b9557d177557dcc4bc69e1deb85efe01.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Capacity Training New Mexico Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant January 25, 2006 Michelle Fry & Paula Feathers Southwest Center for Applied Prevention Technologies
Capacity Training New Mexico Strategic Prevention Framework State Incentive Grant January 25, 2006 Michelle Fry & Paula Feathers Southwest Center for Applied Prevention Technologies
 Capacity Agenda • Welcome and Introductions • Group Work Agreement • Review Objectives • Review-Visit Assessment phase • Explore capacity and systems • Where is your system currently • Community Readiness • Intervening Variable system development • Addressing identified gaps • Report requirements • Closure • Training evaluation
Capacity Agenda • Welcome and Introductions • Group Work Agreement • Review Objectives • Review-Visit Assessment phase • Explore capacity and systems • Where is your system currently • Community Readiness • Intervening Variable system development • Addressing identified gaps • Report requirements • Closure • Training evaluation
 Capacity Training Objectives • Explain capacity as it relates to the consequence logic model • Define community prevention system • Explain what a prevention system addressing Intervening Variables and risky behaviors associated with underage binge drinking and 15 -24 year old alcohol related crashes in their community looks like.
Capacity Training Objectives • Explain capacity as it relates to the consequence logic model • Define community prevention system • Explain what a prevention system addressing Intervening Variables and risky behaviors associated with underage binge drinking and 15 -24 year old alcohol related crashes in their community looks like.
 Capacity Training Objectives Community Readiness: • Describe community readiness. • Explain the 9 stages of readiness. • Analyze their community in the statewide readiness survey and identify community strengths, weaknesses, and key stakeholders who need to be brought into the system. • Identify tools available to gauge community readiness.
Capacity Training Objectives Community Readiness: • Describe community readiness. • Explain the 9 stages of readiness. • Analyze their community in the statewide readiness survey and identify community strengths, weaknesses, and key stakeholders who need to be brought into the system. • Identify tools available to gauge community readiness.
 Capacity Training Objectives Mobilization: • Identify stake holder’s necessary to implement environmental strategies. • Map existing system and identify who needs to be included. • Identify strategies to educate and mobilize identified stakeholders.
Capacity Training Objectives Mobilization: • Identify stake holder’s necessary to implement environmental strategies. • Map existing system and identify who needs to be included. • Identify strategies to educate and mobilize identified stakeholders.
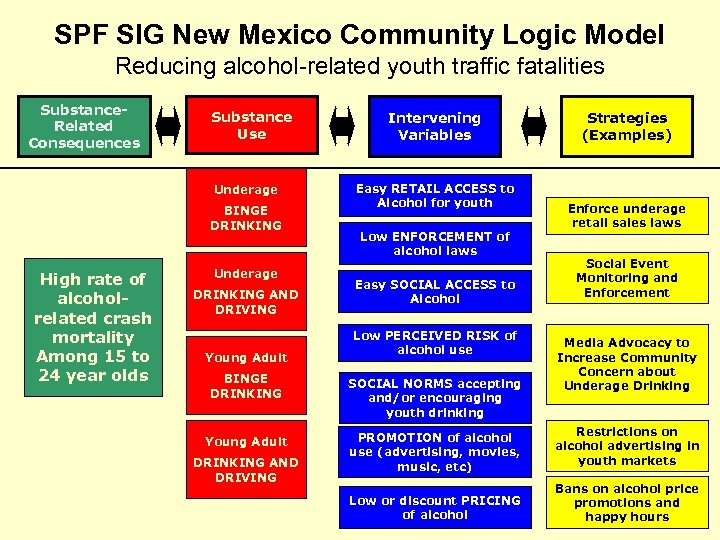 SPF SIG New Mexico Community Logic Model Reducing alcohol-related youth traffic fatalities Substance. Related Consequences Substance Use Underage BINGE DRINKING High rate of alcoholrelated crash mortality Among 15 to 24 year olds Underage DRINKING AND DRIVING Young Adult Intervening Variables Easy RETAIL ACCESS to Alcohol for youth Low ENFORCEMENT of alcohol laws Easy SOCIAL ACCESS to Alcohol Low PERCEIVED RISK of alcohol use Strategies (Examples) Enforce underage retail sales laws Social Event Monitoring and Enforcement Media Advocacy to Increase Community Concern about Underage Drinking BINGE DRINKING SOCIAL NORMS accepting and/or encouraging youth drinking Young Adult PROMOTION of alcohol use (advertising, movies, music, etc) Restrictions on alcohol advertising in youth markets Low or discount PRICING of alcohol Bans on alcohol price promotions and happy hours DRINKING AND DRIVING
