5fcb4bf7e56eb8af6758ff5c7469bd92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 CADIP 2002 Program Jerry Stach, Ph. D. Eun Kyo Park, Ph. D. Agent Life Forms Laboratory School of Interdisciplinary Computing and Engineering University of Missouri – Kansas City
CADIP 2002 Program Jerry Stach, Ph. D. Eun Kyo Park, Ph. D. Agent Life Forms Laboratory School of Interdisciplinary Computing and Engineering University of Missouri – Kansas City
 CADIP Project Biologic Agency for Search of Intractable Spaces Opening Soon at UMKCALFworld!
CADIP Project Biologic Agency for Search of Intractable Spaces Opening Soon at UMKCALFworld!
 Research Vision To develop a mobile, rational agent, capable of accepting a payload and by process or data driven signature, migrating to locations in a network to optimally complete its computational task.
Research Vision To develop a mobile, rational agent, capable of accepting a payload and by process or data driven signature, migrating to locations in a network to optimally complete its computational task.
 Applicable Domains l Software robots l Web Computing l Grid Computing l Document Processing l Intelligent Search l Collaborative Computing
Applicable Domains l Software robots l Web Computing l Grid Computing l Document Processing l Intelligent Search l Collaborative Computing
 Limitation l CPU becomes band limited as problem scales – mobility decision/agent planning and reasoning time for site/service selection – Service Place executions implying control of arrival rates – communication between mobile agents and to situated agents (e. g. Traders)
Limitation l CPU becomes band limited as problem scales – mobility decision/agent planning and reasoning time for site/service selection – Service Place executions implying control of arrival rates – communication between mobile agents and to situated agents (e. g. Traders)
 Limitation l Links become band limited as problem scales – message exchanges between agents, both situated and mobile – agent transportation (payload and code) – Trader Updates
Limitation l Links become band limited as problem scales – message exchanges between agents, both situated and mobile – agent transportation (payload and code) – Trader Updates
 Approach provide computational autonomy, strong mobility and self regulation to damp bandwidth – adopt a biological (A-Life) computing model for the MAS – provide an artificial world infrastructure for agent computing – seek performance and scaling via emergent behaviors as opposed to policy and protocol – endow agents with social conscience (e. g. congestion avoidance when possible), preferences and rationality in decision making
Approach provide computational autonomy, strong mobility and self regulation to damp bandwidth – adopt a biological (A-Life) computing model for the MAS – provide an artificial world infrastructure for agent computing – seek performance and scaling via emergent behaviors as opposed to policy and protocol – endow agents with social conscience (e. g. congestion avoidance when possible), preferences and rationality in decision making
 Research Problems a) since there is no MAUF, perception is by characteristic function b) fuzzy reasoning over Service Places c) desirable population behaviors are emergent, not first order effects of policy d) operating system and network support of strong mobility does not exist e) existing agent architecture and design patterns are not robust enough to support architecture
Research Problems a) since there is no MAUF, perception is by characteristic function b) fuzzy reasoning over Service Places c) desirable population behaviors are emergent, not first order effects of policy d) operating system and network support of strong mobility does not exist e) existing agent architecture and design patterns are not robust enough to support architecture
 Completed Work Mobility Decision Simulations l modeled optimal mobility decisions based upon graph theoretic solution l results provided experiential basis for proceeding to perception l simulator provides an observational basis for prediction of agent colony behavior and performance l results do not scale
Completed Work Mobility Decision Simulations l modeled optimal mobility decisions based upon graph theoretic solution l results provided experiential basis for proceeding to perception l simulator provides an observational basis for prediction of agent colony behavior and performance l results do not scale
 Completed Work White Paper on Strong Mobility In strong mobility, not only code and data state are moved, but also the execution state, in order to restart the execution exactly from the point where it was stopped before movement. Strong Mobility is frequently used in load leveling applications
Completed Work White Paper on Strong Mobility In strong mobility, not only code and data state are moved, but also the execution state, in order to restart the execution exactly from the point where it was stopped before movement. Strong Mobility is frequently used in load leveling applications
 Strong Mobility Strong mobility has the ability to store and retrieve computations as variables (continuations) and passes these to the other agents (remote continuations). Strong mobility also usually communicates in an asynchronous fashion in which one agent sends messages to other agents but does not wait for answers. Whenever one of the communication partners of an agent dies, the agent continues, even if it is waiting for some action of the dead partner.
Strong Mobility Strong mobility has the ability to store and retrieve computations as variables (continuations) and passes these to the other agents (remote continuations). Strong mobility also usually communicates in an asynchronous fashion in which one agent sends messages to other agents but does not wait for answers. Whenever one of the communication partners of an agent dies, the agent continues, even if it is waiting for some action of the dead partner.
