c20eca6473a2a2f7f6ebb22034c106ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Capturing and Modeling Neuro-Radiological Knowledge on a Community Basis: The Head Injury Scenario. Alexander Garcia, Zhuo Zhang, Menaka Rajapakse, Christopher J. O. Baker, and Suisheng Tang Data Mining Department Institute for Infocomm Research Singapore
Capturing and Modeling Neuro-Radiological Knowledge on a Community Basis: The Head Injury Scenario. Alexander Garcia, Zhuo Zhang, Menaka Rajapakse, Christopher J. O. Baker, and Suisheng Tang Data Mining Department Institute for Infocomm Research Singapore
 Outline • • Motivation Mi. Bank – Head Injury Database Ontology Development Collective Intelligence The “facebook” approach Medical Image Annotator Discussion and Conclusions
Outline • • Motivation Mi. Bank – Head Injury Database Ontology Development Collective Intelligence The “facebook” approach Medical Image Annotator Discussion and Conclusions
 Motivation • National Neurological Institute Singapore (NII) has 500+ head injury patients each year with Brain, Scalp, Skull, Internal bleeding requiring rapid diagnosis. • Clinical radiology reports comprise of multiple series of Computed Tomography (CT) Images with unstructured text associated to images) • Computationally a weak association between images and words, cannot retrieve similar images. • Conceptually a tightly coupled association between Image and Diagnosis • Mi. Bank database of DICOM files, (http: //dicom. i 2 r. a-star. edu. sg/pacsone/)
Motivation • National Neurological Institute Singapore (NII) has 500+ head injury patients each year with Brain, Scalp, Skull, Internal bleeding requiring rapid diagnosis. • Clinical radiology reports comprise of multiple series of Computed Tomography (CT) Images with unstructured text associated to images) • Computationally a weak association between images and words, cannot retrieve similar images. • Conceptually a tightly coupled association between Image and Diagnosis • Mi. Bank database of DICOM files, (http: //dicom. i 2 r. a-star. edu. sg/pacsone/)
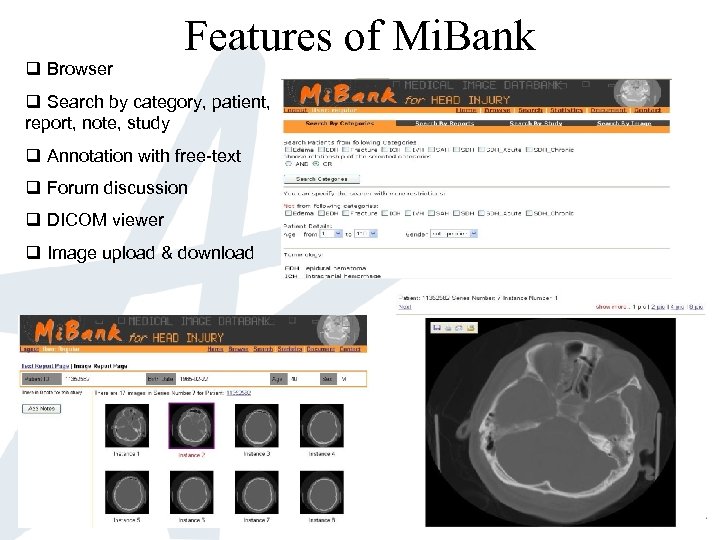 q Browser Features of Mi. Bank q Search by category, patient, report, note, study q Annotation with free-text q Forum discussion q DICOM viewer q Image upload & download
q Browser Features of Mi. Bank q Search by category, patient, report, note, study q Annotation with free-text q Forum discussion q DICOM viewer q Image upload & download
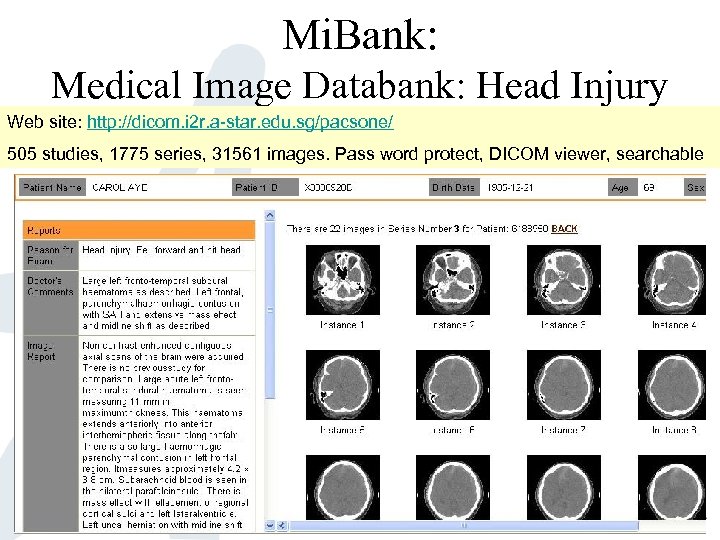 Mi. Bank: Medical Image Databank: Head Injury Web site: http: //dicom. i 2 r. a-star. edu. sg/pacsone/ 505 studies, 1775 series, 31561 images. Pass word protect, DICOM viewer, searchable
