Cadherins Cadherin signaling Glycogen synthase kinase









































4_cadherins_wnt_hedgehog_notch_tgfb_ros_no.ppt
- Размер: 10.2 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 53
Описание презентации Cadherins Cadherin signaling Glycogen synthase kinase по слайдам
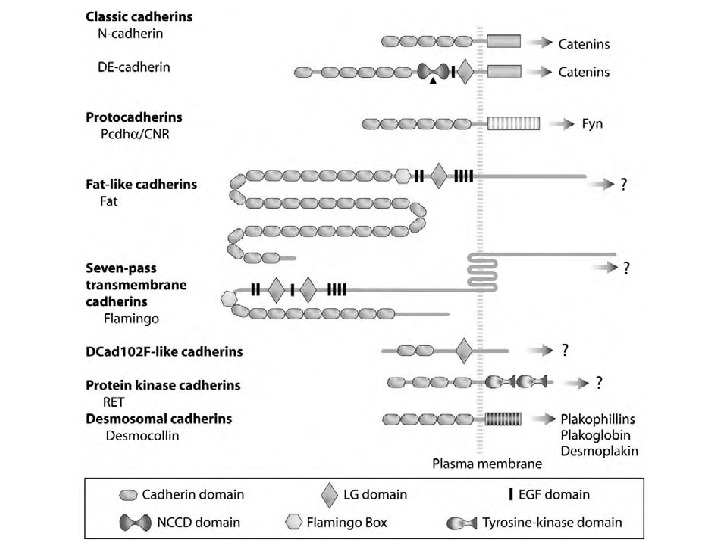
 Cadherins
Cadherins

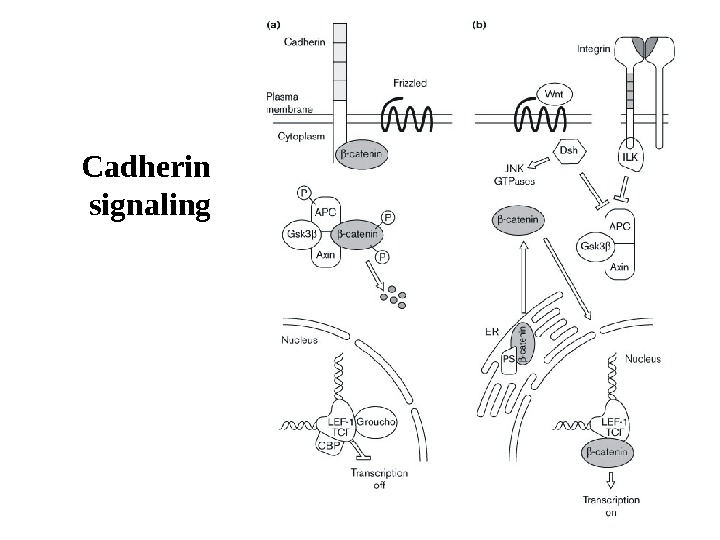
 Cadherin signaling
Cadherin signaling
 Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3 beta) GSK-3 Akt/PKB ILK Dsh p 90 RSKPI-3 kinase Wnt ERK Glycogen synthase Cy. Dc-jun -catenin. Integrins
Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3 beta) GSK-3 Akt/PKB ILK Dsh p 90 RSKPI-3 kinase Wnt ERK Glycogen synthase Cy. Dc-jun -catenin. Integrins
 Cadherins and integrins crosstalk
Cadherins and integrins crosstalk
 Tyrosine phosphorylation of β -catenin
Tyrosine phosphorylation of β -catenin
 Phosphorylation in cadherin-dependent contacts
Phosphorylation in cadherin-dependent contacts
