
Camel breeding

Vocabulary • • • Colt – верблюжонок Hump – горб felted pouches – войлочные сумки to bear or carry - нести или носить Adult – взрослый Spotted – пятнистый scarce – дефицитный nomad tribes – кочевые племена an available – доступный Heel – пятка Saddle - седло

• A camel is an even-toed ungulate within the genus Camelus, bearing distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. The two surviving species of camel are the dromedary, or one-humped camel (dromedarius), which inhabits the Middle East and the Horn of Africa; and the bactrian, or two-humped camel (bactrianus), which inhabits Central Asia. Both species have been domesticated; they provide milk, meat, hair for textiles or goods such as felted pouches, and are working animals. • The term "camel" is derived via Latin and Greek (camelus and kamēlos respectively) from Hebrew or Phoenician gāmāl, which has later been transferred to a verb root meaning to bear or carry (in Arabic jamala). The are two true camels: the dromedary and bactrian, and the four South American camelids: the llama and alpaca are called "New World camels", while the guanaco and vicuña are called "South American camels".

Complete the sentences with the words: camel, can, average life, weigh The …expectancy of a camel is 40 to 50 years. A full-grown adult …. stands 1. 85 m at the shoulder and 2. 15 m at the hump. Camels … run at up to 65 km/h in short bursts and sustain speeds of up to 40 km/h. Bactrian camels … 300 to 1, 000 kg and dromedaries 300 to 600 kg.
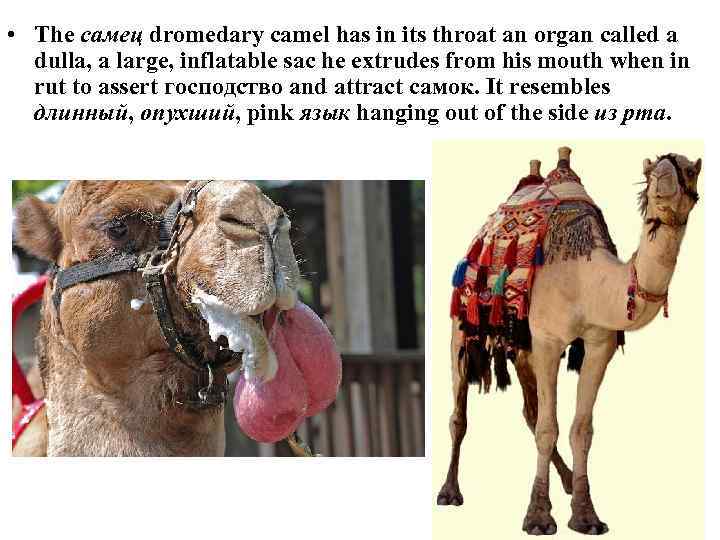
• The самец dromedary camel has in its throat an organ called a dulla, a large, inflatable sac he extrudes from his mouth when in rut to assert господство and attract самок. It resembles длинный, опухший, pink язык hanging out of the side из рта.

Wild Bactrian Camel camelus bactrianus ferus They are listed as critically endangered with approximately 600 surviving in China and 300 in Mongolia. Studies suggest a significant DNA difference. Compared to domestic camels, wild camels have smaller humps, smaller feet, shorter hair and a more slender body shape.

Dromedary Camelus Dromedarius Are from the Middle East and North Africa. Single hump. Head and body length: 9. 6 -11 feet. Shoulder height: 5. 8 -7. 5 feet. Weight: 700 -1500 pounds. Their color ranges from white, brown, tan, red, black and spotted. With their longer legs they can easly out run the Bactrian camel. Bactrian Camelus Bactrianus These are Asian camels, which come form the deserts of China and Mongolia. They have two-humps, shorter-legges, are usually a beige color with hair that ranges from short to long depending on the season. Head and body length: 10 -12 feet. Shoulder height: 6 -7. 6 feet. Weight: 1300 -2100 pounds. Height of humps: up to 9 feet.

