f4ff229a7fa41cbd9dbeee03c9528bc5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Caching Herng-Yow Chen 1
Caching Herng-Yow Chen 1
 Outline n n n How caches improve performance and reduce cost How to measure their effectiveness Where to place caches to maximize impact Also explain how HTTP keeps cached copies fresh How caches interact with other caches and servers 2
Outline n n n How caches improve performance and reduce cost How to measure their effectiveness Where to place caches to maximize impact Also explain how HTTP keeps cached copies fresh How caches interact with other caches and servers 2
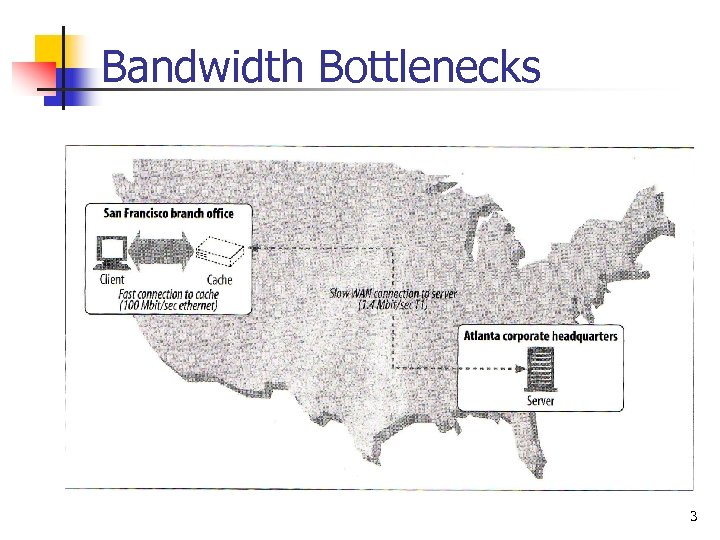 Bandwidth Bottlenecks 3
Bandwidth Bottlenecks 3
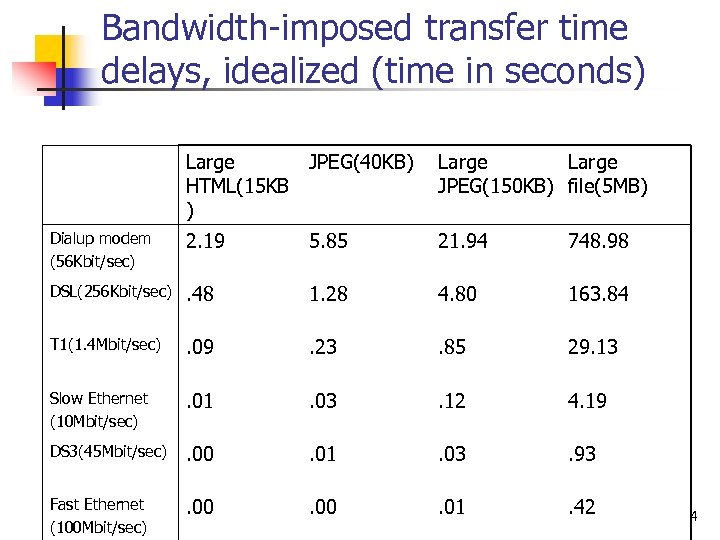 Bandwidth-imposed transfer time delays, idealized (time in seconds) Large JPEG(40 KB) HTML(15 KB ) Large JPEG(150 KB) file(5 MB) Dialup modem (56 Kbit/sec) 2. 19 5. 85 21. 94 748. 98 DSL(256 Kbit/sec) . 48 1. 28 4. 80 163. 84 T 1(1. 4 Mbit/sec) . 09 . 23 . 85 29. 13 Slow Ethernet (10 Mbit/sec) . 01 . 03 . 12 4. 19 DS 3(45 Mbit/sec) . 00 . 01 . 03 . 93 Fast Ethernet (100 Mbit/sec) . 00 . 01 . 42 4
Bandwidth-imposed transfer time delays, idealized (time in seconds) Large JPEG(40 KB) HTML(15 KB ) Large JPEG(150 KB) file(5 MB) Dialup modem (56 Kbit/sec) 2. 19 5. 85 21. 94 748. 98 DSL(256 Kbit/sec) . 48 1. 28 4. 80 163. 84 T 1(1. 4 Mbit/sec) . 09 . 23 . 85 29. 13 Slow Ethernet (10 Mbit/sec) . 01 . 03 . 12 4. 19 DS 3(45 Mbit/sec) . 00 . 01 . 03 . 93 Fast Ethernet (100 Mbit/sec) . 00 . 01 . 42 4
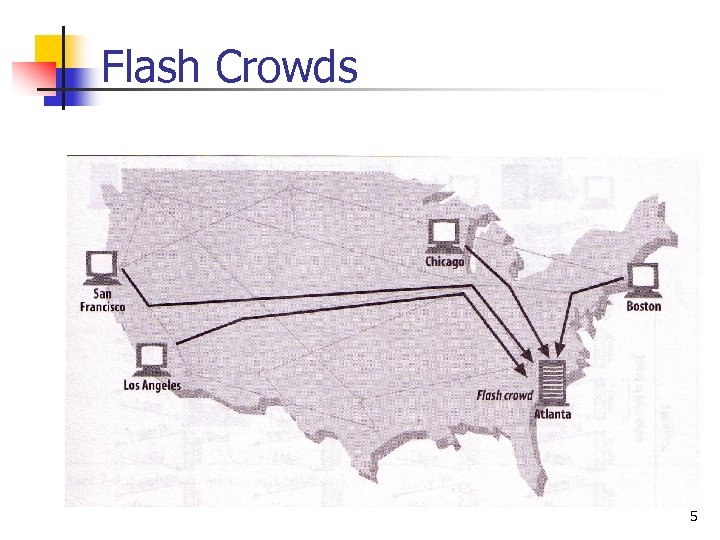 Flash Crowds 5
Flash Crowds 5
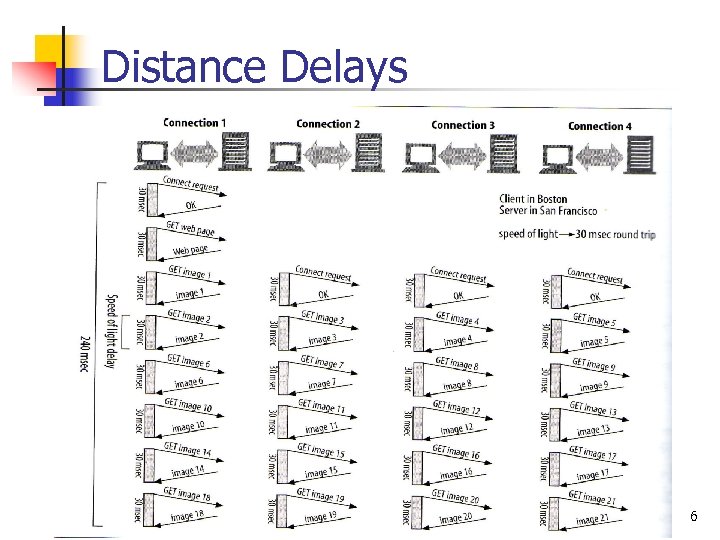 Distance Delays 6
Distance Delays 6
