4b5ce8b8a6e2e00ec1b054ad38fc96ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

CAPWAP Objectives Saravanan Govindan Panasonic 8 November, 2004 <draft-govindan-capwap-objectives-00. txt> 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 1
Background • Based on discussions in previous meeting and on mailing list • Follows outline in charter goals; – Requirements that address Problem Statement – Advantages to a CAPWAP protocol – Customer requirements 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 2
Adaptive Interfaces • Enables protocol support for both local MAC and split MAC designs • Allows for mixed deployments of both types of WTPs in a single WLAN domain – e. g. Split-MAC WTPs in local office and local-MAC WTPs in remote offices • Results in a protocol that achieves true interoperability • Based on scenario of <draft-cheng-capwap-classifications-01> 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 3
Support for Logical Networks • Prevalent business trend in sharing physical WLAN resources – ISPs seeking cost-efficiencies in building and managing networks • Sharing infrastructure addresses these concerns – Multiple logical network are created within one physical WLAN – Each logical network is assigned to a different ISP or subscriber group • Protocol that supports this objective directly addresses cost concerns 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 4
Multiple Authentication Mechanisms • With spread of WLANs, there is a diversity of authentication needs – Corporate network uses certificates and keys – Coffee shop issues temporary passcodes with each cup • Differences can be present even within a single large WLAN • CAPWAP protocol needs to recognize and relay different authentication information • Enabling support for different authentication mechanisms is therefore crucial 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 5
Automated Processes • New WTPs are designed for low cost and installation ease – Redeploying a WTP from one location to another becomes simple and also frequent • Each redeployment requires discovery and initialization processes – These processes can become intensive and errorprone in large networks • Advantages of automating discovery & initialization – WLAN management is simplified – Operational costs are reduced 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 6
WLAN Status Monitoring • Large scale of WLAN deployments means there are multiple points for complication – Numerous WTPs and users – Dynamic nature of wireless medium • So network requires constant monitoring in order to react to any complications • For effective management, status monitoring needs to be integral to CAPWAP protocol • Regular status information also helps with higher level functions like charging and accounting 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 7
Qo. S • Vo. IP is a major service over WLANs • System-wide Qo. S is crucial for its support • This includes Qo. S over both – Switching segment (AC-WTPs) – Wireless medium segment (WTP-users) • Protocol has to coordinate performance over both these segments • CAPWAP needs to enable Qo. S because it affects – User perception – Business performance 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 8
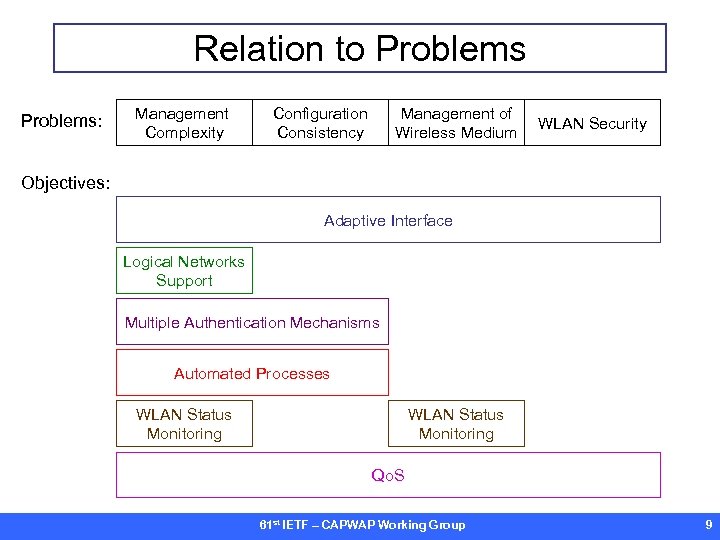
Relation to Problems: Management Complexity Configuration Consistency Management of Wireless Medium WLAN Security Objectives: Adaptive Interface Logical Networks Support Multiple Authentication Mechanisms Automated Processes WLAN Status Monitoring Qo. S 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 9

Next Steps • Discuss objectives further 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 10

Questions? Comments? 61 st IETF – CAPWAP Working Group 11
4b5ce8b8a6e2e00ec1b054ad38fc96ba.ppt