SPF SIG New Mexico Community Logic Model Reducing alcohol-related youth traffic fatalities Substance. Related Consequences Substance Use Underage BINGE DRINKING High rate of alcoholrelated crash mortality Among 15 to 24 year olds Underage DRINKING AND DRIVING Young Adult Intervening Variables Easy RETAIL ACCESS to Alcohol for youth Low ENFORCEMENT of alcohol laws Easy SOCIAL ACCESS to Alcohol Low PERCEIVED RISK of alcohol use Strategies (Examples) Enforce underage retail sales laws Social Event Monitoring and Enforcement Media Advocacy to Increase Community Concern about Underage Drinking BINGE DRINKING SOCIAL NORMS accepting and/or encouraging youth drinking Young Adult PROMOTION of alcohol use (advertising, movies, music, etc) Restrictions on alcohol advertising in youth markets Low or discount PRICING of alcohol Bans on alcohol price promotions and happy hours DRINKING AND DRIVING
 Assessment Check In In your communities, answer the following questions: 1. What good things have you learned about your community as a result of your assessment efforts? 2. What has been challenging? 3. What resources or allies did you discover during this process? 4. Which allies are not currently present?
Assessment Check In In your communities, answer the following questions: 1. What good things have you learned about your community as a result of your assessment efforts? 2. What has been challenging? 3. What resources or allies did you discover during this process? 4. Which allies are not currently present?
 Intervening Variables Review Community Activity: • Groups will get an envelope that has Intervening Variables and examples of Intervening Variables. • Match the examples with the correct Intervening Variable.
Intervening Variables Review Community Activity: • Groups will get an envelope that has Intervening Variables and examples of Intervening Variables. • Match the examples with the correct Intervening Variable.
 Intervening Variables Review Easy Retail Access • Lack of compliance checks • High number of alcohol outlets Low Enforcement • Low number of sobriety check points • Alcohol is being sold to intoxicated patrons
Intervening Variables Review Easy Retail Access • Lack of compliance checks • High number of alcohol outlets Low Enforcement • Low number of sobriety check points • Alcohol is being sold to intoxicated patrons
 Intervening Variables Review Social Access • Parents host house parties • Keg parties near college campuses Low Perceived Risk • The person who drinks the least is the safest driver • People believe there is no police patrol in certain areas
Intervening Variables Review Social Access • Parents host house parties • Keg parties near college campuses Low Perceived Risk • The person who drinks the least is the safest driver • People believe there is no police patrol in certain areas
 Intervening Variables Review Social Norms • Freshmen in college believe they are expected to drink every weekend • Every celebration has alcohol Promotion • The Tecate softball tournament gives a 6 pack to anyone who hits a homerun • Every other add on the radio is for club-18 to enter 21 to drink
Intervening Variables Review Social Norms • Freshmen in college believe they are expected to drink every weekend • Every celebration has alcohol Promotion • The Tecate softball tournament gives a 6 pack to anyone who hits a homerun • Every other add on the radio is for club-18 to enter 21 to drink
 Intervening Variables Review Discount Pricing • Happy hours offer $2. 00 pitchers • Buy 16 oz. Beer for the price of a 12 oz.
Intervening Variables Review Discount Pricing • Happy hours offer $2. 00 pitchers • Buy 16 oz. Beer for the price of a 12 oz.
 Capacity • Mobilization of resources within a geographic area. • Convening key stakeholders, coalitions, and service providers to plan and implement sustainable prevention efforts • Mobilization includes financial and organizational resources in addition to forming partnerships.
