f2dcbf90c167f356782bfb2b623196f1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Can physiotherapists predict within 72 hours the functional outcome in stroke patients ? Eghidemwivbie NT and Schneeweis VA
Can physiotherapists predict within 72 hours the functional outcome in stroke patients ? Eghidemwivbie NT and Schneeweis VA
 Content Introduction Importance of early prediction Research question Method and materials Statistics and results Discussion and conclusion Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 2
Content Introduction Importance of early prediction Research question Method and materials Statistics and results Discussion and conclusion Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 2
 Introduction Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the western world (Department of Health and Human Services, 2009) Due to its disabling nature, predictions of functional outcomes are necessary Stroke units Early prediction is important Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 3
Introduction Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the western world (Department of Health and Human Services, 2009) Due to its disabling nature, predictions of functional outcomes are necessary Stroke units Early prediction is important Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 3
 Importance of early prediction Inform patients and relatives Plan discharge Treatment goals Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 4
Importance of early prediction Inform patients and relatives Plan discharge Treatment goals Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 4
 Research Question How accurate can physiotherapists predict, within 72 hours after stroke onset and at hospital discharge, the functional outcome in terms of dexterity, walking ability, ADLs at six months and place of living at three and six months post stroke? Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 5
Research Question How accurate can physiotherapists predict, within 72 hours after stroke onset and at hospital discharge, the functional outcome in terms of dexterity, walking ability, ADLs at six months and place of living at three and six months post stroke? Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 5
 Method & Materials 221 patients 27 trained assessors 10 hospitals Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 6
Method & Materials 221 patients 27 trained assessors 10 hospitals Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 6
 First prediction Within 72 hours • • • Dexterity Gait ADL Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 7
First prediction Within 72 hours • • • Dexterity Gait ADL Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 7
 Dexterity Measured with the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) 0 -57 points • • Fully functional (=57 points) Almost fully functional (53 -56 points) Recovered to some extent (10 -52 points) Non functional (0 -9 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 8
Dexterity Measured with the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT) 0 -57 points • • Fully functional (=57 points) Almost fully functional (53 -56 points) Recovered to some extent (10 -52 points) Non functional (0 -9 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 8
 ADL Measured with the Barthel Index (BI) 0 -20 points • • • Complete recovery (19 -20 points) Slightly limited (14 -18 points) Moderately limited (10 -13 points) Severely limited (4 -9 points) Very severely limited (0 -3 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 9
