canning.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 CANNING
CANNING
 canning q Canning means, the preservation of food in permanent, hermetically sealed containers (of metal, glass, thermostable plastic, or a multi-layered flexible pouch) through agency of heat. q Heating is the principle factor to destroy the microorganisms and the permanent sealing is to prevent re-infection.
canning q Canning means, the preservation of food in permanent, hermetically sealed containers (of metal, glass, thermostable plastic, or a multi-layered flexible pouch) through agency of heat. q Heating is the principle factor to destroy the microorganisms and the permanent sealing is to prevent re-infection.
 history 4 Nicholas Appert invented the canning process in 1809. 4 Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte of France was the first to use it. 4 19 th-20 th century- canned food used mainly by military. 4 20 th century- commercialization of canning.
history 4 Nicholas Appert invented the canning process in 1809. 4 Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte of France was the first to use it. 4 19 th-20 th century- canned food used mainly by military. 4 20 th century- commercialization of canning.
 containers for canned foods Must be: 1 -) Capable of being hermetically sealed to prevent entry of microorganisms. 2 -) Impermeable to liquids and gases, including water vapour. 3 -) Maintain the state of biological stability (i. e, commercial sterility) that was induced by thermal process alone or in combination with other chemical and physical processes. 4 -) Physically protect the contents against damage during transportation, storage and distribution.
containers for canned foods Must be: 1 -) Capable of being hermetically sealed to prevent entry of microorganisms. 2 -) Impermeable to liquids and gases, including water vapour. 3 -) Maintain the state of biological stability (i. e, commercial sterility) that was induced by thermal process alone or in combination with other chemical and physical processes. 4 -) Physically protect the contents against damage during transportation, storage and distribution.
 important canned food groups Low acid foods: meat fish, poultry, diary fall into a p. H range of 5 -6. 8 and hence commonly referred to as low acid food. Acid foods: fruits such as pears, oranges, apricots and tomatoes with p. H values between 4. 5 -3. 7 fall in this class. High acid foods: pickeled products, fermented foods and also jam and jellies with p. H values ranging from 3. 7 down to 2. 3
important canned food groups Low acid foods: meat fish, poultry, diary fall into a p. H range of 5 -6. 8 and hence commonly referred to as low acid food. Acid foods: fruits such as pears, oranges, apricots and tomatoes with p. H values between 4. 5 -3. 7 fall in this class. High acid foods: pickeled products, fermented foods and also jam and jellies with p. H values ranging from 3. 7 down to 2. 3
 4 can materials (a) Metal- Steel & Aluminium: most frequent used package for canning food. Tinplate, tin-free steel, and nickel-plated steel coated with a very thin film of tin are the materials used to manufacture metal food cans. Cans used in the food industry are coated on the inside with two general kinds of organic coatingsv acid-resistant: used primarily for fruit. v sulfur-resistant: used primarily for Meat products. (b) Plastic (c) Glass containers and metal closures
4 can materials (a) Metal- Steel & Aluminium: most frequent used package for canning food. Tinplate, tin-free steel, and nickel-plated steel coated with a very thin film of tin are the materials used to manufacture metal food cans. Cans used in the food industry are coated on the inside with two general kinds of organic coatingsv acid-resistant: used primarily for fruit. v sulfur-resistant: used primarily for Meat products. (b) Plastic (c) Glass containers and metal closures
 procedure
procedure
 procedure The canning process itself consists of several stages: 1. Cleaning- passing the raw food through tanks of water or under highpressure water sprays 2. Preparing the raw food material- vegetable or other products are cut, peeled, cored, sliced, graded, soaked, pureed, and so on 3. Blanching- immersion in hot water or steam 4. Filling the containers- usually under a vacuum; 5. Closing and sealing the container- done automatically by machines; cans are filled with solid contents and, in many cases, with an accompanying liquid (often brine or syrup) in order to replace as much of the air in the can as possible 6. Sterilizing the canned products- they are heated at temperatures high enough and for a long enough time to destroy all microorganisms (bacteria, molds, yeasts) that might still be present in the food contents. The heating is done in high-pressure steam kettles, or cookers, usually using temperatures around 240° F (116° C). 7. Labeling and warehousing the finished goods- cans are then cooled in cold water or air, after which they are labeled.
procedure The canning process itself consists of several stages: 1. Cleaning- passing the raw food through tanks of water or under highpressure water sprays 2. Preparing the raw food material- vegetable or other products are cut, peeled, cored, sliced, graded, soaked, pureed, and so on 3. Blanching- immersion in hot water or steam 4. Filling the containers- usually under a vacuum; 5. Closing and sealing the container- done automatically by machines; cans are filled with solid contents and, in many cases, with an accompanying liquid (often brine or syrup) in order to replace as much of the air in the can as possible 6. Sterilizing the canned products- they are heated at temperatures high enough and for a long enough time to destroy all microorganisms (bacteria, molds, yeasts) that might still be present in the food contents. The heating is done in high-pressure steam kettles, or cookers, usually using temperatures around 240° F (116° C). 7. Labeling and warehousing the finished goods- cans are then cooled in cold water or air, after which they are labeled.