Mi. Bank: Medical Image Databank: Head Injury Web site: http: //dicom. i 2 r. a-star. edu. sg/pacsone/ 505 studies, 1775 series, 31561 images. Pass word protect, DICOM viewer, searchable
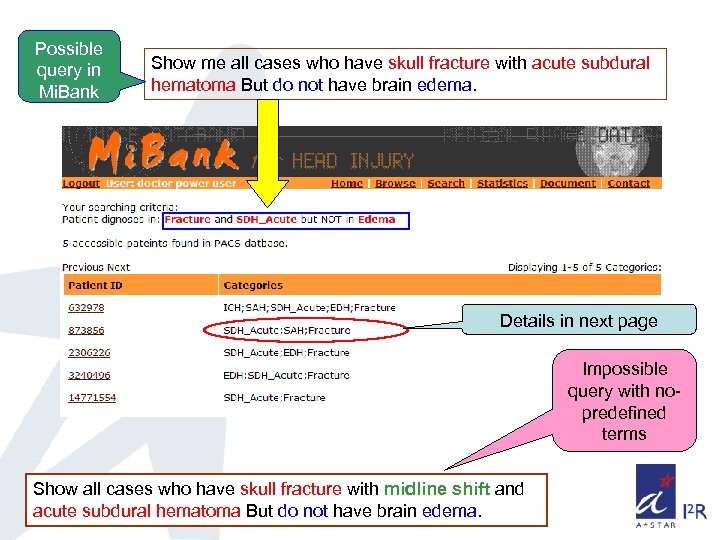 Possible query in Mi. Bank Show me all cases who have skull fracture with acute subdural hematoma But do not have brain edema. Details in next page Impossible query with nopredefined terms Show all cases who have skull fracture with midline shift and acute subdural hematoma But do not have brain edema.
Possible query in Mi. Bank Show me all cases who have skull fracture with acute subdural hematoma But do not have brain edema. Details in next page Impossible query with nopredefined terms Show all cases who have skull fracture with midline shift and acute subdural hematoma But do not have brain edema.
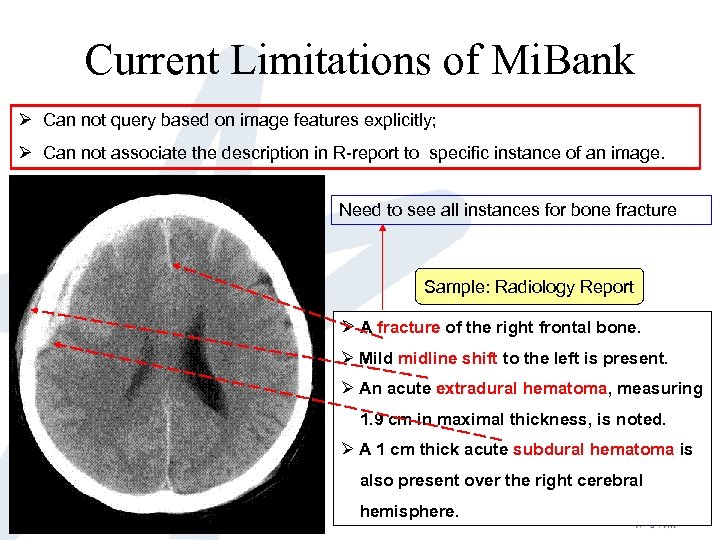 Current Limitations of Mi. Bank Ø Can not query based on image features explicitly; Ø Can not associate the description in R-report to specific instance of an image. Need to see all instances for bone fracture Sample: Radiology Report Ø A fracture of the right frontal bone. Ø Mild midline shift to the left is present. Ø An acute extradural hematoma, measuring 1. 9 cm in maximal thickness, is noted. Ø A 1 cm thick acute subdural hematoma is also present over the right cerebral hemisphere.
Current Limitations of Mi. Bank Ø Can not query based on image features explicitly; Ø Can not associate the description in R-report to specific instance of an image. Need to see all instances for bone fracture Sample: Radiology Report Ø A fracture of the right frontal bone. Ø Mild midline shift to the left is present. Ø An acute extradural hematoma, measuring 1. 9 cm in maximal thickness, is noted. Ø A 1 cm thick acute subdural hematoma is also present over the right cerebral hemisphere.
 What do we want… What do we need? • Retrieve patients with right midnight shifts of less than 3 mm for whom there has been no reported haematoma • Retrieve all images similar to this one • Properly annotated data: images, radiology reports • Meaningful associations between reports, images, and across images • …an ontology ….
What do we want… What do we need? • Retrieve patients with right midnight shifts of less than 3 mm for whom there has been no reported haematoma • Retrieve all images similar to this one • Properly annotated data: images, radiology reports • Meaningful associations between reports, images, and across images • …an ontology ….