ADL Measured with the Barthel Index (BI) 0 -20 points • • • Complete recovery (19 -20 points) Slightly limited (14 -18 points) Moderately limited (10 -13 points) Severely limited (4 -9 points) Very severely limited (0 -3 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 9
 Gait Measured with the Functional Ambulation Categories (FAC) 0 -5 points • Complete recovery on uneven surfaces and slopes (5 points) • Almost complete recovery, safe on even surfaces (4 points) • Only under supervision possible (3 points) • Only with physical support possible (0 -2 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 10
Gait Measured with the Functional Ambulation Categories (FAC) 0 -5 points • Complete recovery on uneven surfaces and slopes (5 points) • Almost complete recovery, safe on even surfaces (4 points) • Only under supervision possible (3 points) • Only with physical support possible (0 -2 points) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 10
 Second prediction At hospital discharge • • Dexterity ADL Gait Place of living Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 11
Second prediction At hospital discharge • • Dexterity ADL Gait Place of living Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 11
 Place of living At three and six months Categorized • • • Home with help for basic ADLs Rehabilitation center Nursing home Hospital Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 12
Place of living At three and six months Categorized • • • Home with help for basic ADLs Rehabilitation center Nursing home Hospital Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 12
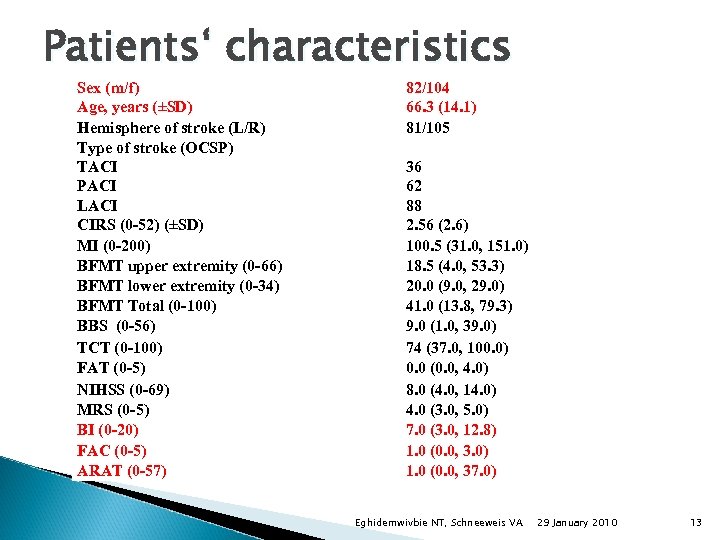 Patients‘ characteristics Sex (m/f) Age, years (±SD) Hemisphere of stroke (L/R) Type of stroke (OCSP) TACI PACI LACI CIRS (0 -52) (±SD) MI (0 -200) BFMT upper extremity (0 -66) BFMT lower extremity (0 -34) BFMT Total (0 -100) BBS (0 -56) TCT (0 -100) FAT (0 -5) NIHSS (0 -69) MRS (0 -5) BI (0 -20) FAC (0 -5) ARAT (0 -57) 82/104 66. 3 (14. 1) 81/105 36 62 88 2. 56 (2. 6) 100. 5 (31. 0, 151. 0) 18. 5 (4. 0, 53. 3) 20. 0 (9. 0, 29. 0) 41. 0 (13. 8, 79. 3) 9. 0 (1. 0, 39. 0) 74 (37. 0, 100. 0) 0. 0 (0. 0, 4. 0) 8. 0 (4. 0, 14. 0) 4. 0 (3. 0, 5. 0) 7. 0 (3. 0, 12. 8) 1. 0 (0. 0, 3. 0) 1. 0 (0. 0, 37. 0) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 13
Patients‘ characteristics Sex (m/f) Age, years (±SD) Hemisphere of stroke (L/R) Type of stroke (OCSP) TACI PACI LACI CIRS (0 -52) (±SD) MI (0 -200) BFMT upper extremity (0 -66) BFMT lower extremity (0 -34) BFMT Total (0 -100) BBS (0 -56) TCT (0 -100) FAT (0 -5) NIHSS (0 -69) MRS (0 -5) BI (0 -20) FAC (0 -5) ARAT (0 -57) 82/104 66. 3 (14. 1) 81/105 36 62 88 2. 56 (2. 6) 100. 5 (31. 0, 151. 0) 18. 5 (4. 0, 53. 3) 20. 0 (9. 0, 29. 0) 41. 0 (13. 8, 79. 3) 9. 0 (1. 0, 39. 0) 74 (37. 0, 100. 0) 0. 0 (0. 0, 4. 0) 8. 0 (4. 0, 14. 0) 4. 0 (3. 0, 5. 0) 7. 0 (3. 0, 12. 8) 1. 0 (0. 0, 3. 0) 1. 0 (0. 0, 37. 0) Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 13
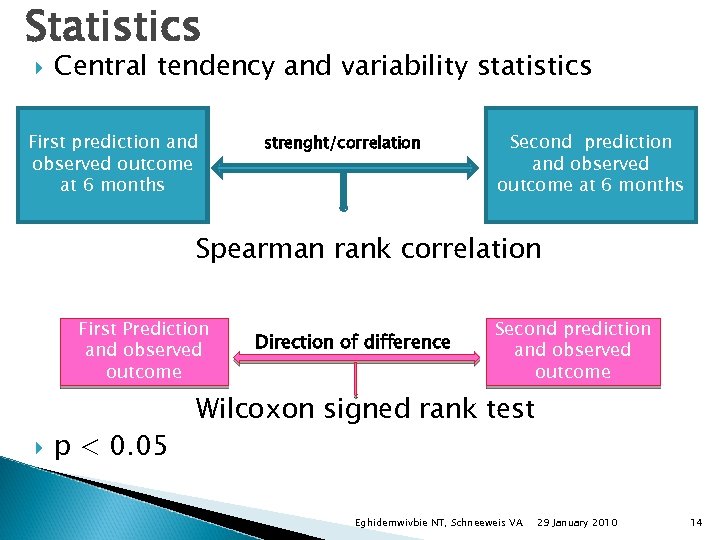 Statistics Central tendency and variability statistics First prediction and observed outcome at 6 months strenght/correlation Second prediction and observed outcome at 6 months Spearman rank correlation First Prediction and observed outcome p < 0. 05 Direction of difference Second prediction and observed outcome Wilcoxon signed rank test Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 14
