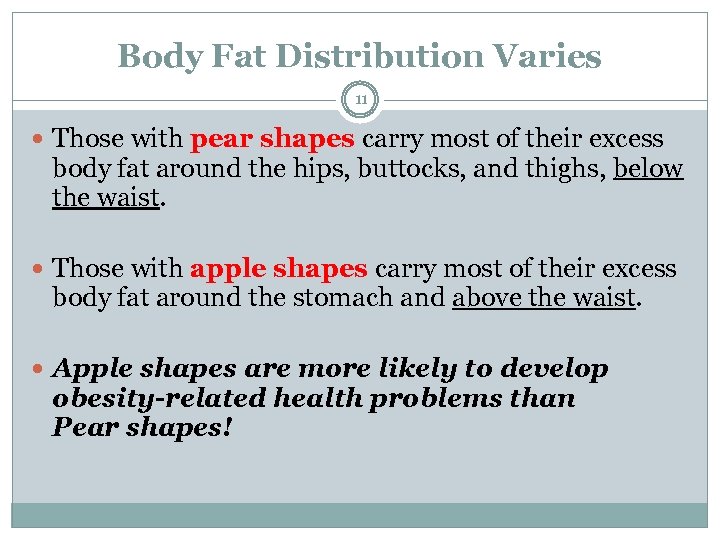
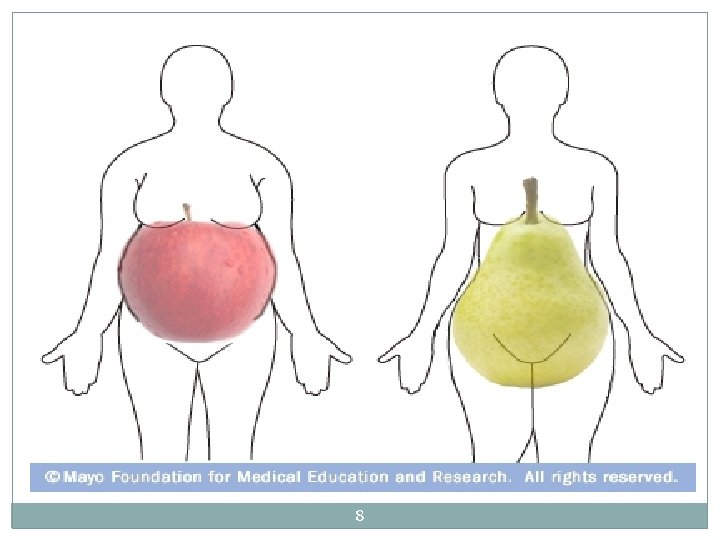
Body Fat Distribution Varies 11 Those with pear shapes carry most of their excess body fat around the hips, buttocks, and thighs, below the waist. Those with apple shapes carry most of their excess body fat around the stomach and above the waist. Apple shapes are more likely to develop obesity-related health problems than Pear shapes!
Body Shapes 12 To determine body shape, divide waist measurement by hip measurement. This will give a waist-to-hip ratio. Apple-Shaped: Women with waist-to-hip ratio more than 0. 8. Men with waist-to-hip ratio more than 1. 0.
Elevated Blood Pressure 13 Systolic blood pressure > 120 or a diastolic blood pressure > 80 Taking medication for hypertension
Fasting Glucose 14 > 100 mg/d. L Taking medication for elevated glucose
Triglycerides, LDL Cholesterol 15 Triglycerides > 150 mg/d. L Taking medication for elevated triglycerides Low HDL < 40 mg/d. L, men < 50 mg/d. L, women Taking medication for low HDL

Why is Cardiometabolic Syndrome Important? 16 Increased risk for a variety of health conditions, e. g. , type 2 diabetes, arthritis, chronic pain, and heart disease Increased health care costs
Data 17 Prevalence ↑ from 29. 8% in 2004 to 32. 1% in 2006
Diabetes is Costly 18 Direct care costs (hospital & provider charges, medications) $116 billion annually Indirect are costs (lost work time, productivity losses, disabilities) $58 billion annually

