1aecd1e5c3fdb29e9cc03c43a60ee7c8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

Campus Induction Coordinator: Roles and Responsibilities Preparing for the 2015 -16 School Year Vanessa Nieto-Gomez vnietogo@houstonisd. org Jean Duffey jduffey@teacher-mentors. com HISD Mentoring Program “Its all about student achievement. ”

Morning Agenda • • • Introductions and Norms Problem-Solving Practice Elements of Induction The CIC Program Overview CIC Roles and Responsibilities Mentor Activity System (MAS)

Learning Objectives • Participants will: • be aware of the kinds of problems a CIC may have to solve and know possible approaches to solutions. • know the necessary elements of a successful induction program. • understand the concept of the CIC program. • understand accept the responsibilities of a CIC. • be proficient in the use of MAS.

Norms • • • Active Listening Appropriate use of electronics Equity of voice Respect for all perspectives Confidentiality

Problem Solving Practice As a CIC, you will sometimes have to be a problem-solver. Perhaps, the most difficult problems involve people who are not fulfilling their responsibilities, so you will explore some scenarios and brainstorm possible solutions. Your table will be assigned a scenario to read for the discussion of possible approaches to address the problem. First, however, we will demonstrate a process in finding the best approach for a particular situation.

Problem-Solving Brainstorming Demonstration A BT comes to you and tells you that her mentor, Jim, is not meeting with her regularly. When they do meet, Jim is preoccupied, and he has never followed through with supporting her. You know that Jim is a wonderful teacher and has previously been a highly rated mentor. With some inquiry, you learn that Jim is going through a very bitter divorce, and his personal life is a wreck. When you talk with him, he tells you how he’s struggling and how badly he needs the mentor stipend.

Possible Approaches • Hold off going to principal • Check MAS • Have an inquiry discussion with Jim then • Work with Jim - He must make amends with his BT - He must catch up and then stay on track - You must monitor attentively or • Go to the principal and have Jim replaced - Maintain rapport with Jim - Monitor the new relationship

Problem-Solving Scenario #1 It’s the end of September, and you are in the process of visiting BTs and mentors individually. You talked with a mentor first, who tells you everything is going well and that everything with her BT is on track. However, when visiting with the BT, he says that he has never had more than a 5 -minute conversation with his mentor since they met in August. Your principal proudly chose this mentor because she is an award-winning teacher and serves on several prestigious district committees.

Problem-Solving Scenario #2 A first-time mentor comes to you in October and tells you that she has not been able to establish a rapport with her BT. They meet every week and engage in fairly productive CAL conversations, and each follow up with their obligations. They see each other during team and department meetings, but the BT declines invitations to sit with the mentor and then sits by herself. The mentor knows that the BT would likely not come to her with a problem, either professional or personal. The mentor is discouraged.

Problem-Solving Scenario #3 A mentor becomes aware of his BT’s questionable behavior with 4 eighth-grade basketball players. They are often in her room after practice, when most teachers have longgone home. He learns that she frequently asks for those students during homeroom. He talks with her and she admits that she doesn’t tutor them, they just “hang out. ” She is defensive when he explains that this behavior is questionable. After an early dismissal, she invites the boys across the street to a Deli where she is having lunch with some teacher friends. Those teachers complain to the mentor, who asks your advice.