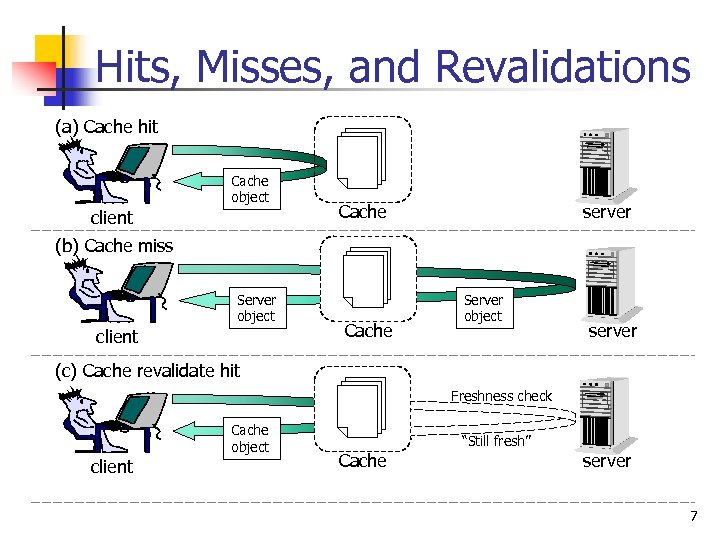 Hits, Misses, and Revalidations (a) Cache hit Cache object client Cache server (b) Cache miss Server object client Cache Server object server (c) Cache revalidate hit Freshness check Cache object client “Still fresh” Cache server 7
Hits, Misses, and Revalidations (a) Cache hit Cache object client Cache server (b) Cache miss Server object client Cache Server object server (c) Cache revalidate hit Freshness check Cache object client “Still fresh” Cache server 7
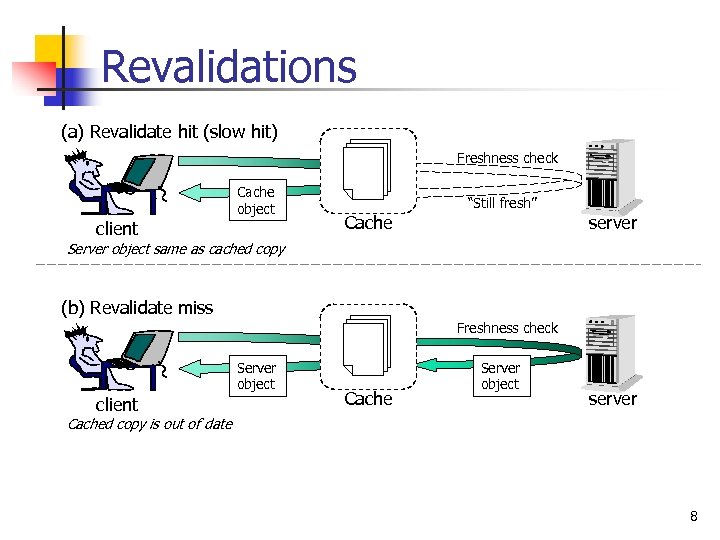 Revalidations (a) Revalidate hit (slow hit) Freshness check Cache object client “Still fresh” Cache server Server object same as cached copy (b) Revalidate miss Freshness check Server object client Cache Server object server Cached copy is out of date 8
Revalidations (a) Revalidate hit (slow hit) Freshness check Cache object client “Still fresh” Cache server Server object same as cached copy (b) Revalidate miss Freshness check Server object client Cache Server object server Cached copy is out of date 8
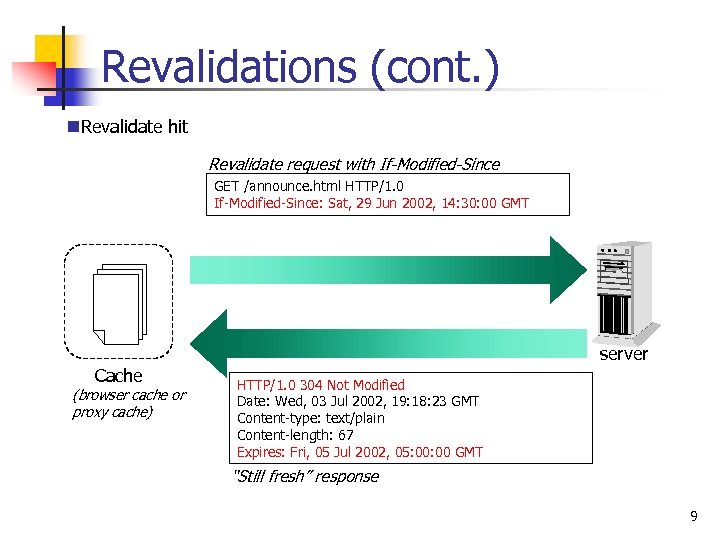 Revalidations (cont. ) n. Revalidate hit Revalidate request with If-Modified-Since GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT server Cache (browser cache or proxy cache) HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT “Still fresh” response 9
Revalidations (cont. ) n. Revalidate hit Revalidate request with If-Modified-Since GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT server Cache (browser cache or proxy cache) HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT “Still fresh” response 9
 Three cases in revalidation n Revalidate hit n n Revalidate miss n n 304 Not Modified response 200 OK response, with the full content Object deleted n 404 Not Found response 10