Capacity • Mobilization of resources within a geographic area. • Convening key stakeholders, coalitions, and service providers to plan and implement sustainable prevention efforts • Mobilization includes financial and organizational resources in addition to forming partnerships.
 Capacity Other considerations: • Community Readiness • Cultural Competence • Leadership All are strengthened by education and training
Capacity Other considerations: • Community Readiness • Cultural Competence • Leadership All are strengthened by education and training
 Capacity Benchmarks • Partnerships – Continuation and creation of new ones – MOAs (memorandums of agreement) – Directory • Education and training sessions • Meetings and workshops with key stakeholders
Capacity Benchmarks • Partnerships – Continuation and creation of new ones – MOAs (memorandums of agreement) – Directory • Education and training sessions • Meetings and workshops with key stakeholders
 Capacity and the SPF SIG Our Logic Model is data driven. • Who, When and Where of consequence • Use patterns • Surveys, questionnaires, focus groups of Intervening Variables.
Capacity and the SPF SIG Our Logic Model is data driven. • Who, When and Where of consequence • Use patterns • Surveys, questionnaires, focus groups of Intervening Variables.
 Capacity and the SPF SIG Capacity is built around the logic model. To create effective prevention , looking at the logic model, where does capacity need to be centered? Answer: INTERVENING VARIABLES
Capacity and the SPF SIG Capacity is built around the logic model. To create effective prevention , looking at the logic model, where does capacity need to be centered? Answer: INTERVENING VARIABLES
 Prevention as a System system: 1. Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. 2. A collection of personnel, equipment, and methods organized to accomplish a set of specific functions.
Prevention as a System system: 1. Any organized assembly of resources and procedures united and regulated by interaction or interdependence to accomplish a set of specific functions. 2. A collection of personnel, equipment, and methods organized to accomplish a set of specific functions.
 Prevention as a System What would a comprehensive, united, prevention system look like using this logic model? Answer: One that addresses each Intervening Variable. Each community will build capacity around Intervening Variables.
Prevention as a System What would a comprehensive, united, prevention system look like using this logic model? Answer: One that addresses each Intervening Variable. Each community will build capacity around Intervening Variables.
 Prevention as a System What is the goal of the prevention system we want to create in our communities with the SPF SIG? Answer: Reduce the rate of 15 -24 year olds involved in fatal alcohol-related vehicle crashes.
Prevention as a System What is the goal of the prevention system we want to create in our communities with the SPF SIG? Answer: Reduce the rate of 15 -24 year olds involved in fatal alcohol-related vehicle crashes.
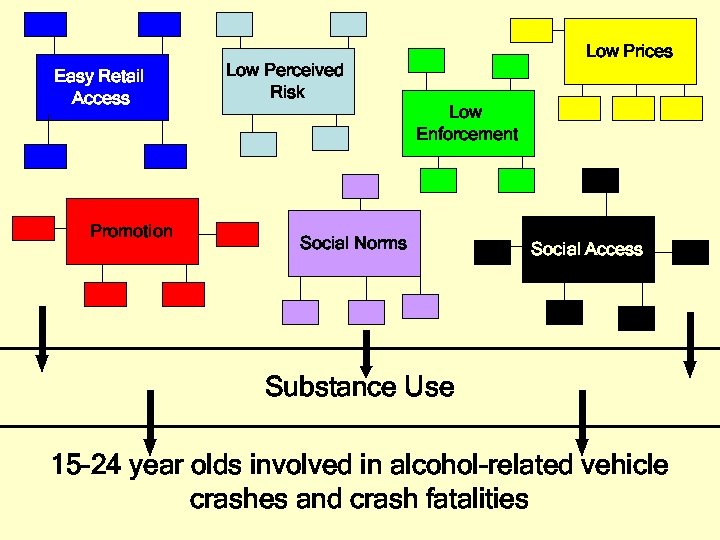 Easy Retail Access Promotion Low Prices Low Perceived Risk Low Enforcement Social Norms Social Access Substance Use 15 -24 year olds involved in alcohol-related vehicle crashes and crash fatalities