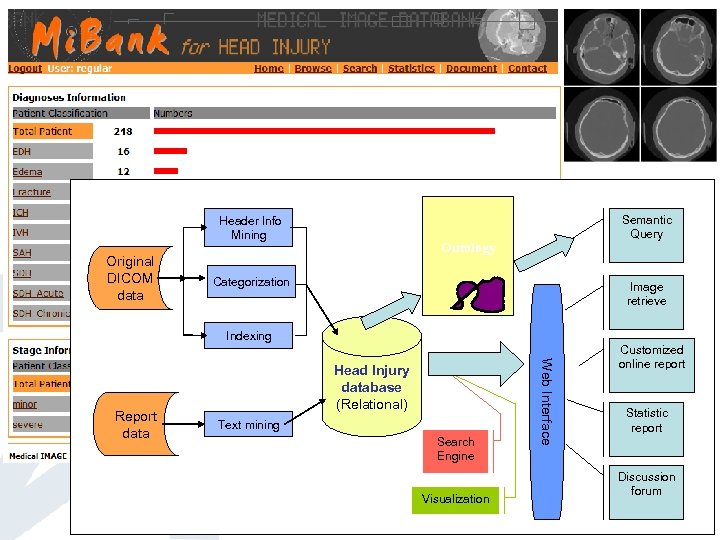 Header Info Mining Original DICOM data Semantic Query Ontology Categorization Image retrieve Indexing Text mining Search Engine Visualization Web Interface Report data Head Injury database (Relational) Customized online report Statistic report Discussion forum
Header Info Mining Original DICOM data Semantic Query Ontology Categorization Image retrieve Indexing Text mining Search Engine Visualization Web Interface Report data Head Injury database (Relational) Customized online report Statistic report Discussion forum
 The Role of the Ontology • Community defined controlled vocabulary for annotation of radiology images. • Hierarchical descriptions of medical terms relevant to anatomy, pathology and head injury specific features found in medical images. • Consensus model of head injury terminology generated through community engagement for knowledge reuse in medical information systems. • Query model for semantic search
The Role of the Ontology • Community defined controlled vocabulary for annotation of radiology images. • Hierarchical descriptions of medical terms relevant to anatomy, pathology and head injury specific features found in medical images. • Consensus model of head injury terminology generated through community engagement for knowledge reuse in medical information systems. • Query model for semantic search
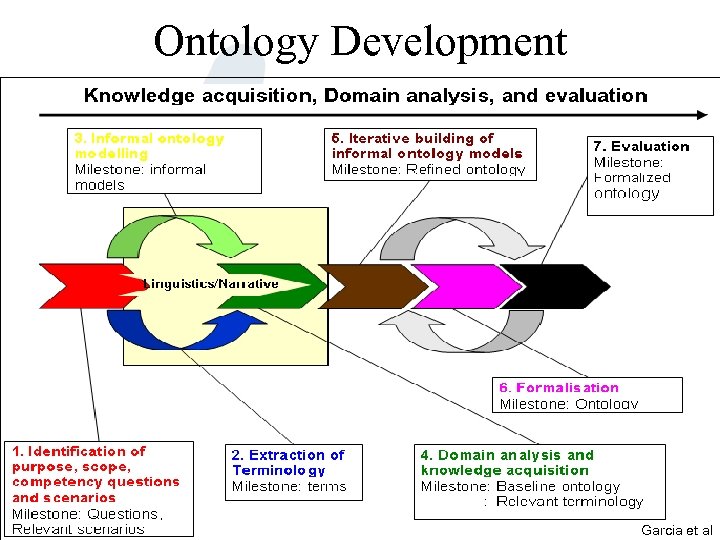 Ontology Development Garcia et al
Ontology Development Garcia et al
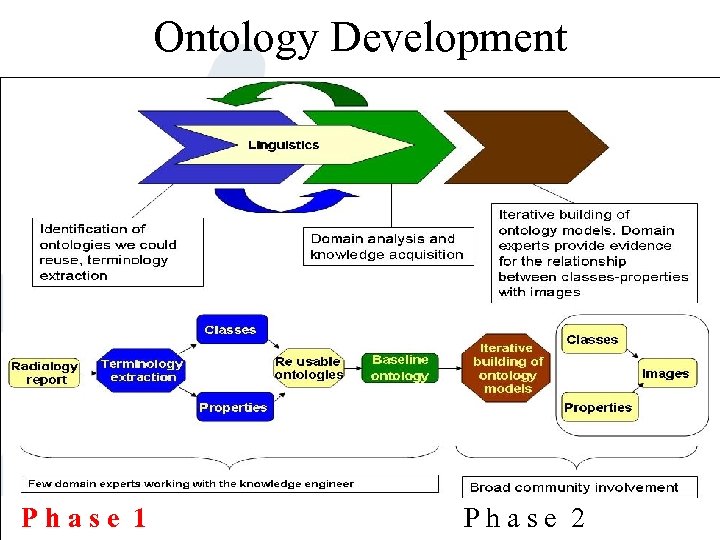 Ontology Development Phase 1 Phase 2
Ontology Development Phase 1 Phase 2
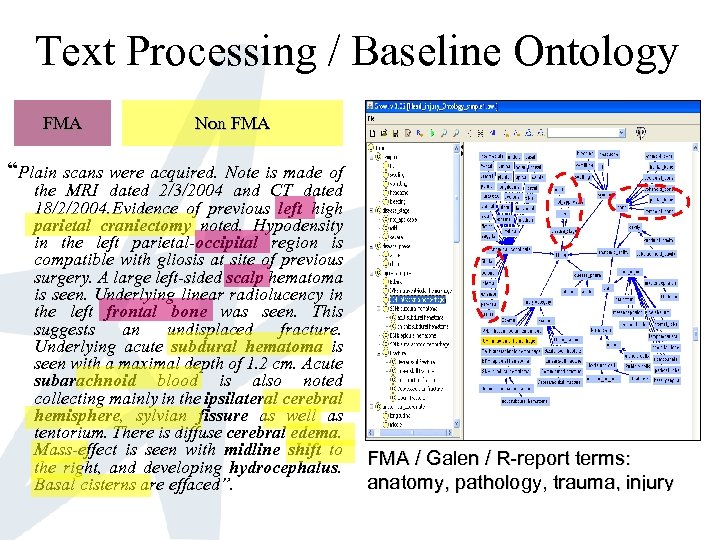 Text Processing / Baseline Ontology FMA Non FMA “Plain scans were acquired. Note is made of the MRI dated 2/3/2004 and CT dated 18/2/2004. Evidence of previous left high parietal craniectomy noted. Hypodensity in the left parietal-occipital region is compatible with gliosis at site of previous surgery. A large left-sided scalp hematoma is seen. Underlying linear radiolucency in the left frontal bone was seen. This suggests an undisplaced fracture. Underlying acute subdural hematoma is seen with a maximal depth of 1. 2 cm. Acute subarachnoid blood is also noted collecting mainly in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere, sylvian fissure as well as tentorium. There is diffuse cerebral edema. Mass-effect is seen with midline shift to the right, and developing hydrocephalus. Basal cisterns are effaced”. FMA / Galen / R-report terms: anatomy, pathology, trauma, injury
Text Processing / Baseline Ontology FMA Non FMA “Plain scans were acquired. Note is made of the MRI dated 2/3/2004 and CT dated 18/2/2004. Evidence of previous left high parietal craniectomy noted. Hypodensity in the left parietal-occipital region is compatible with gliosis at site of previous surgery. A large left-sided scalp hematoma is seen. Underlying linear radiolucency in the left frontal bone was seen. This suggests an undisplaced fracture. Underlying acute subdural hematoma is seen with a maximal depth of 1. 2 cm. Acute subarachnoid blood is also noted collecting mainly in the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere, sylvian fissure as well as tentorium. There is diffuse cerebral edema. Mass-effect is seen with midline shift to the right, and developing hydrocephalus. Basal cisterns are effaced”. FMA / Galen / R-report terms: anatomy, pathology, trauma, injury