 two methods of processing canned foods: 4 Water-bath processing- Canning jars filled with food and with special canning lids are secured completely and immersed in boiling water for an amount of time specified in the canning recipe. 4 After processing, as the jars cool, a vacuum seal is formed. 4 It can only heat the food to the temperature of boiling water.
two methods of processing canned foods: 4 Water-bath processing- Canning jars filled with food and with special canning lids are secured completely and immersed in boiling water for an amount of time specified in the canning recipe. 4 After processing, as the jars cool, a vacuum seal is formed. 4 It can only heat the food to the temperature of boiling water.
 Contd… 4 Pressure processing-A pressure canner is a heavy-duty piece of equipment with a vent, a pressure gauge and screw clamps. It is capable of heating the food in the jars to hotter than the temperature of boiling water.
Contd… 4 Pressure processing-A pressure canner is a heavy-duty piece of equipment with a vent, a pressure gauge and screw clamps. It is capable of heating the food in the jars to hotter than the temperature of boiling water.
 spoilage of canned foods Low Acid canned foods Acid foods High acid foods • Flat-sour spoilage- Bacillus stearothermophilus and B. coagulans • Sulfide spoilage- Clostridium nigrificans and C. bifermentans. • Gaseous spoilage- C. butyricum. • Undergo flat-sour and gaseous spoilage. • Spoilage is usually due to nonspore forming mesophiles like yeasts, molds and lactic acid bacteria.
spoilage of canned foods Low Acid canned foods Acid foods High acid foods • Flat-sour spoilage- Bacillus stearothermophilus and B. coagulans • Sulfide spoilage- Clostridium nigrificans and C. bifermentans. • Gaseous spoilage- C. butyricum. • Undergo flat-sour and gaseous spoilage. • Spoilage is usually due to nonspore forming mesophiles like yeasts, molds and lactic acid bacteria.
 contd. . 4 Botulism caused by Clostridium botulinum produce 4 4 4 § § toxin in a sealed jar of food. Home-canned vegetables are the most common cause of botulism outbreaks in the United States. From 1996 to 2008, there were 116 outbreaks of foodborne botulism reported to CDC. These outbreaks often occur becausehome canners did not follow canning instructions did not use pressure cookers/canners ignored signs of food spoilage were unaware of the risk of botulism from improperly preserving vegetables.
contd. . 4 Botulism caused by Clostridium botulinum produce 4 4 4 § § toxin in a sealed jar of food. Home-canned vegetables are the most common cause of botulism outbreaks in the United States. From 1996 to 2008, there were 116 outbreaks of foodborne botulism reported to CDC. These outbreaks often occur becausehome canners did not follow canning instructions did not use pressure cookers/canners ignored signs of food spoilage were unaware of the risk of botulism from improperly preserving vegetables.
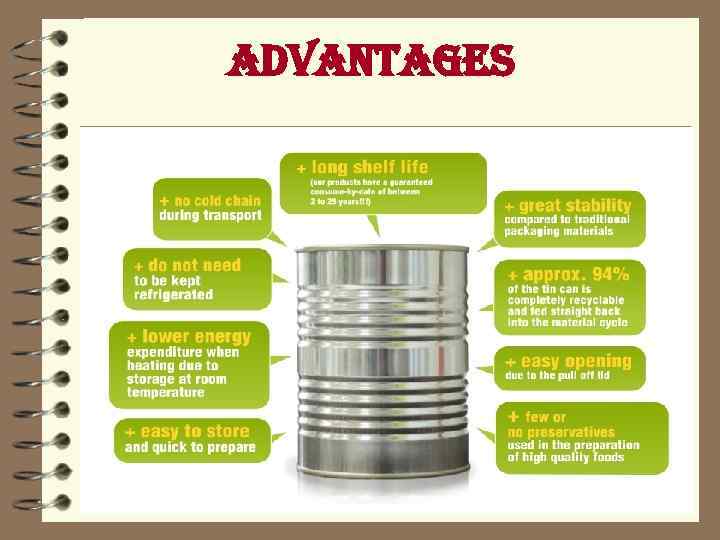 advantages
advantages
 disadvantages High in Sodium • Salt helps preserve the food, but can elevate blood pressure. High in Sugar • The added sugar increases the calorie and carbohydrate count of the final product. Fewer Nutrients • Removing the peel of a fruit or vegetable reduces its fiber content. Since this is a common practice in canned foods, Vitamin C gets destroyed during the cooking and canning process.
disadvantages High in Sodium • Salt helps preserve the food, but can elevate blood pressure. High in Sugar • The added sugar increases the calorie and carbohydrate count of the final product. Fewer Nutrients • Removing the peel of a fruit or vegetable reduces its fiber content. Since this is a common practice in canned foods, Vitamin C gets destroyed during the cooking and canning process.