Importance of Induction • The cost to recruit, hire, prepare, and then lose a teacher is upwards of $50, 000. • A revolving door of inexperienced teachers put students significantly behind in math and English. • A student who has 3 first-year teachers in elementary school is 50% less likely to graduate from high school. • High turnover erodes the pool of mentors and veteran role models, which erodes student success • Attrition is getting worse. The average years of experience for a teacher has shrunk from 15 years to 5 years since 2008. • An effective induction program combats those statistics.
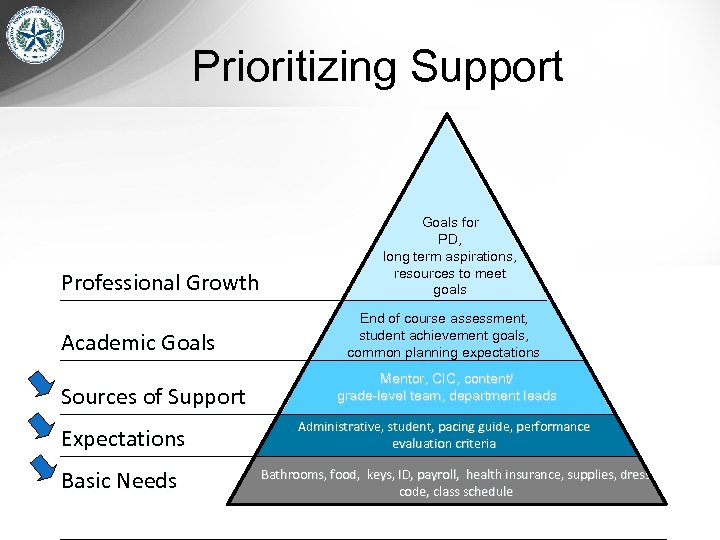
Prioritizing Support Professional Growth Academic Goals Sources of Support Expectations Basic Needs Goals for PD, long term aspirations, resources to meet goals End of course assessment, student achievement goals, common planning expectations Mentor, CIC, content/ grade-level team, department leads Administrative, student, pacing guide, performance evaluation criteria Bathrooms, food, keys, ID, payroll, health insurance, supplies, dress code, class schedule

Basic Needs • Where can teachers find what they need (materials, resources, copies, etc. )? • Where are the important locations in the building (cafeteria, gym, office, teacher boxes)? • How can I get tech support? • What are my schedules (bell, lunch, testing, grading periods)? • What is my class roster?

Expectations • • • What are my principal’s expectations? What is my school’s vision? How often will I be observed and by whom? What will be looked at when I am observed? What are the policies/procedures for student conduct? • What are ELL, SPED, and GT policies/ procedures?

Sources of Support • To whom should I talk if I have instructional challenges? • With whom will I work in my content/ grade-level team? • Is there an opportunity to meet those who provide support services to the students? • When will I meet my mentor? This question shouldn’t have to be asked. BTs should expect to be assigned a mentor within a few days of being hired. It will be up to you to develop a system on your campus for learning when BTs are hired and for getting a mentor assigned immediately. A suggested process is outlined in CIC Document #3.

Where are you in this picture?
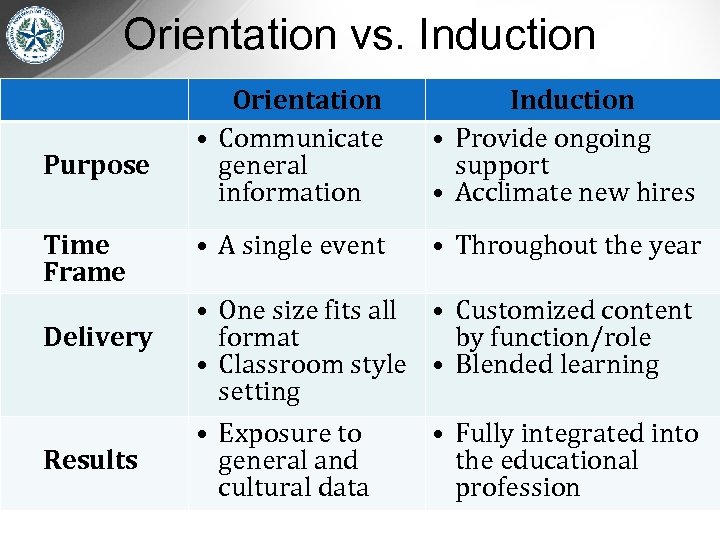
Orientation vs. Induction Purpose Time Frame Delivery Results Orientation • Communicate general information Induction • Provide ongoing support • Acclimate new hires • A single event • Throughout the year • One size fits all • Customized content format by function/role • Classroom style • Blended learning setting • Exposure to • Fully integrated into general and the educational cultural data profession

