11fab674aae458213bb2ecb5ef675867.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Calibration of an Ionisation Chamber for use in Megavoltage Dosimetry An insight into the Radiotherapy Placement undertaken by a Part 1 Trainee Clinical Scientist Will Mairs Princess Royal Hospital - Hull 1

Overview of talk ¡ Why we do dosimetry l ¡ What we use l l ¡ Thimble ion chambers Hierarchy traceable to NPL Method of calibration l ¡ Need to know dose delivered Following IPSM COP Chamber factor in practice l How linked to routine QA 2

Why do we carry out dosimetry? ¡ Radiation causes biological damage ¡ Need to quantify dose delivered l Delivery of prescription 3

Bragg-Gray Principle Absorbed dose in a given material can be deduced from the ionisation produced in a small gas-filled cavity within that material l Tissue Ξ water 4
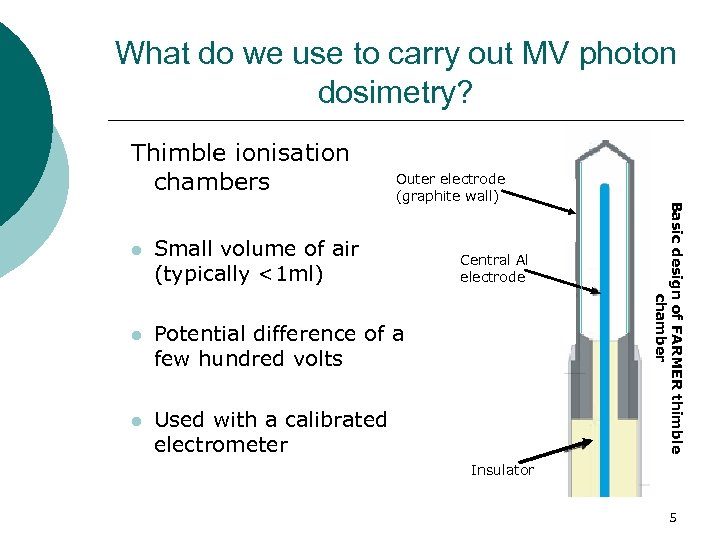
What do we use to carry out MV photon dosimetry? Thimble ionisation chambers l Small volume of air (typically <1 ml) l Potential difference of a few hundred volts l Used with a calibrated electrometer Central Al electrode Basic design of FARMER thimble chamber Outer electrode (graphite wall) Insulator 5
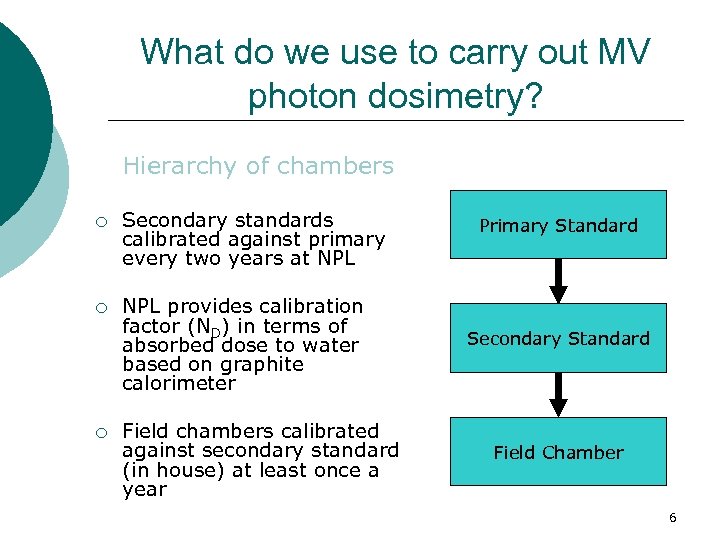
What do we use to carry out MV photon dosimetry? Hierarchy of chambers ¡ Secondary standards calibrated against primary every two years at NPL ¡ NPL provides calibration factor (ND) in terms of absorbed dose to water based on graphite calorimeter ¡ Field chambers calibrated against secondary standard (in house) at least once a year Primary Standard Secondary Standard Field Chamber 6
Summary of calibration method ¡ Described in IPSM COP ¡ Intercompare chambers – using same radiation qualities as will be measured by the field chamber ¡ Correct for Ion recombination losses ¡ Measure Q. I. to find NPL correction factor ¡ Calculate chamber factor to convert electrometer reading to absorbed dose to water 7
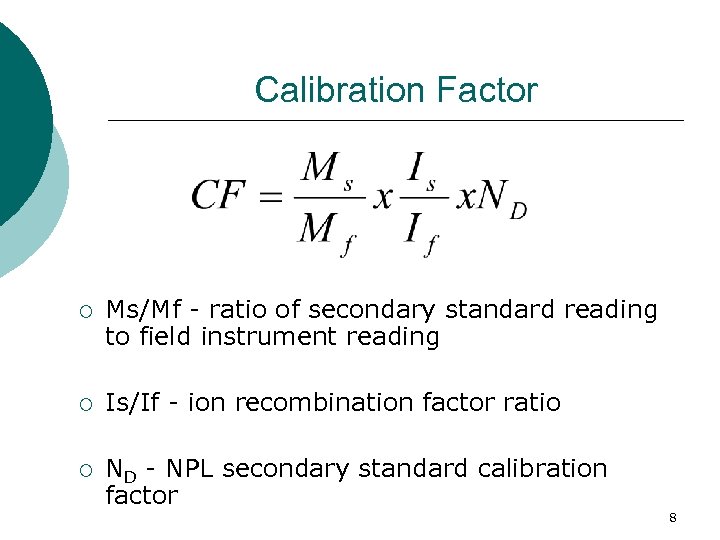
Calibration Factor ¡ Ms/Mf - ratio of secondary standard reading to field instrument reading ¡ Is/If - ion recombination factor ratio ¡ ND - NPL secondary standard calibration factor 8

