Carbohydrate metabolism 2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55

Carbohydrate metabolism
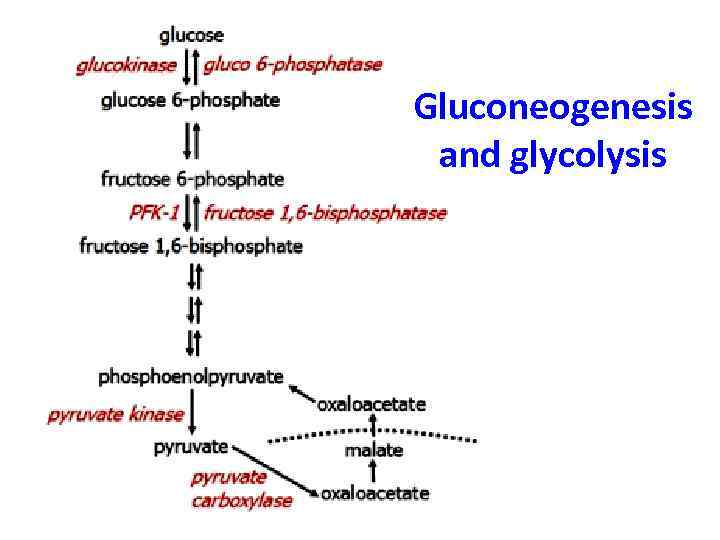
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis
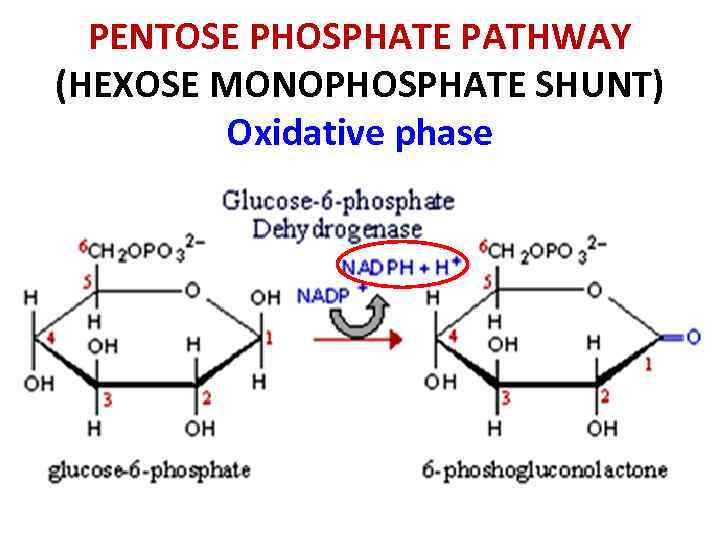
PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY (HEXOSE MONOPHOSPHATE SHUNT) Oxidative phase

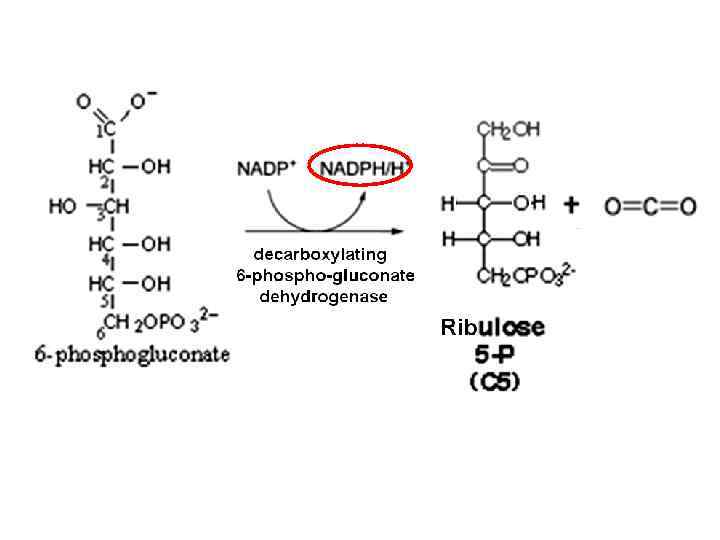
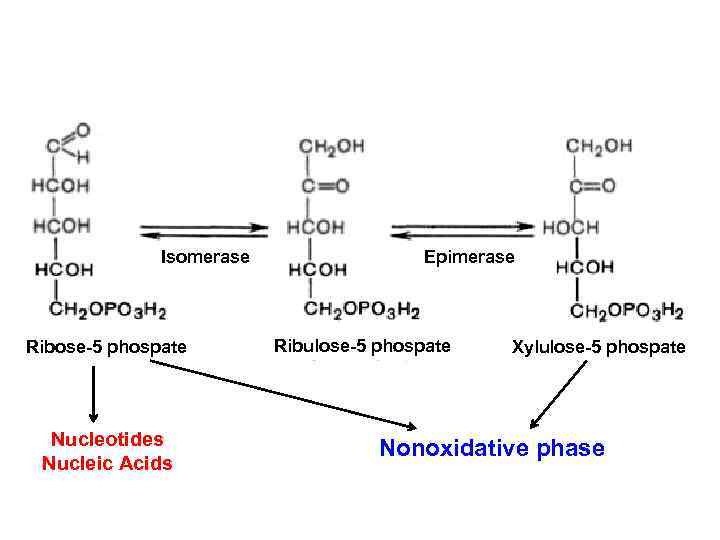
Isomerase Ribose-5 phospate Nucleotides Nucleic Acids Epimerase Ribulose-5 phospate Xylulose-5 phospate Nonoxidative phase
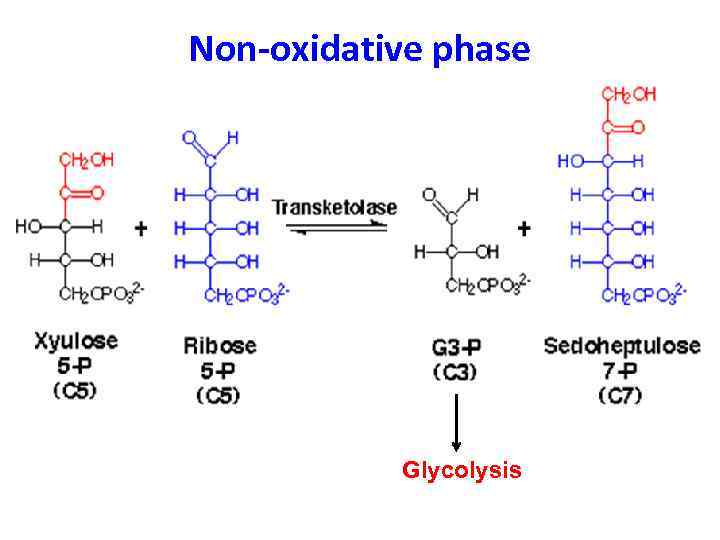
Non-oxidative phase Glycolysis

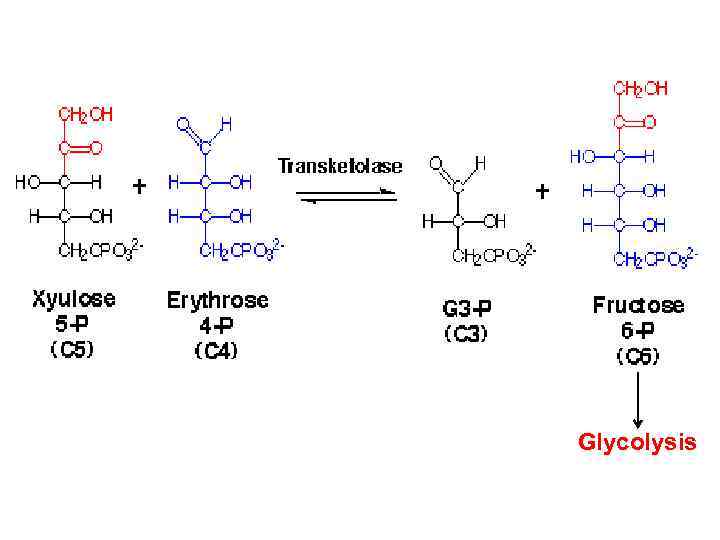
Glycolysis