Three cases in revalidation n Revalidate hit n n Revalidate miss n n 304 Not Modified response 200 OK response, with the full content Object deleted n 404 Not Found response 10
 Cache Performance measurement n Hit Rate (Hit Ratio) n n The fraction of requests that are served from cache. Sometimes it is called document hit ratio. The hit rate ranges from 0 to 1 but is often described as a percentage, e. g. , 0%, 40% (decent) , 100% Goal: even a modest-sized cache may contain enough popular documents to significantly improve performance and reduce traffic. 11
Cache Performance measurement n Hit Rate (Hit Ratio) n n The fraction of requests that are served from cache. Sometimes it is called document hit ratio. The hit rate ranges from 0 to 1 but is often described as a percentage, e. g. , 0%, 40% (decent) , 100% Goal: even a modest-sized cache may contain enough popular documents to significantly improve performance and reduce traffic. 11
 Another metric: Byte Hit Rate n n Represent the faction of all bytes transferred that were served from cache. This metric captures the degree of traffic savings. (e. g. , 100% no traffic went out across the Internet). Is preferred by people who are billed for each byte of traffic. Document hit rate doesn’t tell the whole story, because documents are not all the same size. Some large objects might be accessed less often but contribute more to overall traffic. Document Hit ratio vs. Byte Hit ratio n n Optimize for overall latency reduction. (document hit) Optimize for bandwidth saving (byte hit) 12
