3c32f90605913cf58afad32e0825bc1c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

California Integrated Waste Management Board The Compost Solution Workshop Compost Use on California Highways February 28, 2007 Brian Larimore www. ciwmb. ca. gov
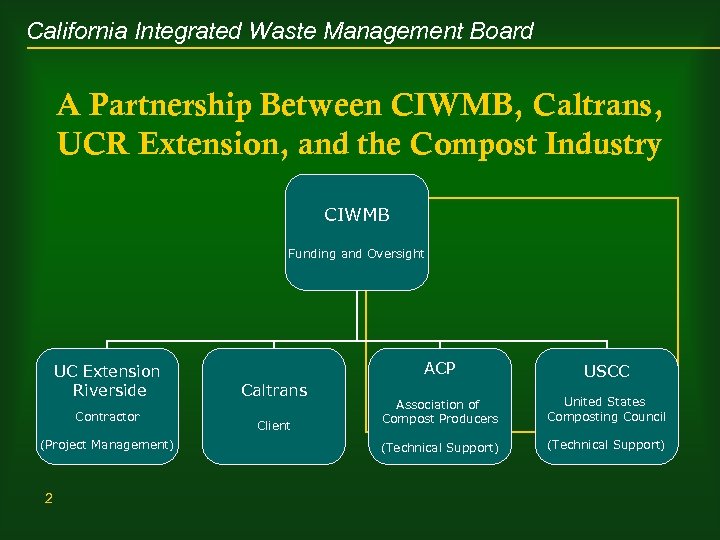
California Integrated Waste Management Board A Partnership Between CIWMB, Caltrans, UCR Extension, and the Compost Industry CIWMB Funding and Oversight UC Extension Riverside Contractor (Project Management) 2 ACP Caltrans Client USCC Association of Compost Producers United States Composting Council (Technical Support)
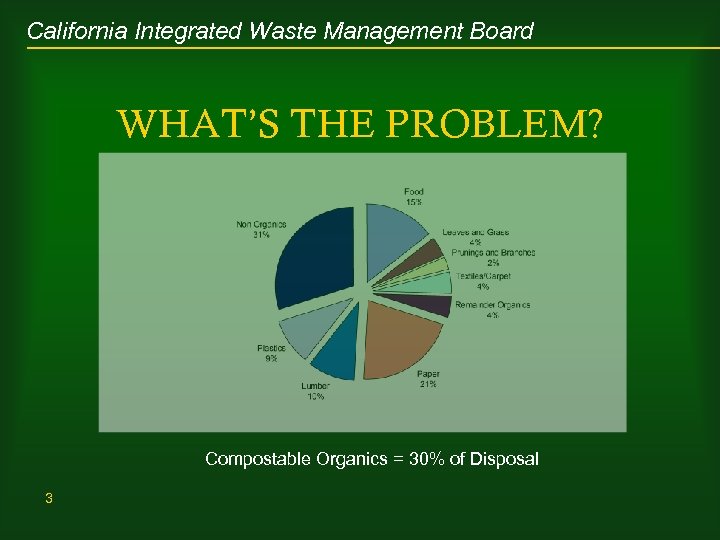
California Integrated Waste Management Board WHAT’S THE PROBLEM? Compostable Organics = 30% of Disposal 3

California Integrated Waste Management Board FUTURE ORGANICS FLOWS? ® Rice straw and other agricultural residuals from burning phase-outs ® Waste from logging, wood processing (e. g. sudden oak death and So. Cal. Bark Beetle issue) ® Biosolids and dairy manure ® Increased green waste due to population increase 4

California Integrated Waste Management Board Caltrans has the Potential to Greatly Increase Compost/Mulch Purchases ® Caltrans uses compost statewide, primarily in hydroseeding for erosion control ® US Composting Council (USCC) estimates that Caltrans has a potential market for compost of between 3. 35 -6. 72 M cu. yds. ® Approximately 90% used in construction, the remainder in maintenance 5