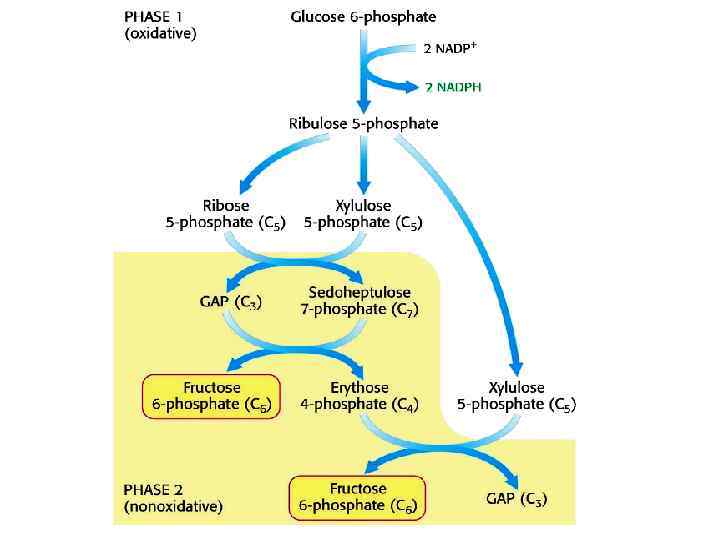

The overall equation: 6 G-6 -P + 12 NADP+ + 7 H 2 O 5 G-6 -P + 12 NADPH + 6 CO 2 + 12 H +
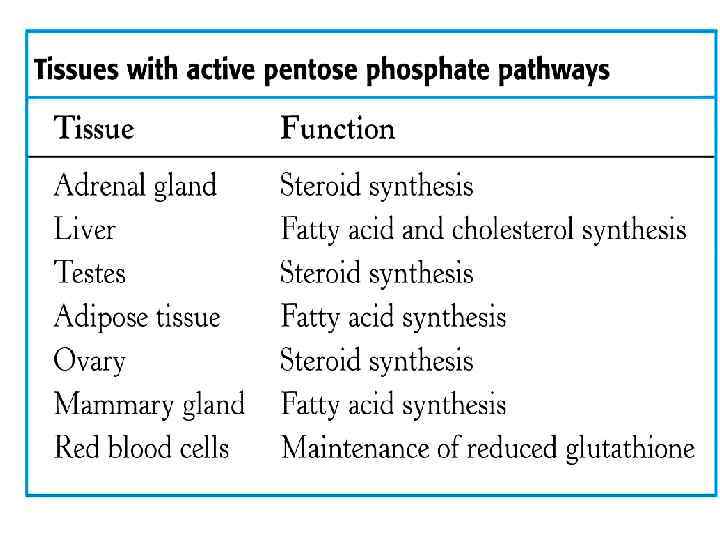
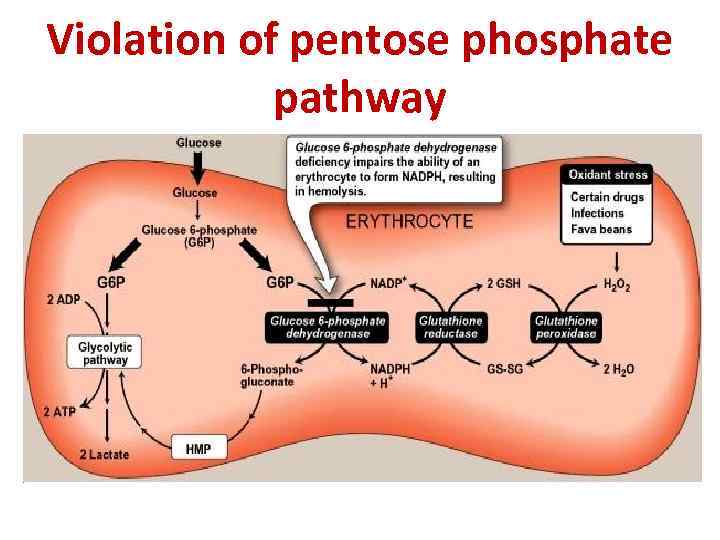
Violation of pentose phosphate pathway

Ethanol metabolism
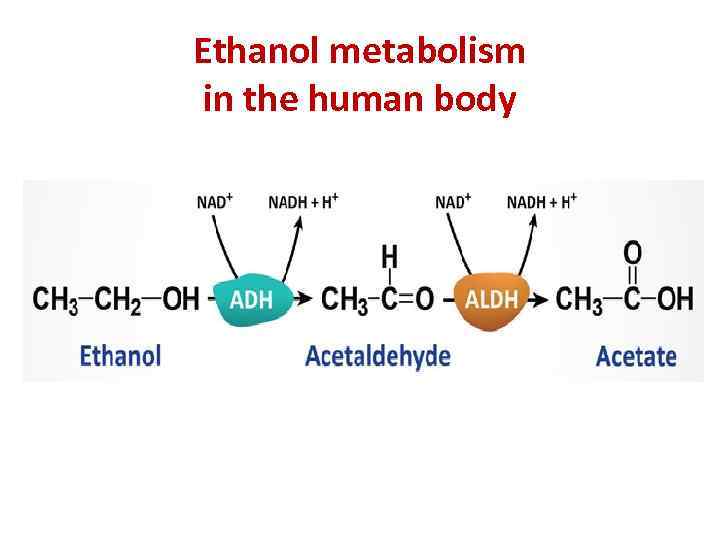
Ethanol metabolism in the human body
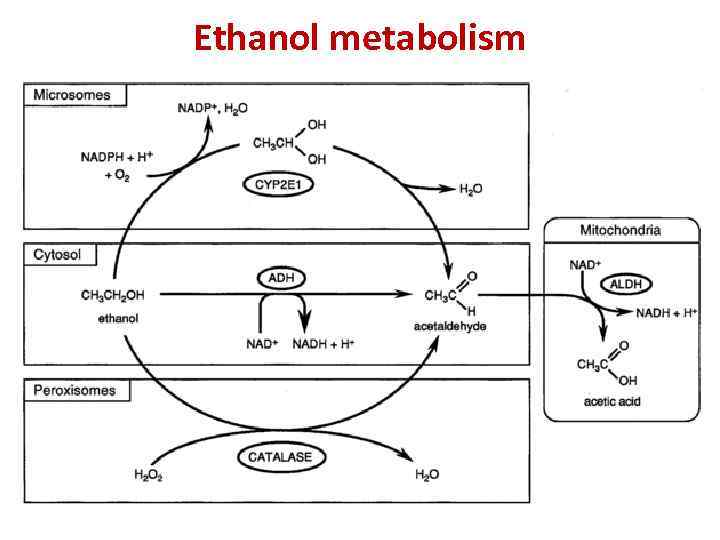
Ethanol metabolism
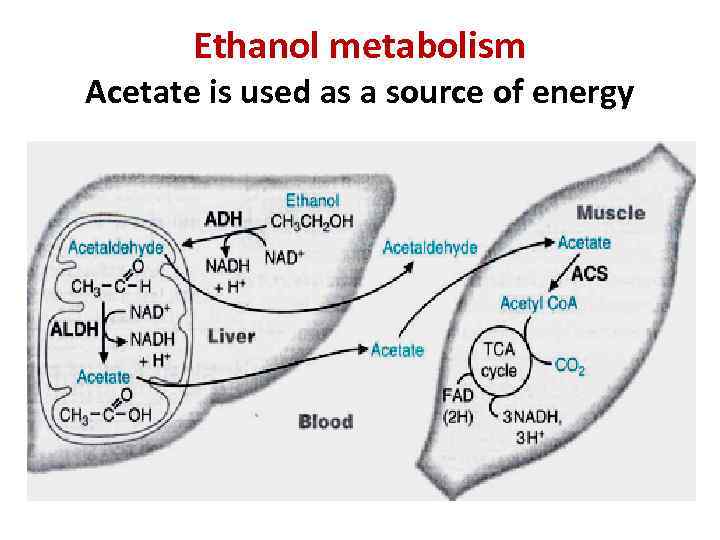
Ethanol metabolism Acetate is used as a source of energy

Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen in the cell
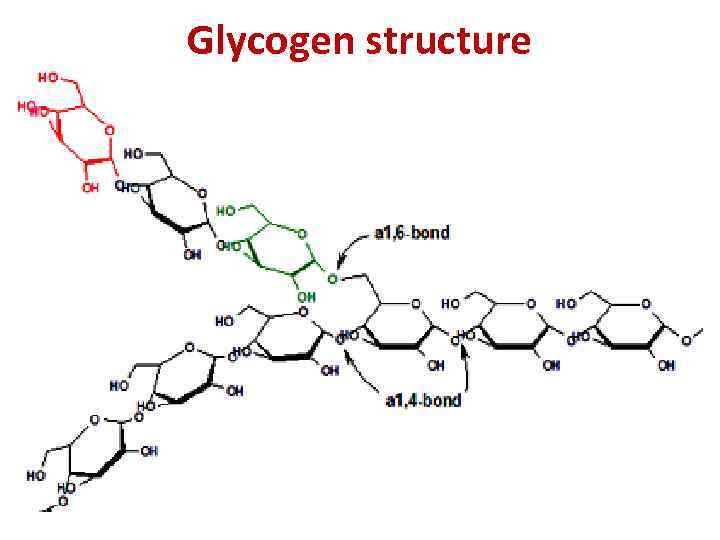
Glycogen structure
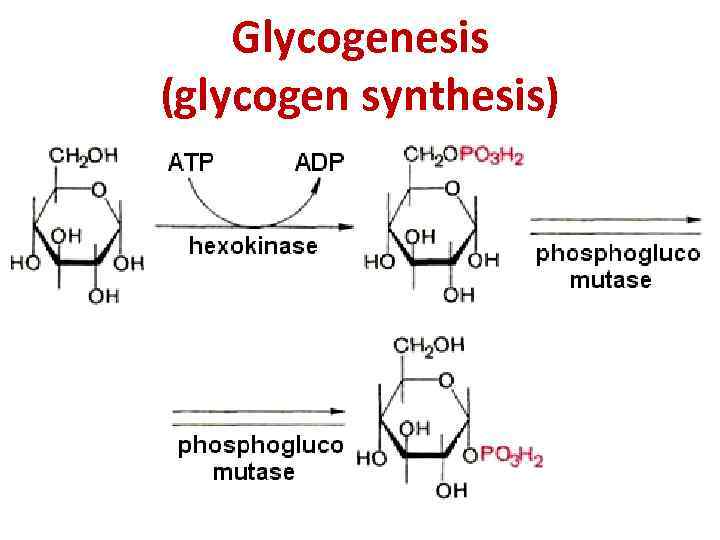