 Capturing Knowledge: Phase 1 Not an easy task • Inside expert’s head • Difficult to describe concepts and relations • Difficult for nonexperts to understand. Disadvantages • Requires excessive amount of time • Experts – easily bored – no short term result. • Results in the creation of unstructured knowledge stores that are difficult to reuse and maintain. • Skimping on validation may include errors, omissions, inconsistencies & irrelevances • Experts are not always capturing the evidence – rather explaining context • Storing the knowledge that is not machine-readable
Capturing Knowledge: Phase 1 Not an easy task • Inside expert’s head • Difficult to describe concepts and relations • Difficult for nonexperts to understand. Disadvantages • Requires excessive amount of time • Experts – easily bored – no short term result. • Results in the creation of unstructured knowledge stores that are difficult to reuse and maintain. • Skimping on validation may include errors, omissions, inconsistencies & irrelevances • Experts are not always capturing the evidence – rather explaining context • Storing the knowledge that is not machine-readable
 Ontology Development Maintenance Evolution Phase 1 Phase 2
Ontology Development Maintenance Evolution Phase 1 Phase 2
 Capturing Knowledge: Phase 2 • Knowledge Elicitation via • Collective Knowledge Collective Intelligence Resources – The capacity to provide useful information based on human contributions which gets better as more people participate. – intelligent collection? – Data Types • mix of structured, machine-readable data and unstructured data from human input – what we all know but hadn’t got around to saying in public before • collaborative bookmarking, searching – “database of intentions” • clicking, rating, tagging, buying - Amazon • blogs, wikis, discussion lists -
Capturing Knowledge: Phase 2 • Knowledge Elicitation via • Collective Knowledge Collective Intelligence Resources – The capacity to provide useful information based on human contributions which gets better as more people participate. – intelligent collection? – Data Types • mix of structured, machine-readable data and unstructured data from human input – what we all know but hadn’t got around to saying in public before • collaborative bookmarking, searching – “database of intentions” • clicking, rating, tagging, buying - Amazon • blogs, wikis, discussion lists -
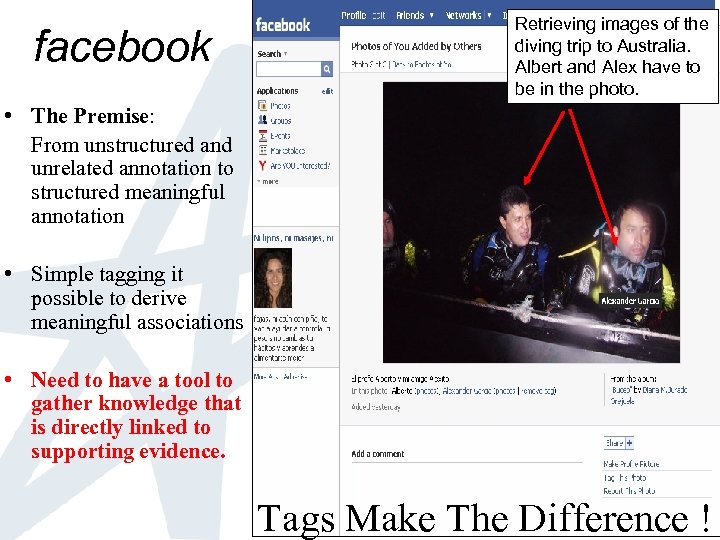 facebook Retrieving images of the diving trip to Australia. Albert and Alex have to be in the photo. • The Premise: From unstructured and unrelated annotation to structured meaningful annotation • Simple tagging it possible to derive meaningful associations • Need to have a tool to gather knowledge that is directly linked to supporting evidence. Tags Make The Difference !