Statistics Central tendency and variability statistics First prediction and observed outcome at 6 months strenght/correlation Second prediction and observed outcome at 6 months Spearman rank correlation First Prediction and observed outcome p < 0. 05 Direction of difference Second prediction and observed outcome Wilcoxon signed rank test Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 14
 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 15
Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 15
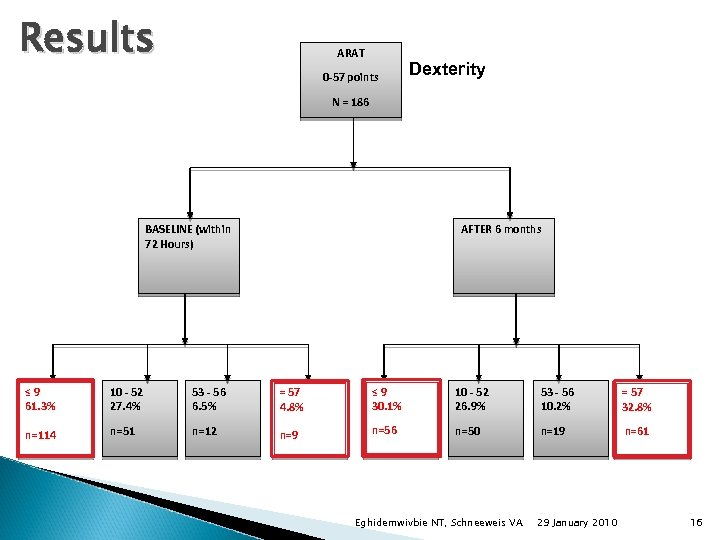 Results ARAT 0 -57 points Dexterity N = 186 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) AFTER 6 months ≤ 9 61. 3% 10 - 52 27. 4% 53 - 56 6. 5% = 57 4. 8% ≤ 9 30. 1% 10 - 52 26. 9% 53 - 56 10. 2% = 57 32. 8% n=114 n=51 n=12 n=9 n=56 n=50 n=19 n=61 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 16
Results ARAT 0 -57 points Dexterity N = 186 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) AFTER 6 months ≤ 9 61. 3% 10 - 52 27. 4% 53 - 56 6. 5% = 57 4. 8% ≤ 9 30. 1% 10 - 52 26. 9% 53 - 56 10. 2% = 57 32. 8% n=114 n=51 n=12 n=9 n=56 n=50 n=19 n=61 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 16
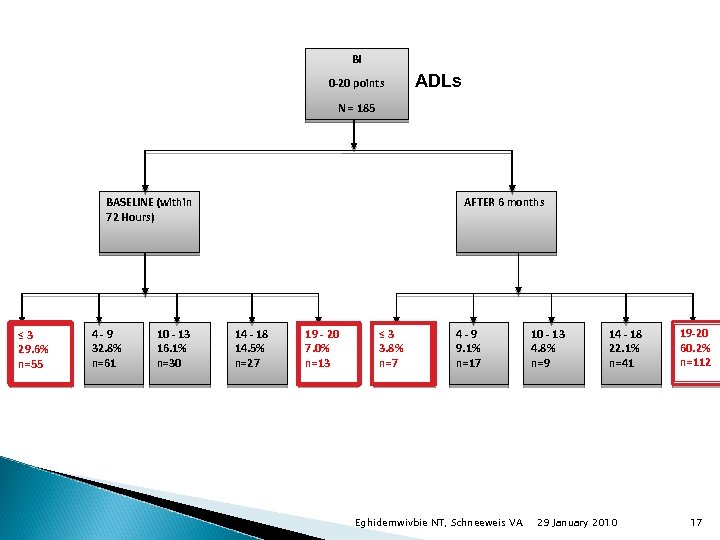 BI 0 -20 points ADLs N = 185 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) ≤ 3 29. 6% n=55 4 -9 32. 8% n=61 10 - 13 16. 1% n=30 AFTER 6 months 14 - 18 14. 5% n=27 19 -20 19 - 20 7. 0% n=13 ≤ 3 3. 8% n=7 4 -9 9. 1% n=17 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 10 - 13 4. 8% n=9 14 - 18 22. 1% n=41 29 January 2010 19 -20 60. 2% n=112 17
BI 0 -20 points ADLs N = 185 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) ≤ 3 29. 6% n=55 4 -9 32. 8% n=61 10 - 13 16. 1% n=30 AFTER 6 months 14 - 18 14. 5% n=27 19 -20 19 - 20 7. 0% n=13 ≤ 3 3. 8% n=7 4 -9 9. 1% n=17 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 10 - 13 4. 8% n=9 14 - 18 22. 1% n=41 29 January 2010 19 -20 60. 2% n=112 17
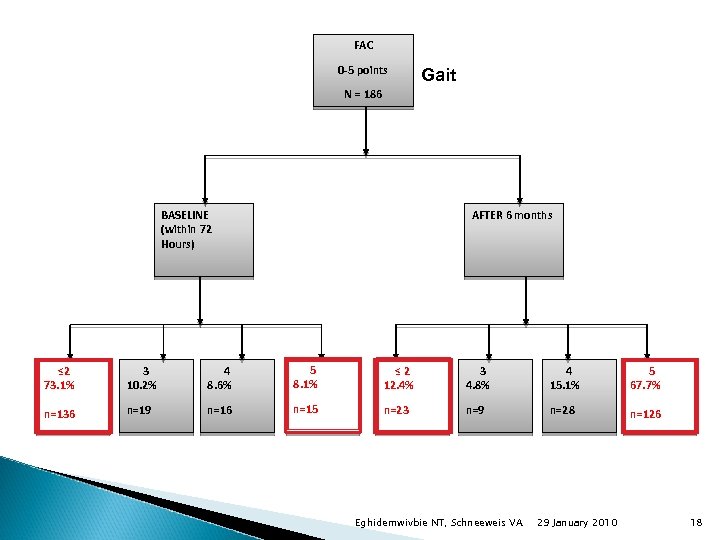 FAC 0 -5 points Gait N = 186 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) AFTER 6 months ≤ 2 73. 1% 3 10. 2% 4 8. 6% 5 8. 1% ≤ 2 12. 4% 3 4. 8% 4 15. 1% 5 67. 7% n=136 n=19 n=16 n=15 n=23 n=9 n=28 n=126 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 18
FAC 0 -5 points Gait N = 186 BASELINE (within 72 Hours) AFTER 6 months ≤ 2 73. 1% 3 10. 2% 4 8. 6% 5 8. 1% ≤ 2 12. 4% 3 4. 8% 4 15. 1% 5 67. 7% n=136 n=19 n=16 n=15 n=23 n=9 n=28 n=126 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 18
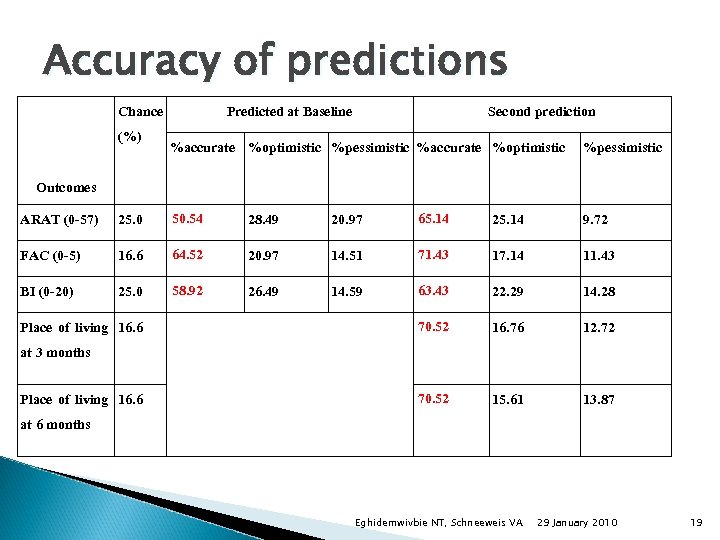 Accuracy of predictions Chance (%) Predicted at Baseline Second prediction %accurate %optimistic %pessimistic Outcomes ARAT (0 -57) 25. 0 50. 54 28. 49 20. 97 65. 14 25. 14 9. 72 FAC (0 -5) 16. 6 64. 52 20. 97 14. 51 71. 43 17. 14 11. 43 BI (0 -20) 25. 0 58. 92 26. 49 14. 59 63. 43 22. 29 14. 28 70. 52 16. 76 12. 72 70. 52 15. 61 13. 87 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 Place of living 16. 6 at 3 months Place of living 16. 6 at 6 months 19
Accuracy of predictions Chance (%) Predicted at Baseline Second prediction %accurate %optimistic %pessimistic Outcomes ARAT (0 -57) 25. 0 50. 54 28. 49 20. 97 65. 14 25. 14 9. 72 FAC (0 -5) 16. 6 64. 52 20. 97 14. 51 71. 43 17. 14 11. 43 BI (0 -20) 25. 0 58. 92 26. 49 14. 59 63. 43 22. 29 14. 28 70. 52 16. 76 12. 72 70. 52 15. 61 13. 87 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 Place of living 16. 6 at 3 months Place of living 16. 6 at 6 months 19
