30b6bfa525bc0cbb337ec7ba085cb039.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Capital Markets Group Making Capital Markets Work for Infrastructure Finance Presentation to Finance Forum 2004 Prepared by: Varsha Marathe, Michel Noel and Sophie Sirtaine
Capital Markets Group Making Capital Markets Work for Infrastructure Finance Presentation to Finance Forum 2004 Prepared by: Varsha Marathe, Michel Noel and Sophie Sirtaine
 Making Capital Markets Work for Infrastructure Finance, a Pressing Need in LDCs Infrastructure investments needs remain enormous in LDCs in all regions Yet Ø public funds available for infrastructure financing remain limited private funds invested in infrastructure in LDCs have shrunk significantly since 1997 Ø and, institutional investors (on the capital markets) have never shown much interest in infrastructure financing Ø Therefore, mechanisms to re-attract more private funds, including from capital market participants, are crucially needed 1
Making Capital Markets Work for Infrastructure Finance, a Pressing Need in LDCs Infrastructure investments needs remain enormous in LDCs in all regions Yet Ø public funds available for infrastructure financing remain limited private funds invested in infrastructure in LDCs have shrunk significantly since 1997 Ø and, institutional investors (on the capital markets) have never shown much interest in infrastructure financing Ø Therefore, mechanisms to re-attract more private funds, including from capital market participants, are crucially needed 1
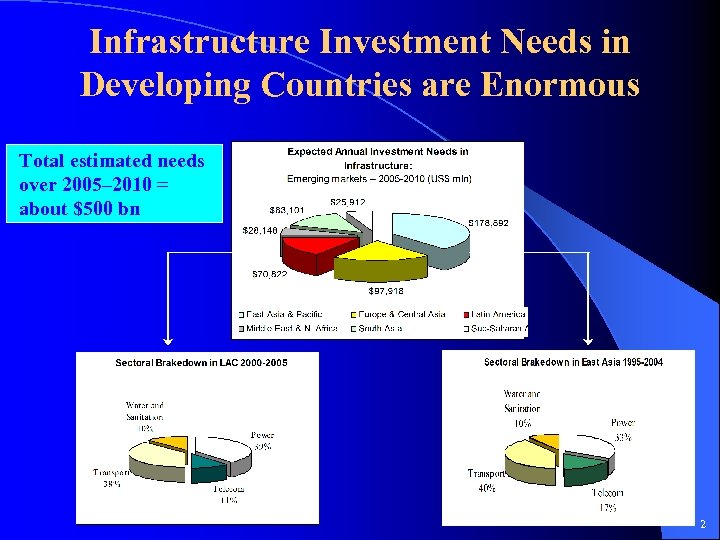 Infrastructure Investment Needs in Developing Countries are Enormous Total estimated needs over 2005– 2010 = about $500 bn 2
Infrastructure Investment Needs in Developing Countries are Enormous Total estimated needs over 2005– 2010 = about $500 bn 2
 The Traditional Public Financing Model Requires Room for New Public Debt… Public Finance Model Borrowing by sovereign and sub-sovereign on own account Part of general government debt Headroom for general government borrowing varies greatly across countries, but is generally limited 3
The Traditional Public Financing Model Requires Room for New Public Debt… Public Finance Model Borrowing by sovereign and sub-sovereign on own account Part of general government debt Headroom for general government borrowing varies greatly across countries, but is generally limited 3
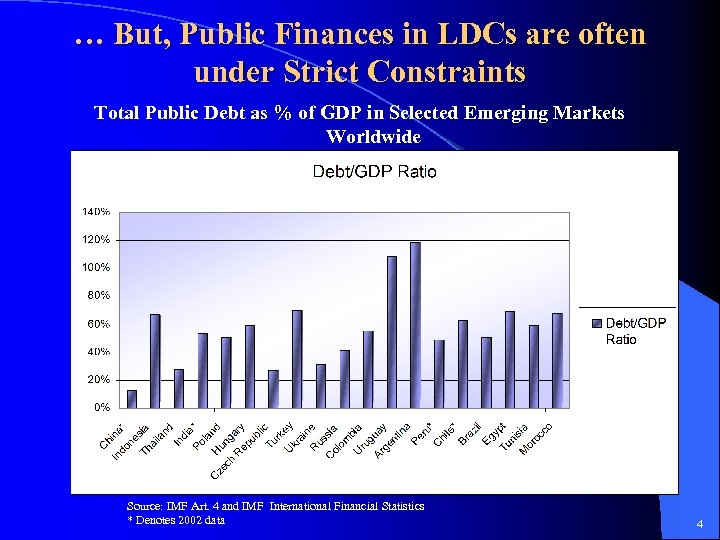 … But, Public Finances in LDCs are often under Strict Constraints Total Public Debt as % of GDP in Selected Emerging Markets Worldwide Source: IMF Art. 4 and IMF International Financial Statistics * Denotes 2002 data 4
… But, Public Finances in LDCs are often under Strict Constraints Total Public Debt as % of GDP in Selected Emerging Markets Worldwide Source: IMF Art. 4 and IMF International Financial Statistics * Denotes 2002 data 4
 PPP Models Present an Interesting Alternative Public-Private Partnership Model Structures: u Concessions, BOOs and BOTs: special-purpose company responsible for investment and operations u Divestiture: privatization of existing infrastructure company Financing: u If private sector >50% of special purpose or existing company, debt no longer part of general government debt u Private investor finances investments and opex with equity and debt 5