facebook Retrieving images of the diving trip to Australia. Albert and Alex have to be in the photo. • The Premise: From unstructured and unrelated annotation to structured meaningful annotation • Simple tagging it possible to derive meaningful associations • Need to have a tool to gather knowledge that is directly linked to supporting evidence. Tags Make The Difference !
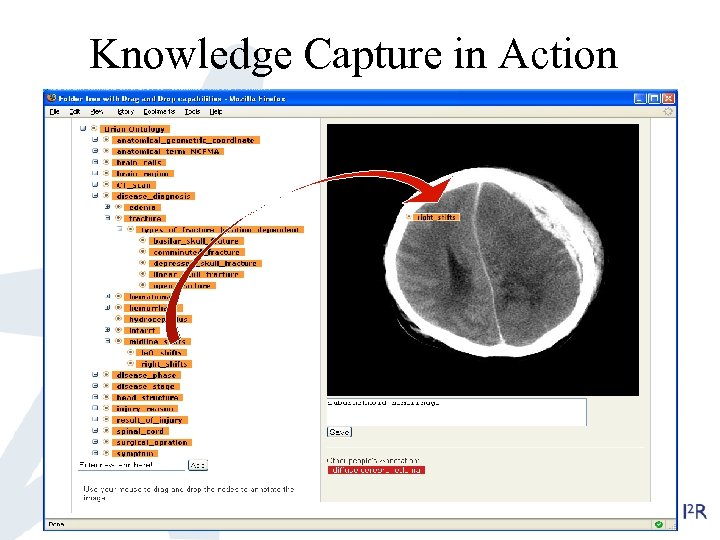
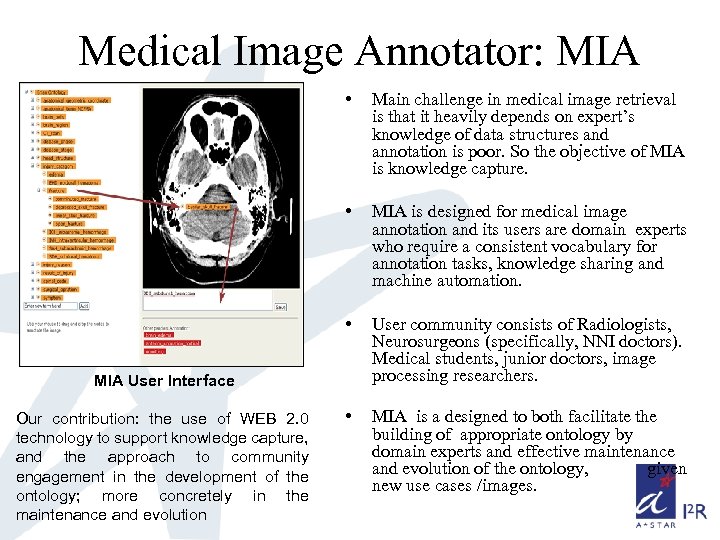 Medical Image Annotator: MIA • Main challenge in medical image retrieval is that it heavily depends on expert’s knowledge of data structures and annotation is poor. So the objective of MIA is knowledge capture. • MIA is designed for medical image annotation and its users are domain experts who require a consistent vocabulary for annotation tasks, knowledge sharing and machine automation. • User community consists of Radiologists, Neurosurgeons (specifically, NNI doctors). Medical students, junior doctors, image processing researchers. • MIA is a designed to both facilitate the building of appropriate ontology by domain experts and effective maintenance and evolution of the ontology, given new use cases /images. MIA User Interface Our contribution: the use of WEB 2. 0 technology to support knowledge capture, and the approach to community engagement in the development of the ontology; more concretely in the maintenance and evolution
Medical Image Annotator: MIA • Main challenge in medical image retrieval is that it heavily depends on expert’s knowledge of data structures and annotation is poor. So the objective of MIA is knowledge capture. • MIA is designed for medical image annotation and its users are domain experts who require a consistent vocabulary for annotation tasks, knowledge sharing and machine automation. • User community consists of Radiologists, Neurosurgeons (specifically, NNI doctors). Medical students, junior doctors, image processing researchers. • MIA is a designed to both facilitate the building of appropriate ontology by domain experts and effective maintenance and evolution of the ontology, given new use cases /images. MIA User Interface Our contribution: the use of WEB 2. 0 technology to support knowledge capture, and the approach to community engagement in the development of the ontology; more concretely in the maintenance and evolution
