68f4dad12543a4cc7510bf758677ac34.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Capital Market Development in Korea Can It be a New Growth Engine? 2008. 6. 11 Changyong Rhee Vice Chairman Financial Services Commission
Contents 1 Capital Market in the Past 2 Changes after the Crisis 3 Challenges and Prospect 2

Financial Market in Korea: Past 1. Bank-Dominated Financial Structure 2. Underdeveloped Capital Market 3. 4. * Liquid but highly volatile Stock Market * Large but illiquid Bond Market 5. 3. Lack of basic infrastructure 6. * underdeveloped government bonds market: no benchmark 7. * inactive credit rating & pricing agencies 3

Bond Market Development After the Crisis Bank-Dominated Financial Market and underdeveloped Local bond markets before the currency crisis: l l Markets for government bonds and government-guaranteed bonds were not well-developed (conservative fiscal policy) Corporate bond market was relatively large, but - Predominated by guaranteed-corp. bonds - “buy-and-hold” investors / no “marked-to-market” system Dazzling Development of Local bond markets after the currency crisis: l l Government bond Market: To finance public fund for financial restructuring and boost depressed economy by fiscal pump priming (Government-led Development) Corporate bond Market: To raise funds from bond markets to overcome Banks’ reluctance to extend loans (unexpected by-product of crisis / presenting new challenges and opportunities) 4
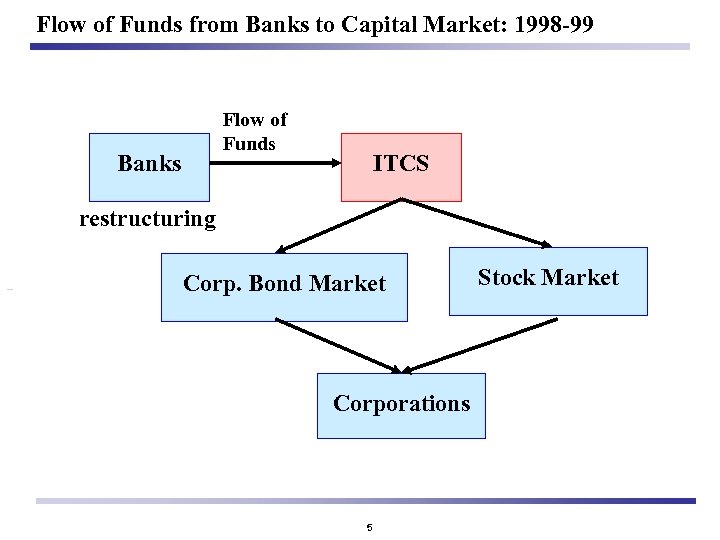
Flow of Funds from Banks to Capital Market: 1998 -99 Flow of Funds Banks ITCS restructuring Corp. Bond Market Corporations 5 Stock Market
Changes in Fund Flow Before & After the financial Crisis (Indirect Financing) (Commercial Paper) (Stock) (Corporate Bond) Financing (billion won) 6
![Role of the Capital Market in the Fast Recovery [1] Contribution: “Spare-Tire theory” by Role of the Capital Market in the Fast Recovery [1] Contribution: “Spare-Tire theory” by](https://present5.com/presentation/68f4dad12543a4cc7510bf758677ac34/image-7.jpg)
Role of the Capital Market in the Fast Recovery [1] Contribution: “Spare-Tire theory” by A. Greenspan * Corporations mitigated credit crunch problems by issuing massive amount of corp. bonds: Capital market as a parallel circuit * Market interest rates were stabilized since corp. credit crunch problems were mitigated & thereby it contributed to high growth in 1999. [2] No Free Lunch * Maturity Concentration & credit crunch in 2001! * Unviable firms could extend their lives. * Easy financing reduced Chaebol’s incentive to restructure their businesses. - massive default and recurrent credit crunch - increased ultimate costs of restructuring! [3] Despite these problems, it contributed to the sophistication of capital market. (Securitization, Derivatives, Ratings, etc. ) 7
![Lessons from Capital Market Development l [Spare Tire] Capital market can develop rapidly even Lessons from Capital Market Development l [Spare Tire] Capital market can develop rapidly even](https://present5.com/presentation/68f4dad12543a4cc7510bf758677ac34/image-8.jpg)
Lessons from Capital Market Development l [Spare Tire] Capital market can develop rapidly even where all finance has previously run through the banking system. l [Spare Tire or Donut Tire] While capital market financing may add flexibility, it may not necessarily be more efficient at allocating resources than the banking system. - Only large firms had access to direct financing via bond or equity. - Funding from bonds was even more concentrated than bank lending. - Capital markets seem to have many pre-requisites, such as reliable credit rating agencies, no `too big to fail' beliefs, and so on. 8
![Lessons from Financial and Corporate Restructuring • [Developing NPL Market & its by-product] NPL Lessons from Financial and Corporate Restructuring • [Developing NPL Market & its by-product] NPL](https://present5.com/presentation/68f4dad12543a4cc7510bf758677ac34/image-9.jpg)
Lessons from Financial and Corporate Restructuring • [Developing NPL Market & its by-product] NPL resolution process was excessively dominated by foreign capital, but it provided many opportunities for upgrading and diversifying Korean financial Market. - Realize the importance of ‘Track Record’ and ‘Financial knowledge’ of domestic financial institutions, rather than the lack of supply of risky capital - Adapting advanced financial skills such as securitization, corporate restructuring, M&A, etc. - upgrading legal system prepared for efficient NPL disposition such as the ABS Law, Consolidated Bankruptcy Act, and Corporate Restructuring Promotion Act, and so on. * [Transparency] Understanding the importance of “Transparency” as a basic financial infrastructure (upgrading financial reporting system, transparent regulations, credit rating systems, etc. ) 9

