49d15d1983c3e94c0bcc11c35cd2772b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Canada and the Great Depression
Canada and the Great Depression
 Overview l There is debate about what caused the Great Depression l It was a combination of events and decisions that caused the Great Depression. (Rasmussen, Hannah )
Overview l There is debate about what caused the Great Depression l It was a combination of events and decisions that caused the Great Depression. (Rasmussen, Hannah )
 The Economic Impact of WWI l After WWI (1914 -1918) Europe was trying to rebuild l Many European countries struggled to pay their war debts and reparations l Most owned a lot of money to American banks l These loans were so high the countries could not pay them l Economic problems in many countries in Europe (Rasmussen, Hannah )
The Economic Impact of WWI l After WWI (1914 -1918) Europe was trying to rebuild l Many European countries struggled to pay their war debts and reparations l Most owned a lot of money to American banks l These loans were so high the countries could not pay them l Economic problems in many countries in Europe (Rasmussen, Hannah )
 The Economic Impact of WWI l The US government would not reduce/ forgive debts l The US economy began to slow down l European countries began to find it difficult to borrow money. l USA also had high tariffs l Europeans could not make money selling their products in the US market l Countries began to default on their loans. (Rasmussen, Hannah ) l In Germany by 1922 their bank notes were of so little value people burned them to keep warm
The Economic Impact of WWI l The US government would not reduce/ forgive debts l The US economy began to slow down l European countries began to find it difficult to borrow money. l USA also had high tariffs l Europeans could not make money selling their products in the US market l Countries began to default on their loans. (Rasmussen, Hannah ) l In Germany by 1922 their bank notes were of so little value people burned them to keep warm
 Here in Canada in the post WWI era l Prices were on the rise , for example, 1 lb of beef cost $0. 10 in 1914 but by 1918 it was $0. 39. l The Communist Revolution in Russia had started with labor unrest/strikes l Canadians worried as many here threatened to strike l Soldiers returned from war to few job opportunities l The government offered support temporarily but cut programs in 1921 - many disabled veterans were unemployed l Protests followed- unions were formed- strikes followed (Winnipeg 1919)
Here in Canada in the post WWI era l Prices were on the rise , for example, 1 lb of beef cost $0. 10 in 1914 but by 1918 it was $0. 39. l The Communist Revolution in Russia had started with labor unrest/strikes l Canadians worried as many here threatened to strike l Soldiers returned from war to few job opportunities l The government offered support temporarily but cut programs in 1921 - many disabled veterans were unemployed l Protests followed- unions were formed- strikes followed (Winnipeg 1919)
 The Roaring Twenties l The 1920 s were a boom time in Canada. l There was a high demand for raw materials (forestry, mining, pulp & paper) and industries developed mass production techniques- l Exports such as wheat became of primary importance in the Canadian economy Unemployment was low and earnings for individuals and companies were high. l
The Roaring Twenties l The 1920 s were a boom time in Canada. l There was a high demand for raw materials (forestry, mining, pulp & paper) and industries developed mass production techniques- l Exports such as wheat became of primary importance in the Canadian economy Unemployment was low and earnings for individuals and companies were high. l
 The Roaring Twenties l People were able to spend and consume huge amounts. l Foreign investment in Canadian markets increased l l USA accounted for 58% of foreign investment in Canada) l Credit as a way to buy things was introduced- impact on how people played the stock market l But prosperity came to a halt with the stock market collapse around the world in October 1929.
The Roaring Twenties l People were able to spend and consume huge amounts. l Foreign investment in Canadian markets increased l l USA accounted for 58% of foreign investment in Canada) l Credit as a way to buy things was introduced- impact on how people played the stock market l But prosperity came to a halt with the stock market collapse around the world in October 1929.
 THE CRASH of ’ 29 (Black Tuesday) l Uncontrolled buying = shares above “true” value. l Big investors see this and sell. l Panic selling occurs with smaller investors l Bank reserves drop l Consumers put off purchases l Production of goods slows down –manufacturers had large inventories they could not sell l People are laid off
THE CRASH of ’ 29 (Black Tuesday) l Uncontrolled buying = shares above “true” value. l Big investors see this and sell. l Panic selling occurs with smaller investors l Bank reserves drop l Consumers put off purchases l Production of goods slows down –manufacturers had large inventories they could not sell l People are laid off
 In Canada l 1928 wheat crop crash l Work money and food began to run low l Federal Department of Labor that a family needed between $1200 and $1500 l At that time, 60% of men and 82% of women made less than $1000 a year. l GNP fell from $6. 1 billion in 1929 to $3. 5 billion in 1933 "The Great Depression of Canada Homepage”
In Canada l 1928 wheat crop crash l Work money and food began to run low l Federal Department of Labor that a family needed between $1200 and $1500 l At that time, 60% of men and 82% of women made less than $1000 a year. l GNP fell from $6. 1 billion in 1929 to $3. 5 billion in 1933 "The Great Depression of Canada Homepage”
 Effect on Canadian Economy l Canadian economy dependent on exports (trade with other nations (Europe and USA) l Foreign countries stopped buying l Countries imposed tariffs l 1930 – 1939 severe winter with little snow l drought in western Canada = crop failures
Effect on Canadian Economy l Canadian economy dependent on exports (trade with other nations (Europe and USA) l Foreign countries stopped buying l Countries imposed tariffs l 1930 – 1939 severe winter with little snow l drought in western Canada = crop failures
 Effect on average citizens l Those who do still work have to take pay cuts l Canada had many employed in staple trades and manufacturing l Many lose jobs l The unemployed begin to default on mortgage payments.