Excellent Induction Program Must have: 1. Differentiated support for new teachers 2. Orientation 3. Culture of trust (district initiative) 4. CIC Plan 5. Training/support for teacher leaders

1. Differentiated Support • • • The following are supported by mentors who determine BTs’ individual needs in order to accelerate their professional growth: Beginning teachers in ACP* Beginning teachers who are certified Experienced international recruits *ACP and SBEC include MAS data for certification determination. The following are supported by buddies (not a stipend assignment) by providing procedural information: Experienced teachers new to the district Experienced HISD teachers new to your campus

2. Orientation for all teachers new to campus http: //houstonisdpsd. org Objectives are to: • assure that new teachers feel welcome and supported (have their mentor, buddy, or a stand-in to attend orientation with them). • provide priority information to new teachers according to the above “Prioritizing Support” pyramid. • give a tour of the campus and know who some of the key people are. You are not responsible for naming buddies for experienced teachers, but you are responsible for sending invitation emails to new teachers, mentors, and buddies. A suggested email to buddies and an orientation checklist is included on the website above for preparing the New Teacher Orientation.

3. Culture of Trust BTs should feel that they are: • Welcome • Supported • Safe to share concerns • Set up for success and not given: - a stripped-down classroom, or worse, a floating assignment - multi-preps - unnecessary extra duties - a disproportionate number of difficult students/classes

4. CIC Plan To be successful, you must: • Be committed to your program • Get mentors named ASAP • Get buy-in from your principal - Make sure he/she knows what you do - Make sure he/she knows your successes • Incorporate district requisites • Monitor BT/mentor relationships • Monitor MAS

5. Training/Support for Teacher Leaders • CICs - District training by district coordinators - One-on-one contact with district coordinators • Mentors - District training by district coordinators - Campus forums by CICs - MAS monitoring • Buddies - Emails - Option to attend campus forums
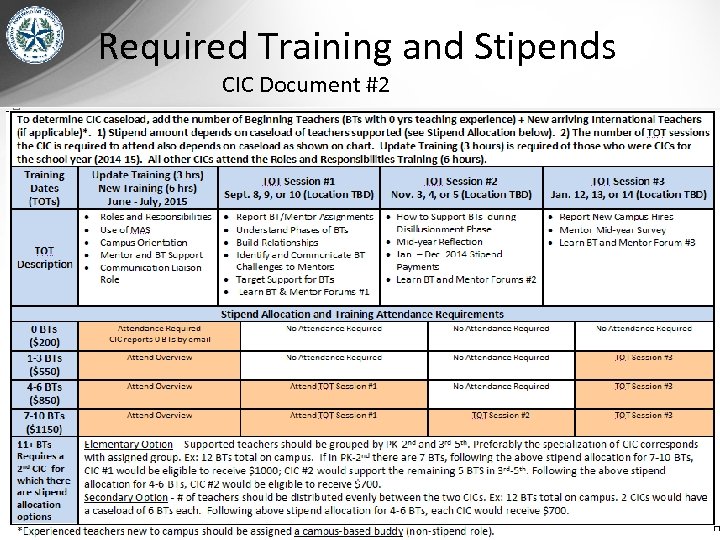
Required Training and Stipends CIC Document #2
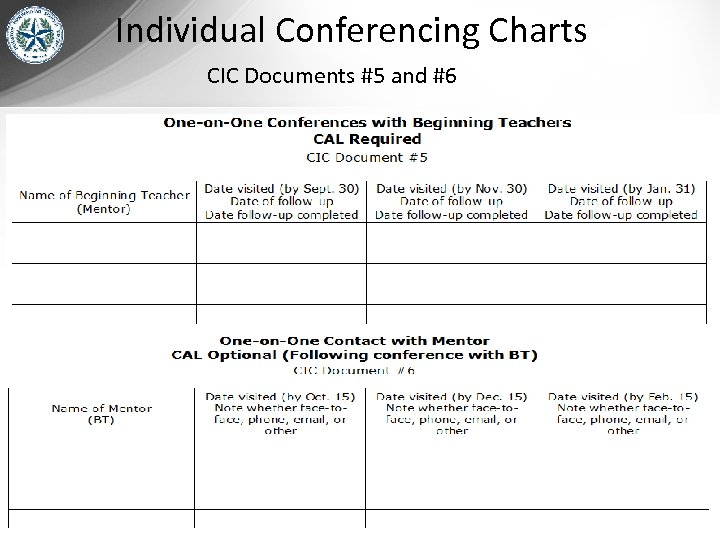
Individual Conferencing Charts CIC Documents #5 and #6