 Completed Work continued Built ALFworld – a 40 node Beowulf
Completed Work continued Built ALFworld – a 40 node Beowulf
 Plan for Today l Sketch of artificial world - situated and mobile agents l Take a look at a few perception functions – congestion, reliability, difference l Conclude with 2003 Activities
Plan for Today l Sketch of artificial world - situated and mobile agents l Take a look at a few perception functions – congestion, reliability, difference l Conclude with 2003 Activities
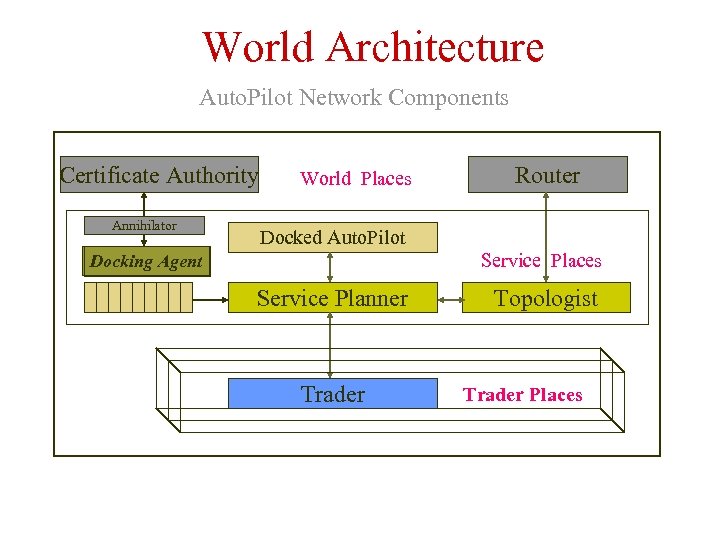 World Architecture Auto. Pilot Network Components Certificate Authority Annihilator World Places Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Places Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist Trader Places
World Architecture Auto. Pilot Network Components Certificate Authority Annihilator World Places Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Places Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist Trader Places
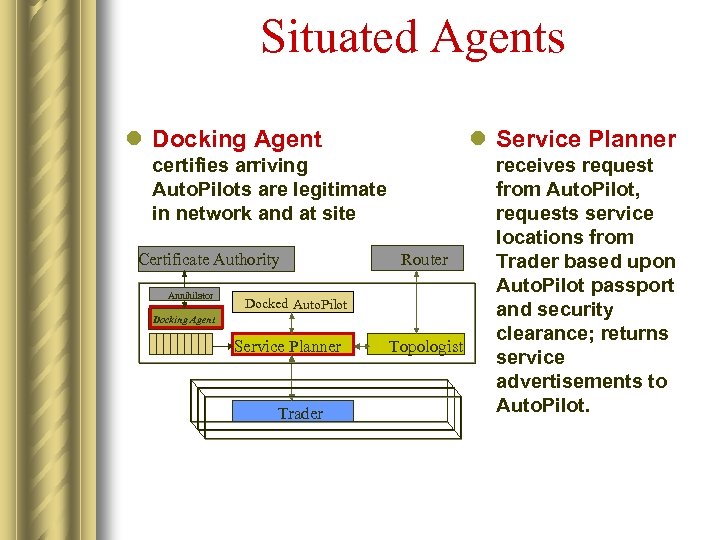 Situated Agents l Docking Agent l Service Planner certifies arriving Auto. Pilots are legitimate in network and at site Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist receives request from Auto. Pilot, requests service locations from Trader based upon Auto. Pilot passport and security clearance; returns service advertisements to Auto. Pilot.
Situated Agents l Docking Agent l Service Planner certifies arriving Auto. Pilots are legitimate in network and at site Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist receives request from Auto. Pilot, requests service locations from Trader based upon Auto. Pilot passport and security clearance; returns service advertisements to Auto. Pilot.
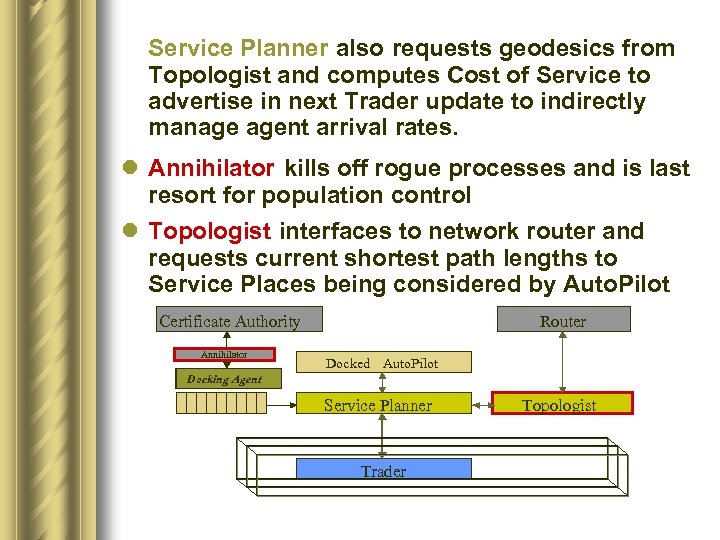 Service Planner also requests geodesics from Topologist and computes Cost of Service to advertise in next Trader update to indirectly manage agent arrival rates. l Annihilator kills off rogue processes and is last resort for population control l Topologist interfaces to network router and requests current shortest path lengths to Service Places being considered by Auto. Pilot Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist
Service Planner also requests geodesics from Topologist and computes Cost of Service to advertise in next Trader update to indirectly manage agent arrival rates. l Annihilator kills off rogue processes and is last resort for population control l Topologist interfaces to network router and requests current shortest path lengths to Service Places being considered by Auto. Pilot Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist
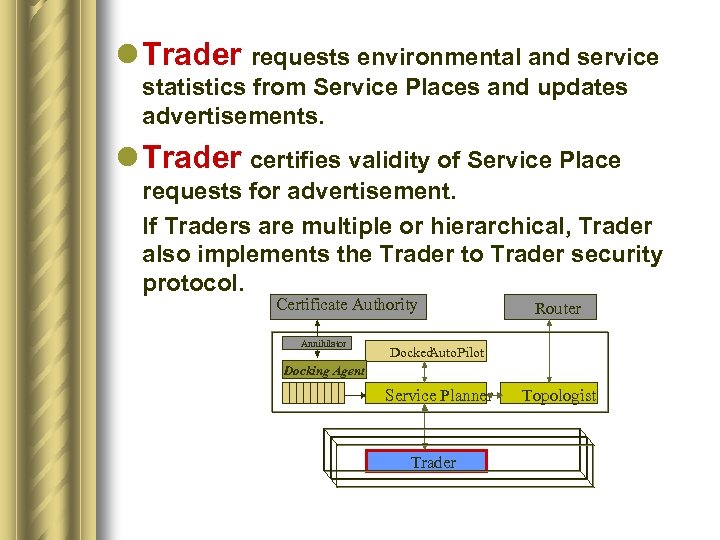 l Trader requests environmental and service statistics from Service Places and updates advertisements. l Trader certifies validity of Service Place requests for advertisement. If Traders are multiple or hierarchical, Trader also implements the Trader to Trader security protocol. Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist
l Trader requests environmental and service statistics from Service Places and updates advertisements. l Trader certifies validity of Service Place requests for advertisement. If Traders are multiple or hierarchical, Trader also implements the Trader to Trader security protocol. Certificate Authority Annihilator Router Docked Auto. Pilot Docking Agent Service Planner Trader Topologist