Method for MV calibration ¡ Chambers placed in intercomparison jig in water tank l l l Depth of 5 cm in 10 x 10 cm field 95 cm TSD 100 mu delivered Interchanged Ratio calculated Lasers Secondary standard Field chamber Thin window in plotting tank 9

Measuring Quality Index ¡ ¡ Measure of radiation quality Ratio of ion recombination corrected instrument readings – l l l ¡ 20 cm and 10 cm depths 10 x 10 cm field Constant TCD of 100 cm Used to find NPL calibration factor from certificate 10
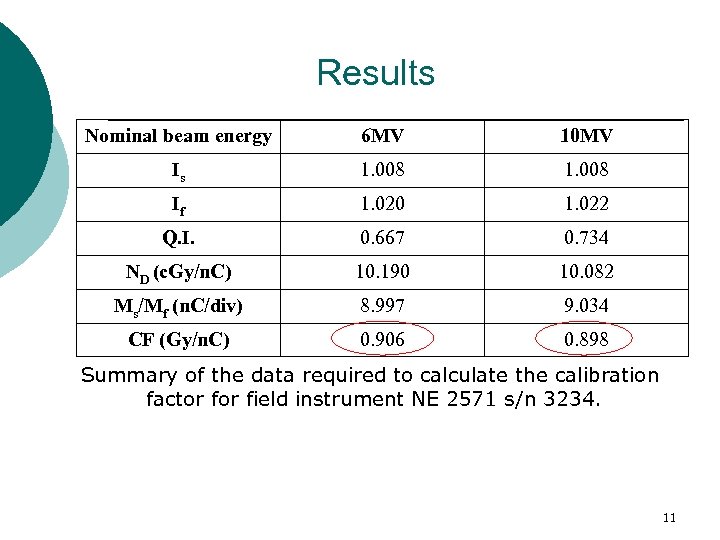
Results Nominal beam energy 6 MV 10 MV Is 1. 008 If 1. 020 1. 022 Q. I. 0. 667 0. 734 ND (c. Gy/n. C) 10. 190 10. 082 Ms/Mf (n. C/div) 8. 997 9. 034 CF (Gy/n. C) 0. 906 0. 898 Summary of the data required to calculate the calibration factor field instrument NE 2571 s/n 3234. 11

Calibration factors in practice ¡ LINAC calibrated to give 1 Gy l l 5 cm depth 10 x 10 cm field 100 mu TSD of 95 cm ¡ Calibration in Perspex rather than water ¡ Requires PBF 12
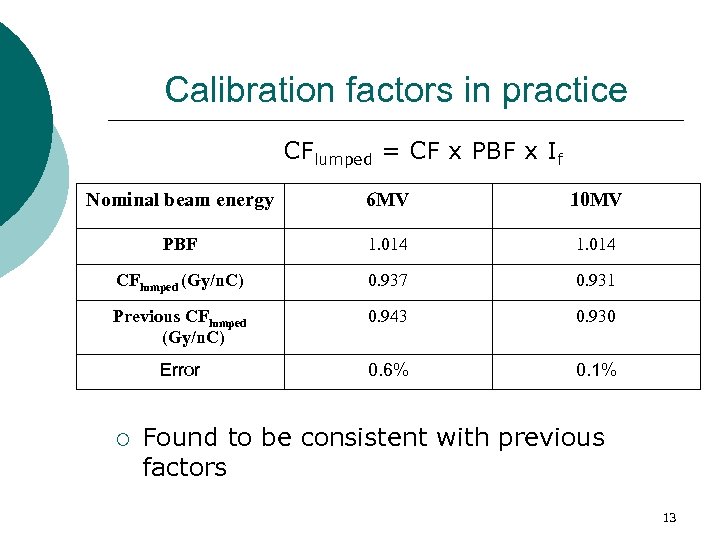
Calibration factors in practice CFlumped = CF x PBF x If Nominal beam energy 6 MV 10 MV PBF 1. 014 CFlumped (Gy/n. C) 0. 937 0. 931 Previous CFlumped (Gy/n. C) 0. 943 0. 930 Error 0. 6% 0. 1% ¡ Found to be consistent with previous factors 13

Summary ¡ It is necessary to carry out dosimetry ¡ Field chambers are traceable to national standards ¡ Calibration carried out in house following COP ¡ Chamber used in the field for QA 14
¡ Thank you for listening 15
11fab674aae458213bb2ecb5ef675867.ppt