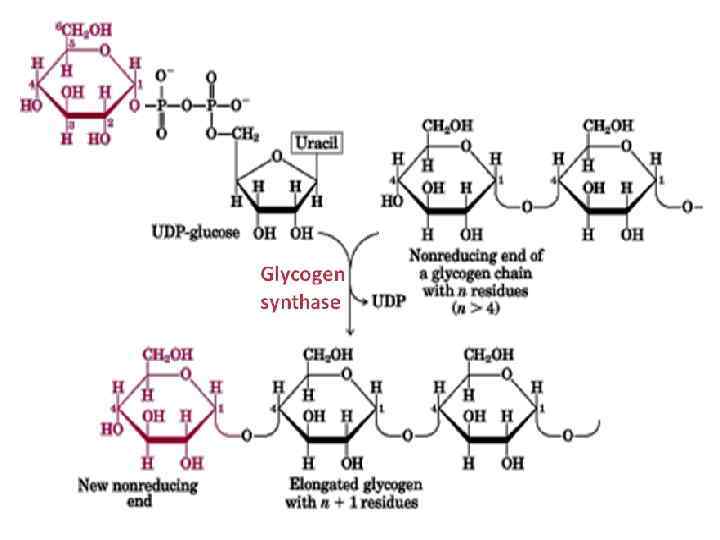
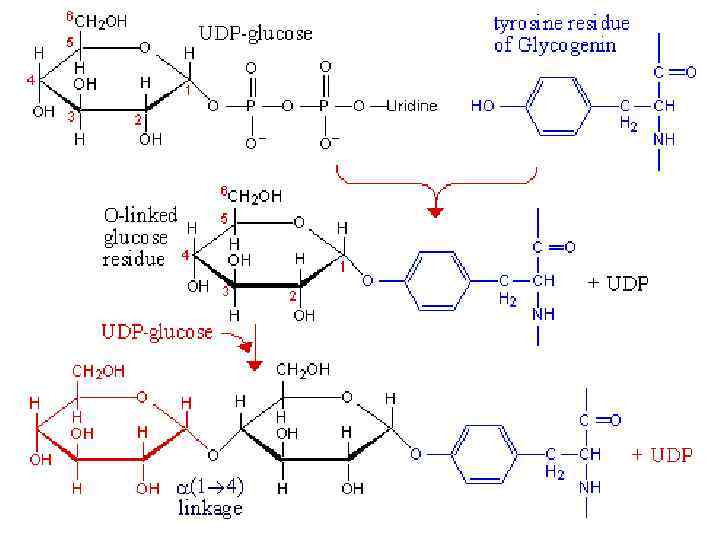
Glycogenesis (glycogen synthesis)
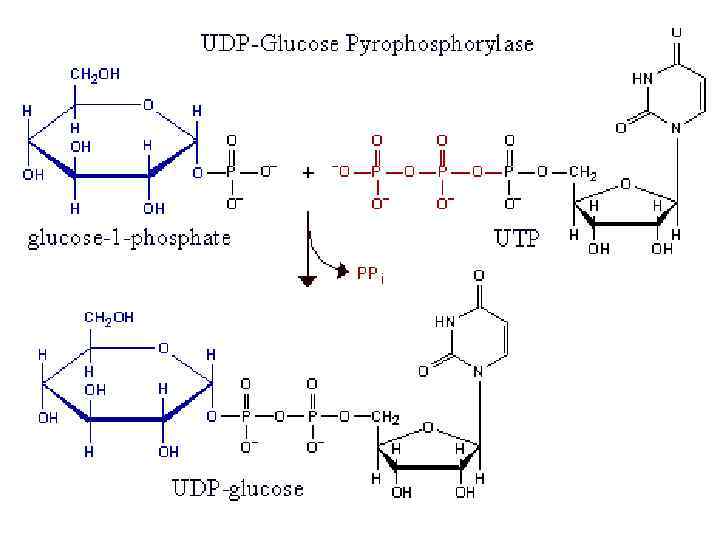

Glycogen syntase
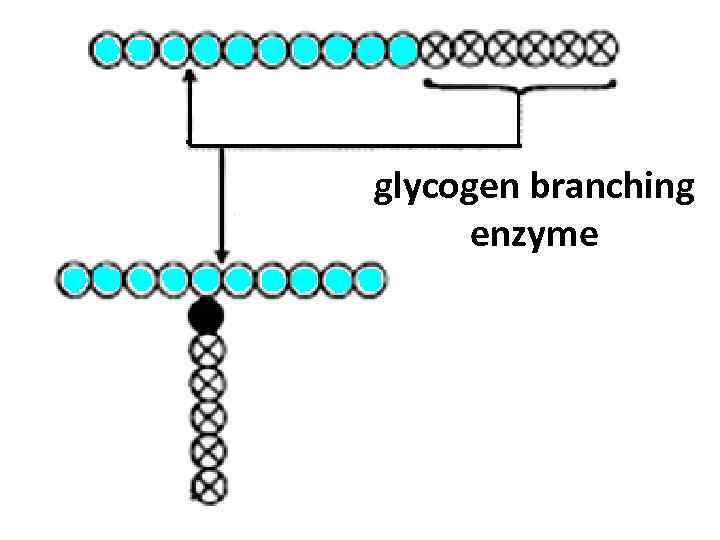
glycogen branching enzyme
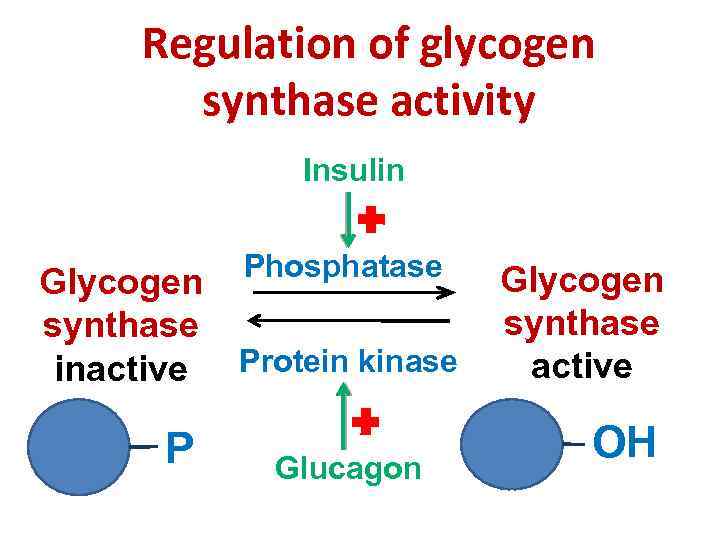
Regulation of glycogen synthase activity Insulin Glycogen synthase inactive P Phosphatase Protein kinase Glucagon Glycogen synthase active OH
Degradation of glycogen Glycogen phosphorylase
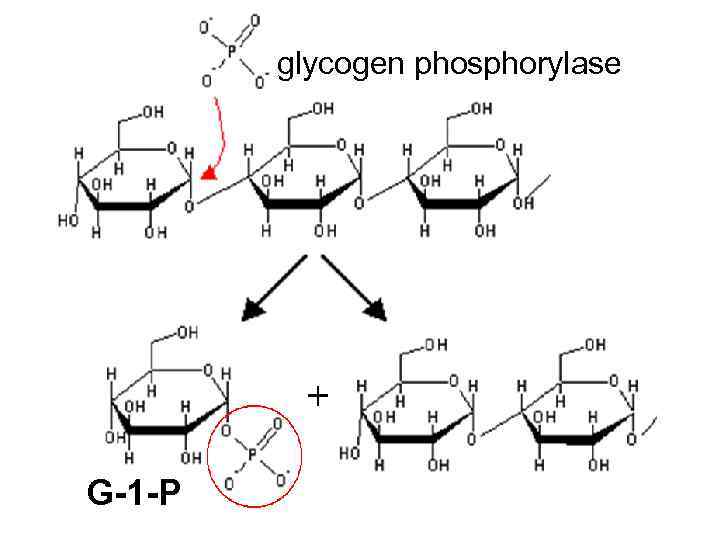
glycogen phosphorylase G-1 -P
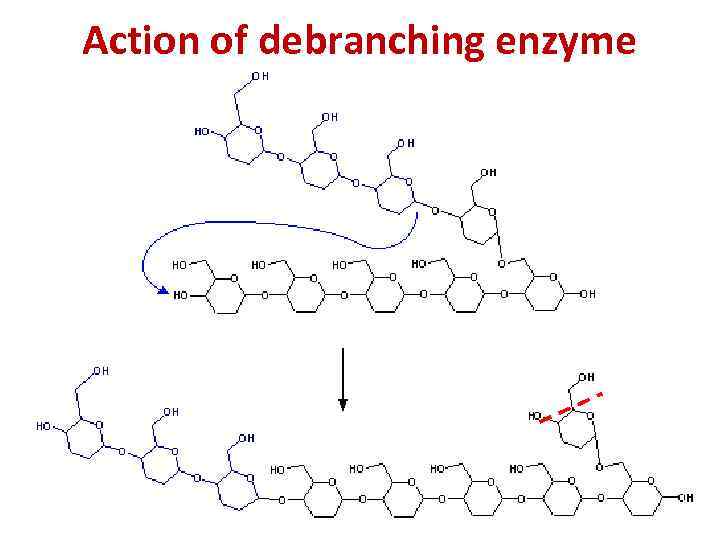
Action of debranching enzyme
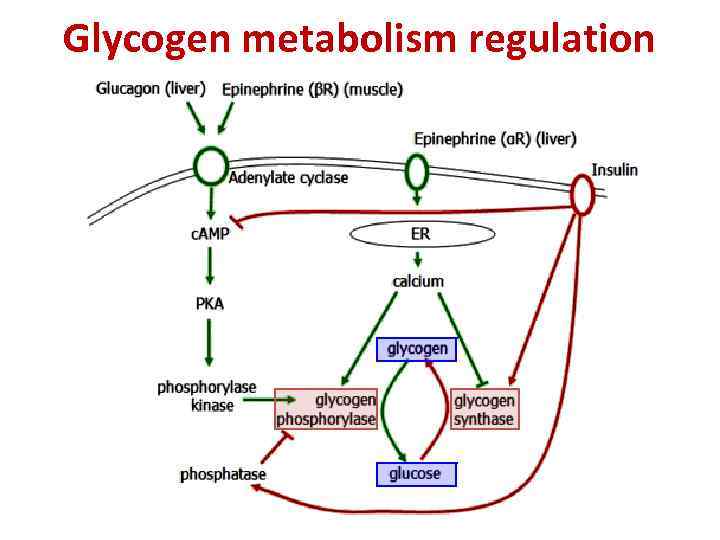