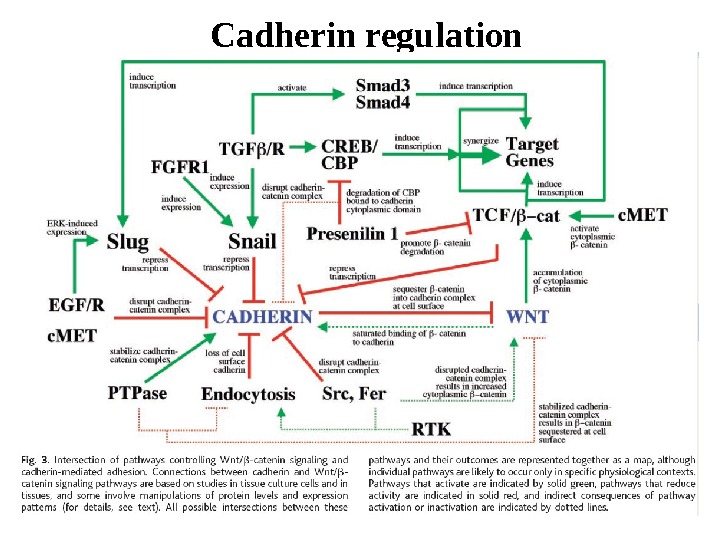
 Cadherin regulation
Cadherin regulation
 Wnt signaling
Wnt signaling
 Major morphogens: — Wnts — Hedgehogs — Notch ligands (Delta-like/Jugged) — BMPs (Bone Morphogenic Proteins) — FGFs — Retinoids
Major morphogens: — Wnts — Hedgehogs — Notch ligands (Delta-like/Jugged) — BMPs (Bone Morphogenic Proteins) — FGFs — Retinoids
 Wnt palmitoylation
Wnt palmitoylation
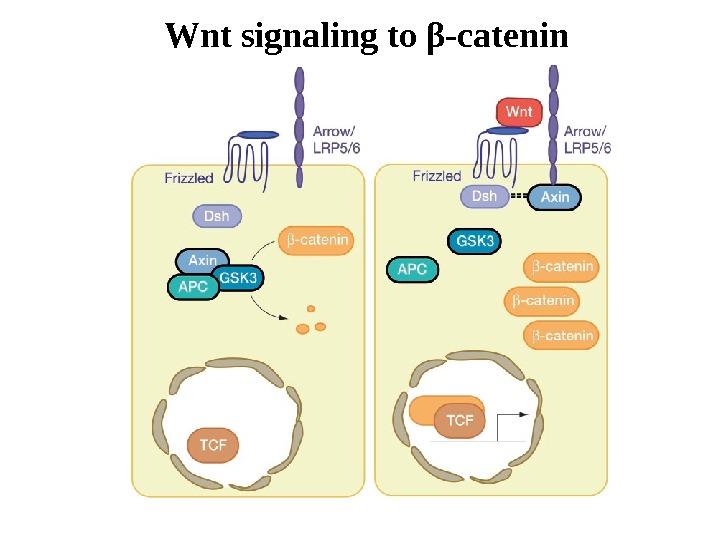
 Wnt signaling to β -catenin
Wnt signaling to β -catenin
 More Wnt signaling to β -catenin
More Wnt signaling to β -catenin
 Wnt signaling to Ca and Rho
Wnt signaling to Ca and Rho
 Hedgehog signaling
Hedgehog signaling
 Mammalian hedgehogs: — Sonic hedgehod (SHH) — Indian hedgehog (IHH) — Desert hedgehog (DHH)
Mammalian hedgehogs: — Sonic hedgehod (SHH) — Indian hedgehog (IHH) — Desert hedgehog (DHH)
 Hedgehog modifications
Hedgehog modifications
 Hedgehog modifications
Hedgehog modifications
 Hedgehog secretion