 Discussion Accuracy level Optimism Consequences Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 20
Discussion Accuracy level Optimism Consequences Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 20
 Take home message and conclusion Physiotherapists can early predict the functional outcome in terms of dexterity, gait, ADL as well as place of living at three and six months post stroke Prediction models Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 21
Take home message and conclusion Physiotherapists can early predict the functional outcome in terms of dexterity, gait, ADL as well as place of living at three and six months post stroke Prediction models Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 21
 Acknowledgement Prof. Dr. Gert Kwakkel and EPOS consortium Janne Veerbeek and Rinske Nijland Frank van Hartingsveld WCF-KNGF St. Jacob, Zonnehuis en Cordaan/Berkenstede in Amsterdam Laurens Antonius Binnenweg en Reumaverpleeghuis in Rotterdam Albert van Koningsbruggen in Utrecht en Wiekendaal in Roosendaal Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 22
Acknowledgement Prof. Dr. Gert Kwakkel and EPOS consortium Janne Veerbeek and Rinske Nijland Frank van Hartingsveld WCF-KNGF St. Jacob, Zonnehuis en Cordaan/Berkenstede in Amsterdam Laurens Antonius Binnenweg en Reumaverpleeghuis in Rotterdam Albert van Koningsbruggen in Utrecht en Wiekendaal in Roosendaal Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 22
 References Brauer SG, Bew PG, Kuys SS, Lynch MR and Morrison G. Prediction of discharge destination after stroke using motor assessment scale on Admission: A prospective multisite study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. ; 2008; 89: 1061 -1065. Censori B, Camerlingo M, Caso L, Ferraro B, Gazzaniga GC, Cesana B et al. Prognostic factors in first-ever stroke in the carotid artery territory seen within 6 hours after onset. Stroke; 1993; 24: 532 -5. Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke 1989; 20(10): 1407 -31. Chaiyawat P, Kulkantrakorn K, Sritipsukho P. Effectiveness of home rehabilitation for ischemic stroke. Neurology international 2009; 1(1). Collin C, Wade, DT, Davies S, Horne V. The Barthel ADL Index: A reliability study. BI Disability & Rehabilitation; 1988; 10(2): 61 -63. Department of Health and Human Services. Deaths: Final data for 2006. National Vital Statistics Report; 2009; 57(14). Dewey H, Macdonell R, Donnan G, Mc. Neil J, Freeman E, Thrift A, Sharples C. Inter-rater reliability of stroke sub-type classification by neurologists and nurses within a community-based stroke incidence study. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience; 2001; 8(1), 14– 17. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 23
References Brauer SG, Bew PG, Kuys SS, Lynch MR and Morrison G. Prediction of discharge destination after stroke using motor assessment scale on Admission: A prospective multisite study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. ; 2008; 89: 1061 -1065. Censori B, Camerlingo M, Caso L, Ferraro B, Gazzaniga GC, Cesana B et al. Prognostic factors in first-ever stroke in the carotid artery territory seen within 6 hours after onset. Stroke; 1993; 24: 532 -5. Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke 1989; 20(10): 1407 -31. Chaiyawat P, Kulkantrakorn K, Sritipsukho P. Effectiveness of home rehabilitation for ischemic stroke. Neurology international 2009; 1(1). Collin C, Wade, DT, Davies S, Horne V. The Barthel ADL Index: A reliability study. BI Disability & Rehabilitation; 1988; 10(2): 61 -63. Department of Health and Human Services. Deaths: Final data for 2006. National Vital Statistics Report; 2009; 57(14). Dewey H, Macdonell R, Donnan G, Mc. Neil J, Freeman E, Thrift A, Sharples C. Inter-rater reliability of stroke sub-type classification by neurologists and nurses within a community-based stroke incidence study. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience; 2001; 8(1), 14– 17. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 23
 References (2) Duncan PW, Goldstein LB, Matchar D, Divine GW, Feussner J: Measurement of motor recovery after stroke. Outcome assessment and sample size requirements. Stroke 1992; 23; 1084 -89. Engberg A, Bentzen L, Garde B. Rehabilitation after stroke: predictive power of Barthel Index versus a cognitive and a motor index. Acta Neurologia Scandinavica; 1995; 91: 28 – 36. Feys H, De Weer W, Nuyens G, Van de winckel A, Selz B, Kiekens C. Predicting motor recovery of the upper limb after stroke rehabilitation: value of a clinical examination. Physiotherapy research international; 2000; 5(1). Galski T, Bruno RL, Zorowitz R, Walker J. Predicting length of stay, functional outcome and aftercare in the rehabilitation of stroke patients: the dominant role of higher-order cognition. Stroke; 1993; 24; 1794 -1800. Gresham GE, Duncan PW, Statson WB. Priorities for future research. Post stroke rehabilitation. Clinical practice guideline number 16, Rockville, MD: US Dept Health and Human Services, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1995, AHCPR publication no. 95– 0662. Henley S, Pettit S, Todd-Pokropek A, Tupper A. Who goes home? Predictive factors in stroke recovery. Jornal of Neurology Neurosurvery and Psychiatry; 1985; 48: 1 -6. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 24
References (2) Duncan PW, Goldstein LB, Matchar D, Divine GW, Feussner J: Measurement of motor recovery after stroke. Outcome assessment and sample size requirements. Stroke 1992; 23; 1084 -89. Engberg A, Bentzen L, Garde B. Rehabilitation after stroke: predictive power of Barthel Index versus a cognitive and a motor index. Acta Neurologia Scandinavica; 1995; 91: 28 – 36. Feys H, De Weer W, Nuyens G, Van de winckel A, Selz B, Kiekens C. Predicting motor recovery of the upper limb after stroke rehabilitation: value of a clinical examination. Physiotherapy research international; 2000; 5(1). Galski T, Bruno RL, Zorowitz R, Walker J. Predicting length of stay, functional outcome and aftercare in the rehabilitation of stroke patients: the dominant role of higher-order cognition. Stroke; 1993; 24; 1794 -1800. Gresham GE, Duncan PW, Statson WB. Priorities for future research. Post stroke rehabilitation. Clinical practice guideline number 16, Rockville, MD: US Dept Health and Human Services, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1995, AHCPR publication no. 95– 0662. Henley S, Pettit S, Todd-Pokropek A, Tupper A. Who goes home? Predictive factors in stroke recovery. Jornal of Neurology Neurosurvery and Psychiatry; 1985; 48: 1 -6. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 24