Effect on average citizens l Those who do still work have to take pay cuts l Canada had many employed in staple trades and manufacturing l Many lose jobs l The unemployed begin to default on mortgage payments.
 Effect on average citizens
Effect on average citizens
 Roaring Twenties- Dirty Thirties: l The 1930’s are referred to as the dirty thirties l Suffering, unemployment, and homelessness. l Sandstorms- also known as the “Dust Bowl” l Soil very fine- drought- no rain to keep topsoil in place l Soil easily picked up to blow across the countryside l Conditions were very bad in the Prairie Provinces.
Roaring Twenties- Dirty Thirties: l The 1930’s are referred to as the dirty thirties l Suffering, unemployment, and homelessness. l Sandstorms- also known as the “Dust Bowl” l Soil very fine- drought- no rain to keep topsoil in place l Soil easily picked up to blow across the countryside l Conditions were very bad in the Prairie Provinces.
 Dust Storm Link to crop prices
Dust Storm Link to crop prices
 Grasshoppers: l Clouds of grasshoppers would black out the sky. l They would pass by and eat anything in their way l The things that they did not eat they would spoil so that it would become useless
Grasshoppers: l Clouds of grasshoppers would black out the sky. l They would pass by and eat anything in their way l The things that they did not eat they would spoil so that it would become useless
 Grasshoppers
Grasshoppers
 Riding the Rods/ Riding the Rails: l Jobless and homeless men were on the move- looking for work l Hide under trains for a free ride l Unable to leave once the train is in motion. l Incredibly dangerous
Riding the Rods/ Riding the Rails: l Jobless and homeless men were on the move- looking for work l Hide under trains for a free ride l Unable to leave once the train is in motion. l Incredibly dangerous
 Riding the Rods/ Riding the Rails:
Riding the Rods/ Riding the Rails:
 Hobos’ Jungle: l Near every city “jungles” formed l Thousands of homeless men made their camp before passing through to the next town. l Conditions in these camps were deplorable l Concerns over sanitation.
Hobos’ Jungle: l Near every city “jungles” formed l Thousands of homeless men made their camp before passing through to the next town. l Conditions in these camps were deplorable l Concerns over sanitation.
 Hobos’ jungle
Hobos’ jungle
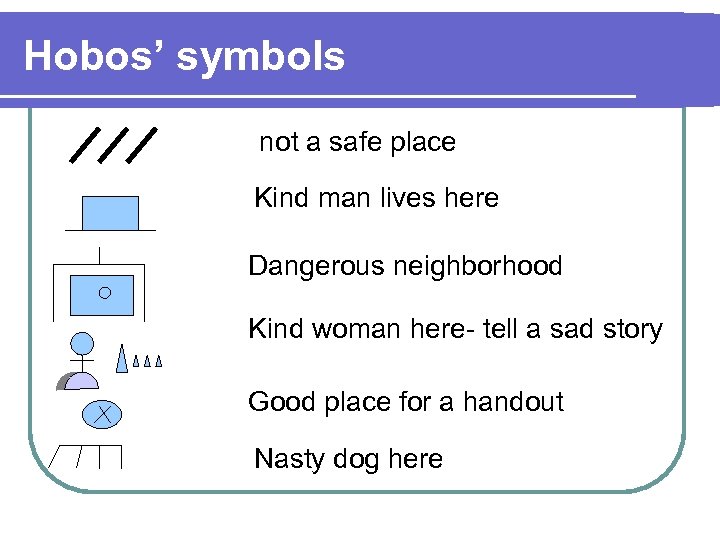 Hobos’ symbols not a safe place Kind man lives here Dangerous neighborhood Kind woman here- tell a sad story Good place for a handout Nasty dog here
Hobos’ symbols not a safe place Kind man lives here Dangerous neighborhood Kind woman here- tell a sad story Good place for a handout Nasty dog here
 Work Camps/ Relief Camps l Intended to handle 2000 men within a year some had 11, 000 l By the end of the depression 170, 248 men had been taken in. l Workers worked 8 hours a day, 4 hours on Saturday for. 20 cents a day. l The physical and psychological conditions within the camps were poor.