PPP Models Present an Interesting Alternative Public-Private Partnership Model Structures: u Concessions, BOOs and BOTs: special-purpose company responsible for investment and operations u Divestiture: privatization of existing infrastructure company Financing: u If private sector >50% of special purpose or existing company, debt no longer part of general government debt u Private investor finances investments and opex with equity and debt 5
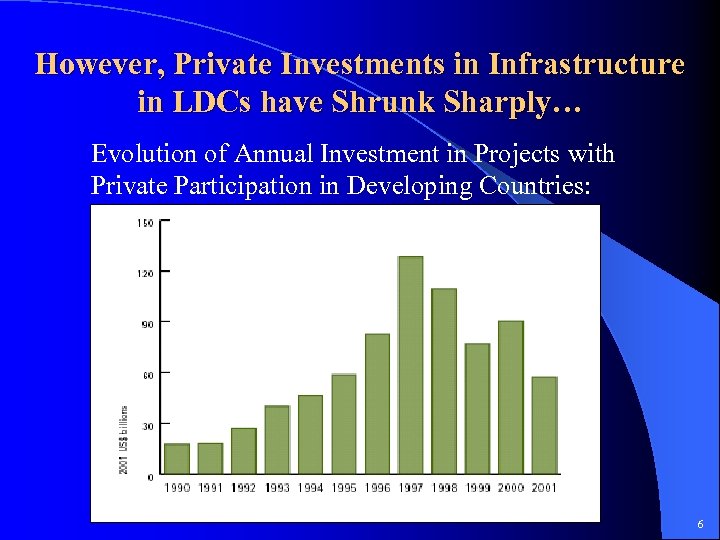 However, Private Investments in Infrastructure in LDCs have Shrunk Sharply… Evolution of Annual Investment in Projects with Private Participation in Developing Countries: 6
However, Private Investments in Infrastructure in LDCs have Shrunk Sharply… Evolution of Annual Investment in Projects with Private Participation in Developing Countries: 6
 … and Capital Market Funding has Continued to Shy Away from Infrastructure Only 200+ bond issues worldwide in 2001 by infrastructure entities: ² ² Nearly 50% of them in telecom Only 20% of them in LDCs (mostly in Asia and Eastern Europe), of which about 33% by public companies Therefore, only about 30 private issues in LDCs, of which about 15 by telecom companies Most with strict covenants and other protections against project risks (guarantees, insurance, etc) 7
… and Capital Market Funding has Continued to Shy Away from Infrastructure Only 200+ bond issues worldwide in 2001 by infrastructure entities: ² ² Nearly 50% of them in telecom Only 20% of them in LDCs (mostly in Asia and Eastern Europe), of which about 33% by public companies Therefore, only about 30 private issues in LDCs, of which about 15 by telecom companies Most with strict covenants and other protections against project risks (guarantees, insurance, etc) 7
 There are Various Impediments to Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure in LDCs In General: u u Deficiencies in bond market infrastructure Un-developed institutional investors with regulatory constraints for investment For sovereigns: ◆ Lack of strategy to develop money market and long-term government bond For sub-sovereigns ◆ ◆ ◆ Deficiencies in legal and regulatory framework for borrowing (soft budget) Market segmentation Lack of credit enhancement instruments For PPP issues ◆ ◆ Inadequate tariff policies affecting cash flow level and variability Weakness of contractual environment Lack of political/regulatory risk mitigation instruments Lack of exit opportunities for equity investors 8
There are Various Impediments to Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure in LDCs In General: u u Deficiencies in bond market infrastructure Un-developed institutional investors with regulatory constraints for investment For sovereigns: ◆ Lack of strategy to develop money market and long-term government bond For sub-sovereigns ◆ ◆ ◆ Deficiencies in legal and regulatory framework for borrowing (soft budget) Market segmentation Lack of credit enhancement instruments For PPP issues ◆ ◆ Inadequate tariff policies affecting cash flow level and variability Weakness of contractual environment Lack of political/regulatory risk mitigation instruments Lack of exit opportunities for equity investors 8