 References (3) Holden MK, Gill KM, Magliozzi MR. Clinical gait assessment in the neurological impaired: reliability and meaningfulness. Phys Ther 1984; 64: 35– 40. Holden MK, Gill KM, Magliozzi MR. Gait assessment for neurologically impaired patients. Standards for outcome assessment. Phys Ther 1986; 66: 1530– 1539. Jørgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS. Recovery of walking function in stroke patients: the Copenhagen stroke study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76(8): 7889. Kollen B, van de Port I, Lindeman E, Twisk J, Kwakkel G. Predicting improvement in gait after stroke. A longitudinal prospective study. Stroke. 2005; 36: 2682 -6. Kwakkel, G, van Dijk GM, Wagenaar RC. Accuracy of physical and occupational therapists’ early predictions of recovery after severe middle cerebral artery stroke. Clinical Rehabilitaion. 2000; 14: 28 -41. Kwakkel G, Kollen BJ, van der Grond J, Prevo AJH. Probability of Regaining Dexterity in the Flaccid Upper Limb: Impact of Severity of Paresis and Time Since Onset in Acute Stroke. 2003; 34; 2181 -86. Lincoln NB, Blackburn M, Ellis S, Jackson J, Edmans JA, Nouri FM et al. An investigation of factors affecting progress of patients on a stroke unit. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry; 1989; 52: 493– 496. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 25
References (3) Holden MK, Gill KM, Magliozzi MR. Clinical gait assessment in the neurological impaired: reliability and meaningfulness. Phys Ther 1984; 64: 35– 40. Holden MK, Gill KM, Magliozzi MR. Gait assessment for neurologically impaired patients. Standards for outcome assessment. Phys Ther 1986; 66: 1530– 1539. Jørgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Olsen TS. Recovery of walking function in stroke patients: the Copenhagen stroke study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 76(8): 7889. Kollen B, van de Port I, Lindeman E, Twisk J, Kwakkel G. Predicting improvement in gait after stroke. A longitudinal prospective study. Stroke. 2005; 36: 2682 -6. Kwakkel, G, van Dijk GM, Wagenaar RC. Accuracy of physical and occupational therapists’ early predictions of recovery after severe middle cerebral artery stroke. Clinical Rehabilitaion. 2000; 14: 28 -41. Kwakkel G, Kollen BJ, van der Grond J, Prevo AJH. Probability of Regaining Dexterity in the Flaccid Upper Limb: Impact of Severity of Paresis and Time Since Onset in Acute Stroke. 2003; 34; 2181 -86. Lincoln NB, Blackburn M, Ellis S, Jackson J, Edmans JA, Nouri FM et al. An investigation of factors affecting progress of patients on a stroke unit. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry; 1989; 52: 493– 496. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 25
 References (4) Loewen SC, Anderson BA. Predictors of stroke outcome using objective measurement scales. Stroke; 1990; 21: 78 -81. Lai S, Duncan PW, Keighley J. Prediction of functional outcome after stroke: comparison of the Orpington prognostic scale and NIH stroke scale. Stroke. 1998; 29: 1838 -42. Lyle RC. A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research. Int J Rehabil Res 1981; 4: 483– 92. Olai, L, Omne-Pontén M, Borgquist, L, Svärdsudd K. Prognosis assessment in stroke patients at discharge from hospital. Age and Ageing. 2006. Parker VM, Wade DT, Langton Hewer R. Loss of arm function after stroke: measurement, frequency, and recovery. International Rehabilitation Medicine. 1986; 8: 69– 73. Schiemanck SV, Kwakkel G, Post MWM, Kappelle J, Prevo AJH. Prediction long-term independency in activities of daily living after middle cerebral artery stroke: does information from MRI have added predictive value compared with clinical information? Stroke; 2006; 37; 1050 -4. Tennant A, Geddes JML, Fear J, Hillman M, Chamberlain MA. Outcome following stroke. Disability and Rehabilitation 1997; 19: 278– 284. Thornton H, Jackson D, Turner-stokes L. Accuracy of prediction of walking for young stroke patients by use of FIM. Physiotherapy research international; 2001; 6(1): 1 -14. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 26