Hedgehog secretion
 Hedgehog signaling
Hedgehog signaling
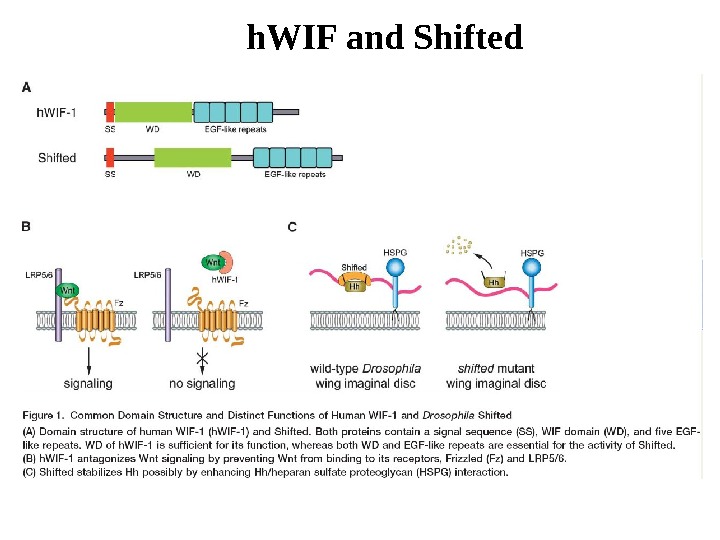
 h. WIF and Shifted
h. WIF and Shifted
 Notch signaling
Notch signaling
 Delta-Notch signaling
Delta-Notch signaling
 Notch signaling — Delta-like/Jugged: Dll 1, 3, 4, Jag 1, 2 — canonical ligands — Notch — receptor — ADAM (TACE, Kuzbanian) – metalloprotease for S 2 cleavage — γ -secretase complex (presenilin-containing) for S 3 cleavage — N ICD , or NICD, or ICN – transcriptionally active Notch fragment — CSL, CBF 1/RBPJk, Su. H (suppressor of hairless) – transcription factor
Notch signaling — Delta-like/Jugged: Dll 1, 3, 4, Jag 1, 2 — canonical ligands — Notch — receptor — ADAM (TACE, Kuzbanian) – metalloprotease for S 2 cleavage — γ -secretase complex (presenilin-containing) for S 3 cleavage — N ICD , or NICD, or ICN – transcriptionally active Notch fragment — CSL, CBF 1/RBPJk, Su. H (suppressor of hairless) – transcription factor
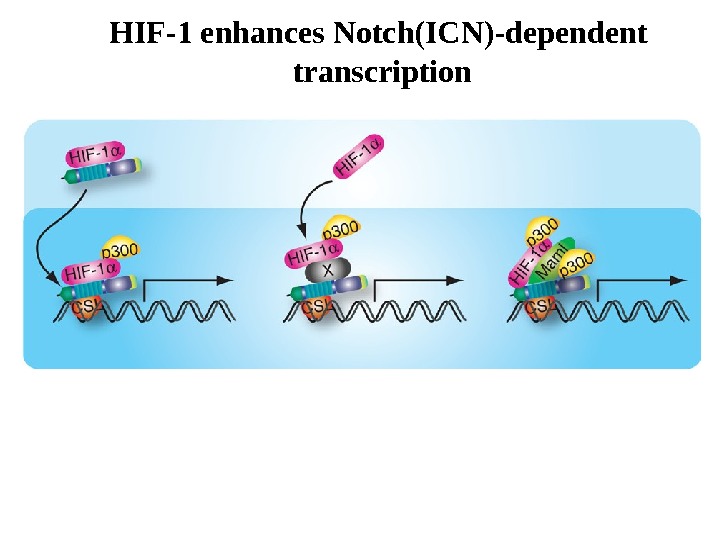