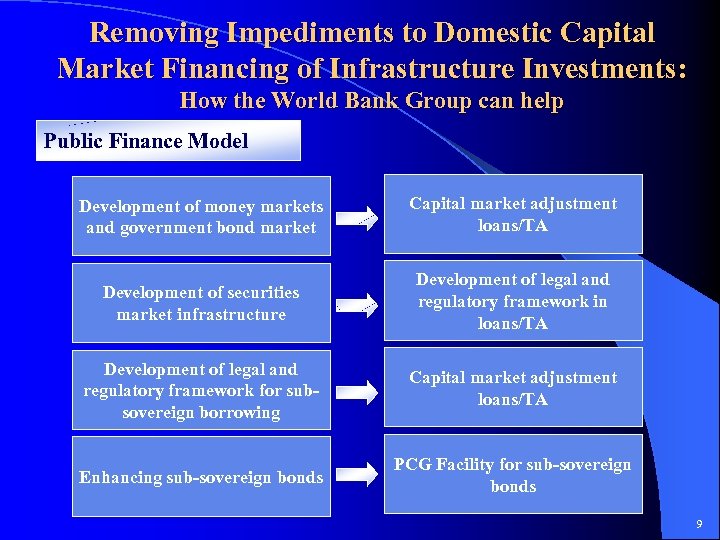 Removing Impediments to Domestic Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure Investments: How the World Bank Group can help Public Finance Model Development of money markets and government bond market Capital market adjustment loans/TA Development of securities market infrastructure Development of legal and regulatory framework in loans/TA Development of legal and regulatory framework for subsovereign borrowing Capital market adjustment loans/TA Enhancing sub-sovereign bonds PCG Facility for sub-sovereign bonds 9
Removing Impediments to Domestic Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure Investments: How the World Bank Group can help Public Finance Model Development of money markets and government bond market Capital market adjustment loans/TA Development of securities market infrastructure Development of legal and regulatory framework in loans/TA Development of legal and regulatory framework for subsovereign borrowing Capital market adjustment loans/TA Enhancing sub-sovereign bonds PCG Facility for sub-sovereign bonds 9
 Removing Impediments to Domestic Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure Investments: How the World Bank Group can help PPP Model Strengthening regulatory framework for PPPs PPP framework adjustment loan/TA Supporting transition to cost -recovery tariffs OBS Budget loan/TA Mobilizing equity for PPP transactions Mitigating political risks • World Bank Infrastructure Fund • First round Private Equity Fund • Second round Local • Infrastructure Investment Trust MIGA PRI facilities IBRD PRG facility 10
Removing Impediments to Domestic Capital Market Financing of Infrastructure Investments: How the World Bank Group can help PPP Model Strengthening regulatory framework for PPPs PPP framework adjustment loan/TA Supporting transition to cost -recovery tariffs OBS Budget loan/TA Mobilizing equity for PPP transactions Mitigating political risks • World Bank Infrastructure Fund • First round Private Equity Fund • Second round Local • Infrastructure Investment Trust MIGA PRI facilities IBRD PRG facility 10
 Innovative Capital Market Products for Infrastructure Finance Public Finance Model PCG facility for sub-sovereign bonds PPP Model World Bank Infrastructure Fund Local Infrastructure Investment Trust PRG Facility to cover political / regulatory risks PRG Facility to cover sub-sovereign breach of contract risk Investment Promotion Finance Facility 11
Innovative Capital Market Products for Infrastructure Finance Public Finance Model PCG facility for sub-sovereign bonds PPP Model World Bank Infrastructure Fund Local Infrastructure Investment Trust PRG Facility to cover political / regulatory risks PRG Facility to cover sub-sovereign breach of contract risk Investment Promotion Finance Facility 11
 The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Concept Under study in Russia Market failure to be resolved: lack of access by regions to long-term financing in local currency at acceptable rates Proposed solution: a IBRD partial credit guarantee facility to cover bonds issued by regions for infrastructure programs financing Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Facility with or without sovereign counter-guarantee 2. Risk management 3. Market test 12