The CIC Model • Is campus based • Is not administration • Provides support for mentors through: - One-on-one conferencing - Campus forums - MAS monitoring • Provides support for BTs through: - One-on-one conferencing - Campus forums - MAS monitoring • Is a campus administration liaison • Promotes an improved campus culture • Advocates for the mentoring program

Mentor Activity System (MAS)

Afternoon Agenda • • • Introductions and Norms Review of BT Induction Chronological Order of Responsibilities Mentor Activity System (MAS) ICF Stances Considering Developmental Phases of the BT • Parting Thoughts

Learning Objectives Participants will: • recall the necessary elements of a successful induction program. • have an easy-to-follow chronological order of CIC responsibilities. • know changes in MAS and review the use of MAS. • appreciate the significance of the phases of BTs’ development when choosing an ICF stance. • begin now to think ahead to the next school year.
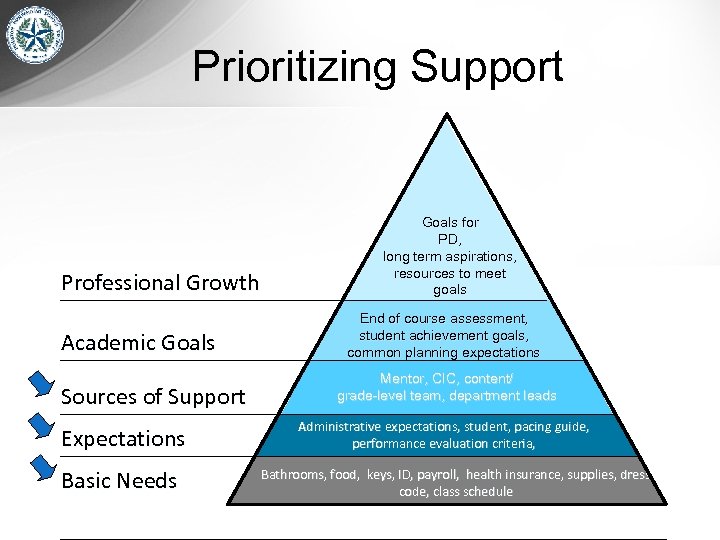
Prioritizing Support Professional Growth Academic Goals Sources of Support Expectations Basic Needs Goals for PD, long term aspirations, resources to meet goals End of course assessment, student achievement goals, common planning expectations Mentor, CIC, content/ grade-level team, department leads Administrative expectations, student, pacing guide, performance evaluation criteria, Bathrooms, food, keys, ID, payroll, health insurance, supplies, dress code, class schedule
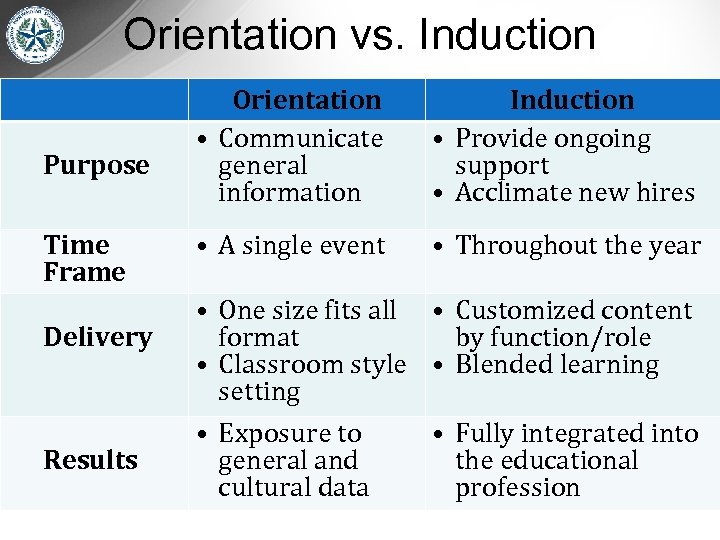
Orientation vs. Induction Purpose Time Frame Delivery Results Orientation • Communicate general information Induction • Provide ongoing support • Acclimate new hires • A single event • Throughout the year • One size fits all • Customized content format by function/role • Classroom style • Blended learning setting • Exposure to • Fully integrated into general and the educational cultural data profession

