bf0a90cb53092ada74e76a26e0487c1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 © Capital Community College A clause is a group of related words containing a subject and a verb. It is different from a phrase in that a phrase does not include a subject and a verb relationship. There are many different kinds of clauses. It would be helpful to review some of the grammar vocabulary we use to talk about clauses.
© Capital Community College A clause is a group of related words containing a subject and a verb. It is different from a phrase in that a phrase does not include a subject and a verb relationship. There are many different kinds of clauses. It would be helpful to review some of the grammar vocabulary we use to talk about clauses.
 Clauses: Types © Capital Community College Clauses go by many names. Here are some definitions: 1. Independent: A clause that can stand by itself and still make sense. An independent clause could be its own sentence, but is often part of a larger structure, combined with other independent clauses and with dependent clauses. Independent clauses are sometimes called essential or restrictive clauses. 2. Dependent: Clause Ae pote mu. Kt hotu n 4 I. te hmexa> potana ko[k A 4 R ma 3 e ko[k ANy ]pr Aa 2 airt hoy 0 e. A clause that cannot stand by itself. It depends on something else, an independent clause, for its meaning. Ap`e 3 p/kar na> Clause pr ivcar kr. I xk. IAe.
Clauses: Types © Capital Community College Clauses go by many names. Here are some definitions: 1. Independent: A clause that can stand by itself and still make sense. An independent clause could be its own sentence, but is often part of a larger structure, combined with other independent clauses and with dependent clauses. Independent clauses are sometimes called essential or restrictive clauses. 2. Dependent: Clause Ae pote mu. Kt hotu n 4 I. te hmexa> potana ko[k A 4 R ma 3 e ko[k ANy ]pr Aa 2 airt hoy 0 e. A clause that cannot stand by itself. It depends on something else, an independent clause, for its meaning. Ap`e 3 p/kar na> Clause pr ivcar kr. I xk. IAe.
 Clauses: Three Main Types Dependent clauses va. Kyma> temna rol Anusar 3 p/kar na> hoy 0 e. They can be identified and classified according to their role in the sentence. © Capital Community College Noun clauses Adjective Clause Adverb Clause • Nehru has written a fine book about how India got freedom.
Clauses: Three Main Types Dependent clauses va. Kyma> temna rol Anusar 3 p/kar na> hoy 0 e. They can be identified and classified according to their role in the sentence. © Capital Community College Noun clauses Adjective Clause Adverb Clause • Nehru has written a fine book about how India got freedom.
 © Capital Community College
© Capital Community College
 ADJECTIVE CLAUSES modify nouns or pronouns in the rest of the sentence. © Capital Community College ADJECTIVE CLAUSES va. Kyma> ko[ p` S 4 ane Aavta nam ke sv. Rnamna ivxe v 2 u maihit Aap. Ine tene modify kre e 0 e. e • The mobile phone, which started out as a means for communication, has become a mobile T. V. . • The man who thinks only of himself is selfish. • The work that interests you most is your hobby. • The money which you save is the money you earn. ju. Ao, Aa vakyoma> kta. R (Subject)ene tena ik/yapd(verb)4 I Adjective Clause dvara Alg pa. Deel 0 e. Aa Adejective Clause Ae ten. I Aag 5 na nam(noun) ivxe v 2 u maiht. I Aape 0 e.
ADJECTIVE CLAUSES modify nouns or pronouns in the rest of the sentence. © Capital Community College ADJECTIVE CLAUSES va. Kyma> ko[ p` S 4 ane Aavta nam ke sv. Rnamna ivxe v 2 u maihit Aap. Ine tene modify kre e 0 e. e • The mobile phone, which started out as a means for communication, has become a mobile T. V. . • The man who thinks only of himself is selfish. • The work that interests you most is your hobby. • The money which you save is the money you earn. ju. Ao, Aa vakyoma> kta. R (Subject)ene tena ik/yapd(verb)4 I Adjective Clause dvara Alg pa. Deel 0 e. Aa Adejective Clause Ae ten. I Aag 5 na nam(noun) ivxe v 2 u maiht. I Aape 0 e.