The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Concept Under study in Russia Market failure to be resolved: lack of access by regions to long-term financing in local currency at acceptable rates Proposed solution: a IBRD partial credit guarantee facility to cover bonds issued by regions for infrastructure programs financing Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Facility with or without sovereign counter-guarantee 2. Risk management 3. Market test 12
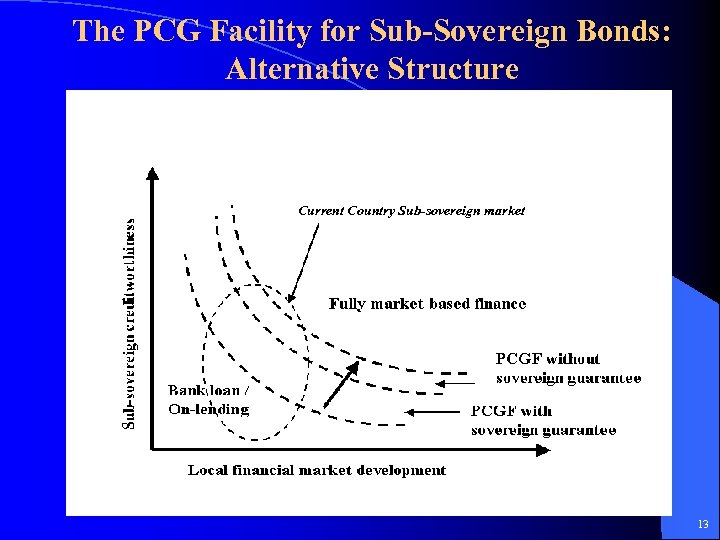 The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Alternative Structure Current Country Sub-sovereign market 13
The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Alternative Structure Current Country Sub-sovereign market 13
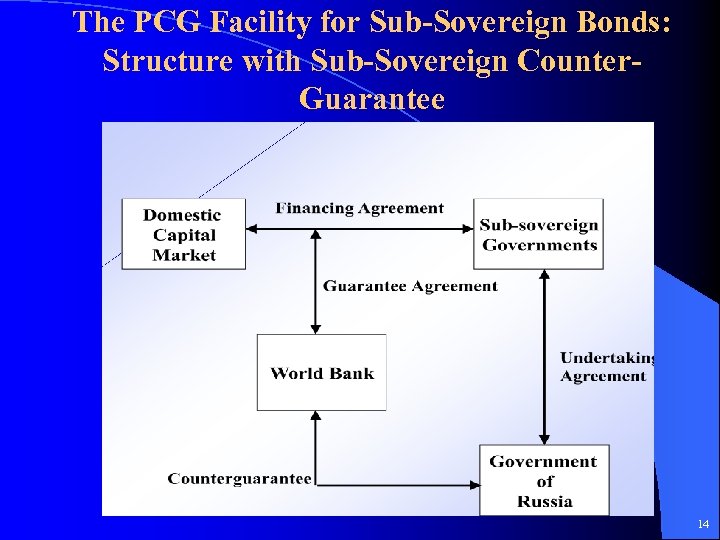 The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Structure with Sub-Sovereign Counter. Guarantee 14
The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Structure with Sub-Sovereign Counter. Guarantee 14
 The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Expected Impact Reduced spread Increased maturity Improved market discipline Improved capacity for investment programming/project selection at regional level 15
The PCG Facility for Sub-Sovereign Bonds: Expected Impact Reduced spread Increased maturity Improved market discipline Improved capacity for investment programming/project selection at regional level 15
 World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Concept Used frequently by investment banks Market failure to be resolved: inadequate climate, legal and regulatory framework for PPI Proposed solution: a fund which provides an interim solution to attract PPI while legal and regulatory framework matures Key issues and challenges: 1. Equity investment by the Bank 2. Requires strong project appraisal skills locally, including in environmental and social matters 3. Board reluctant to delegate decision making power. 16
World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Concept Used frequently by investment banks Market failure to be resolved: inadequate climate, legal and regulatory framework for PPI Proposed solution: a fund which provides an interim solution to attract PPI while legal and regulatory framework matures Key issues and challenges: 1. Equity investment by the Bank 2. Requires strong project appraisal skills locally, including in environmental and social matters 3. Board reluctant to delegate decision making power. 16
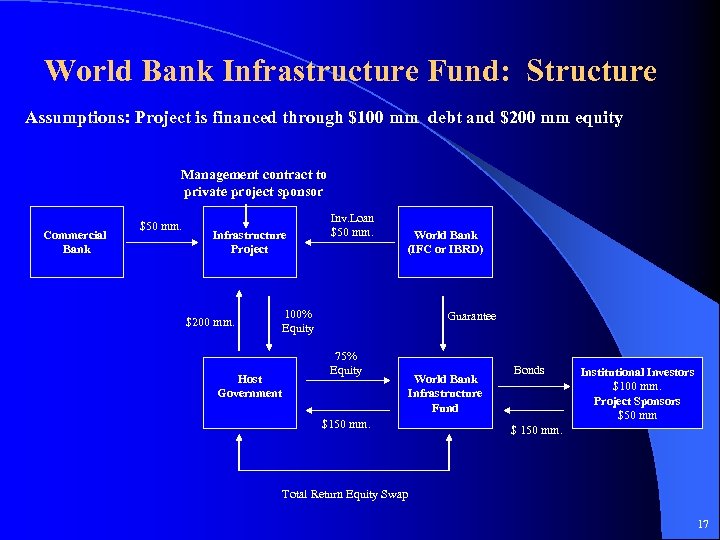 World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Structure Assumptions: Project is financed through $100 mm debt and $200 mm equity Management contract to private project sponsor Commercial Bank $50 mm. Infrastructure Project $200 mm. Host Government Inv. Loan $50 mm. World Bank (IFC or IBRD) 100% Equity Guarantee 75% Equity $150 mm. World Bank Infrastructure Fund Bonds Institutional Investors $100 mm. Project Sponsors $50 mm $ 150 mm. Total Return Equity Swap 17
