L13 grid levelling.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 14

Calculation Excavation and Fill by the grid method

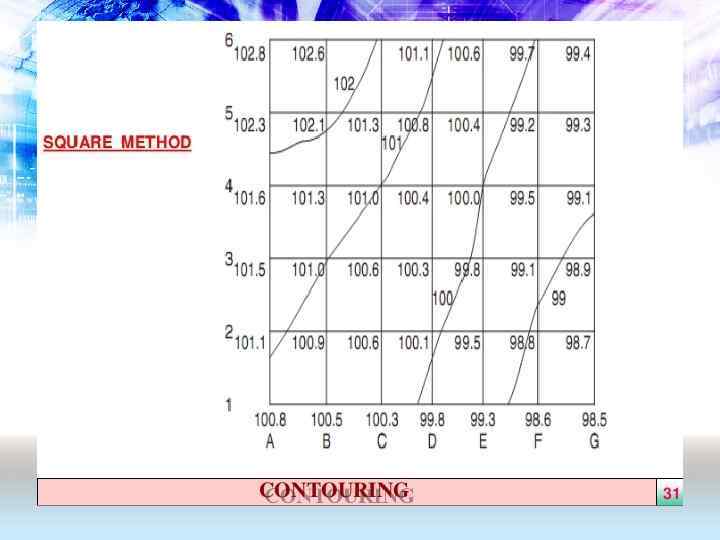
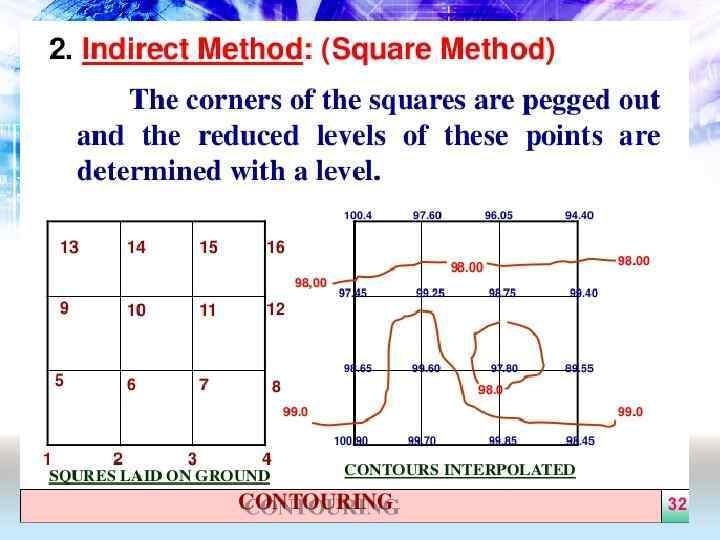
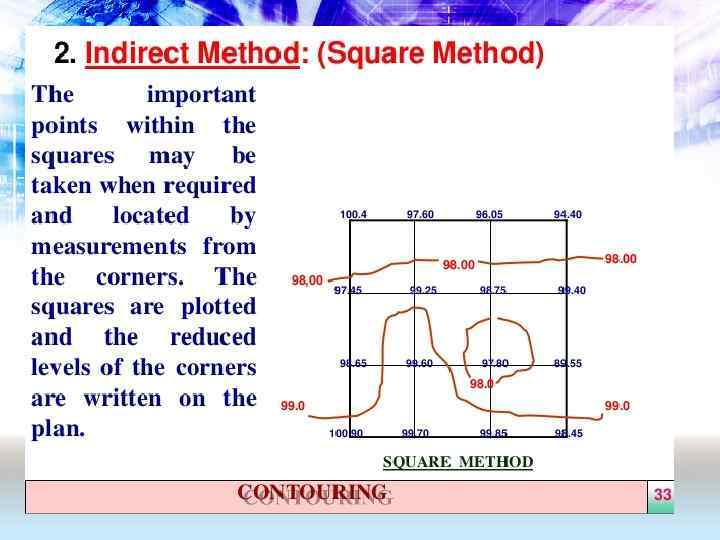
• The grid method of calculation excavation and fill is based on multiple elevations determined by a survey of the site • The site is laid out into a grid. The existing grade is determined and the finished grade is determined at each location on the grid • By adding or subtracting the elevations, the estimator calculates the depth of cut or fill at each point where the grid lines intersect
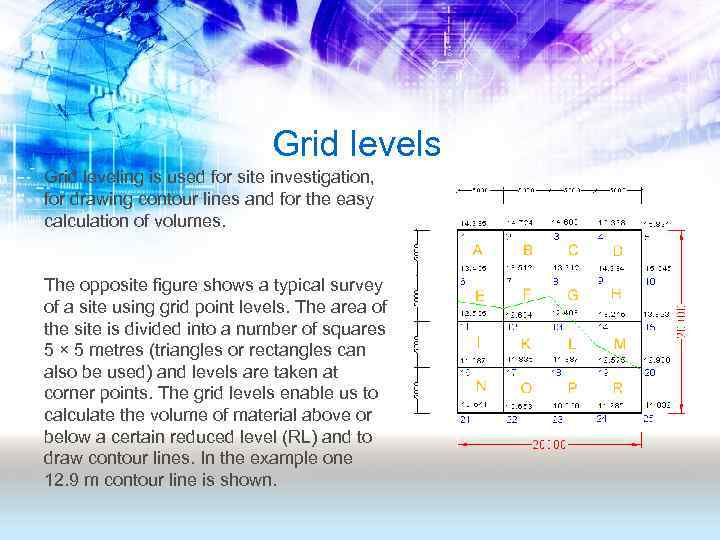
Grid levels Grid leveling is used for site investigation, for drawing contour lines and for the easy calculation of volumes. The opposite figure shows a typical survey of a site using grid point levels. The area of the site is divided into a number of squares 5 × 5 metres (triangles or rectangles can also be used) and levels are taken at corner points. The grid levels enable us to calculate the volume of material above or below a certain reduced level (RL) and to draw contour lines. In the example one 12. 9 m contour line is shown.