Another metric: Byte Hit Rate n n Represent the faction of all bytes transferred that were served from cache. This metric captures the degree of traffic savings. (e. g. , 100% no traffic went out across the Internet). Is preferred by people who are billed for each byte of traffic. Document hit rate doesn’t tell the whole story, because documents are not all the same size. Some large objects might be accessed less often but contribute more to overall traffic. Document Hit ratio vs. Byte Hit ratio n n Optimize for overall latency reduction. (document hit) Optimize for bandwidth saving (byte hit) 12
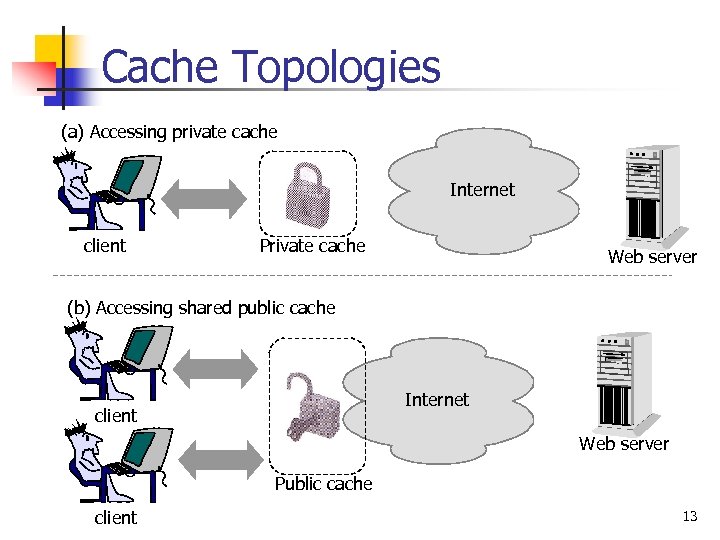 Cache Topologies (a) Accessing private cache Internet client Private cache Web server (b) Accessing shared public cache Internet client Web server Public cache client 13
Cache Topologies (a) Accessing private cache Internet client Private cache Web server (b) Accessing shared public cache Internet client Web server Public cache client 13
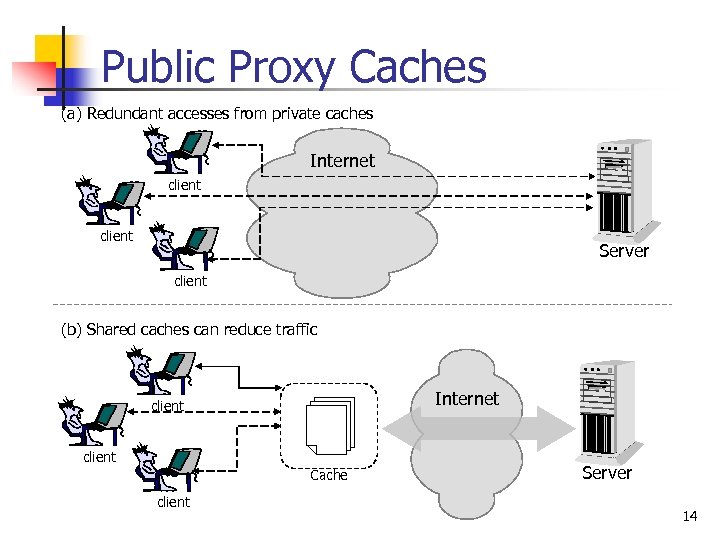 Public Proxy Caches (a) Redundant accesses from private caches Internet client Server client (b) Shared caches can reduce traffic Internet client Cache client Server 14
Public Proxy Caches (a) Redundant accesses from private caches Internet client Server client (b) Shared caches can reduce traffic Internet client Cache client Server 14
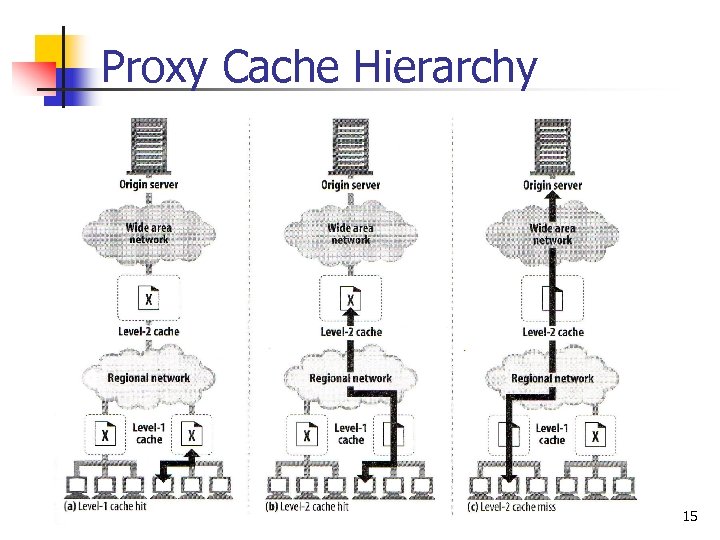 Proxy Cache Hierarchy 15
Proxy Cache Hierarchy 15
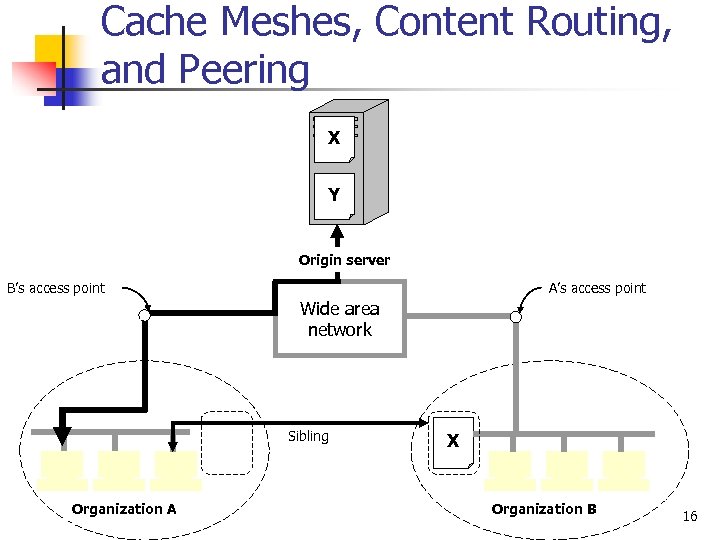 Cache Meshes, Content Routing, and Peering X Y Origin server B’s access point A’s access point Wide area network Sibling Organization A X Organization B 16
Cache Meshes, Content Routing, and Peering X Y Origin server B’s access point A’s access point Wide area network Sibling Organization A X Organization B 16