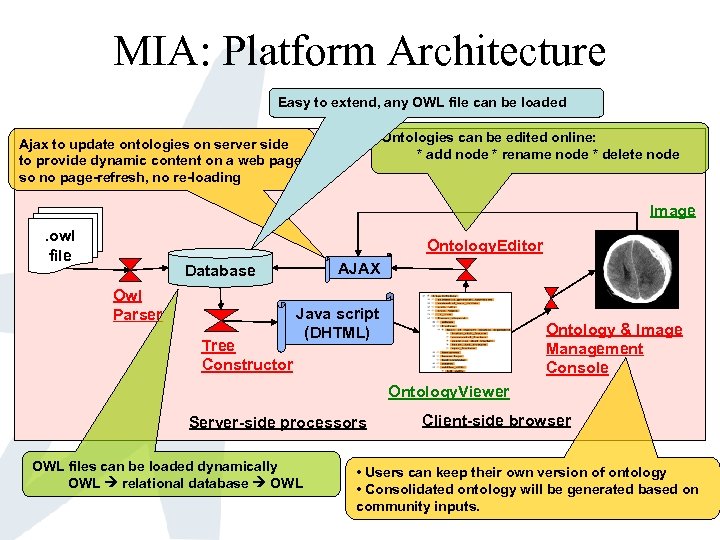 MIA: Platform Architecture Easy to extend, any OWL file can be loaded Ontologies can be edited online: * add node * rename node * delete node Ajax to update ontologies on server side to provide dynamic content on a web page so no page-refresh, no re-loading Image. owl file Ontology. Editor AJAX Database Owl Parser Tree Constructor Java script (DHTML) Ontology & Image Management Console Ontology. Viewer Server-side processors OWL files can be loaded dynamically OWL relational database OWL Client-side browser • Users can keep their own version of ontology • Consolidated ontology will be generated based on community inputs.
MIA: Platform Architecture Easy to extend, any OWL file can be loaded Ontologies can be edited online: * add node * rename node * delete node Ajax to update ontologies on server side to provide dynamic content on a web page so no page-refresh, no re-loading Image. owl file Ontology. Editor AJAX Database Owl Parser Tree Constructor Java script (DHTML) Ontology & Image Management Console Ontology. Viewer Server-side processors OWL files can be loaded dynamically OWL relational database OWL Client-side browser • Users can keep their own version of ontology • Consolidated ontology will be generated based on community inputs.
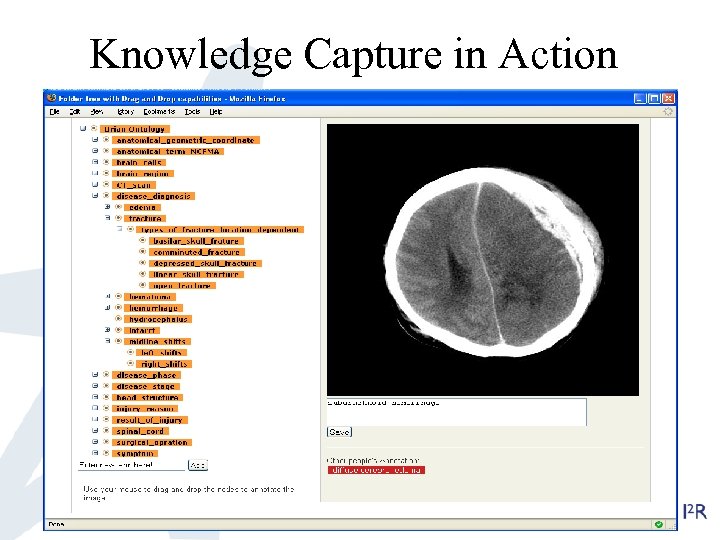 Knowledge Capture in Action
Knowledge Capture in Action
 Knowledge Capture in Action
Knowledge Capture in Action
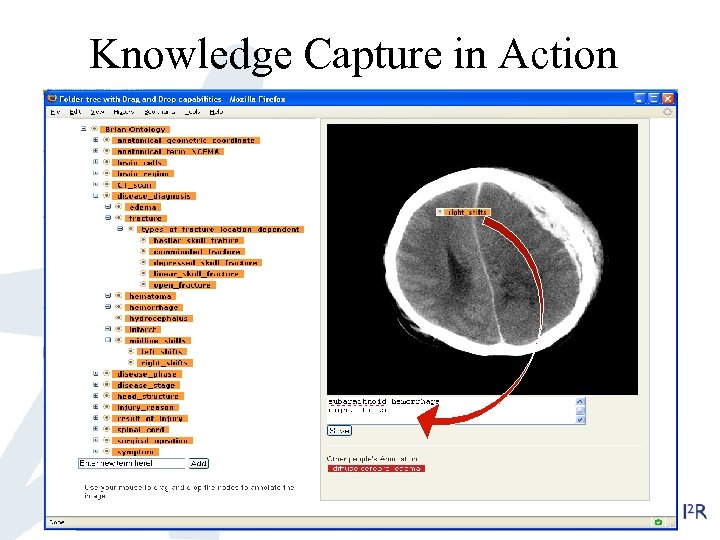 Knowledge Capture in Action
Knowledge Capture in Action
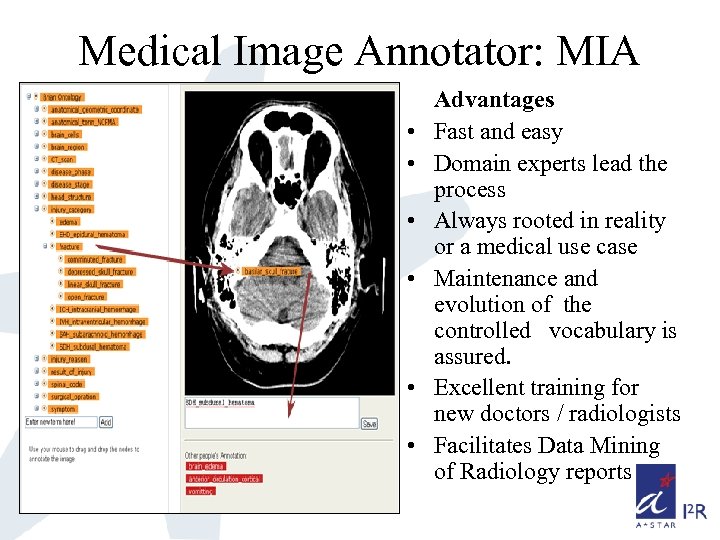 Medical Image Annotator: MIA • • • Advantages Fast and easy Domain experts lead the process Always rooted in reality or a medical use case Maintenance and evolution of the controlled vocabulary is assured. Excellent training for new doctors / radiologists Facilitates Data Mining of Radiology reports
Medical Image Annotator: MIA • • • Advantages Fast and easy Domain experts lead the process Always rooted in reality or a medical use case Maintenance and evolution of the controlled vocabulary is assured. Excellent training for new doctors / radiologists Facilitates Data Mining of Radiology reports