Glycogen metabolism regulation
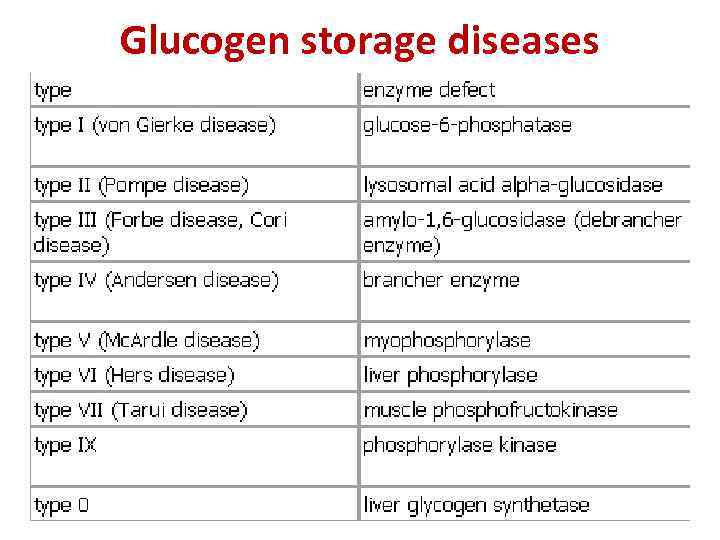
Glucogen storage diseases
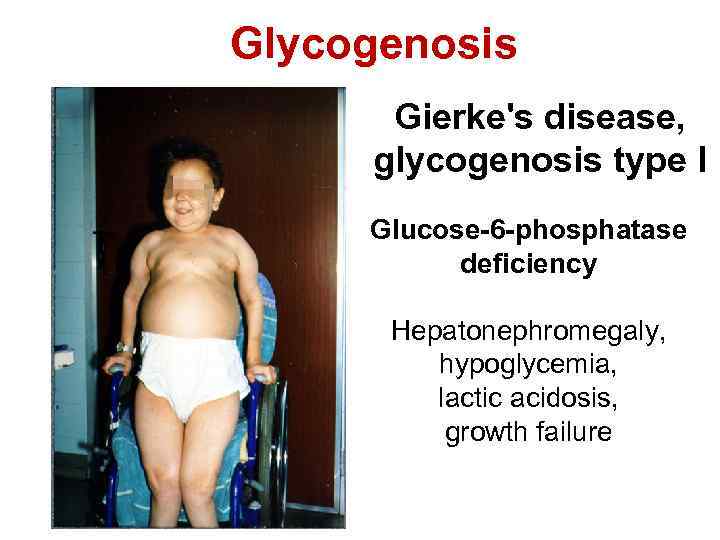
Glycogenosis Gierke's disease, glycogenosis type I Glucose-6 -phosphatase deficiency Hepatonephromegaly, hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, growth failure
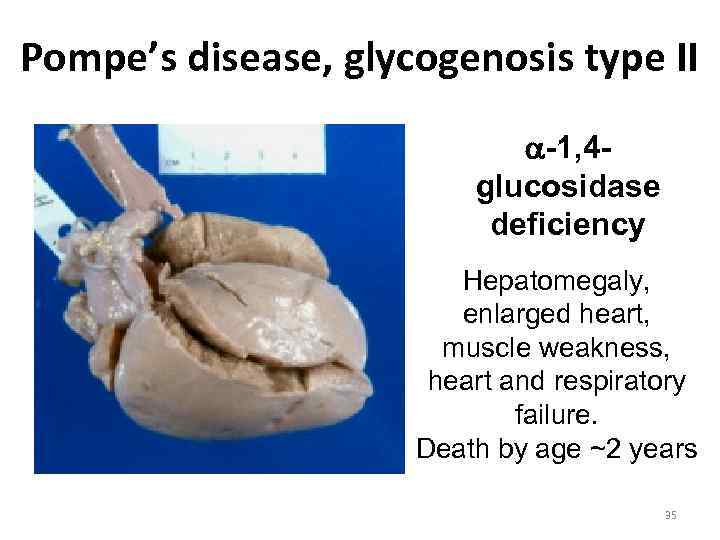
Pompe’s disease, glycogenosis type II -1, 4 glucosidase deficiency Hepatomegaly, enlarged heart, muscle weakness, heart and respiratory failure. Death by age ~2 years 35
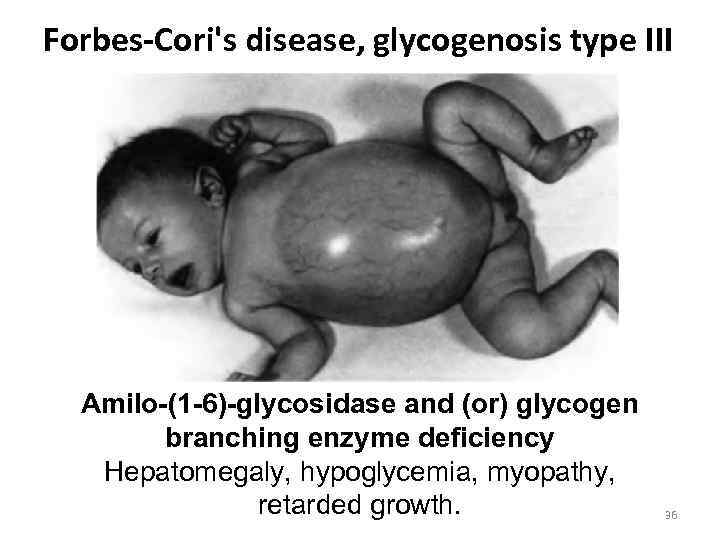
Forbes-Cori's disease, glycogenosis type III Amilo-(1 -6)-glycosidase and (or) glycogen branching enzyme deficiency Hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, myopathy, retarded growth. 36