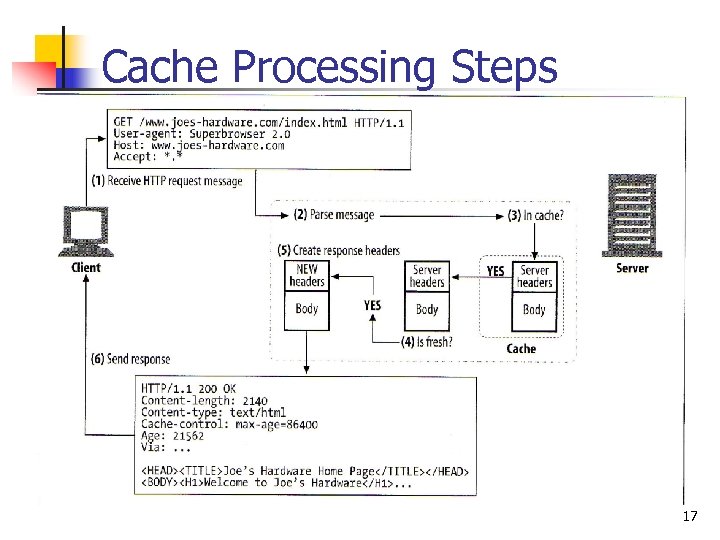 Cache Processing Steps 17
Cache Processing Steps 17
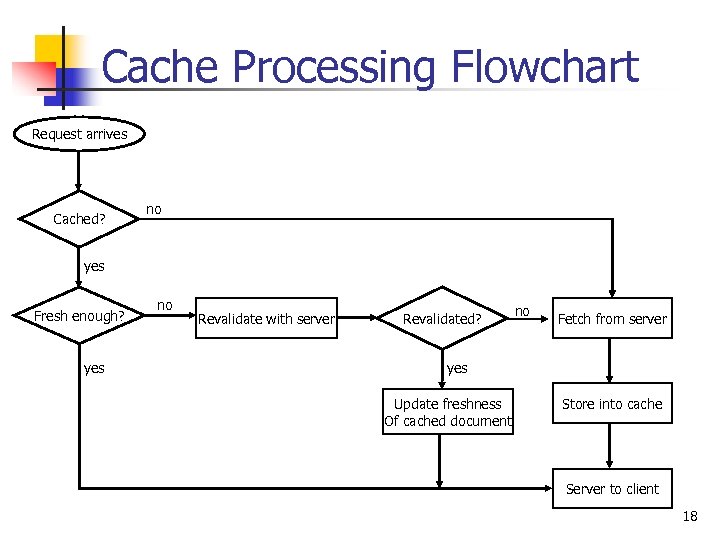 Cache Processing Flowchart Request arrives Cached? no yes Fresh enough? yes no Revalidate with server Revalidated? no Fetch from server yes Update freshness Of cached document Store into cache Server to client 18
Cache Processing Flowchart Request arrives Cached? no yes Fresh enough? yes no Revalidate with server Revalidated? no Fetch from server yes Update freshness Of cached document Store into cache Server to client 18
 Document Expiration HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Cache-Control: max-age=484200 Independence Day sale at Joe’s Hardware Come shop with us today! (a) Expires header (b) Cache-Control: max-age header 19
Document Expiration HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 67 Cache-Control: max-age=484200 Independence Day sale at Joe’s Hardware Come shop with us today! (a) Expires header (b) Cache-Control: max-age header 19
 Expiration response headers Header Description Cache-Control: max-age The max-age value defines the maximum age of the document-the maximum legal elapsed time(in seconds) from when a document is first generated to when it can no longer be considered fresh enough to serve. Cache-Control: max-age=484200 Expires Specifies an absolute expiration date. If the expiration date is in the past, the document is no longer fresh. Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT 20