Lessons from Financial Restructuring l opportunity to change “old” financial practices. - The importance of risk management was recognized. ) - The financial market as an independent industry rather than a tool for the manufacturing sector development - Consumer financing became a part of the financial market - The differences between the manufacturing industry and the financial industry were understood. (The financial industry needs a steady growth rather than a rapid growth) 10
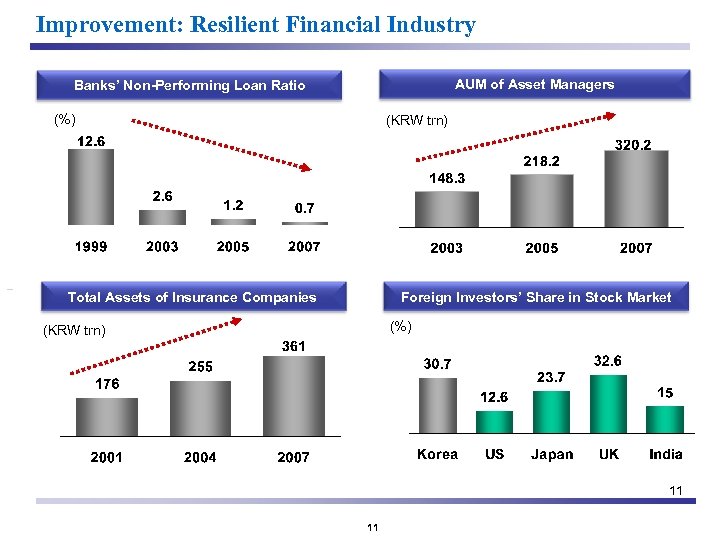
Improvement: Resilient Financial Industry AUM of Asset Managers Banks’ Non-Performing Loan Ratio (%) (KRW trn) Total Assets of Insurance Companies Foreign Investors’ Share in Stock Market (%) (KRW trn) 11 11
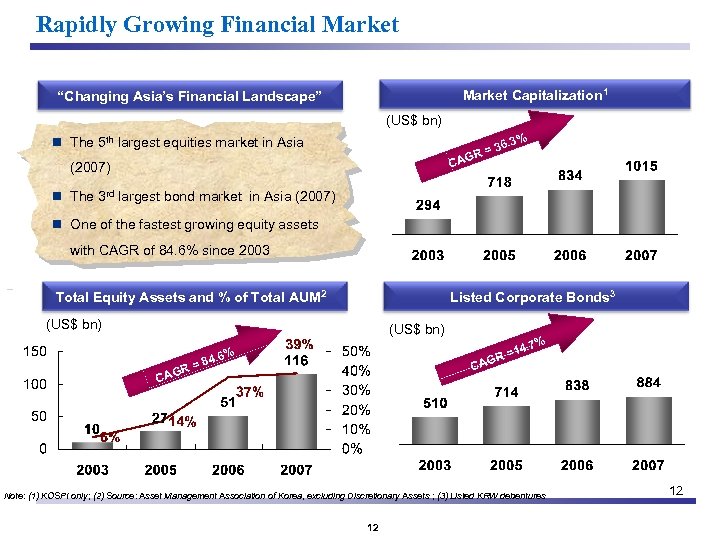
Rapidly Growing Financial Market Capitalization 1 “Changing Asia’s Financial Landscape” (US$ bn) . 3% = 36 R n The 5 th largest equities market in Asia CAG (2007) n The 3 rd largest bond market in Asia (2007) n One of the fastest growing equity assets with CAGR of 84. 6% since 2003 Total Equity Assets and % of Total AUM 2 (US$ bn) Listed Corporate Bonds 3 (US$ bn) R= CAG 8 . 7% 14 R= 4. 6% CAG Note: (1) KOSPI only; (2) Source: Asset Management Association of Korea, excluding Discretionary Assets ; (3) Listed KRW debentures 12 12
Vision and Strategies of New FSC Leader. A Global Leader in in Global Financial Markets Privatization Regulatory Reform Market-Friendly Services 13 13
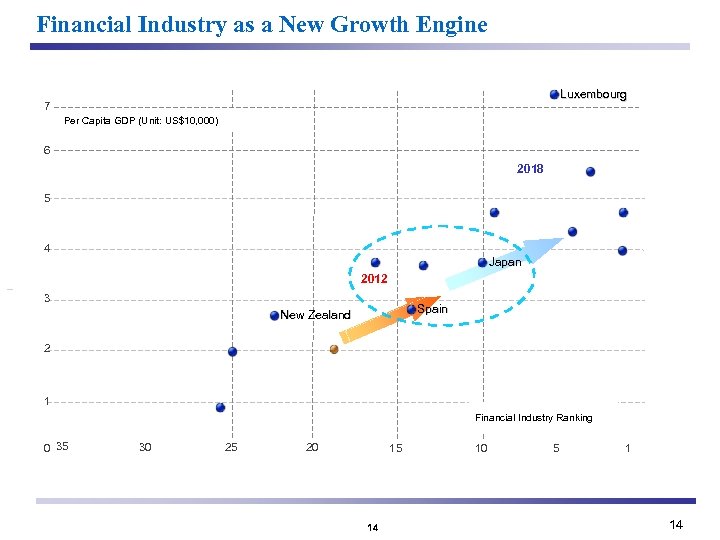
Financial Industry as a New Growth Engine Luxembourg 7 Per Capita GDP (Unit: US$10, 000) 6 2018 5 4 Japan 2012 3 Spain New Zealand 2 1 Financial Industry Ranking 0 35 30 25 20 15 14 10 5 1 14

68f4dad12543a4cc7510bf758677ac34.ppt