 Auto. Pilots are Mobile, Autonomous Agents l Auto. Pilot picks up payload consisting of signature, metadata and preferences from birth location. l Docking Agent obtains passport and security clearance from Certificate Authority. l Autopilot requests for each service in its signature, a set of advertisements from the Service Planner and may prune them. Autopilot returns a set of acceptable advertisements and attribute preference set to Service Planner. Certificate Authority Annihilator Docking Agent Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Planner Trader Service Place Topologist Trader Places
Auto. Pilots are Mobile, Autonomous Agents l Auto. Pilot picks up payload consisting of signature, metadata and preferences from birth location. l Docking Agent obtains passport and security clearance from Certificate Authority. l Autopilot requests for each service in its signature, a set of advertisements from the Service Planner and may prune them. Autopilot returns a set of acceptable advertisements and attribute preference set to Service Planner. Certificate Authority Annihilator Docking Agent Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Planner Trader Service Place Topologist Trader Places
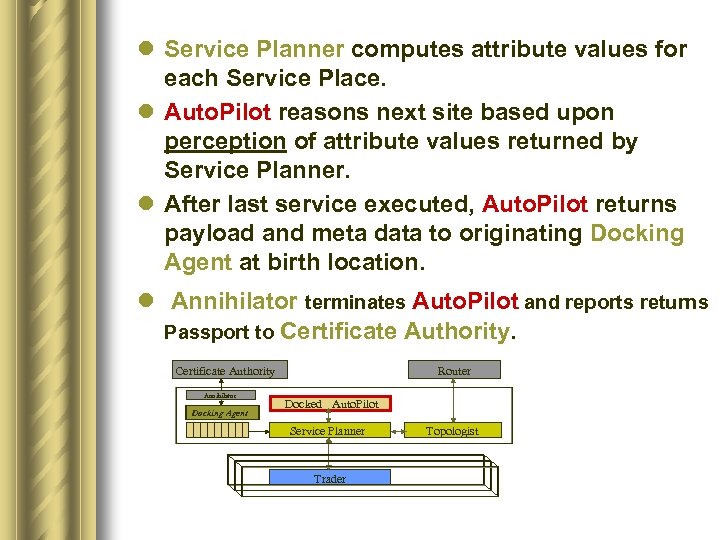 l Service Planner computes attribute values for each Service Place. l Auto. Pilot reasons next site based upon perception of attribute values returned by Service Planner. l After last service executed, Auto. Pilot returns payload and meta data to originating Docking Agent at birth location. l Annihilator terminates Auto. Pilot and reports returns Passport to Certificate Authority Annihilator Docking Agent Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Planner Trader Topologist
l Service Planner computes attribute values for each Service Place. l Auto. Pilot reasons next site based upon perception of attribute values returned by Service Planner. l After last service executed, Auto. Pilot returns payload and meta data to originating Docking Agent at birth location. l Annihilator terminates Auto. Pilot and reports returns Passport to Certificate Authority Annihilator Docking Agent Router Docked Auto. Pilot Service Planner Trader Topologist
 Perception by Characteristic Function Congestion, Reliability, Difference
Perception by Characteristic Function Congestion, Reliability, Difference
 Agent Framework Meta data Behavior Reasoning Perception Sensing Autonomous, Rational Agent • To discriminate between service locations in a network, an agent must be able to sense its environment. • Since all nodes exhibit all attributes, agent preference must govern perception. We perceive local conditions by characteristic functions applied to sensed values. • Reasoning is “fuzzy” being approximate and over uncertain and aged data. • Behavior is limited to nondeterministic choice of service and migration • Meta data provides the context for decision making