Easy Retail Access Promotion Low Prices Low Perceived Risk Low Enforcement Social Norms Social Access Substance Use 15 -24 year olds involved in alcohol-related vehicle crashes and crash fatalities
 What has your data shown you? 1. For each Intervening Variable, map out the issues, trends, and behaviors (constructs) you have identified in your community through your assessments. 2. Use the handouts on Page 5 -7
What has your data shown you? 1. For each Intervening Variable, map out the issues, trends, and behaviors (constructs) you have identified in your community through your assessments. 2. Use the handouts on Page 5 -7
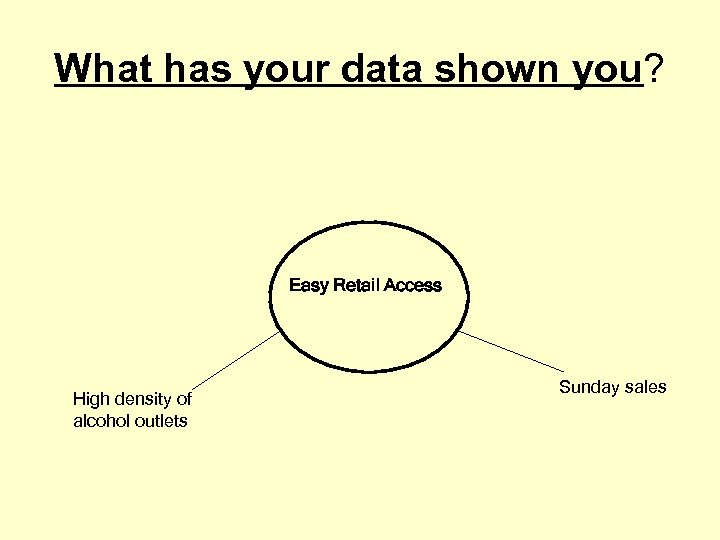 What has your data shown you? Easy Retail Access High density of alcohol outlets Sunday sales
What has your data shown you? Easy Retail Access High density of alcohol outlets Sunday sales
 What has your data shown you? 1. For each Intervening Variable, map out the issues, trends, and behaviors (constructs) you have identified in your community through your assessments. 2. Use the handouts on Page 5 -7
What has your data shown you? 1. For each Intervening Variable, map out the issues, trends, and behaviors (constructs) you have identified in your community through your assessments. 2. Use the handouts on Page 5 -7
 Where is your system now? 1. For each Intervening Variable, identify resources currently actively involved (pg. 8 -14). 2. Refer to the maps you created based on your data as guides. 3. This will be used for the following reasons: • Inventory of current stakeholders • Identifying gaps 4. Use the handout on pg. 16 to list gaps
Where is your system now? 1. For each Intervening Variable, identify resources currently actively involved (pg. 8 -14). 2. Refer to the maps you created based on your data as guides. 3. This will be used for the following reasons: • Inventory of current stakeholders • Identifying gaps 4. Use the handout on pg. 16 to list gaps
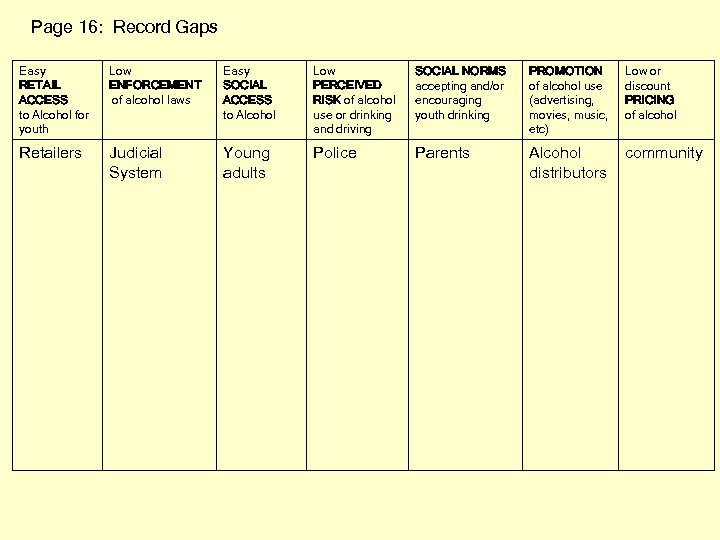 Page 16: Record Gaps Easy RETAIL ACCESS to Alcohol for youth Low ENFORCEMENT of alcohol laws Easy SOCIAL ACCESS to Alcohol Low PERCEIVED RISK of alcohol use or drinking and driving SOCIAL NORMS accepting and/or encouraging youth drinking PROMOTION of alcohol use (advertising, movies, music, etc) Low or discount PRICING of alcohol Retailers Judicial System Young adults Police Parents Alcohol distributors community
Page 16: Record Gaps Easy RETAIL ACCESS to Alcohol for youth Low ENFORCEMENT of alcohol laws Easy SOCIAL ACCESS to Alcohol Low PERCEIVED RISK of alcohol use or drinking and driving SOCIAL NORMS accepting and/or encouraging youth drinking PROMOTION of alcohol use (advertising, movies, music, etc) Low or discount PRICING of alcohol Retailers Judicial System Young adults Police Parents Alcohol distributors community
 Where is your system now? 1. For each Intervening Variable, identify resources currently actively involved (pg. 8 -14). 2. Refer to the maps you created based on your data as guides. 3. This will be used for the following reasons: • Inventory of current stakeholders • Identifying gaps 4. Use the handout on pg. 16 to list gaps
Where is your system now? 1. For each Intervening Variable, identify resources currently actively involved (pg. 8 -14). 2. Refer to the maps you created based on your data as guides. 3. This will be used for the following reasons: • Inventory of current stakeholders • Identifying gaps 4. Use the handout on pg. 16 to list gaps