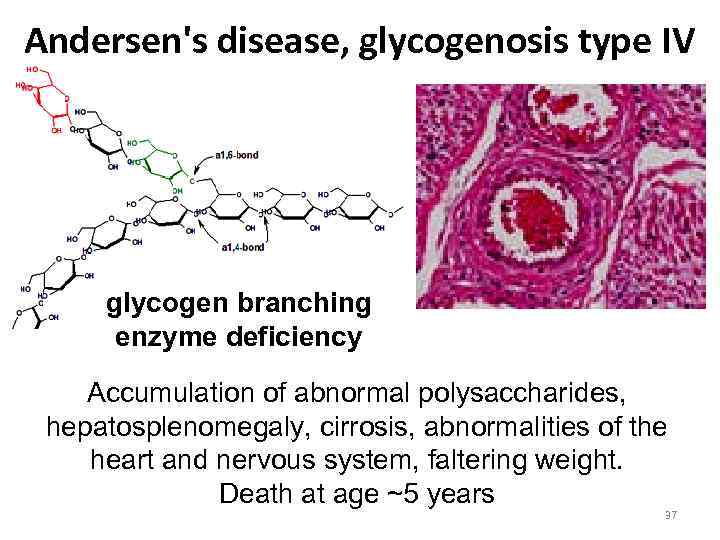
Andersen's disease, glycogenosis type IV glycogen branching enzyme deficiency Accumulation of abnormal polysaccharides, hepatosplenomegaly, cirrosis, abnormalities of the heart and nervous system, faltering weight. Death at age ~5 years 37
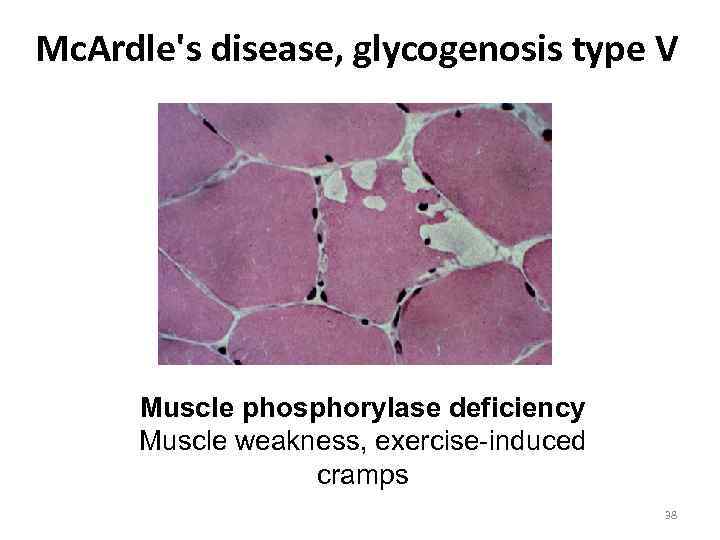
Mc. Ardle's disease, glycogenosis type V Muscle phosphorylase deficiency Muscle weakness, exercise-induced cramps 38

Carbohydrate metabolism regulation
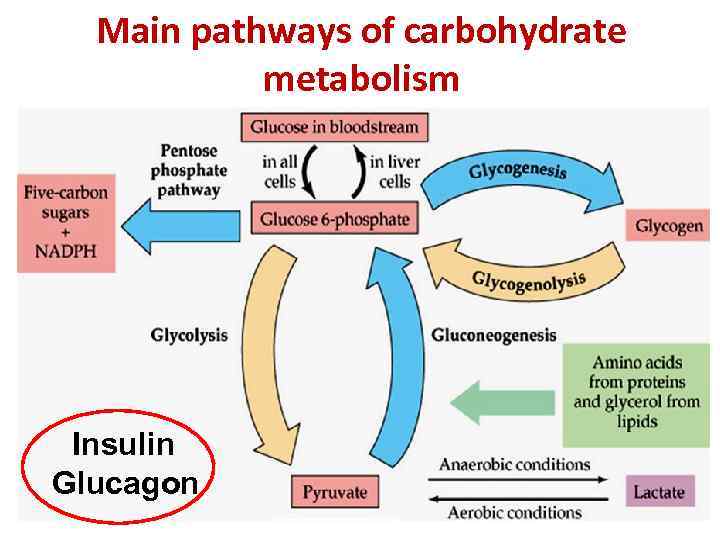
Main pathways of carbohydrate metabolism Insulin Glucagon