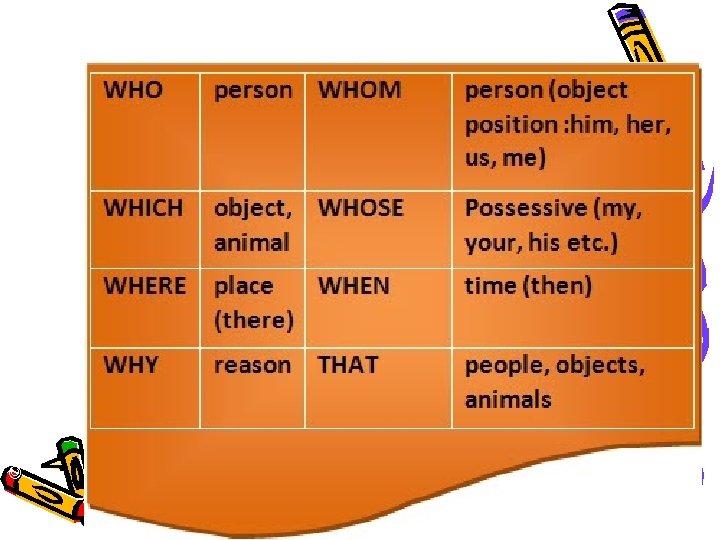
 © Capital Community College Relative Pronoun ( s>yojk) • • • what who that which where when how whose whom why xu> / je koe`/ ko`e /je/je`e ke Kyu> je Kya> jya> kyare jyare kev. I r. Ite/ Ae r. Ite kon>u / jen>u kone / jene kem / ma 3 e
© Capital Community College Relative Pronoun ( s>yojk) • • • what who that which where when how whose whom why xu> / je koe`/ ko`e /je/je`e ke Kyu> je Kya> jya> kyare jyare kev. I r. Ite/ Ae r. Ite kon>u / jen>u kone / jene kem / ma 3 e
 © Capital Community College • Noun + Relative Pronoun + Adjective Clause The The The man who lives here film that we saw school which is near my house boy whose father is a policeman teacher whom I know boy whose pen this is
© Capital Community College • Noun + Relative Pronoun + Adjective Clause The The The man who lives here film that we saw school which is near my house boy whose father is a policeman teacher whom I know boy whose pen this is
 s>yojk Ae j Clauseno kta. R © Capital Community College ke 3 l. I var an adjective clausene s>yojk pote j kta. R hoy 0 e je Clausene rj. U kre 0 e. Sometimes an adjective clause has no subject other than the relative pronoun that introduces the clauses. The book which is there on the table is very interesting. The boy who is sitting there is my brother. The mobile phone that is in your hand is mine. Such clauses — all beginning with “which, ” “that, ” or a form of “who” — are also known as RELATIVE CLAUSES. The relative pronoun serves as the subject of the dependent clause and relates to some word or idea in the independent clause.
s>yojk Ae j Clauseno kta. R © Capital Community College ke 3 l. I var an adjective clausene s>yojk pote j kta. R hoy 0 e je Clausene rj. U kre 0 e. Sometimes an adjective clause has no subject other than the relative pronoun that introduces the clauses. The book which is there on the table is very interesting. The boy who is sitting there is my brother. The mobile phone that is in your hand is mine. Such clauses — all beginning with “which, ” “that, ” or a form of “who” — are also known as RELATIVE CLAUSES. The relative pronoun serves as the subject of the dependent clause and relates to some word or idea in the independent clause.