Agent Framework Meta data Behavior Reasoning Perception Sensing Autonomous, Rational Agent • To discriminate between service locations in a network, an agent must be able to sense its environment. • Since all nodes exhibit all attributes, agent preference must govern perception. We perceive local conditions by characteristic functions applied to sensed values. • Reasoning is “fuzzy” being approximate and over uncertain and aged data. • Behavior is limited to nondeterministic choice of service and migration • Meta data provides the context for decision making
 Perception Function Goals l Functions should produce “reasonable” output l Perceptions should have good correspondence to the subjective notions they represent l Functions should be based in theory, i. e. a characteristic function with PDF and CDF over the universe values of the attribute
Perception Function Goals l Functions should produce “reasonable” output l Perceptions should have good correspondence to the subjective notions they represent l Functions should be based in theory, i. e. a characteristic function with PDF and CDF over the universe values of the attribute
 Perception occurs in subjective time l An Agent’s life is finite in the system l An Agent carries a task signature yielding an expectation of the duration of work l An Agent must “sense” its own mortality in subjective time by half life i. e. sense urgency where N 0 and NT are initial and decayed attribute values respectively
Perception occurs in subjective time l An Agent’s life is finite in the system l An Agent carries a task signature yielding an expectation of the duration of work l An Agent must “sense” its own mortality in subjective time by half life i. e. sense urgency where N 0 and NT are initial and decayed attribute values respectively
 As urgency increases, risk aversion decreases measure of risk aversion OR
As urgency increases, risk aversion decreases measure of risk aversion OR
 Role of Origin and Limit in Perception Functions l In subjective time, the origin corresponds to the agent’s threshold of sensitivity to the service attribute. l In subjective time, the limit corresponds to the agent’s tolerance, i. e. value of indifference for the attribute, beyond which all values are unacceptable. l These two values set the slope over which the perception function is differentiated in order to return a fuzzy membership value.
Role of Origin and Limit in Perception Functions l In subjective time, the origin corresponds to the agent’s threshold of sensitivity to the service attribute. l In subjective time, the limit corresponds to the agent’s tolerance, i. e. value of indifference for the attribute, beyond which all values are unacceptable. l These two values set the slope over which the perception function is differentiated in order to return a fuzzy membership value.
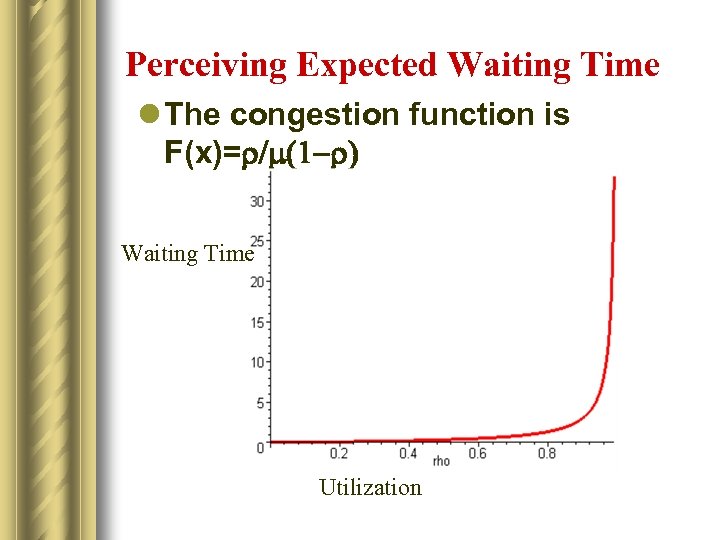 Perceiving Expected Waiting Time l The congestion function is F(x)=r/m(1 -r) Waiting Time Utilization
Perceiving Expected Waiting Time l The congestion function is F(x)=r/m(1 -r) Waiting Time Utilization
 Service Place Population First Order Approximation l let l be arrivals per unit of time and m be services per unit of time.
Service Place Population First Order Approximation l let l be arrivals per unit of time and m be services per unit of time.