Insulin • Stimulate glucose transport into cells • Induses synthesis of glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase activates glycolysis • Activates protein phosphatase * activates pyruvate kinase (activates glycolysis); * increases kinase activity of BIF (activates glycolysis) *activates glycogen synthase and deactivates glycogen phosporylase (activates glycogen synthesis)

Glucagon • Activates protein kinase * increases phosphatase activity of BIF (activates gluconeogenesis) *activates glycogen phosporylase and deactivates glycogen synthase (activates glycogen synthesis)

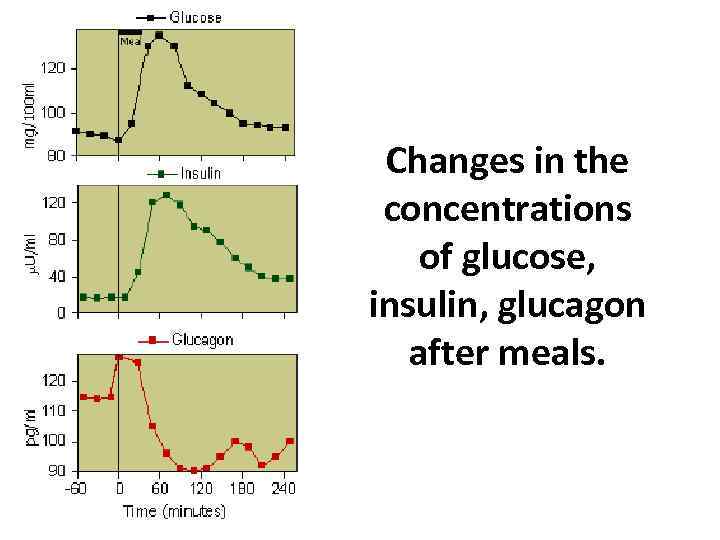
Changes in the concentrations of glucose, insulin, glucagon after meals.