World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Structure Assumptions: Project is financed through $100 mm debt and $200 mm equity Management contract to private project sponsor Commercial Bank $50 mm. Infrastructure Project $200 mm. Host Government Inv. Loan $50 mm. World Bank (IFC or IBRD) 100% Equity Guarantee 75% Equity $150 mm. World Bank Infrastructure Fund Bonds Institutional Investors $100 mm. Project Sponsors $50 mm $ 150 mm. Total Return Equity Swap 17
 World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Expected Impact Structure highlights: • Project Sponsor participates as management and debt holder • Government receives necessary financing and is given time to develop stable regulatory framework • The Bank lends its balance sheet and AAA rating to raise capital market financing for the project • Through a Total Return Equity Swap, fund only takes credit risk on government, but no equity risk on the project • The Bank intermediates potential conflicts Direct benefits: • Fund able to attract institutional investors, including pension funds • Private investors do not need to invest equity until environment is adequate for PPI • Increases local currency financing, thereby reducing FX risk • Creates a commonality of interests so that governments and private investors have both interest in ensuring the company to be privatized is doing well 18
World Bank Infrastructure Fund: Expected Impact Structure highlights: • Project Sponsor participates as management and debt holder • Government receives necessary financing and is given time to develop stable regulatory framework • The Bank lends its balance sheet and AAA rating to raise capital market financing for the project • Through a Total Return Equity Swap, fund only takes credit risk on government, but no equity risk on the project • The Bank intermediates potential conflicts Direct benefits: • Fund able to attract institutional investors, including pension funds • Private investors do not need to invest equity until environment is adequate for PPI • Increases local currency financing, thereby reducing FX risk • Creates a commonality of interests so that governments and private investors have both interest in ensuring the company to be privatized is doing well 18
 Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Concept Under discussion in ECA Market failure to be resolved: lack of exit opportunities for firstround private equity funds in local infrastructure Proposed solution: a fund investing in equity in infrastructure projects after first round investors have turned company around (hence providing a long-term low return investment) Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Redemption requirements and fund liquidity 2. Investment focus 3. Legal/regulatory framework at fund and project level 19
Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Concept Under discussion in ECA Market failure to be resolved: lack of exit opportunities for firstround private equity funds in local infrastructure Proposed solution: a fund investing in equity in infrastructure projects after first round investors have turned company around (hence providing a long-term low return investment) Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Redemption requirements and fund liquidity 2. Investment focus 3. Legal/regulatory framework at fund and project level 19