 Service Place Effectiveness
Service Place Effectiveness
 Service Place Effectiveness continued
Service Place Effectiveness continued
 The Case for Congestion Set Membership l Simply computing a wait time is not sufficient because it is without subjective value to the agent – there may be no wait time below the desired delay contribution – the wait time and utilization alone are insufficient to determine whether a node is in an “unsafe” state – any node not idle is “congested” l “Unsafe state ” is a condition subject to the Agent’s tolerence, i. e. , corresponding to the attribute limit for the sensed value
The Case for Congestion Set Membership l Simply computing a wait time is not sufficient because it is without subjective value to the agent – there may be no wait time below the desired delay contribution – the wait time and utilization alone are insufficient to determine whether a node is in an “unsafe” state – any node not idle is “congested” l “Unsafe state ” is a condition subject to the Agent’s tolerence, i. e. , corresponding to the attribute limit for the sensed value
 Differentiating Rate of Change demands an origin and limit l The rate of change for the exponential function is constant over any interval. l The point at which the derivative of the function matches the average rate of change is the congestion point for the Service Place Utilization. l Average rate of change is of the form f’(x) = f(b)-f(a)/b-a where a, b are the origin and limit respectively.
Differentiating Rate of Change demands an origin and limit l The rate of change for the exponential function is constant over any interval. l The point at which the derivative of the function matches the average rate of change is the congestion point for the Service Place Utilization. l Average rate of change is of the form f’(x) = f(b)-f(a)/b-a where a, b are the origin and limit respectively.
 Unsafe States and Subjective Time l If an Agent has a priority task or is aged relative to its remaining work, its tolerance for delay (r) decreases l This tolerance though subjective, is always bounded 0 origin perceived value limit 1. l To find this point in the congestion function requires we compute rho (r) [on the x axis] and waiting time W(r) [on the y axis].
Unsafe States and Subjective Time l If an Agent has a priority task or is aged relative to its remaining work, its tolerance for delay (r) decreases l This tolerance though subjective, is always bounded 0 origin perceived value limit 1. l To find this point in the congestion function requires we compute rho (r) [on the x axis] and waiting time W(r) [on the y axis].
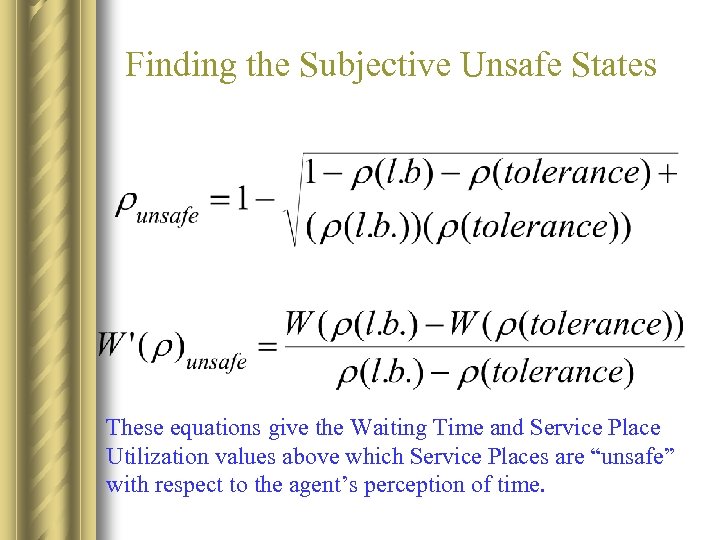 Finding the Subjective Unsafe States These equations give the Waiting Time and Service Place Utilization values above which Service Places are “unsafe” with respect to the agent’s perception of time.
Finding the Subjective Unsafe States These equations give the Waiting Time and Service Place Utilization values above which Service Places are “unsafe” with respect to the agent’s perception of time.
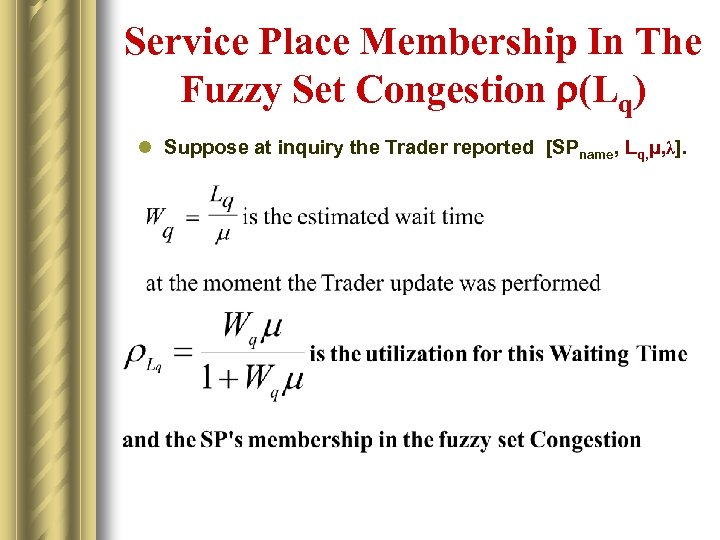 Service Place Membership In The Fuzzy Set Congestion r(Lq) l Suppose at inquiry the Trader reported [SPname, Lq, μ, λ].
Service Place Membership In The Fuzzy Set Congestion r(Lq) l Suppose at inquiry the Trader reported [SPname, Lq, μ, λ].