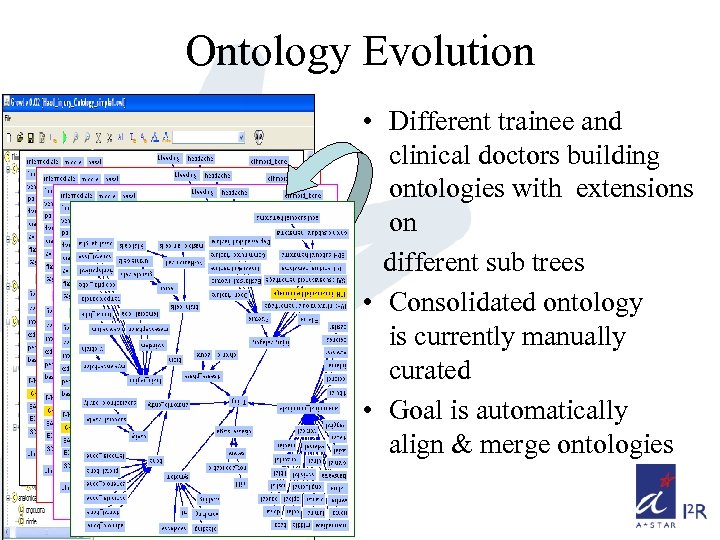 Ontology Evolution • Different trainee and clinical doctors building ontologies with extensions on different sub trees • Consolidated ontology is currently manually curated • Goal is automatically align & merge ontologies
Ontology Evolution • Different trainee and clinical doctors building ontologies with extensions on different sub trees • Consolidated ontology is currently manually curated • Goal is automatically align & merge ontologies
 Query with the Head Injury Ontology 1. Simple ‘ontology-term’ assisted query • • Search for images: based merely on simple combination of ontology terms (and / or) Form based interface linked to SQL Queires 2. Ontology reasoning (A-box) • • Content navigation over R-reports using defined object properties (Knowlegtor) Use of subsumption and object properties
Query with the Head Injury Ontology 1. Simple ‘ontology-term’ assisted query • • Search for images: based merely on simple combination of ontology terms (and / or) Form based interface linked to SQL Queires 2. Ontology reasoning (A-box) • • Content navigation over R-reports using defined object properties (Knowlegtor) Use of subsumption and object properties
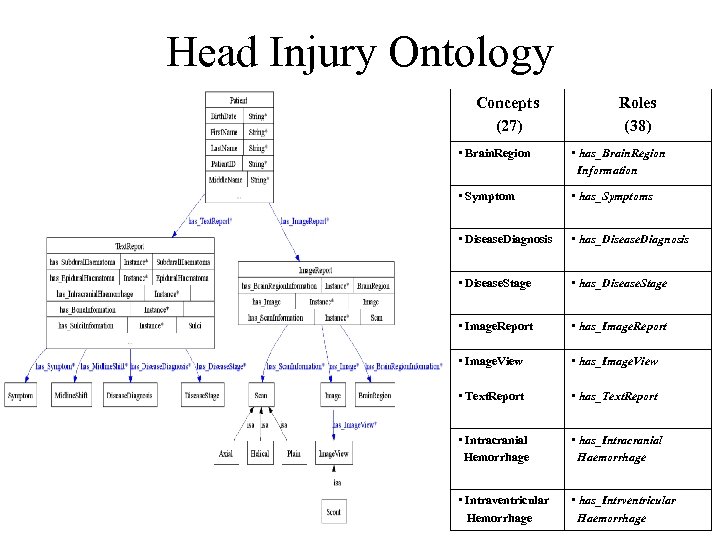 Head Injury Ontology Concepts (27) Roles (38) • Brain. Region • has_Brain. Region Information • Symptom • has_Symptoms • Disease. Diagnosis • has_Disease. Diagnosis • Disease. Stage • has_Disease. Stage • Image. Report • has_Image. Report • Image. View • has_Image. View • Text. Report • has_Text. Report • Intracranial Hemorrhage • has_Intracranial Haemorrhage • Intraventricular Hemorrhage • has_Intrventricular Haemorrhage
Head Injury Ontology Concepts (27) Roles (38) • Brain. Region • has_Brain. Region Information • Symptom • has_Symptoms • Disease. Diagnosis • has_Disease. Diagnosis • Disease. Stage • has_Disease. Stage • Image. Report • has_Image. Report • Image. View • has_Image. View • Text. Report • has_Text. Report • Intracranial Hemorrhage • has_Intracranial Haemorrhage • Intraventricular Hemorrhage • has_Intrventricular Haemorrhage
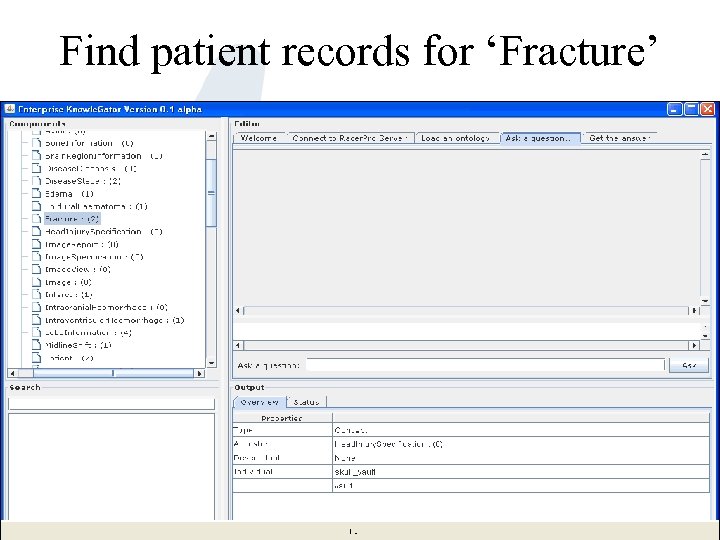 Find patient records for ‘Fracture’
Find patient records for ‘Fracture’