Start CICing Immediately • • Build relationships Get all mentors/buddies assigned ASAP Enter mentor/BT relationships into MAS Have mentors/buddies contact their new teachers as soon as assigned • Prepare to host the New Teacher Orientation • Schedule conference and forums • All CIC documents can be accessed by logging on to http: //houstonisdpsd. org. Follow this pathway: Click on PD Departments >Click on CICs>Scroll down to bottom of page>Click Documents Tab.
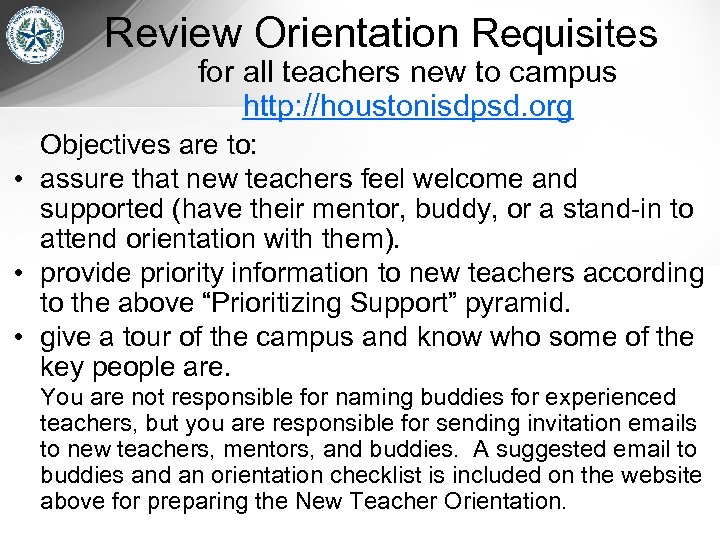
Review Orientation Requisites for all teachers new to campus http: //houstonisdpsd. org Objectives are to: • assure that new teachers feel welcome and supported (have their mentor, buddy, or a stand-in to attend orientation with them). • provide priority information to new teachers according to the above “Prioritizing Support” pyramid. • give a tour of the campus and know who some of the key people are. You are not responsible for naming buddies for experienced teachers, but you are responsible for sending invitation emails to new teachers, mentors, and buddies. A suggested email to buddies and an orientation checklist is included on the website above for preparing the New Teacher Orientation.