Expiration response headers Header Description Cache-Control: max-age The max-age value defines the maximum age of the document-the maximum legal elapsed time(in seconds) from when a document is first generated to when it can no longer be considered fresh enough to serve. Cache-Control: max-age=484200 Expires Specifies an absolute expiration date. If the expiration date is in the past, the document is no longer fresh. Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT 20
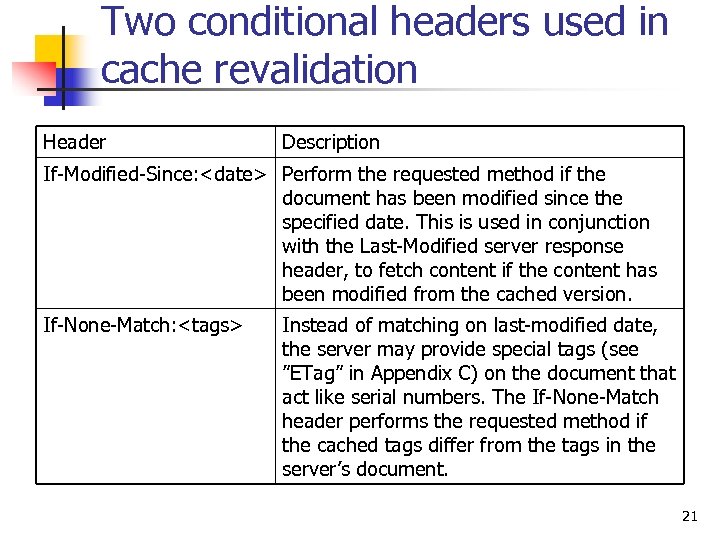 Two conditional headers used in cache revalidation Header Description If-Modified-Since:
Two conditional headers used in cache revalidation Header Description If-Modified-Since:
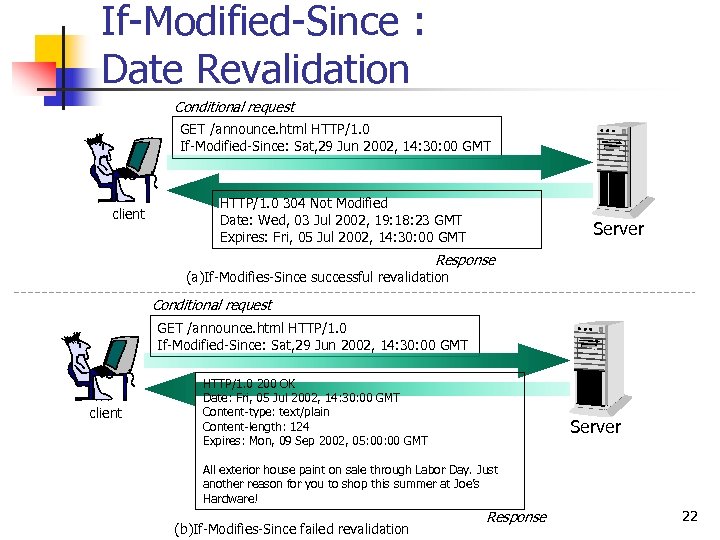 If-Modified-Since : Date Revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT client HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Server Response (a)If-Modifies-Since successful revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT client HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 124 Expires: Mon, 09 Sep 2002, 05: 00 GMT Server All exterior house paint on sale through Labor Day. Just another reason for you to shop this summer at Joe’s Hardware! (b)If-Modifies-Since failed revalidation Response 22
If-Modified-Since : Date Revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT client HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Server Response (a)If-Modifies-Since successful revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Jun 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT client HTTP/1. 0 200 OK Date: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 14: 30: 00 GMT Content-type: text/plain Content-length: 124 Expires: Mon, 09 Sep 2002, 05: 00 GMT Server All exterior house paint on sale through Labor Day. Just another reason for you to shop this summer at Joe’s Hardware! (b)If-Modifies-Since failed revalidation Response 22