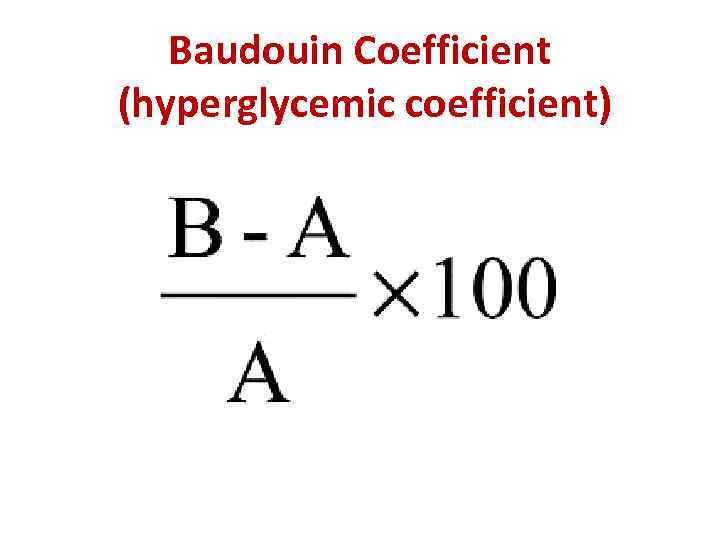
Baudouin Coefficient (hyperglycemic coefficient)
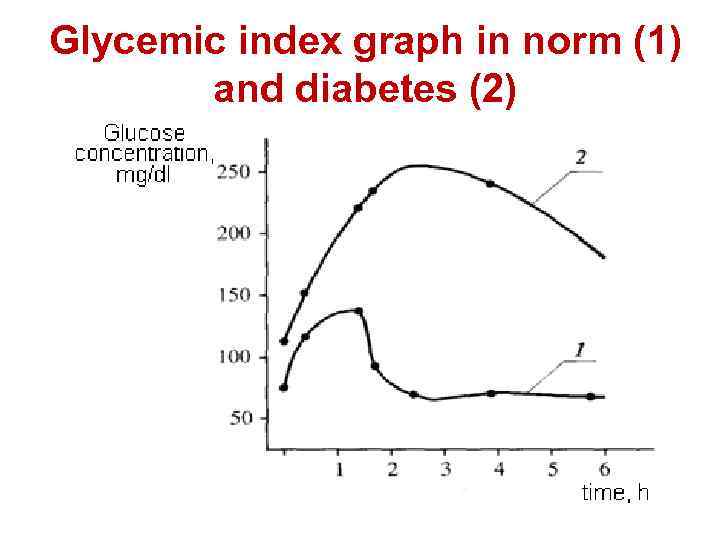
Glycemic index graph in norm (1) and diabetes (2)
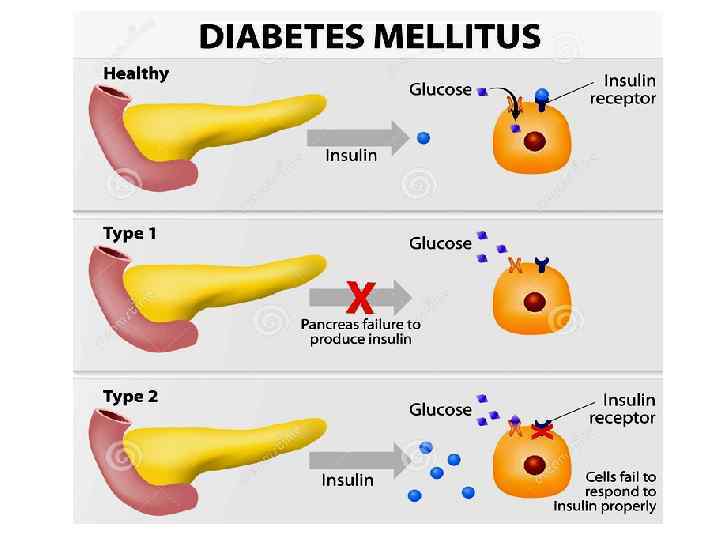
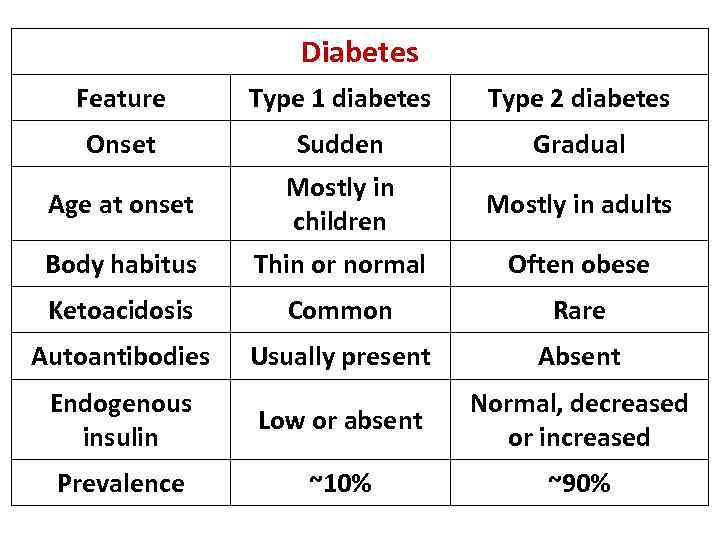
Diabetes Feature Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Onset Sudden Gradual Age at onset Mostly in children Mostly in adults Body habitus Thin or normal Often obese Ketoacidosis Common Rare Autoantibodies Usually present Absent Endogenous insulin Low or absent Normal, decreased or increased Prevalence ~10% ~90%