Chronological Order of Responsibilities CIC Document #1

Mentor Activity System (MAS)
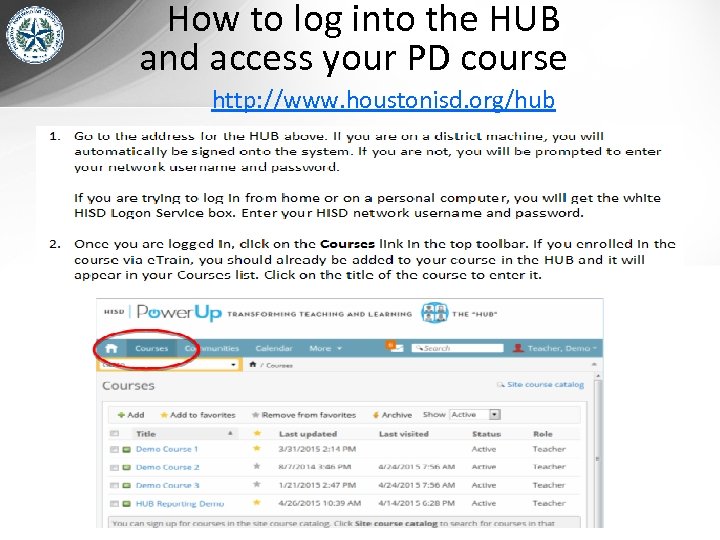
How to log into the HUB and access your PD course http: //www. houstonisd. org/hub
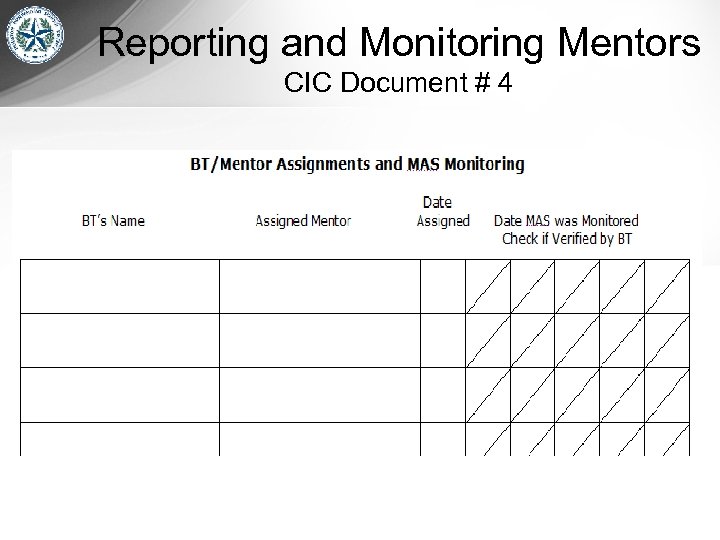
Reporting and Monitoring Mentors CIC Document # 4

Review of ICF Stances Considering BT’s Phases of Development • Review the graphics on the next two slides. • With your table mates, take turns reading each statement on the following slides and discuss which stance to take considering the designated phase of the BT. • Consider how the average BT is probably feeling during the designated phase and to which ICF stance they will likely be most receptive. • Discuss if it would be wise to urge the BT to take a more active position.
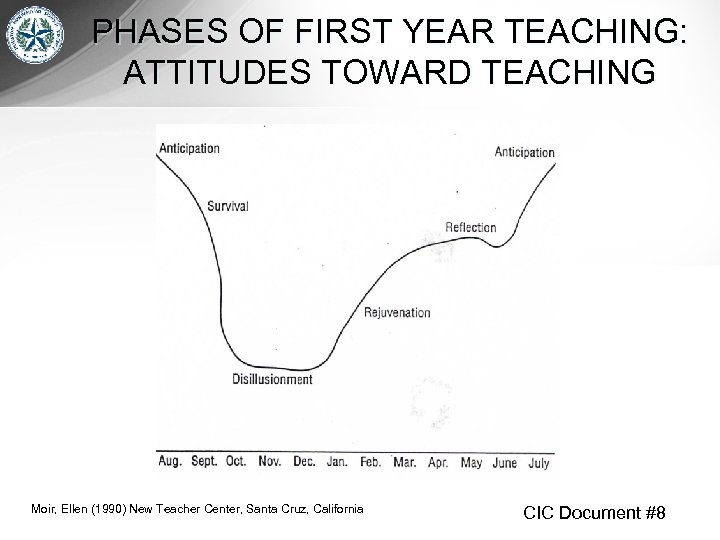
PHASES OF FIRST YEAR TEACHING: ATTITUDES TOWARD TEACHING Moir, Ellen (1990) New Teacher Center, Santa Cruz, California CIC Document #8
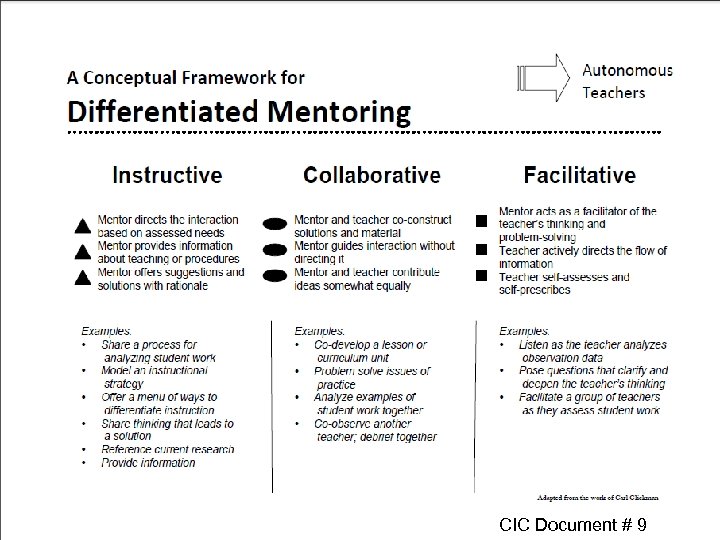
CIC Document # 9