 HIF-1 enhances Notch(ICN)-dependent transcription
HIF-1 enhances Notch(ICN)-dependent transcription
 TGF R-family receptors
TGF R-family receptors
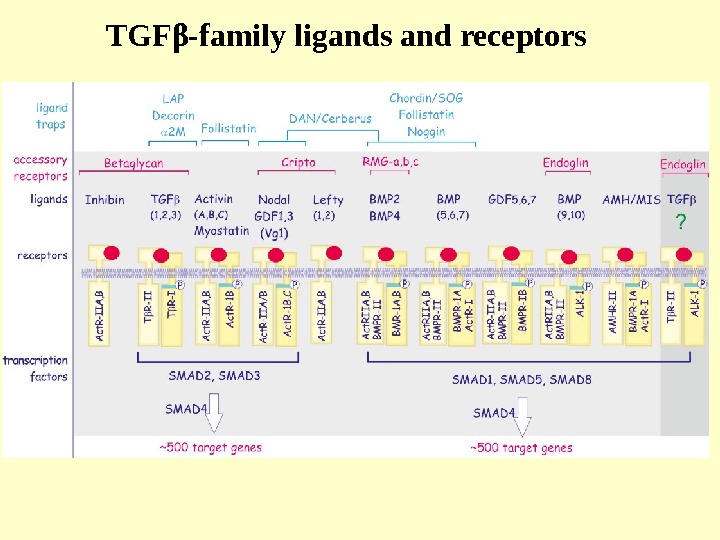
 TGF β -family ligands and receptors
TGF β -family ligands and receptors
 TGF β -family ligands
TGF β -family ligands
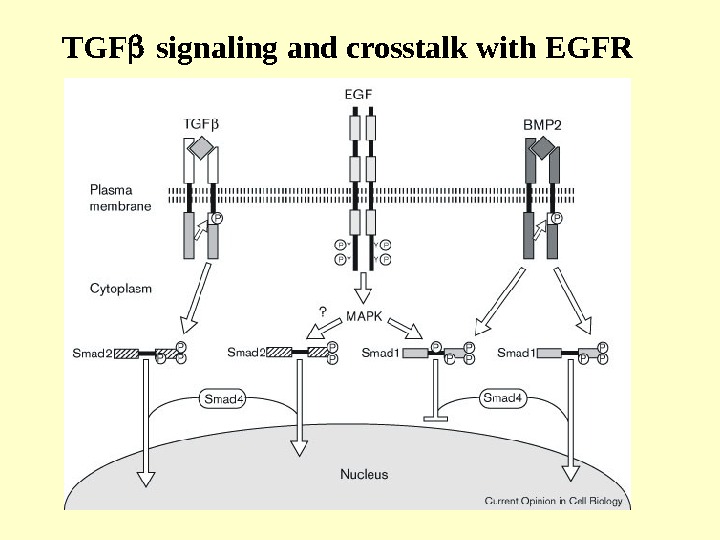
 TGF signaling and crosstalk with EGFR
TGF signaling and crosstalk with EGFR
 TGF Activins co-receptors
TGF Activins co-receptors
 Smad proteins
Smad proteins
 TGF β to p 21 Waf 1 and p 15 Ink
TGF β to p 21 Waf 1 and p 15 Ink
 T R-V signaling
T R-V signaling
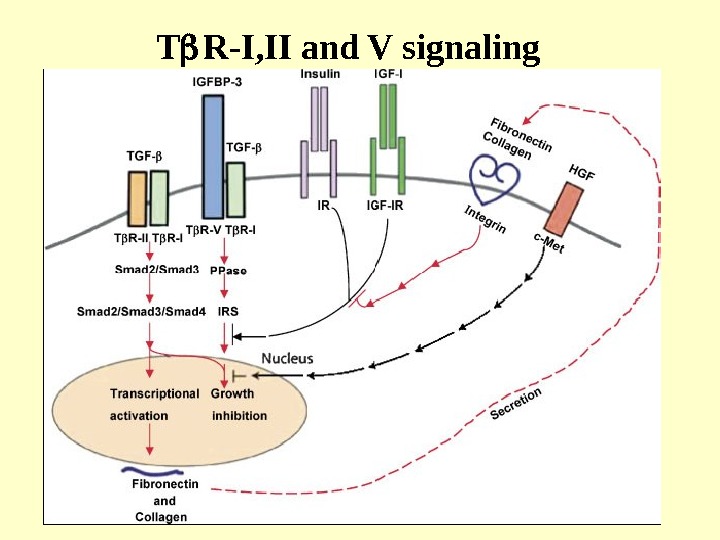
 T R-I, II and V signaling
T R-I, II and V signaling
 T GF -induced growth arrest
T GF -induced growth arrest
 Signaling to gastrulation
Signaling to gastrulation
 STRESS SIGNALING
STRESS SIGNALING
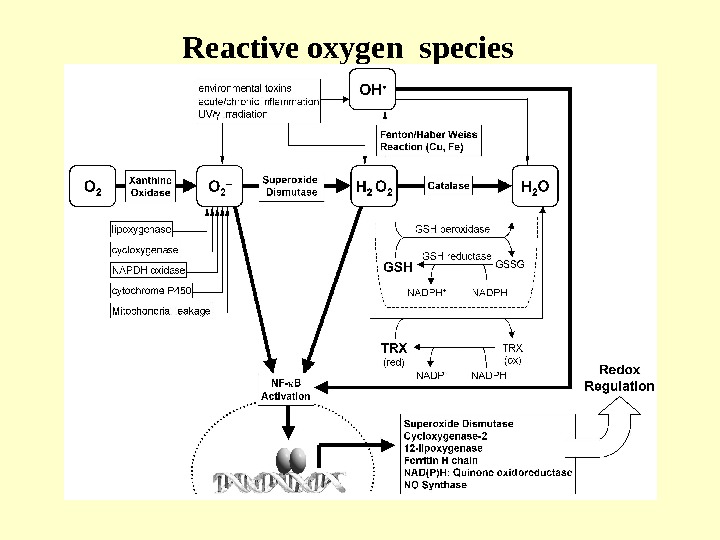
 Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
 Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