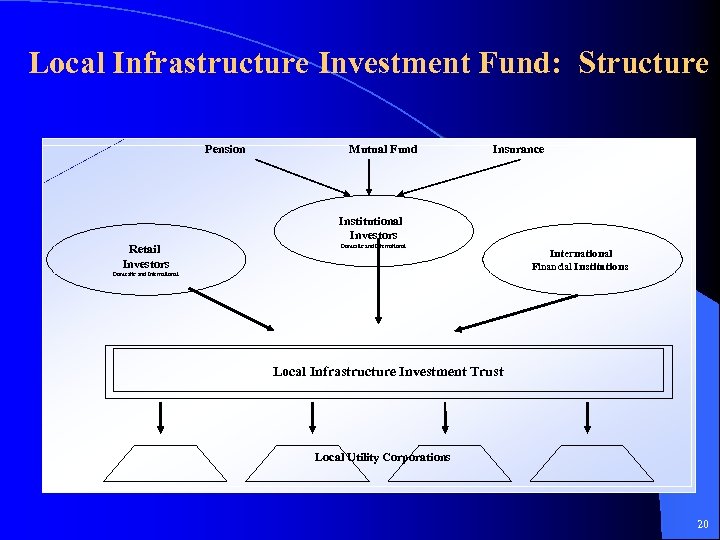 Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Structure Pension Mutual Fund Insurance Institutional Investors Retail Investors Domestic and International Financial Institutions Domestic and International Local Infrastructure Investment Trust Local Utility Corporations 20
Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Structure Pension Mutual Fund Insurance Institutional Investors Retail Investors Domestic and International Financial Institutions Domestic and International Local Infrastructure Investment Trust Local Utility Corporations 20
 Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Expected Impact Improved exit opportunities for first round infrastructure private equity funds Long term private sector commitment to improved management and operations Diversification of quality securities available for local and international institutional investors 21
Local Infrastructure Investment Fund: Expected Impact Improved exit opportunities for first round infrastructure private equity funds Long term private sector commitment to improved management and operations Diversification of quality securities available for local and international institutional investors 21
 PRG Facility to Protect against Political and Regulatory Risks: Concept Under preparation in Peru; demand from several countries in LAC Market failure to be resolved: lack of appropriate political/regulatory risk coverage instrument resulting in heavy losses by private investors despite contractual protection. Proposed solution: A $300 mm facility entitled to award IBRD partial risk guarantees to Peru’s future infrastructure projects (approximately $1. 5 bn project debt guaranteed against government-related risks Key issues and challenges: 1. Requires strong project pipeline 2. Requires strong project appraisal skills locally, including in environmental and social matters 3. Board reluctant to delegate decision making power. 22
PRG Facility to Protect against Political and Regulatory Risks: Concept Under preparation in Peru; demand from several countries in LAC Market failure to be resolved: lack of appropriate political/regulatory risk coverage instrument resulting in heavy losses by private investors despite contractual protection. Proposed solution: A $300 mm facility entitled to award IBRD partial risk guarantees to Peru’s future infrastructure projects (approximately $1. 5 bn project debt guaranteed against government-related risks Key issues and challenges: 1. Requires strong project pipeline 2. Requires strong project appraisal skills locally, including in environmental and social matters 3. Board reluctant to delegate decision making power. 22