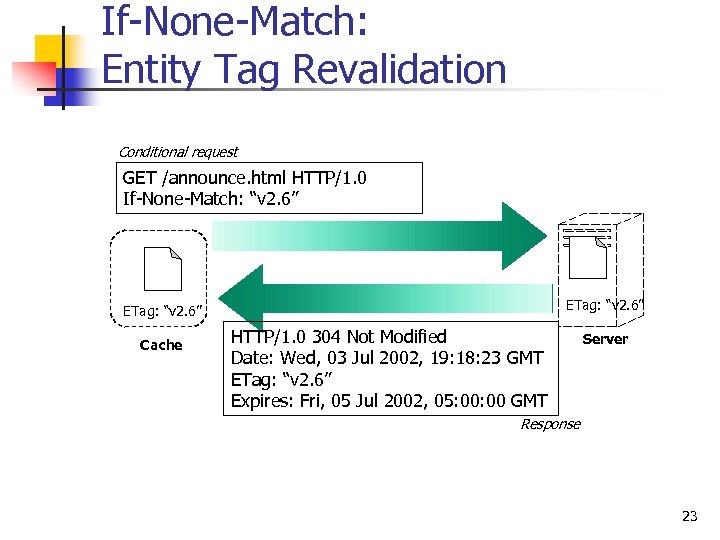 If-None-Match: Entity Tag Revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-None-Match: “v 2. 6” ETag: “v 2. 6” Cache HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT ETag: “v 2. 6” Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT Server Response 23
If-None-Match: Entity Tag Revalidation Conditional request GET /announce. html HTTP/1. 0 If-None-Match: “v 2. 6” ETag: “v 2. 6” Cache HTTP/1. 0 304 Not Modified Date: Wed, 03 Jul 2002, 19: 18: 23 GMT ETag: “v 2. 6” Expires: Fri, 05 Jul 2002, 05: 00 GMT Server Response 23
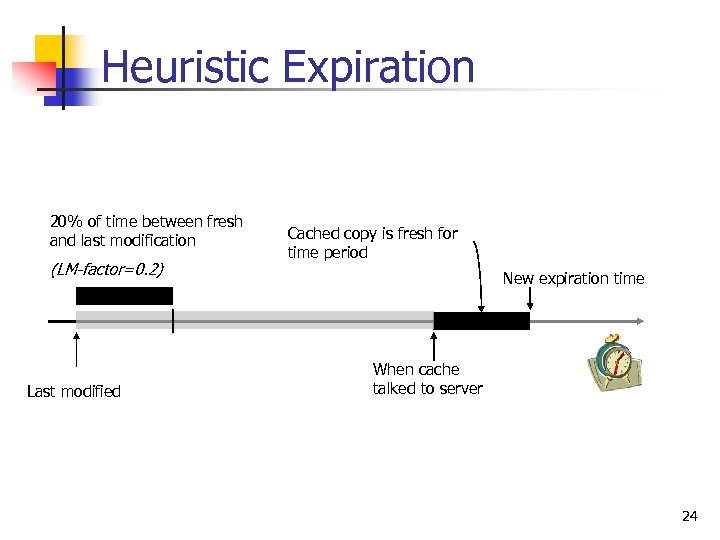 Heuristic Expiration 20% of time between fresh and last modification (LM-factor=0. 2) Last modified Cached copy is fresh for time period New expiration time When cache talked to server 24
Heuristic Expiration 20% of time between fresh and last modification (LM-factor=0. 2) Last modified Cached copy is fresh for time period New expiration time When cache talked to server 24
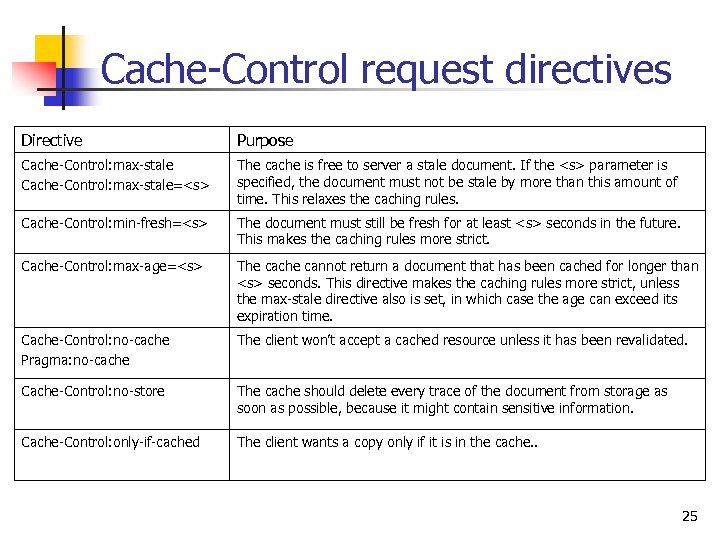 Cache-Control request directives Directive Purpose Cache-Control: max-stale=
Cache-Control request directives Directive Purpose Cache-Control: max-stale= The cache is free to server a stale document. If the parameter is specified, the document must not be stale by more than this amount of time. This relaxes the caching rules. Cache-Control: min-fresh= The document must still be fresh for at least seconds in the future. This makes the caching rules more strict. Cache-Control: max-age= The cache cannot return a document that has been cached for longer than seconds. This directive makes the caching rules more strict, unless the max-stale directive