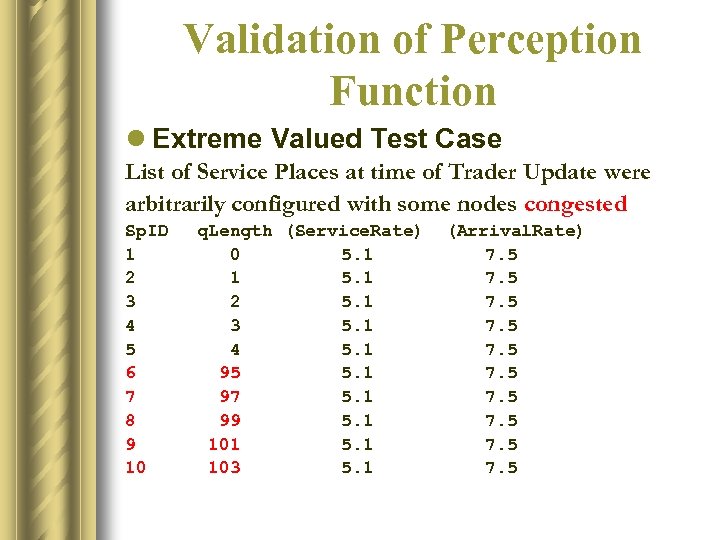 Validation of Perception Function l Extreme Valued Test Case List of Service Places at time of Trader Update were arbitrarily configured with some nodes congested Sp. ID 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 q. Length (Service. Rate) (Arrival. Rate) 0 5. 1 7. 5 1 5. 1 7. 5 2 5. 1 7. 5 3 5. 1 7. 5 4 5. 1 7. 5 95 5. 1 7. 5 97 5. 1 7. 5 99 5. 1 7. 5 101 5. 1 7. 5 103 5. 1 7. 5
Validation of Perception Function l Extreme Valued Test Case List of Service Places at time of Trader Update were arbitrarily configured with some nodes congested Sp. ID 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 q. Length (Service. Rate) (Arrival. Rate) 0 5. 1 7. 5 1 5. 1 7. 5 2 5. 1 7. 5 3 5. 1 7. 5 4 5. 1 7. 5 95 5. 1 7. 5 97 5. 1 7. 5 99 5. 1 7. 5 101 5. 1 7. 5 103 5. 1 7. 5
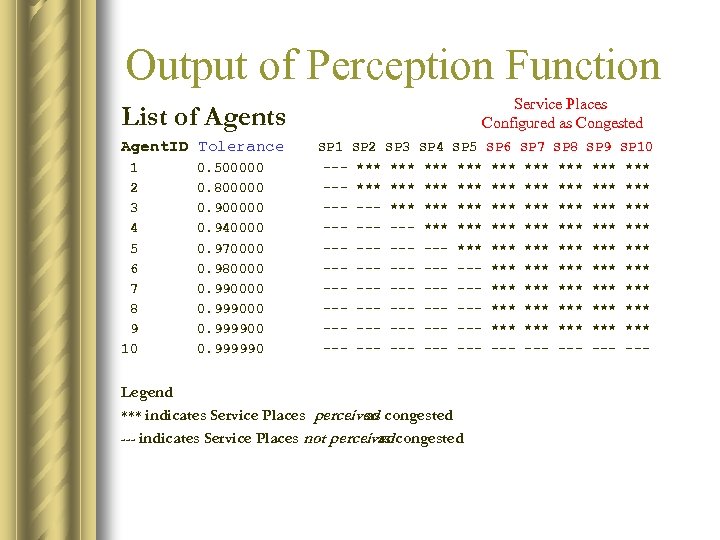 Output of Perception Function List of Agents Service Places Configured as Congested Agent. ID Tolerance SP 1 SP 2 SP 3 SP 4 SP 5 SP 6 SP 7 SP 8 SP 9 SP 10 1 0. 500000 --- *** *** *** 2 0. 800000 --- *** *** *** 3 0. 900000 --- *** *** 4 0. 940000 --- --- *** *** 5 0. 970000 --- --- *** *** *** 6 0. 980000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 7 0. 990000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 8 0. 999000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 9 0. 999900 --- --- --- *** *** *** 10 0. 999990 --- --- --- Legend *** indicates Service Places perceived congested as --- indicates Service Places not perceived congested as
Output of Perception Function List of Agents Service Places Configured as Congested Agent. ID Tolerance SP 1 SP 2 SP 3 SP 4 SP 5 SP 6 SP 7 SP 8 SP 9 SP 10 1 0. 500000 --- *** *** *** 2 0. 800000 --- *** *** *** 3 0. 900000 --- *** *** 4 0. 940000 --- --- *** *** 5 0. 970000 --- --- *** *** *** 6 0. 980000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 7 0. 990000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 8 0. 999000 --- --- --- *** *** *** 9 0. 999900 --- --- --- *** *** *** 10 0. 999990 --- --- --- Legend *** indicates Service Places perceived congested as --- indicates Service Places not perceived congested as
 Interpretation l Service Places 6 to 10 should be considered congested by all agents since they were configured in that condition. l Agents 1 - 9 did perceive Service Places 6 to 10 as congested. l Agents 1 to 5 were to conservative according to their tolerance for delay l Agent 10 was greedy according to its lack of constraint on delay.