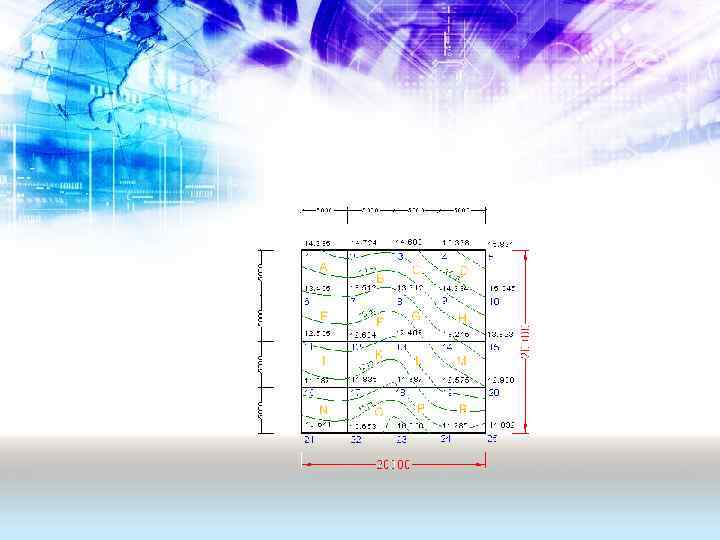
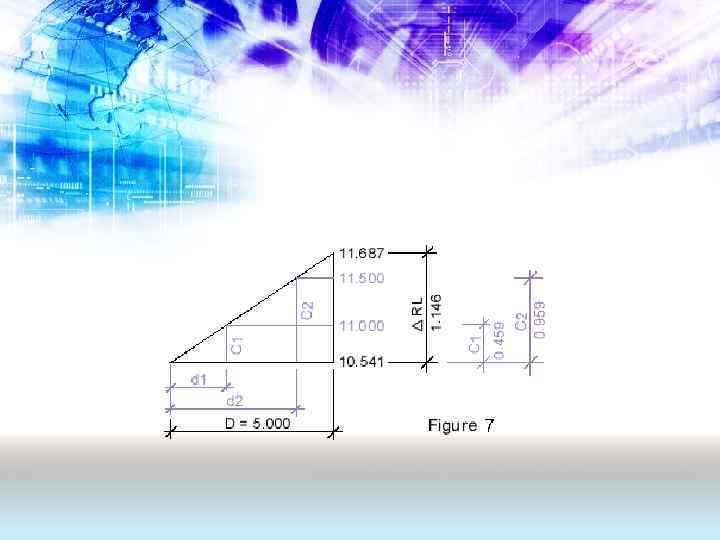

Volume calculation A reference RL must be defined to calculate the volume of the truncated prism A, B, C, etc. The volume of a grid element (A, B, C etc). is the area of the grid element multiplied by the average oft the four corner heights. To calculate the volume correctly each prism is to be considered on its own. Figure 4 below shows the site in isometric view. As can be seen the horizontal plane (green rectangle) at RL = 12. 900 lies between the RL = 10. 000 and RL = 15. 831. If a house is placed on this level then cut (blue area) equals the fill (green area). However, if the FGL (finished ground level) is at RL 10. 00 then all soil of the site need to be removed and if RL 15. 831 soil must be transported to the site.