 ROS levels 1) Moderate (mostly by NADPH-oxidase to GF, cytokines, TNF α -like ligands; needed for mitogenic signaling) 2) High (mostly stress-induced; usually pro-apoptotic) 3) The highest – a consequence of mitochondrial disfunction during apoptosis
ROS levels 1) Moderate (mostly by NADPH-oxidase to GF, cytokines, TNF α -like ligands; needed for mitogenic signaling) 2) High (mostly stress-induced; usually pro-apoptotic) 3) The highest – a consequence of mitochondrial disfunction during apoptosis
 Oxidative modifications of proteins
Oxidative modifications of proteins
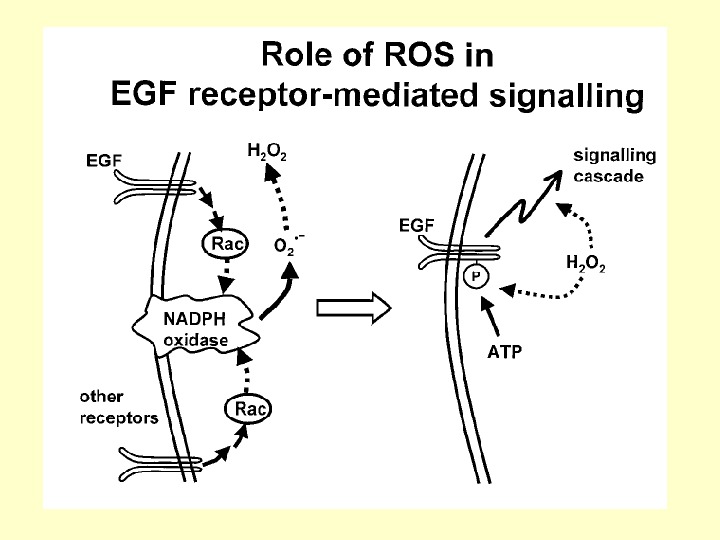
 Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases
Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases

 Cell damage targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD)
Cell damage targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD)
 Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD)
Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD)