Interpretation l Service Places 6 to 10 should be considered congested by all agents since they were configured in that condition. l Agents 1 - 9 did perceive Service Places 6 to 10 as congested. l Agents 1 to 5 were to conservative according to their tolerance for delay l Agent 10 was greedy according to its lack of constraint on delay.
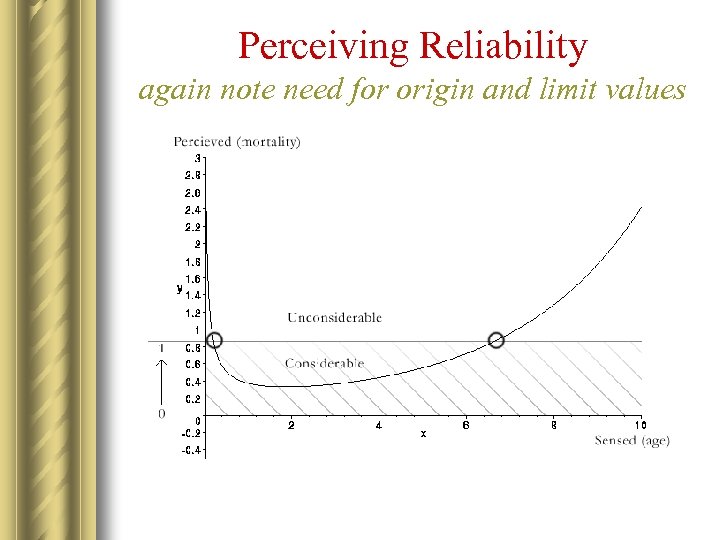 Perceiving Reliability again note need for origin and limit values
Perceiving Reliability again note need for origin and limit values
![The Bath Tub Function General definition of the bathtub-function f(x) = β*x(β-1)*e(α 1*x) [1] The Bath Tub Function General definition of the bathtub-function f(x) = β*x(β-1)*e(α 1*x) [1]](https://present5.com/presentation/5fcb4bf7e56eb8af6758ff5c7469bd92/image-39.jpg) The Bath Tub Function General definition of the bathtub-function f(x) = β*x(β-1)*e(α 1*x) [1] This is a special combination of the Weibull rate and the log linear rate. β is a shaping parameter, which is responsible for the curve and α 1 is a nuisance parameter for fine-tuning the curve (it “controls” the Wear-Out-Phase). Derivative of the Bathtub-function f΄(x) = β 2*x β– 2 *eα 1*x- β*xb-2*eα 1*x + β *xβ-1* α 1*eα 1*x [2]
The Bath Tub Function General definition of the bathtub-function f(x) = β*x(β-1)*e(α 1*x) [1] This is a special combination of the Weibull rate and the log linear rate. β is a shaping parameter, which is responsible for the curve and α 1 is a nuisance parameter for fine-tuning the curve (it “controls” the Wear-Out-Phase). Derivative of the Bathtub-function f΄(x) = β 2*x β– 2 *eα 1*x- β*xb-2*eα 1*x + β *xβ-1* α 1*eα 1*x [2]
 Mortality Sensing Requirements 1. 2. 3. The agent must know its chronological age since birth The agent must know its current half life and (origin, limit) in order to determine its “indifference time” from the mortality function i. e. at the limit all solutions are unacceptable. Origin may be set to zero. The agent must know αi βi from the Trader for the SP or service being evaluated. These are provided from the Sponsor’s empirical experience.
Mortality Sensing Requirements 1. 2. 3. The agent must know its chronological age since birth The agent must know its current half life and (origin, limit) in order to determine its “indifference time” from the mortality function i. e. at the limit all solutions are unacceptable. Origin may be set to zero. The agent must know αi βi from the Trader for the SP or service being evaluated. These are provided from the Sponsor’s empirical experience.
 Perceiving Mortality lmortality age y = βix(βi-1)*e(αix) l membership in the fuzzy failure set is determined
Perceiving Mortality lmortality age y = βix(βi-1)*e(αix) l membership in the fuzzy failure set is determined
 Mortality should be contrasted to the stability of the entity’s mortality age l f’(x) is a kind of stability factor. It indicates the amount of change of the expected mortality, which might be important if the agent is interested in a long-term cooperation or is risk averse. A positive value will indicate an increasing risk, a negative value a decreasing risk.
Mortality should be contrasted to the stability of the entity’s mortality age l f’(x) is a kind of stability factor. It indicates the amount of change of the expected mortality, which might be important if the agent is interested in a long-term cooperation or is risk averse. A positive value will indicate an increasing risk, a negative value a decreasing risk.