 © Capital Community College
© Capital Community College
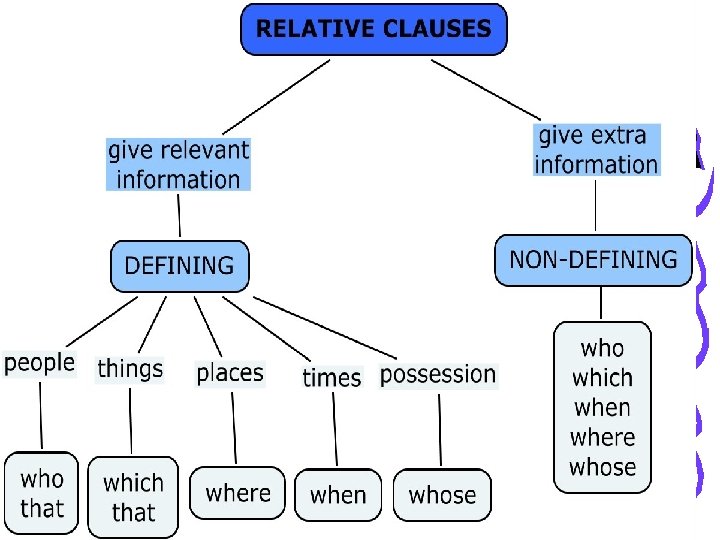
 Recap on Defining Relative Clauses © Capital Community College WHO = people WHICH = animals and things, … “THAT” = can be used instead of ‘WHO’ and ‘WHICH’
Recap on Defining Relative Clauses © Capital Community College WHO = people WHICH = animals and things, … “THAT” = can be used instead of ‘WHO’ and ‘WHICH’
 © Capital Community College THAT • Did you know the student (WHO) THAT came to the lesson yesterday? • The book (WHICH) THAT I’m reading is very interesting.
© Capital Community College THAT • Did you know the student (WHO) THAT came to the lesson yesterday? • The book (WHICH) THAT I’m reading is very interesting.
 © Capital Community College Other Relative Pronouns • WHOSE = possession • WHEN = days, months, years. . • WHERE = for places
© Capital Community College Other Relative Pronouns • WHOSE = possession • WHEN = days, months, years. . • WHERE = for places
 Adjective Clauses © Capital Community College • The main relative pronouns are: • Who: used for humans in subject position: Sonia, who is a teacher, works in Mehsana. • Whom: used for humans in object position: Sarangi, whom Sachin knows well, is an excellent teacher. • Which: used for things and animals in subject or object position: Roshni has a dog which follows her everywhere. M. A. Vianey Martín Núñez
Adjective Clauses © Capital Community College • The main relative pronouns are: • Who: used for humans in subject position: Sonia, who is a teacher, works in Mehsana. • Whom: used for humans in object position: Sarangi, whom Sachin knows well, is an excellent teacher. • Which: used for things and animals in subject or object position: Roshni has a dog which follows her everywhere. M. A. Vianey Martín Núñez
 © Capital Community College
© Capital Community College
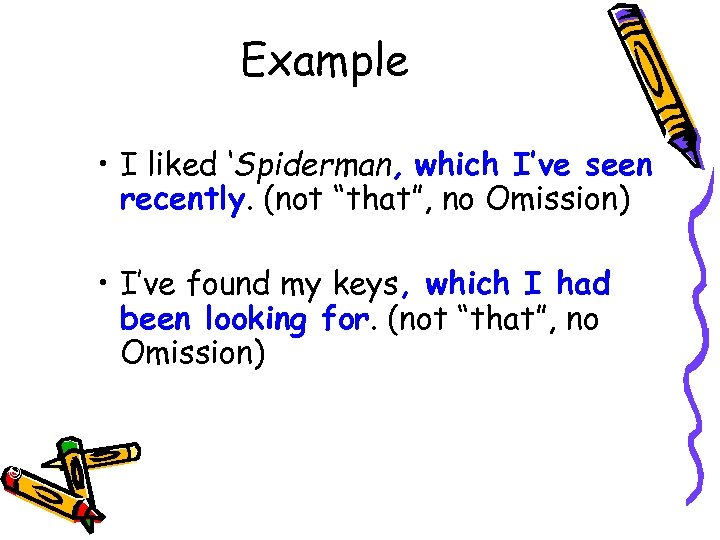 Example © Capital Community College • I liked ‘Spiderman, which I’ve seen recently. (not “that”, no Omission) • I’ve found my keys, which I had been looking for. (not “that”, no Omission)
Example © Capital Community College • I liked ‘Spiderman, which I’ve seen recently. (not “that”, no Omission) • I’ve found my keys, which I had been looking for. (not “that”, no Omission)
 Example © Capital Community College • 1) My sister, who lives in Pakistan, is a doctor.