 Community Prevention System Community Readiness: The capacity of a community to implement programs, policies and other changes that are designed to reduce the likelihood of substance use.
Community Prevention System Community Readiness: The capacity of a community to implement programs, policies and other changes that are designed to reduce the likelihood of substance use.
 Community Readiness Why is it important to know a community’s readiness level? • Helps identify where capacity needs improvement. • Gauges community attitudes • Serves as a catalyst for change
Community Readiness Why is it important to know a community’s readiness level? • Helps identify where capacity needs improvement. • Gauges community attitudes • Serves as a catalyst for change
 Community Readiness Is determined by: 1. Identifying the issue • 15 -24 year olds involved in alcohol related crashes 2. Define the community 3. Conduct interviews 4. Develop strategies based on level of readiness and conduct workshops or trainings to increase readiness.
Community Readiness Is determined by: 1. Identifying the issue • 15 -24 year olds involved in alcohol related crashes 2. Define the community 3. Conduct interviews 4. Develop strategies based on level of readiness and conduct workshops or trainings to increase readiness.
 Community Readiness • 9 Stages of Community Readiness Page 18 • Strategies to Increase Readiness Page 19 -20 During the capacity phase, we will want to focus on the assessment.
Community Readiness • 9 Stages of Community Readiness Page 18 • Strategies to Increase Readiness Page 19 -20 During the capacity phase, we will want to focus on the assessment.
 Community Readiness County Level Data 1. Review the county level readiness survey results. 2. Identify and record potential resources for each Intervening Variable (pg. 8 -14) and gaps (pg. 16).
Community Readiness County Level Data 1. Review the county level readiness survey results. 2. Identify and record potential resources for each Intervening Variable (pg. 8 -14) and gaps (pg. 16).
 County Level Readiness Survey • What information from this survey was beneficial? • How will this worksheet be useful? • Questions or concerns?
County Level Readiness Survey • What information from this survey was beneficial? • How will this worksheet be useful? • Questions or concerns?
 Community Readiness Community Activity 1. Answer: What cultural considerations do we need to take into account when assessing community readiness? 2. Record on Flip Chart 3. Report to larger group
Community Readiness Community Activity 1. Answer: What cultural considerations do we need to take into account when assessing community readiness? 2. Record on Flip Chart 3. Report to larger group
 Community and Intervening Variables Community Activity: 1. Refer to pg. 21 2. Examine Social Access by identifying everyone that has an impact on that Intervening Variable, both positive and negative impacts. 3. Will share with other communities
Community and Intervening Variables Community Activity: 1. Refer to pg. 21 2. Examine Social Access by identifying everyone that has an impact on that Intervening Variable, both positive and negative impacts. 3. Will share with other communities
 Communities and Intervening Variables • What are some new ideas you got from this activity? • How will these worksheets be useful? • Questions or concerns?