 Stability of the mortality age relative to the entity is given *eα ix- β i*xbi-2*eα ix + βxβi-1 αieα ix f’(x) = β i 2 x β i– 2
Stability of the mortality age relative to the entity is given *eα ix- β i*xbi-2*eα ix + βxβi-1 αieα ix f’(x) = β i 2 x β i– 2
 Sample Output Age : 1. 0 Agent. Mortality. Value: 0. 60 Entity. Mortality : 0. 51 Failure. Set. Membership : 0. 86 Stability : -0. 18 Age : 1. 5 Agent. Mortality. Value: 0. 60 Entity. Mortality : 0. 46 Failure. Set. Membership : 0. 76 Stability : -0. 07
Sample Output Age : 1. 0 Agent. Mortality. Value: 0. 60 Entity. Mortality : 0. 51 Failure. Set. Membership : 0. 86 Stability : -0. 18 Age : 1. 5 Agent. Mortality. Value: 0. 60 Entity. Mortality : 0. 46 Failure. Set. Membership : 0. 76 Stability : -0. 07
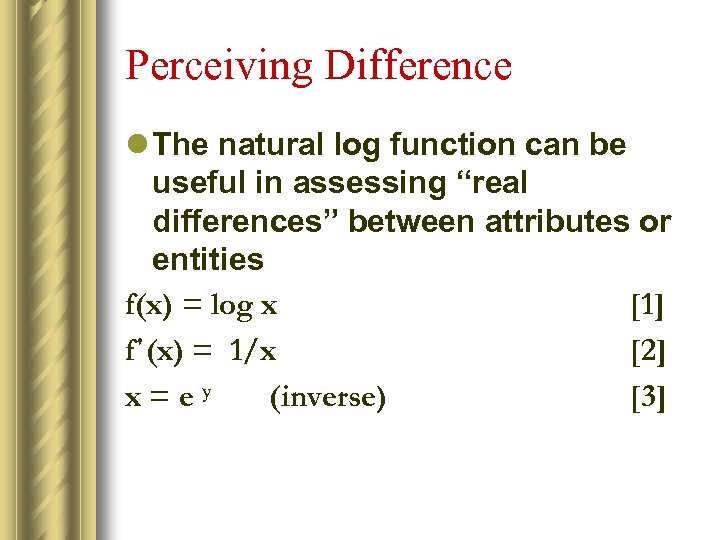 Perceiving Difference l The natural log function can be useful in assessing “real differences” between attributes or entities f(x) = log x [1] f΄(x) = 1/x [2] x=ey (inverse) [3]
Perceiving Difference l The natural log function can be useful in assessing “real differences” between attributes or entities f(x) = log x [1] f΄(x) = 1/x [2] x=ey (inverse) [3]
 We still need origin and limit l Let origin = 0, limit be the point of indifference l Let x be the sensed value l Let y be the preference value l To determine the “perceived difference” between sensed value and preferred value dx = ey , i. e. transform y to x not x to y
We still need origin and limit l Let origin = 0, limit be the point of indifference l Let x be the sensed value l Let y be the preference value l To determine the “perceived difference” between sensed value and preferred value dx = ey , i. e. transform y to x not x to y
 Compute membership value and stability of perceived value l fuzzy membership in the “difference” set is x/dx. l stability of the perception is 1/x XValue YValue Agent. XValue = = service. Place->x. Value; logf(XValue); this->max. YValue; exp(Agent. YValue); Strength. Considerability = XValue/ Agent. XValue; if (Strength. Considerability>1)Strength. Considerability=1;
Compute membership value and stability of perceived value l fuzzy membership in the “difference” set is x/dx. l stability of the perception is 1/x XValue YValue Agent. XValue = = service. Place->x. Value; logf(XValue); this->max. YValue; exp(Agent. YValue); Strength. Considerability = XValue/ Agent. XValue; if (Strength. Considerability>1)Strength. Considerability=1;
![Sample Perceptions Service. Place[4] XValue: 1. 50 YValue: 0. 41 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Sample Perceptions Service. Place[4] XValue: 1. 50 YValue: 0. 41 Agent. YValue: 1. 00](https://present5.com/presentation/5fcb4bf7e56eb8af6758ff5c7469bd92/image-48.jpg) Sample Perceptions Service. Place[4] XValue: 1. 50 YValue: 0. 41 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 0. 55 Stability: 0. 67 Service. Place[5] XValue: 2. 00 YValue: 0. 69 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 0. 74 Stability: 0. 50 Service. Place[6] XValue: 3. 00 YValue: 1. 10 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 1. 00 Stability: 0. 33
Sample Perceptions Service. Place[4] XValue: 1. 50 YValue: 0. 41 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 0. 55 Stability: 0. 67 Service. Place[5] XValue: 2. 00 YValue: 0. 69 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 0. 74 Stability: 0. 50 Service. Place[6] XValue: 3. 00 YValue: 1. 10 Agent. YValue: 1. 00 Agent. XValue: 2. 72 Strength. Considerability: 1. 00 Stability: 0. 33
 2003 Activities l Select method of fuzzy reasoning for mobility decision and validate l Determine COS function using first order queuing approximations l Implement essential ALFworld agents and Trader Update policy l Begin work on design pattern l Begin work on genetic representation of mobile agent
2003 Activities l Select method of fuzzy reasoning for mobility decision and validate l Determine COS function using first order queuing approximations l Implement essential ALFworld agents and Trader Update policy l Begin work on design pattern l Begin work on genetic representation of mobile agent