also is set, in which case the age can exceed its expiration time. Cache-Control: no-cache Pragma: no-cache The client won’t accept a cached resource unless it has been revalidated. Cache-Control: no-store The cache should delete every trace of the document from storage as soon as possible, because it might contain sensitive information. Cache-Control: only-if-cached The client wants a copy only if it is in the cache. . 25
 HTTP-EQUIV tags cause problems, because most software ignores them 26
HTTP-EQUIV tags cause problems, because most software ignores them 26
 Reference: Caching nhttp: //www. w 3. org/protocols/rfc 2616. txt RFC 2616, “Hypertext Transfer Protocol, ” by R. Fielding, J. Gettys, J. Mongul, H. Frystyk, L. Mastinter, P. Leach, and T. Berners-Lee. n. Web Caching Duane Wessels, O’Reilly & Associates, Inc. nhttp: //search. ietf. org/rfc 3040. txt RFC 3040, “Internet Web Replication and Caching Taxonomy. ” n. Web Proxy Servers Ari Luotinen, Prentice Hall Computer Books. nhttp: //search. ietf. org/rfc 3143. txt RFC 3143, “Know HTTP Proxy/Caching Problems. ” nhttp: //www. squid-cache. org Squid Web Proxy Cache. 28
Reference: Caching nhttp: //www. w 3. org/protocols/rfc 2616. txt RFC 2616, “Hypertext Transfer Protocol, ” by R. Fielding, J. Gettys, J. Mongul, H. Frystyk, L. Mastinter, P. Leach, and T. Berners-Lee. n. Web Caching Duane Wessels, O’Reilly & Associates, Inc. nhttp: //search. ietf. org/rfc 3040. txt RFC 3040, “Internet Web Replication and Caching Taxonomy. ” n. Web Proxy Servers Ari Luotinen, Prentice Hall Computer Books. nhttp: //search. ietf. org/rfc 3143. txt RFC 3143, “Know HTTP Proxy/Caching Problems. ” nhttp: //www. squid-cache. org Squid Web Proxy Cache. 28