Communities and Intervening Variables • What are some new ideas you got from this activity? • How will these worksheets be useful? • Questions or concerns?
 Community and Intervening Variables These worksheets (pg. 21 -27) will need to be completed for each Intervening Variable when you go back to your communities.
Community and Intervening Variables These worksheets (pg. 21 -27) will need to be completed for each Intervening Variable when you go back to your communities.
 Addressing Gaps 1. Use page 16 as a guide for identified gaps. 2. List strategies to fill those gaps. – Networking – Win-Win Selling Points – Education sessions 3. Strategies will be shared with other communities.
Addressing Gaps 1. Use page 16 as a guide for identified gaps. 2. List strategies to fill those gaps. – Networking – Win-Win Selling Points – Education sessions 3. Strategies will be shared with other communities.
 Strategies to Address Gaps • How was this activity beneficial? • How will this worksheet be useful? • Questions or concerns?
Strategies to Address Gaps • How was this activity beneficial? • How will this worksheet be useful? • Questions or concerns?
 Report Requirements Michael Coop
Report Requirements Michael Coop
 Capacity Training Objectives • Explain capacity as it relates to the consequence logic model • Define community prevention system • Explain what a prevention system addressing Intervening Variables and risky behaviors associated with underage binge drinking and 15 -24 year old alcohol related crashes in their community looks like.
Capacity Training Objectives • Explain capacity as it relates to the consequence logic model • Define community prevention system • Explain what a prevention system addressing Intervening Variables and risky behaviors associated with underage binge drinking and 15 -24 year old alcohol related crashes in their community looks like.
 Capacity Training Objectives Community Readiness: • Describe community readiness. • Explain the 9 stages of readiness. • Analyze their community in the statewide readiness survey and identify community strengths, weaknesses, and key stakeholders who need to be brought into the system. • Identify tools available to gauge community readiness.
Capacity Training Objectives Community Readiness: • Describe community readiness. • Explain the 9 stages of readiness. • Analyze their community in the statewide readiness survey and identify community strengths, weaknesses, and key stakeholders who need to be brought into the system. • Identify tools available to gauge community readiness.
 Capacity Training Objectives Mobilization: • Identify stake holder’s necessary to implement environmental strategies. • Map existing system and identify who needs to be included. • Identify strategies to educate and mobilize identified stakeholders.
Capacity Training Objectives Mobilization: • Identify stake holder’s necessary to implement environmental strategies. • Map existing system and identify who needs to be included. • Identify strategies to educate and mobilize identified stakeholders.
 Evaluation • Final thoughts or concerns? • Please fill out evaluation-only for today’s training, please do not include yesterday’s meeting. Thank you and safe travels! Power. Point can be found at: http: //captus. samhsa. gov/ Click on Southwest CAPT, then on the state of New Mexico.
Evaluation • Final thoughts or concerns? • Please fill out evaluation-only for today’s training, please do not include yesterday’s meeting. Thank you and safe travels! Power. Point can be found at: http: //captus. samhsa. gov/ Click on Southwest CAPT, then on the state of New Mexico.