References (4) Loewen SC, Anderson BA. Predictors of stroke outcome using objective measurement scales. Stroke; 1990; 21: 78 -81. Lai S, Duncan PW, Keighley J. Prediction of functional outcome after stroke: comparison of the Orpington prognostic scale and NIH stroke scale. Stroke. 1998; 29: 1838 -42. Lyle RC. A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research. Int J Rehabil Res 1981; 4: 483– 92. Olai, L, Omne-Pontén M, Borgquist, L, Svärdsudd K. Prognosis assessment in stroke patients at discharge from hospital. Age and Ageing. 2006. Parker VM, Wade DT, Langton Hewer R. Loss of arm function after stroke: measurement, frequency, and recovery. International Rehabilitation Medicine. 1986; 8: 69– 73. Schiemanck SV, Kwakkel G, Post MWM, Kappelle J, Prevo AJH. Prediction long-term independency in activities of daily living after middle cerebral artery stroke: does information from MRI have added predictive value compared with clinical information? Stroke; 2006; 37; 1050 -4. Tennant A, Geddes JML, Fear J, Hillman M, Chamberlain MA. Outcome following stroke. Disability and Rehabilitation 1997; 19: 278– 284. Thornton H, Jackson D, Turner-stokes L. Accuracy of prediction of walking for young stroke patients by use of FIM. Physiotherapy research international; 2001; 6(1): 1 -14. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 26
 References (5) Van Peppen RPS, Hendriksa HJM, Van Meeteren NLU, Helders PJM and Kwakkel G. The development of a clinical practice stroke guideline for physiotherapists in The Netherlands: A systematic review of available evidence. Disability and Rehabilitation; 2007; 29(10): 767 -73. Wade DT, Langton Hewer R, Wood VA, Skilbeck CE, Ismail HM. The hemiplegic arm after stroke: measurement and recovery. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1983 a; 46: 521– 524. Wade DT, Skilbeck CE, Langton Hewer R. Predicting Barthel ADL Score at 6 months after an acute stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1983 b; 64: 24– 28 Wade DT, Collin C. The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int Disabil Stud 1988; 10: 64– 67. WHO. Recommendations on stroke prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Report of the WHO Task Force on Stroke and other Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke 1989; 20(10): 1407 -31. Wolframalpha. Cerebrovascular disease. Computational Knowledge Engine. 2009. Zhu HF, Newcommon NN, Cooper, ME, Green TL, Seal B, Klein G, Weir NU, Coutts SB, Watson T, Barber PA, Demchuk, AM, Hill MD. Impact of a Stroke Unit on Length of Hospital Stay and In-Hospital Case Fatality. Stroke 2009; 40(1): 18 -23. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 27