California Integrated Waste Management Board Why Caltrans Uses Compost ® Safety – Planting for headlight glare screen, roadway delineation, wind break, & fire suppression ® Aesthetics ® Environmental Compliance – – 6 Revegetation Mitigation Planting Erosion Control Stormwater

California Integrated Waste Management Board Construction Site Sediment ®#1 Discharged Pollutant ® 80, 000 Tons/Year ® 20 -1, 000 Times More Sediment than Other Land Uses 7

California Integrated Waste Management Board THE SOLUTION? Compost and Mulch Benefits the Environment in a Number of Ways ® Decreases runoff and erosion ® Improves roadside revegetation establishment ® Reduces irrigation requirements ® Supplies significant quantities of organic matter ® Improves drainage of clay-based soils and water- holding capacity of sand-based soils ® Improves and stabilizes soil p. H ® Improves cation exchange capacity (CEC) of soils, improving their ability to hold nutrients for plant use 8

California Integrated Waste Management Board Compost and Mulch Benefits the Environment in a Number of Ways ® Supplies macro- and micronutrients ® Supplies beneficial microorganism ® Suppresses certain soil-borne diseases ® Binds and degrades specific pollutants ® Reduces the need for fertilizers and pesticides ® Encourages slow release of nitrogen ® Improves drought tolerance ® Improves plant health and vigor 9
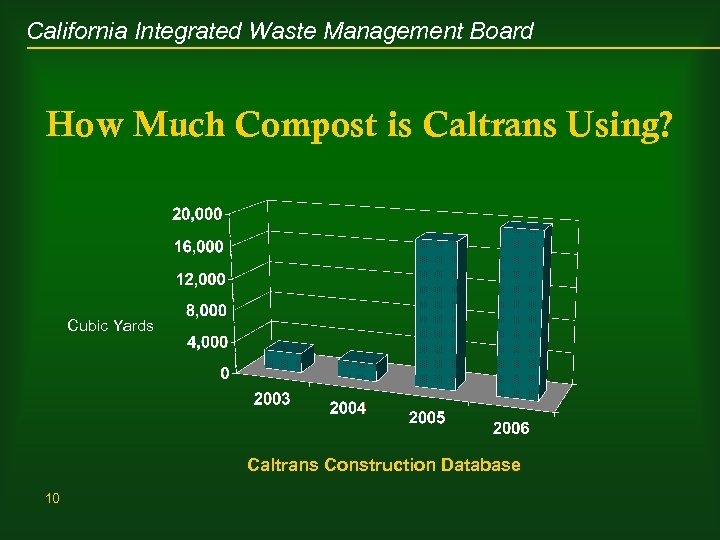
California Integrated Waste Management Board How Much Compost is Caltrans Using? Cubic Yards Caltrans Construction Database 10

California Integrated Waste Management Board Barriers to Increased Compost Use ®Cost ®Product quality ®Lack of compost specifications ®Education 11

California Integrated Waste Management Board Cost Barrier ® Current weighted average (applied) >$300/CY ® High price due to: – Bagged materials – Application method (primarily hydroseeding) ® Caltrans goals: – Reduce cost to $40/CY (applied) – More bulk purchases, less bagged 12

California Integrated Waste Management Board Product Quality ®USCC Seal of Testing Assurance Program (STA) – Testing of compost product – STA certified labs – TMECC (standard testing methodologies) – Report testing results 13

California Integrated Waste Management Board 14

California Integrated Waste Management Board New/Revised Compost Specifications ® STA ® p. H ® Moisture content ® Organic matter content ® Soluble salts 15 ® Maturity ® Stability ® Particle size ® Phytotoxicity ® Pathogens (pass CIWMB standard) ® Heavy metals (pass CIWMB standard)

California Integrated Waste Management Board New/Revised Specifications Require: ®STA participation ®Compost technical data sheet ®Detailed certificate of compliance ®Lab test results 16