Main manifestations of diabetes • Polyuria and polydipsia • Hyperglycemia • Decreased synthesis and deposition of glycogen and fat • Hyperlipoproteinemia • Ketonemia • Azotemia and azoturia
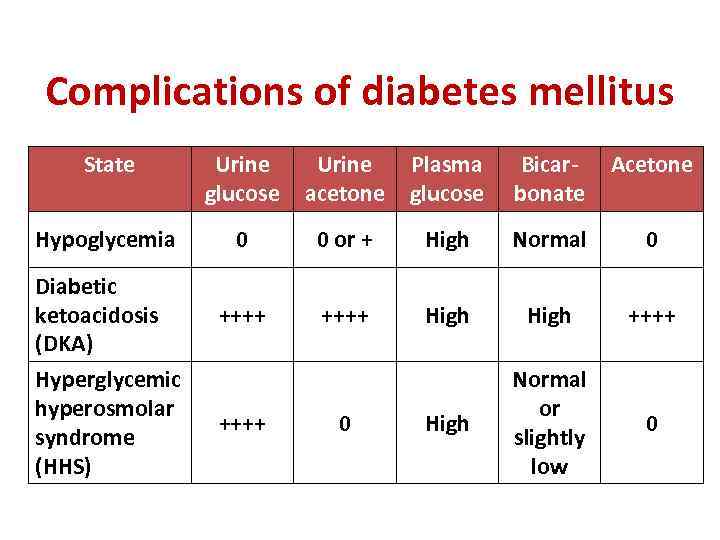
Complications of diabetes mellitus State Urine glucose Urine acetone Plasma glucose Bicarbonate Acetone Hypoglycemia 0 0 or + High Normal 0 Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) ++++ High Normal or slightly low 0 Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome (HHS) ++++ 0
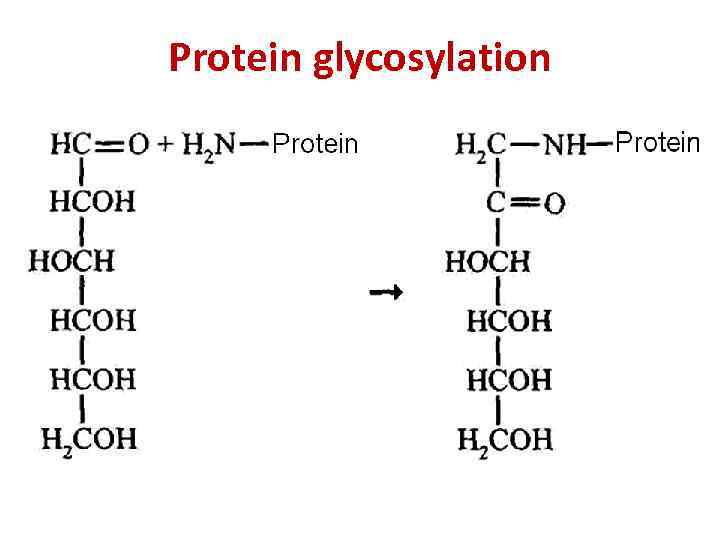
Protein glycosylation
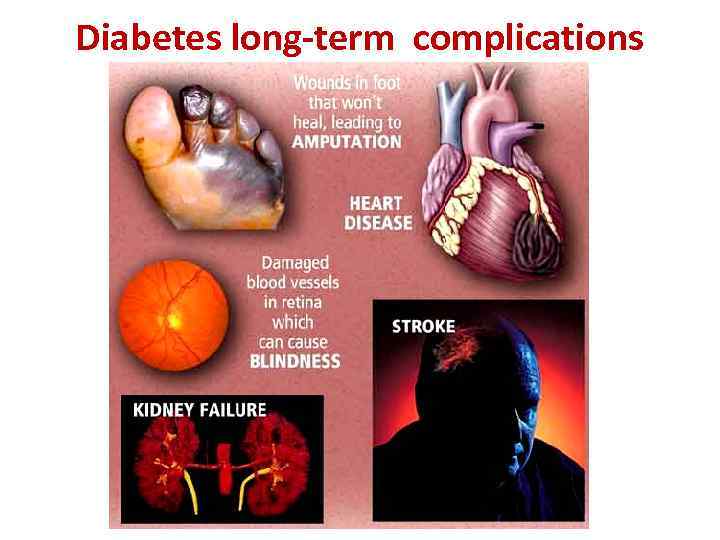
Diabetes long-term complications
Insuline preparations

Glucometer
Insulin pump
Carbohydrate metabolism 2.ppt