 PRG Facility to Protect against Political and Regulatory Risks: Expected Impact Direct impact: • Improves the credit rating of projects by several notches • Enables banks and pension funds to provide project finance to non viable projects • Increases the volume and tenors of available financing and decreases its cost. Benefits for PPI: • Decreases required equity by increasing access to bank and bond financing • Decreases exposure to foreign exchange risk by increasing local currency financing • Eliminates exposure to government risk Long term benefits for Peru: • Increases the probability of success of the government PPI program • Decreases cost for the government (lower subsidies or higher price, resulting from lower financing costs and increased bidding competition) and tariffs for consumers • Enables pension funds to diversify away from sovereign risk without increasing risk • Develops local capital market by extending tenors. 23
PRG Facility to Protect against Political and Regulatory Risks: Expected Impact Direct impact: • Improves the credit rating of projects by several notches • Enables banks and pension funds to provide project finance to non viable projects • Increases the volume and tenors of available financing and decreases its cost. Benefits for PPI: • Decreases required equity by increasing access to bank and bond financing • Decreases exposure to foreign exchange risk by increasing local currency financing • Eliminates exposure to government risk Long term benefits for Peru: • Increases the probability of success of the government PPI program • Decreases cost for the government (lower subsidies or higher price, resulting from lower financing costs and increased bidding competition) and tariffs for consumers • Enables pension funds to diversify away from sovereign risk without increasing risk • Develops local capital market by extending tenors. 23
 Partial Risk Guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk Under study in Romania Market failure to be resolved: reluctance of private investors to invest in local utilities due to high risk of breach of contract with local governments and low possibility of contract enforcement in judicial and extra-judicial proceedings Proposed solution: a IBRD partial risk guarantee facility to cover sub-sovereign breach of contract risk Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Legal and regulatory framework for PPP transactions 2. Risk management 3. Market test 24
Partial Risk Guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk Under study in Romania Market failure to be resolved: reluctance of private investors to invest in local utilities due to high risk of breach of contract with local governments and low possibility of contract enforcement in judicial and extra-judicial proceedings Proposed solution: a IBRD partial risk guarantee facility to cover sub-sovereign breach of contract risk Key issues for feasibility studies: 1. Legal and regulatory framework for PPP transactions 2. Risk management 3. Market test 24
 Partial risk guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk: Structure 25
Partial risk guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk: Structure 25
 Partial risk guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk: Expected Impact Reduced spread Maturity extension Improved market discipline 26
Partial risk guarantee Facility to Cover Against Sub-Sovereign Breach of Contract Risk: Expected Impact Reduced spread Maturity extension Improved market discipline 26