I, C, or F during First Anticipation? • The mentor assists with arranging the BT’s classroom. • The mentor demonstrates a classroom procedure. • The mentor conferences with the BT about setting professional goals.

I, C, or F during Survival? • The mentor and BT co-teach a lesson. • The mentor demonstrates a classroom procedure. • The mentor and BT role-play a parent conference.

I, C, or F during Disillusionment? • The mentor demonstrates an effective strategy for engaging students. • The mentor arranges for the BT to observe another teacher. • The mentor shares a lesson plan with the BT.

I, C, or F during Rejuvenation? • The mentor shares a lesson plan with the BT. • The mentor suggests options for the BT to address challenging student behavior. • The mentor gives the BT objective data collected during a walk-through.

I, C, or F during Reflection? • The mentor conferences with the BT about professional goals. • The mentor videos the BT teaching and asks the BT to reflect on her presentation. • The mentor listens to the BT as he analyzes examples of student work.

Start CICing Immediately • • Build relationships Get all mentors/buddies assigned ASAP Enter mentor/BT relationships into MAS Have mentors/buddies contact their new teachers as soon as assigned • Prepare to host the New Teacher Orientation • Schedule conference and forums • All CIC documents can be accessed by logging on to http: //houstonisdpsd. org. Follow this pathway: Click on PD Departments >Click on CICs>Scroll down to bottom of page>Click Documents Tab.

The Importance of Attitude How can you see each negative below as a positive for you? • Low performing campus • Inexperienced mentors • High teacher turn-over rate • Campus administration doesn’t know what to expect from the CIC program

Assurances to Stakeholders • BTs must know that they can talk with you in absolute confidence and that they are your most important concern. • Mentors must know that you want them to be successful. • Administrators must know that you will do all you can to support campus goals and district initiatives. • Mentor coordinators must know that you are developing a positive campus culture and monitoring successful BT/mentor relationships.

Complete the CAL Evaluation • What’s working? – What are the positives about today’s training? • What are your concerns/challenges/focuses? – What about today’s information concerns you? What challenges do you anticipate facing? • What are your next steps? – What are your takeaways from today’s training? • What can the program directors do to help you? – What can Vanessa and Jean do to improve the training, the program, and/or how you are supported?

Thank you for being a leader! Coming together is a beginning, staying together is progress, and working together is success. -Henry Ford
1aecd1e5c3fdb29e9cc03c43a60ee7c8.ppt