F 1 Camel Is the result of cross breeding of Dromedary and Bactrian camel. This method of mating is prevalent in Afghanistan, Iran, Russia, and Turkey. Crossbreeding generally produces a bigger and heavier offspring than either parent. For example; they get up to 7. 6 feet shoulder height and 2000 to 2200 lb. That is why they are often used as draft animals for carrying loads and plowing. They are easier to work, more patient and tolerant. Furthermore, these hybrid camels mature faster than the Dromedary and Bactrian camels. . . In Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan they are called; Tulu, Majen, Iver and Bertuar. In Iran the males are called Boghor and the females are called Hachamaia.

Make the right sentences F 2 Bactrian Camel F 2 Dromedary Camel what is called an F 2 Bactrian. , what is called an F 2 Dromedary. between a Bactrian, The cross breeding, hybrid breeding, and a F 1 hybrid produces, between a Dromedary produces, This produces, bred and a F 1, This three-quarter, riding, most Bactrians, faster seldom done these days. and than, a three-quarter, camel stronger Dromedary type, mix that is, than most Dromedary. produces a larger, but this is, and stronger, These, hybrids are found, mostly in Kazakhstan.

Baby Dromedary Camel This is Gabriel, he is a two week old dromedary baby. Often camels are born white and will turn brown as they are growing up. The way you can tell if they will turn brown is that their nose and toes are not pure white. At birth a baby camel will weight only about 90 pounds and it can take a few hours before they are able to stand up. Snow-white Baby Dromedary This one has a pure white nose and toes and will stay pure white as he grows up. White camels are becoming a lot more common these days, with their beauty it's not surprising. In foreign countries white camels are a lot more common than in the U. S. A.

Purebred Bactrian bull calf As you can see even as babies, bactrain camels have shorter legs and a heavier built body than Dromedaries camels. Baby male camels are called bull calves. It's not hard to fall in love with such a little beauty like this sweet guy. White Bactrian Babies Just take a look at these beautiful white Bactrian baby camels. You can see two of the babies front humps have not yet come up. White Bactrian camels are even more scarce than white Dromedary camels, and these white baby camels will bring a high price.

F 2 Bactrian Hybrid baby • Female baby camels are called Multicolor Camels heifers. At only 4 weeks old her Here we have three very adorable humps have not yet come up. Dromedary baby paint camels. As Hybrids mature more rapidly you can see camels do come in all than other breeds. Baby camels colors, including spotted. These can grow in height at close to an three spotted Dromedary camels inch a week are beautiful !!!

There around 14 million camels alive as of 2010, with 90% being dromedaries. Dromedaries alive today are domesticated animals (mostly living in the Horn of Africa, the Sahel, Maghreb, Middle East and South Asia). They provide nomadic people in Somalia (which has the largest camel herd in the world) and Ethiopia with milk, food, and transportation.
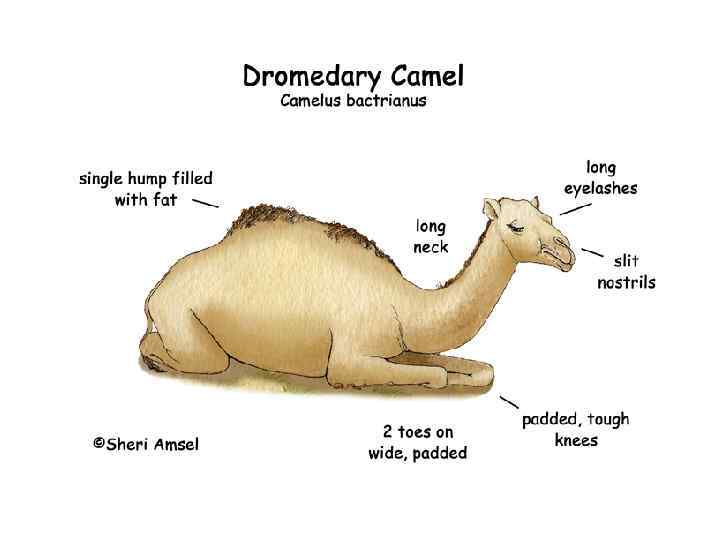
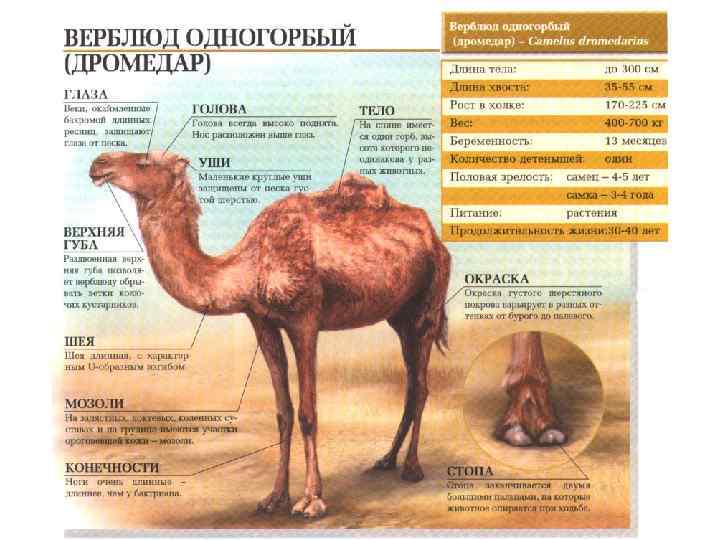

Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. Unlike other mammals, their red blood cells are oval rather than circular in shape. This facilitates the flow of red blood cells during dehydration and makes them better at withstanding high osmotic variation without rupturing when drinking large amounts of water: a 600 kg camel can drink 200 L of water in three minutes.

• Camel milk is a staple food of desert nomad tribes and is sometimes considered a meal in and of itself; a nomad can live on only camel milk for almost a month. Camel milk is rich in vitamins, minerals, proteins, and immunoglobulins; compared to cow's milk, it is lower in fat and lactose, and higher in potassium, iron, and vitamin C. Camel milk can readily be made into a drinkable yogurt, as well as butter or cheese, though the yields for cheese tend to be low. • Camel milk has been made into ice cream in a Netherlands camel farm.

• A camel carcass can provide a substantial amount of meat. The brisket, ribs and loin are among the preferred parts, and the hump is considered a delicacy. The hump contains "white and sickly fat", which can be used to make the khli (preserved meat) of mutton, beef, or camel. • Camel meat has been eaten for centuries. It has been recorded by ancient Greek writers as an available dish at banquets in ancient Persia, usually roasted whole. The ancient Roman emperor Heliogabalus enjoyed camel's heel. Camel meat is still eaten in certain regions, including Eritrea, Somalia, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Syria, Libya, Sudan, Ethiopia, Kazakhstan, and other arid regions.

Dromedary Camel • Location and Habitat Like horses, the majority of Dromedary Camels have been domesticated for their many uses. They thrive in arid climates, and are found in the Arabian Peninsula and other parts of the Middle East, the Sahara Desert, and parts of India. A wild population has also been introduced to Australia. • Diet Dromedary camels are opportunistic herbivores that will eat virtually any vegetation that can be found in the desert. This wide range of food allows them to eat plants that other animals will not eat, including thorny plants. • Size and Description Dromedary Camels range from about 1000 pounds to 1500 pounds, making them approximately the same size as large horses. They measure 6 - 6. 5 feet at shoulder height, and can approach 10 feet in height at its hump. One of the most notable features of the Dromedary Camel is its single hump. Its close relative, the Bactrian Camel, has two humps. The hump is used to store fatty tissue, which the camel uses as a food and water source when food and water are not available. The neck of a camel is long and curved. The eyelids of a camel are heavily lashed to help protect its eyes from blowing sand in the desert. Camels have thick lips to aid them in eating thorny plants. Camels have large bodies and woolly coats. The hair of the Dromedary Camel is generally shorter than that of Bactrian Camels. • Reproduction The pregnancy period of a female Dromedary camel is approximately 12 - 13 months. They will most often have one calf but can have two or more.

Various camel saddles Here are three styles of camel riding saddles showing some of the different ways they are made. The on the left has fold up legs, the center one is a very common type and the right one is a Bedouin type. These types of saddles do not fit the larger camels found in Australia or America.

Dromedary Saddle

Thank you for your attention!