 The Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh: Concept Under preparation in Bangladesh Market failure to be resolved: lack of access to long term finance and poor infrastructure identified as two major hurdles to private sector development. Bangladesh has one of the lowest infrastructure indicators in the world (Bangladesh Investment Climate Assessment). Proposed solution ² Separation of IDA support into Capital Grant & Market Based funds to allow substantive investment discretion for investment managers ² Taka facility to finance smaller projects through Credit line, partial credit Guarantee, & Takeout & interest rate support (CGT) ² Able to offer a wider range of support: senior & subordinate debt, preferred stock, equity etc. for large & small projects ² Allows private sector investment advisers to work with promoters to develop private infrastructure & term capital investments 27
The Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh: Concept Under preparation in Bangladesh Market failure to be resolved: lack of access to long term finance and poor infrastructure identified as two major hurdles to private sector development. Bangladesh has one of the lowest infrastructure indicators in the world (Bangladesh Investment Climate Assessment). Proposed solution ² Separation of IDA support into Capital Grant & Market Based funds to allow substantive investment discretion for investment managers ² Taka facility to finance smaller projects through Credit line, partial credit Guarantee, & Takeout & interest rate support (CGT) ² Able to offer a wider range of support: senior & subordinate debt, preferred stock, equity etc. for large & small projects ² Allows private sector investment advisers to work with promoters to develop private infrastructure & term capital investments 27
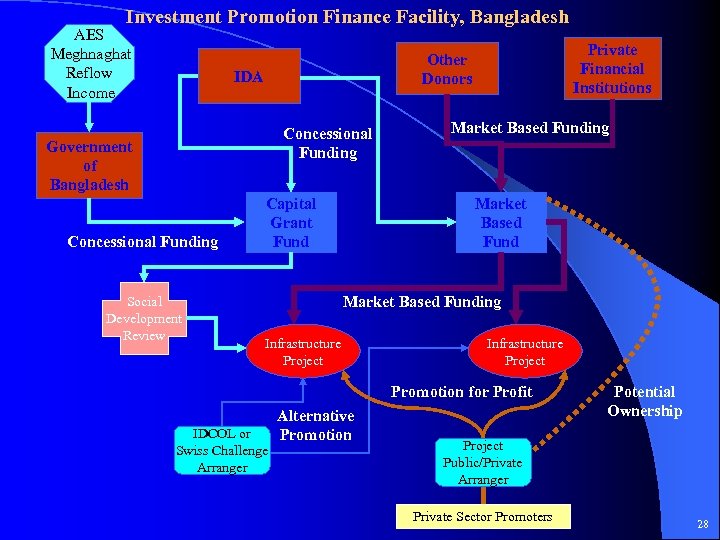 Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh AES Meghnaghat Reflow Income IDA Concessional Funding Government of Bangladesh Concessional Funding Social Development Review Private Financial Institutions Other Donors Capital Grant Fund Market Based Funding Infrastructure Project Promotion for Profit IDCOL or Swiss Challenge Arranger Alternative Promotion Potential Ownership Project Public/Private Arranger Private Sector Promoters 28
Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh AES Meghnaghat Reflow Income IDA Concessional Funding Government of Bangladesh Concessional Funding Social Development Review Private Financial Institutions Other Donors Capital Grant Fund Market Based Funding Infrastructure Project Promotion for Profit IDCOL or Swiss Challenge Arranger Alternative Promotion Potential Ownership Project Public/Private Arranger Private Sector Promoters 28
 The Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh: Expected Impact Provide long term finance to fill gap not provided by local markets Provide technical assistance to develop projects & establish governmental processes to support public private partnerships Build local private sector capacity for term finance 29
The Investment Promotion Finance Facility, Bangladesh: Expected Impact Provide long term finance to fill gap not provided by local markets Provide technical assistance to develop projects & establish governmental processes to support public private partnerships Build local private sector capacity for term finance 29