California Integrated Waste Management Board Compost-Based BMPs ®Reduce Runoff Volume ®Reduce Runoff Rate ®Improve Infiltration ®Improve Soil Fertility ®Improve Vegetation Establishment 17

California Integrated Waste Management Board Hydroseed (Type C & Type D) ® Used to control erosion, typically ® ® ® on slopes where vegetation has been removed by construction activities or fire Type C - straw required Type D – straw not required Seed Compost – fine material (3/8” minus, 1/64” thick layer) Bagged material only (assists getting up/into truck tank) Stabilizing emulsion (processed organic adhesive used as a soil tackifier) Compost and hydroseeding application, Lake Tahoe, courtesy of Caltrans 18

California Integrated Waste Management Board Soil Amendment (Backfill) ® Also referred to as ® ® 19 amendment or “soil prep” Compost used as a component of backfill Use as a soil amendment/backfill for container sized plant material. Planting backfill benefits trees and shrubs that would otherwise be planted in poor soils Early improved plant growth can be attributed to backfill amendment Backfill, photo courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Blanket (Not Incorporated) ® Layer of loosely applied compost placed over disturbed areas to control erosion ® Seed can be incorporated into compost before placement or broadcast onto surface after placement 20 Compost blanket (not incorporated), courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Benefits of Compost Blankets ® Provides soil protection from ® ® rain “splash impact” Adds organic material to soil (promotes establishment of permanent vegetation instead of weeds) Promotes percolation/infiltration Reduces need for irrigation Removes pollutants, improving downstream water quality Slope after incorporation of compost, photo courtesy of Caltrans 21

California Integrated Waste Management Board Blanket (Compost Incorporated) ® Placed in disturbed areas ® Incorporated to a depth of 18 inches ® Alternative to netting, stabilizing emulsions or polymers ® Typically vegetated by broadcasting seed onto the surface after 22 incorporation Compost incorporation, Placer County, Route 267, photo courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Filter Sock ® Stabilization of disturbed ® ® 23 slopes, storm water pollutant reduction/removal (erosion control on steep slopes, inlet control for storm drains) Can be used in place of silt fence or straw bale barrier Can be vegetated or nonvegetated Pollutants removed by filtration and adsorption to compost particles (higher removal efficiency than silt fence) Traps total suspended solids, particulate metals, oil Filter sock – courtesy of Dr. Britt Faucette, Filtrexx

California Integrated Waste Management Board Filter Berm ® A dike of compost placed ® ® ® 24 perpendicular to sheet flow runoff to control erosion An alternative to silt fencing Generally placed along perimeter of site or at intervals along a slope Can be used as a check dam in small drainage ditches Can be vegetated (generally left in place) or unvegetated (usually broken down once construction is complete and spread around site as mulch) Retains sediment and other pollutants (e. g. , suspended solids, metals, oils and grease) while allowing cleaned water to flow through Installation of filter berm, photo courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Biofiltration Strips (Biostrips) ® Biofiltration strips are typically ® ® ® 25 vegetated land areas over which storm water flows as sheet flow Pollutants removed by filtration through the vegetation, sedimentation, adsorption to soil/compost particles, and infiltration Traps litter, total suspended solids, and particulate metals Compost, soil amendments, organic material or granular soils may be used to improve filtration and vegetation establishment Vegetated by planting native grass plugs, planting low growing groundcover, or through hydroseeding Preferred plant material has a dense continuous top growth (including grasses, grass-like species, forbs and some broad-leafed species) Biofiltration strip, photo courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Biofiltration Swales (Bioswales) ® Vegetated channels or drainage swales, typically trapezoidal or v-shaped channels that receive and convey storm water while ® Other characteristics are similar to biostrips 26 Biofiltration swale, courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Drill Seed ® Seed applied with agricultural drill seeding equipment after compost is applied and incorporated into topsoil ® Used on flat areas, such as highway medians ® Purpose is to amend the soil to enhance seed germination and vegetation establishment 27 Drill seeding equipment, courtesy of Caltrans