 HIF-
HIF-
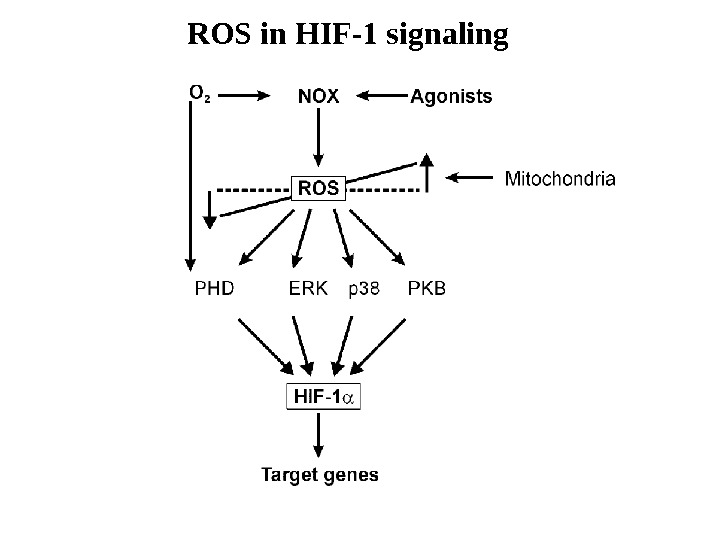
 ROS in HIF-1 signaling
ROS in HIF-1 signaling
 Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD) — ASK-1 ( via thioredoxin) — JNK ( via GSTp) — PKC — Ras — IKK (to NFk. B) — AP-1, p 53 ( via Ref-1)
Signaling targets of ROS — Tyrosine phosphatases — Proline hydroxylase (PHD) — ASK-1 ( via thioredoxin) — JNK ( via GSTp) — PKC — Ras — IKK (to NFk. B) — AP-1, p 53 ( via Ref-1)
 NO
NO
 NO-synthases — i. NOS (inducible) — e. NOS (endothelial) — n. NOS (neuronal)
NO-synthases — i. NOS (inducible) — e. NOS (endothelial) — n. NOS (neuronal)
 Mechanisms of NO action — S-nitrosylation of proteins — peroxynitryl formation — co-factor for soluble guanylate cyclase
Mechanisms of NO action — S-nitrosylation of proteins — peroxynitryl formation — co-factor for soluble guanylate cyclase
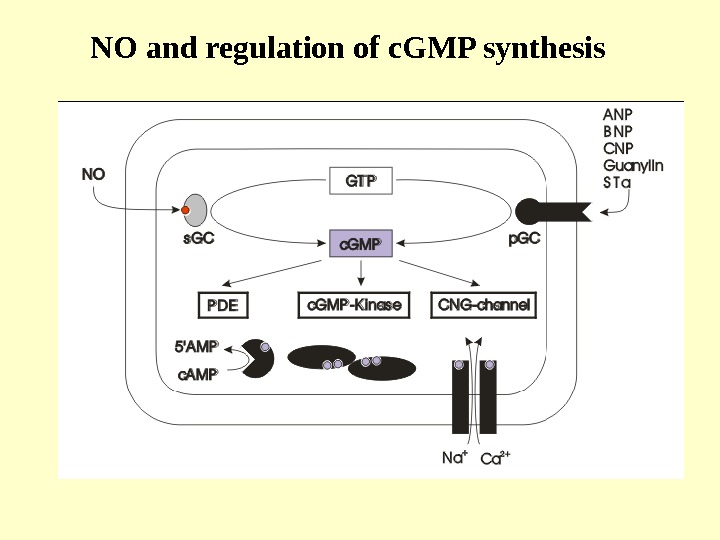
 NO and regulation of c. GMP synthesis
NO and regulation of c. GMP synthesis
 PKG
PKG