More Cost Data Cost /year of individual w/ diabetes $11, 744/yr Cost/year of individual w/out diabetes $5, 095/year People with diabetes who control their disease by keeping their blood sugar within target ranges cost employers only $24 a month, compared with the $115 a month for people with diabetes who do not control their blood sugar.
How to Define “control” 20 Follows meal plan Adheres to medication regimen Maintains lab/clinical values within normal range Adheres to standards of care

Standards of Care 21 Daily Care Routine tests Identifying and treating problems www. texasdiabetescouncil. org

Self Management Training 22 AADE and 7 self care behaviors Healthy eating Being active Monitoring Taking medications Problem-solving Healthy coping Reducing risks

Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors 23 Age Obesity Ethnicity Hypertension, cardiovascular disease Family history of type 2 diabetes or GDM
Treatment 24 STOP SMOKING!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Regular physical activity Weight loss Healthy food choices
Physical Activity 25 150 minutes per week 30 minutes “most days” for “heart health” One hour/day to lose weight Just Move!!!!!!!
Weight Loss 26 Losing only 5 -7% of present body weight decreases chances of developing heart disease by 58%

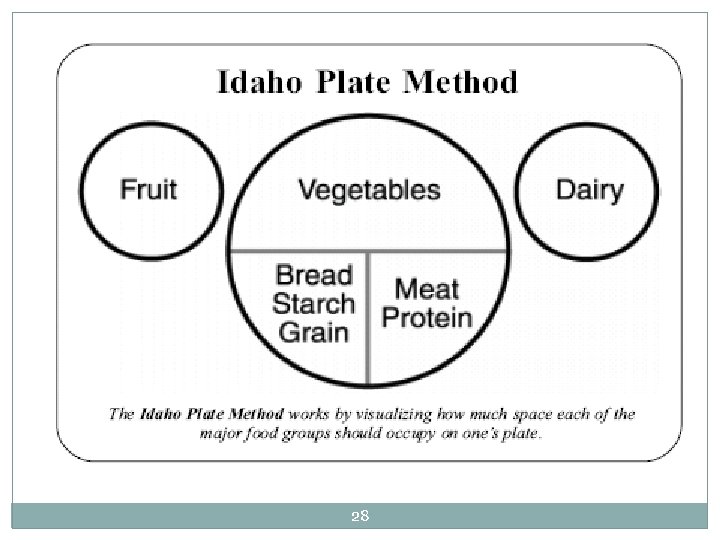
Eating Healthy 27 5 -a-Day Portion control Limit processed foods Don’t make all changes at once Get support from family & friends Use Idaho Plate Method
28

Question of the Day 29 In what 2 settings can you influence your health significantly?


When at the grocery… 31 Select fresh fruits and vegetables as often as possible Minimize processed foods Read food labels Select foods high in fiber Look at the first 3 ingredients Select colorful foods Avoid HFCS

What is the best choice?


In the kitchen… 34 Sautee rather than fry Steam rather than fry Bake rather than fry Cook with less salt, butter, dressings DASH diet

At the table… 35 Use less salt Use less fats & oils Limit animal fats Limit alcohol Eat slowly

At the table… Eat more whole grains Eat more tubers & legumes Eat more fruits and vegetables Drink more water Eat a hearty breakfast

At Work… 37


Worksite Wellness Programs Reduce absenteeism Increase presenteeism Reduce medical costs Increase productivity

Worksite wellness, cont’d. Reduce Worker’s compensation claims Increase morale and loyalty Reduce injuries

Challenges? 41 Time Limited resources “Buy-in” from management Physical space Other……

Diabetes at Work FREE Online resource Fact sheets Lesson plans Copyright-free www. diabetesatwork. org

Other Resources Texas Diabetes Program materials www. texasdiabetescouncil. org CDC’s Workplace Health Model CDC’s Workplace Health Development Program Checklist www. cdc. gov NDEP materials www. ndep. gov

Contact information 44 SUSAN. YOUNG@DSHS. STATE. TX. US 512 -458 -7111. 6122 888 -963 -7111. 6122
33845882bc0a3c673a8c929d1918a80d.ppt