California Integrated Waste Management Board Mulch ® Applied to highway roadside to prevent erosion, suppress ® ® ® 28 weed growth, and biodegrade slowly Coarse to very coarse particle size Ideally would not have to be reapplied for 2 -3 years Not seeded or hydroseeded after application Used to cover ground between existing container-sized plants Minimal trash may be okay
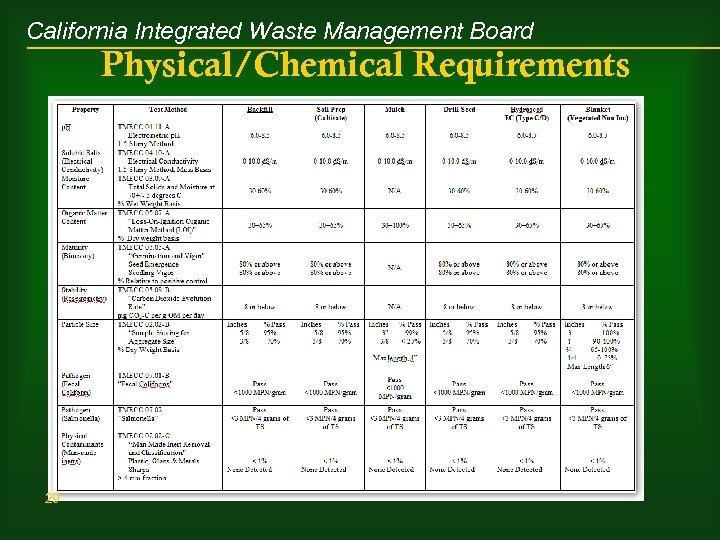
California Integrated Waste Management Board Physical/Chemical Requirements 29

California Integrated Waste Management Board Where Can I Find the Specifications? 30

California Integrated Waste Management Board Education ® Correct misinformation such as: – “Compost mulch not suitable for 2: 1 slopes” – “Compost isn’t suited for native plants” ® Roll out new/revised specifications ® Educate Caltrans staff and its contractors on compost-based BMPs ® Follow-up 31

California Integrated Waste Management Board Caltrans Workshops ® Improving Revegetation and Erosion Control Through Compost-Based BMPs ® Workshops Were Held August through October 2006 in: – – – 32 Los Angeles San Diego Oakland Fresno Sacramento

California Integrated Waste Management Board Compost Use for Landscape and Environmental Enhancement ® Designed primarily for use by Caltrans and its contractors ® Contributors: UC Cooperative Extension, UC Riverside, Caltrans, CIWMB, and Association of Compost Producers ® Information on soils, composts and composting, compost uses and specifications, and landscape plant establishment 33

California Integrated Waste Management Board Next Steps ® Caltrans use of compost and mulch will be measured in 2007 and succeeding years ® Will develop recommendations on further increasing compost use by Caltrans ® Work more closely with Caltrans stormwater and maintenance staff ® Outreach to local government ® Additional workshops will be held Summer/Fall 2007 34

California Integrated Waste Management Board For Further Information Caltrans Specifications at: www. dot. ca. gov/hq/Land. Arch/standards/ (under review) http: //www. dot. ca. gov/hq/esc/oe/specifications/SSPs/ 2006 -SSPs/Sec_10/20/ (posted on server) Compost and Mulch Suppliers at: www. ciwmb. ca. gov/Organics/Supplier. List/ General Information at: www. ciwmb. ca. gov/Organics

California Integrated Waste Management Board Any Questions?

California Integrated Waste Management Board Compost Use on California Highways THANK YOU 37

California Integrated Waste Management Board The Compost Solutions Workshop Compost Use on California Highways February 28, 2007 Brian Larimore www. ciwmb. ca. gov

www. ciwmb. ca. gov
3c32f90605913cf58afad32e0825bc1c.ppt