 Discussion and Conclusions • Medical images should be better annotated in order to facilitate information retrieval • Collective knowledge is real… “FAQ-o-Sphere” • Controlled vocabularies (CVs) and/or ontologies are being developed by communities • Simple tagging combined with knowledge elicitation methods supports ontology development • Collective knowledge capture requires dedicated infrastructure that supports specific tasks • Querability can be improved through the use of explicit tags and CVs/ontologies
Discussion and Conclusions • Medical images should be better annotated in order to facilitate information retrieval • Collective knowledge is real… “FAQ-o-Sphere” • Controlled vocabularies (CVs) and/or ontologies are being developed by communities • Simple tagging combined with knowledge elicitation methods supports ontology development • Collective knowledge capture requires dedicated infrastructure that supports specific tasks • Querability can be improved through the use of explicit tags and CVs/ontologies
 Challenges for the Community • How to get knowledge from all those intelligent people on the Internet • How to give everyone the benefit of everyone else’s experience • How to leverage and contribute to the ecosystem that has created today’s web. Social Web Life Science Social + Semantic Web
Challenges for the Community • How to get knowledge from all those intelligent people on the Internet • How to give everyone the benefit of everyone else’s experience • How to leverage and contribute to the ecosystem that has created today’s web. Social Web Life Science Social + Semantic Web
 Acknowledgments • Bonarges Aleman-Meza – Social Web • Tom Gruber - Semantic-Social Web • MIA Developers - Zhang Zhuo and Menaka Rajapakse • Suisheng Tang M. D. and Project PI, - Coordinator of domain experts and builder of baseline ontology • Tchoyoson Lim – Radiologist NNI (National Neuroscience Institute, Singapore)
Acknowledgments • Bonarges Aleman-Meza – Social Web • Tom Gruber - Semantic-Social Web • MIA Developers - Zhang Zhuo and Menaka Rajapakse • Suisheng Tang M. D. and Project PI, - Coordinator of domain experts and builder of baseline ontology • Tchoyoson Lim – Radiologist NNI (National Neuroscience Institute, Singapore)