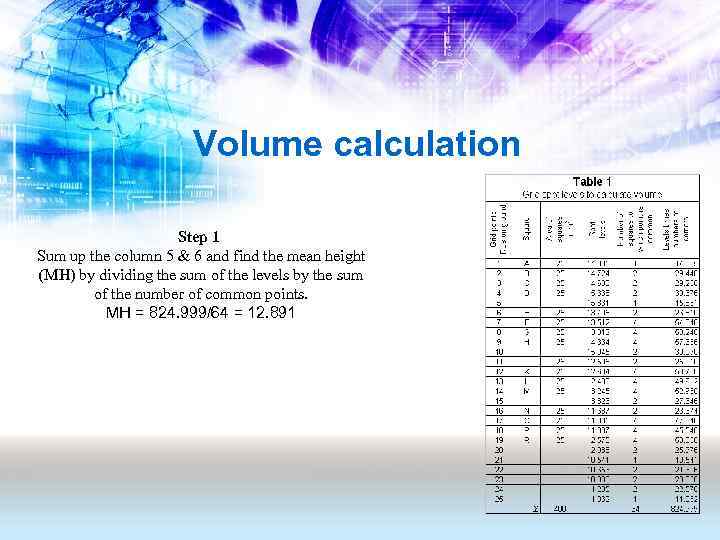
Volume calculation Step 1 Sum up the column 5 & 6 and find the mean height (MH) by dividing the sum of the levels by the sum of the number of common points. MH = 824. 999/64 = 12. 891
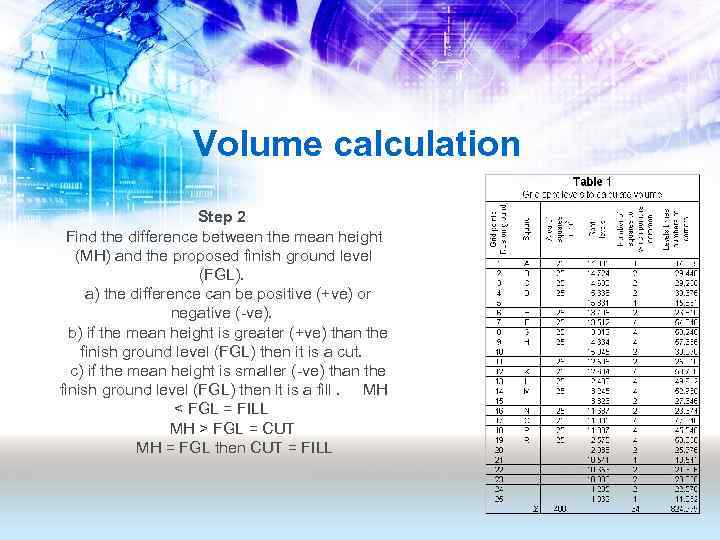
Volume calculation Step 2 Find the difference between the mean height (MH) and the proposed finish ground level (FGL). a) the difference can be positive (+ve) or negative (-ve). b) if the mean height is greater (+ve) than the finish ground level (FGL) then it is a cut. c) if the mean height is smaller (-ve) than the finish ground level (FGL) then it is a fill. MH < FGL = FILL MH > FGL = CUT MH = FGL then CUT = FILL
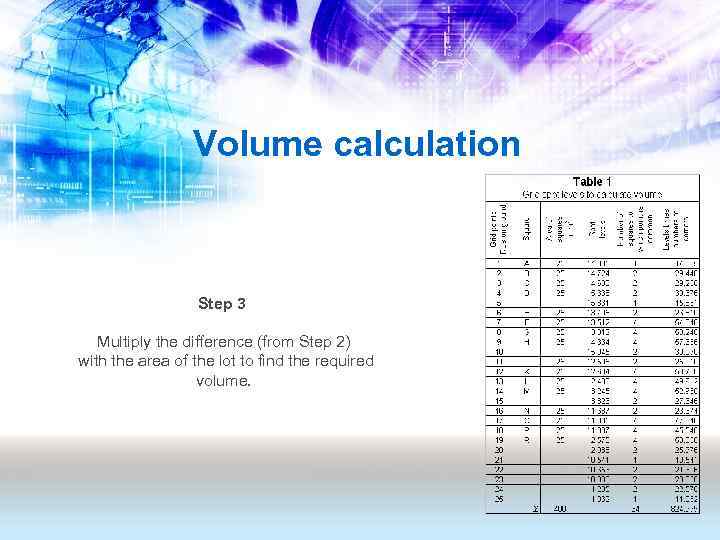
Volume calculation Step 3 Multiply the difference (from Step 2) with the area of the lot to find the required volume.
L13 grid levelling.pptx