Work Camps/ Relief Camps l Intended to handle 2000 men within a year some had 11, 000 l By the end of the depression 170, 248 men had been taken in. l Workers worked 8 hours a day, 4 hours on Saturday for. 20 cents a day. l The physical and psychological conditions within the camps were poor.
 Work Camps/ Relief Camps
Work Camps/ Relief Camps
 Families l Families who could not afford food or lodging were broken up l Link to family budget l Parents would sometimes barter their children away to pay for essentials l they could not afford to support them
Families l Families who could not afford food or lodging were broken up l Link to family budget l Parents would sometimes barter their children away to pay for essentials l they could not afford to support them
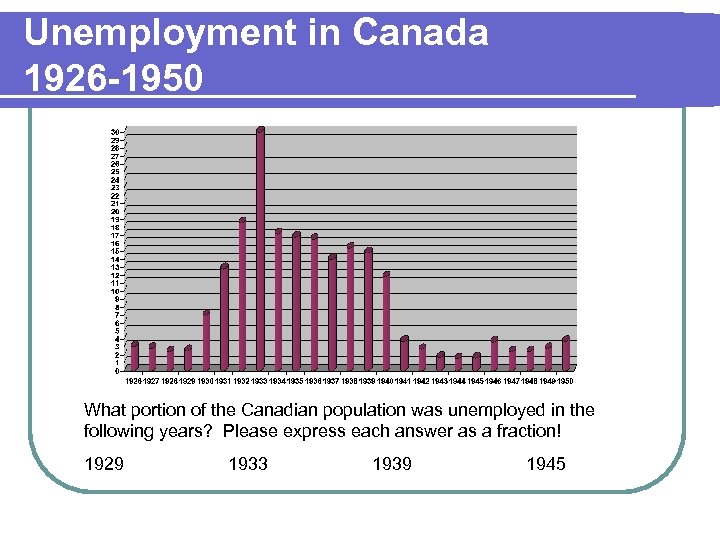 Unemployment in Canada 1926 -1950 What portion of the Canadian population was unemployed in the following years? Please express each answer as a fraction! 1929 1933 1939 1945
Unemployment in Canada 1926 -1950 What portion of the Canadian population was unemployed in the following years? Please express each answer as a fraction! 1929 1933 1939 1945
 On to Ottawa Trek l April – June 1935 1500 men left the relief camps and gathered in Vancouver l Started a march to Ottawa l They were going to demand better wages and working conditions
On to Ottawa Trek l April – June 1935 1500 men left the relief camps and gathered in Vancouver l Started a march to Ottawa l They were going to demand better wages and working conditions
 The On to Ottawa Trek 1935
The On to Ottawa Trek 1935
 The Regina Riots l June 14, 1935 2000 trekkers in Regina l Prime Minister R. B. Bennett (Conservative) proposed a meeting with the leaders- all others would have to stay behind l Bennett offered nothing to them and said the camps were fine l The police attempted to arrest the leaders when the returned to Regina-a riot ensued l I officer died many protesters and police were injured- nothing changed l Bennett was not re-elected and William Lyon Mackenzie King’s Liberal government returned to power
The Regina Riots l June 14, 1935 2000 trekkers in Regina l Prime Minister R. B. Bennett (Conservative) proposed a meeting with the leaders- all others would have to stay behind l Bennett offered nothing to them and said the camps were fine l The police attempted to arrest the leaders when the returned to Regina-a riot ensued l I officer died many protesters and police were injured- nothing changed l Bennett was not re-elected and William Lyon Mackenzie King’s Liberal government returned to power
 The Regina Riots
The Regina Riots
 Government Response l Before the Depression the government interfered as little as possible with the economy l Believed that a free market would take care of the economy l Churches and communities would take care of societal issues l During the depression the government had to step in and create the following: a) b) c) minimum hourly wages standard work week unemployment insurance
Government Response l Before the Depression the government interfered as little as possible with the economy l Believed that a free market would take care of the economy l Churches and communities would take care of societal issues l During the depression the government had to step in and create the following: a) b) c) minimum hourly wages standard work week unemployment insurance
 Works Cited l l l "1926 -1950 - Extension History, Since 1909. " UThink: Blogs at the University of Minnesota. Web. 16 May 2010.
Works Cited l l l "1926 -1950 - Extension History, Since 1909. " UThink: Blogs at the University of Minnesota. Web. 16 May 2010.