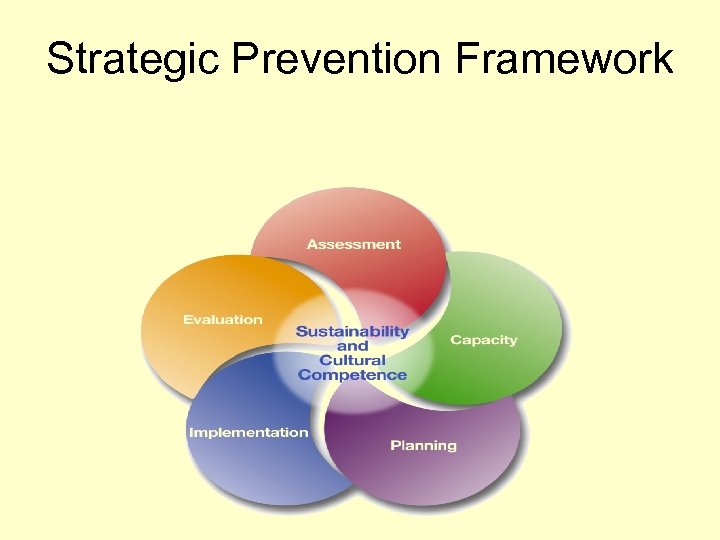 Strategic Prevention Framework
Strategic Prevention Framework
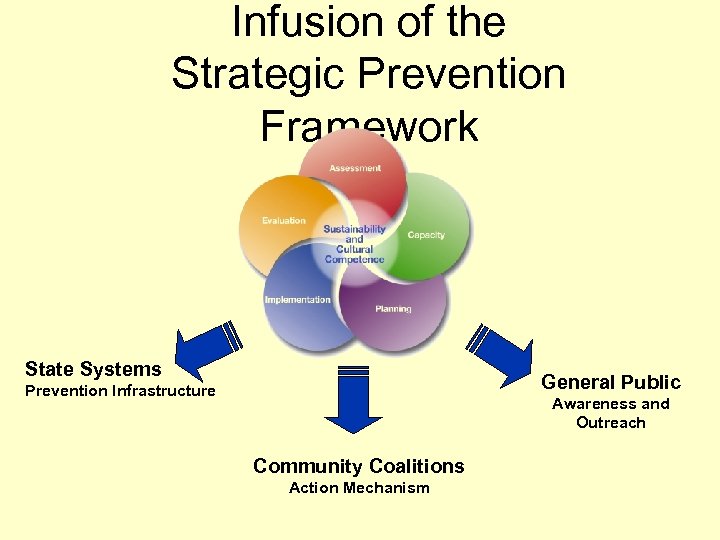 Infusion of the Strategic Prevention Framework State Systems General Public Prevention Infrastructure Awareness and Outreach Community Coalitions Action Mechanism
Infusion of the Strategic Prevention Framework State Systems General Public Prevention Infrastructure Awareness and Outreach Community Coalitions Action Mechanism
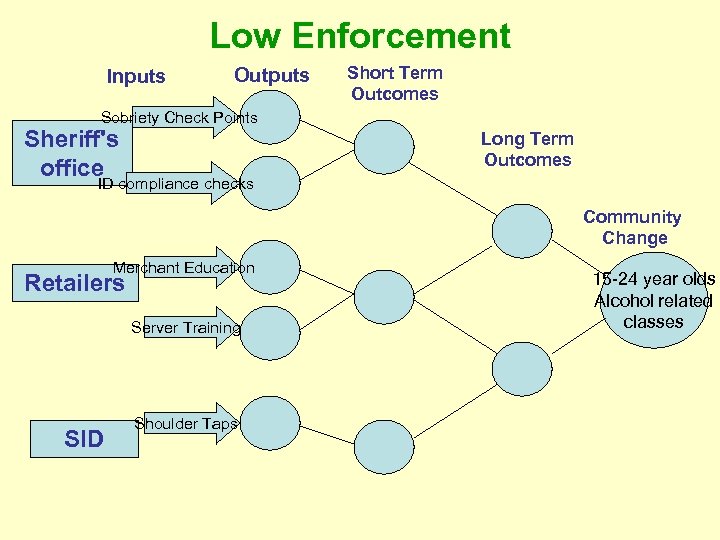 Low Enforcement Inputs Outputs Short Term Outcomes Sobriety Check Points Sheriff's office Long Term Outcomes ID compliance checks Community Change Merchant Education Retailers Server Training SID Shoulder Taps 15 -24 year olds Alcohol related classes
Low Enforcement Inputs Outputs Short Term Outcomes Sobriety Check Points Sheriff's office Long Term Outcomes ID compliance checks Community Change Merchant Education Retailers Server Training SID Shoulder Taps 15 -24 year olds Alcohol related classes