References (5) Van Peppen RPS, Hendriksa HJM, Van Meeteren NLU, Helders PJM and Kwakkel G. The development of a clinical practice stroke guideline for physiotherapists in The Netherlands: A systematic review of available evidence. Disability and Rehabilitation; 2007; 29(10): 767 -73. Wade DT, Langton Hewer R, Wood VA, Skilbeck CE, Ismail HM. The hemiplegic arm after stroke: measurement and recovery. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1983 a; 46: 521– 524. Wade DT, Skilbeck CE, Langton Hewer R. Predicting Barthel ADL Score at 6 months after an acute stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1983 b; 64: 24– 28 Wade DT, Collin C. The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int Disabil Stud 1988; 10: 64– 67. WHO. Recommendations on stroke prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. Report of the WHO Task Force on Stroke and other Cerebrovascular Disorders. Stroke 1989; 20(10): 1407 -31. Wolframalpha. Cerebrovascular disease. Computational Knowledge Engine. 2009. Zhu HF, Newcommon NN, Cooper, ME, Green TL, Seal B, Klein G, Weir NU, Coutts SB, Watson T, Barber PA, Demchuk, AM, Hill MD. Impact of a Stroke Unit on Length of Hospital Stay and In-Hospital Case Fatality. Stroke 2009; 40(1): 18 -23. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 27
 Limitations of the study Homogenous group Therapy received 11 patients were discharged within 72 hours did not have a second prediction Variety of clinimetrics normal setting Physiotherapists‘ characteristics Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 28
Limitations of the study Homogenous group Therapy received 11 patients were discharged within 72 hours did not have a second prediction Variety of clinimetrics normal setting Physiotherapists‘ characteristics Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 28
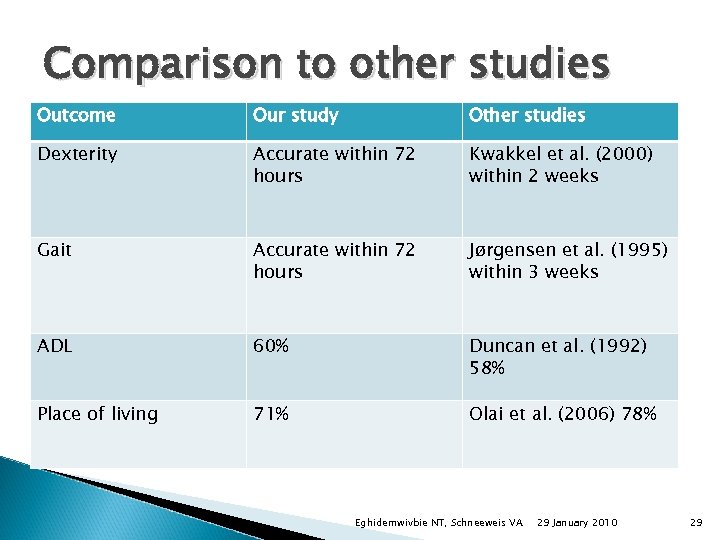 Comparison to other studies Outcome Our study Other studies Dexterity Accurate within 72 hours Kwakkel et al. (2000) within 2 weeks Gait Accurate within 72 hours Jørgensen et al. (1995) within 3 weeks ADL 60% Duncan et al. (1992) 58% Place of living 71% Olai et al. (2006) 78% Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 29
Comparison to other studies Outcome Our study Other studies Dexterity Accurate within 72 hours Kwakkel et al. (2000) within 2 weeks Gait Accurate within 72 hours Jørgensen et al. (1995) within 3 weeks ADL 60% Duncan et al. (1992) 58% Place of living 71% Olai et al. (2006) 78% Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 29
 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Clinical first-ever stroke in the anterior (carotid) territory Above 18 years of age A hemiparesis within the first 72 hours Able to follow instructions (either verbally or non-verbally) Pre-existent not limited in performing basic ADLs (Barthel Index >18) Informed consent. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 30
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Clinical first-ever stroke in the anterior (carotid) territory Above 18 years of age A hemiparesis within the first 72 hours Able to follow instructions (either verbally or non-verbally) Pre-existent not limited in performing basic ADLs (Barthel Index >18) Informed consent. Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 30
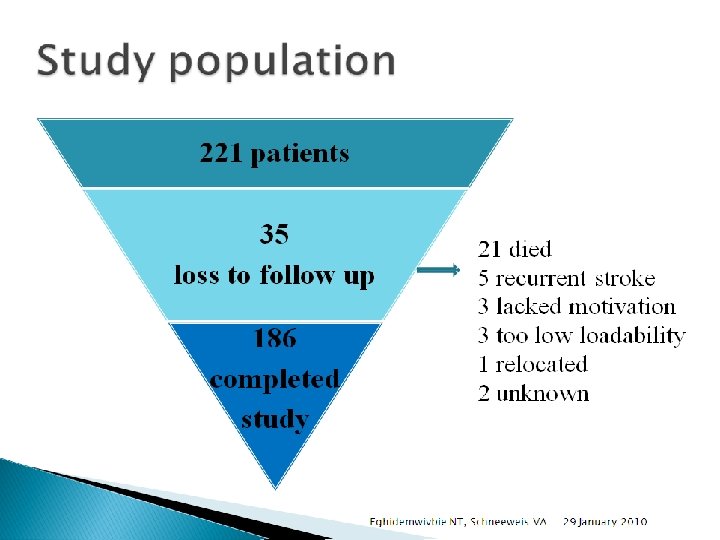
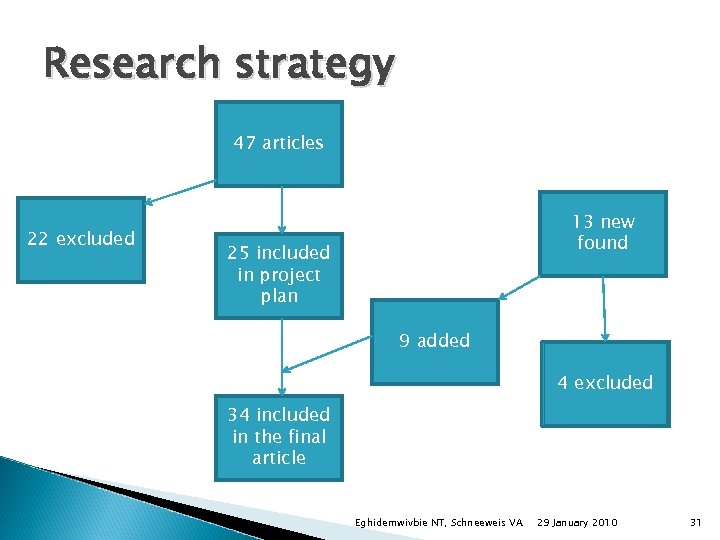 Research strategy 47 articles 22 excluded 13 new found 25 included in project plan 9 added 4 excluded 34 included in the final article Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 31
Research strategy 47 articles 22 excluded 13 new found 25 included in project plan 9 added 4 excluded 34 included in the final article Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 31
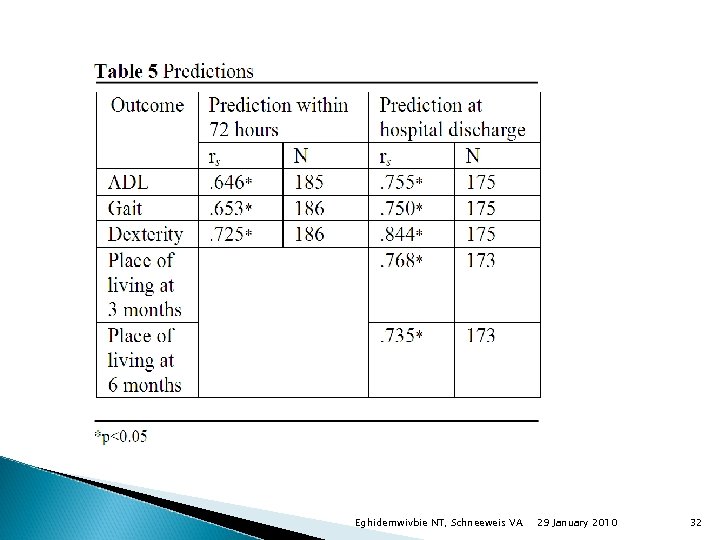 Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 32
Eghidemwivbie NT, Schneeweis VA 29 January 2010 32