Example © Capital Community College • 1) My sister, who lives in Pakistan, is a doctor.
![© Capital Community College Prepositions • • • • on ]pr in ma> over © Capital Community College Prepositions • • • • on ]pr in ma> over](https://present5.com/presentation/bf0a90cb53092ada74e76a26e0487c1b/image-17.jpg) © Capital Community College Prepositions • • • • on ]pr in ma> over na ]pr under n. Ice behind pa 05 for ma 3 e to ne at na trf About na ivxe with n. I sa 4 e against na ivru@2 after n. I pa 05 before na phela>
© Capital Community College Prepositions • • • • on ]pr in ma> over na ]pr under n. Ice behind pa 05 for ma 3 e to ne at na trf About na ivxe with n. I sa 4 e against na ivru@2 after n. I pa 05 before na phela>
 © Capital Community College • Noun + Preposition + Relative Pronoun + Adjective Clause • The boy with whom you study • The teacher in whose class you sit • The shopkeeper from whom you buy • The class in which I study
© Capital Community College • Noun + Preposition + Relative Pronoun + Adjective Clause • The boy with whom you study • The teacher in whose class you sit • The shopkeeper from whom you buy • The class in which I study
 © Capital Community College The chair on which the old man is sitting is made of plastic.
© Capital Community College The chair on which the old man is sitting is made of plastic.
 © Capital Community College The boy to whom Sunil is beating is his brother.
© Capital Community College The boy to whom Sunil is beating is his brother.
 © Capital Community College I like the film ‘Don’ in which Amitabh Bachchan was the don.
© Capital Community College I like the film ‘Don’ in which Amitabh Bachchan was the don.
 © Capital Community College The reason for which Anna was on fast is very serious for our country.
© Capital Community College The reason for which Anna was on fast is very serious for our country.
 © Capital Community College The man with whom Gandhiji is walking is Sardar Patel.
© Capital Community College The man with whom Gandhiji is walking is Sardar Patel.
 © Capital Community College The pen with which Shalini is writing was gifted by her dady.
© Capital Community College The pen with which Shalini is writing was gifted by her dady.
 © Capital Community College I don’t know the person with whom Mrs. Sharma is talking on he mobile phone.
© Capital Community College I don’t know the person with whom Mrs. Sharma is talking on he mobile phone.
 © Capital Community College The gentleman with whom Miss Shalini is shaking hand is the manager of the company.
© Capital Community College The gentleman with whom Miss Shalini is shaking hand is the manager of the company.
 © Capital Community College The picture in which you are watching the spiderman has been taken from Internet.
© Capital Community College The picture in which you are watching the spiderman has been taken from Internet.
 © Capital Community College Sardar Patel was the leader under whose leadership Bardoli Satyagraha became successful.
© Capital Community College Sardar Patel was the leader under whose leadership Bardoli Satyagraha became successful.
 © Capital Community College This is the house in which I live.
© Capital Community College This is the house in which I live.
 © Capital Community College The man from whom I bought this bunglow has gone to U. S. A. .
© Capital Community College The man from whom I bought this bunglow has gone to U. S. A. .
 © Capital Community College • 2) Flat screen televisions, which are very expensive, have a better picture quality.
© Capital Community College • 2) Flat screen televisions, which are very expensive, have a better picture quality.
 © Capital Community College • 4) The teachers at this school who arrive late for class will be dismissed. 5)The students, who had tickets, went into the museum
© Capital Community College • 4) The teachers at this school who arrive late for class will be dismissed. 5)The students, who had tickets, went into the museum
 © Capital Community College • The book ____ I bought yesterday cost over £ 10 pounds • The house ____ I live in now is smaller than the old one.
© Capital Community College • The book ____ I bought yesterday cost over £ 10 pounds • The house ____ I live in now is smaller than the old one.
 © Capital Community College Summary • Defining Relative • No commas • Omit the relative pronoun except when SUBJECT Non-Defining Relative Between commas No omission Relative Pronouns WHO: refers to people WHICH: refers to things WHOSE: for possession WHEN: for time WHERE : for places.
© Capital Community College Summary • Defining Relative • No commas • Omit the relative pronoun except when SUBJECT Non-Defining Relative Between commas No omission Relative Pronouns WHO: refers to people WHICH: refers to things WHOSE: for possession WHEN: for time WHERE : for places.
 Clauses: Building Blocks for Sentences © Capital Community College Understanding CLAUSES and how they are connected within the larger structure of your sentence will help you avoid Sentence Fragments Run-on Sentences and make it possible for you to punctuate your sentences properly and write confidently with a variety of sentence structures.
Clauses: Building Blocks for Sentences © Capital Community College Understanding CLAUSES and how they are connected within the larger structure of your sentence will help you avoid Sentence Fragments Run-on Sentences and make it possible for you to punctuate your sentences properly and write confidently with a variety of sentence structures.
 ADJECTIVE CLAUSES modify nouns or pronouns in the rest of the sentence. © Capital Community College ADJECTIVE CLAUSES va. Kyma> ko[ p` S 4 ane Aavta nam ke sv. Rnamna ivxe v 2 u maihit Aap. Ine tene modify kre e 0 e. e • The Internet, which started out as a means for military and academic types to share documents, has become a household necessity. • Tim Berners-Lee, who developed the World Wide Web, could never have foreseen the popularity of his invention. • The graphical user interface (GUI) that we all take for granted nowadays is actually a late development in the World Wide Web. Notice, now, how the subject is often separated from its verb by information represented by the dependent clause.
ADJECTIVE CLAUSES modify nouns or pronouns in the rest of the sentence. © Capital Community College ADJECTIVE CLAUSES va. Kyma> ko[ p` S 4 ane Aavta nam ke sv. Rnamna ivxe v 2 u maihit Aap. Ine tene modify kre e 0 e. e • The Internet, which started out as a means for military and academic types to share documents, has become a household necessity. • Tim Berners-Lee, who developed the World Wide Web, could never have foreseen the popularity of his invention. • The graphical user interface (GUI) that we all take for granted nowadays is actually a late development in the World Wide Web. Notice, now, how the subject is often separated from its verb by information represented by the dependent clause.
 © Capital Community College
© Capital Community College
 © Capital Community College
© Capital Community College
 WHOSE © Capital Community College That’s the woman whose son ran over my cat
WHOSE © Capital Community College That’s the woman whose son ran over my cat
 WHEN, WHERE © Capital Community College Tell me when you expect to arrive The hotel where we stayed was excellent
WHEN, WHERE © Capital Community College Tell me when you expect to arrive The hotel where we stayed was excellent
 WHICH • Refers to the whole of the sentence before © Capital Community College • Can be used to make a comment about the whole situation described in a main clause The teacher arrived on time, which amazed everybody They had everything ready for us, which was nice
WHICH • Refers to the whole of the sentence before © Capital Community College • Can be used to make a comment about the whole situation described in a main clause The teacher arrived on time, which amazed everybody They had everything ready for us, which was nice
 http: //www. englishcorner. vacau. com/grammar/intera ctive/rcos 3. html © Capital Community College • I read the letter • Which letter? • We need more detail. • The one that arrived this morning.
http: //www. englishcorner. vacau. com/grammar/intera ctive/rcos 3. html © Capital Community College • I read the letter • Which letter? • We need more detail. • The one that arrived this morning.


