78efadf0e09736e89a83ce0e2f27af0d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Caching Dynamic Skyline Queries D. Sacharidis 1, P. Bouros 1, T. Sellis 1, 2 1 National Technical University of Athens 2 Institute for Management of Information Systems – R. C. Athena July 29 HDMS'08
Caching Dynamic Skyline Queries D. Sacharidis 1, P. Bouros 1, T. Sellis 1, 2 1 National Technical University of Athens 2 Institute for Management of Information Systems – R. C. Athena July 29 HDMS'08
 Outline • Introduction – Skyline (SL) and dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Related work • Evaluating dynamic skyline queries – Computing orthant skylines (OSL) – Computing dynamic skyline via caching • LRU, LFU, LPP cache replacement policies • Experimental evaluation • Conclusions and Future work July 29 HDMS'08
Outline • Introduction – Skyline (SL) and dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Related work • Evaluating dynamic skyline queries – Computing orthant skylines (OSL) – Computing dynamic skyline via caching • LRU, LFU, LPP cache replacement policies • Experimental evaluation • Conclusions and Future work July 29 HDMS'08
 Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one July 29 HDMS'08
Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one July 29 HDMS'08
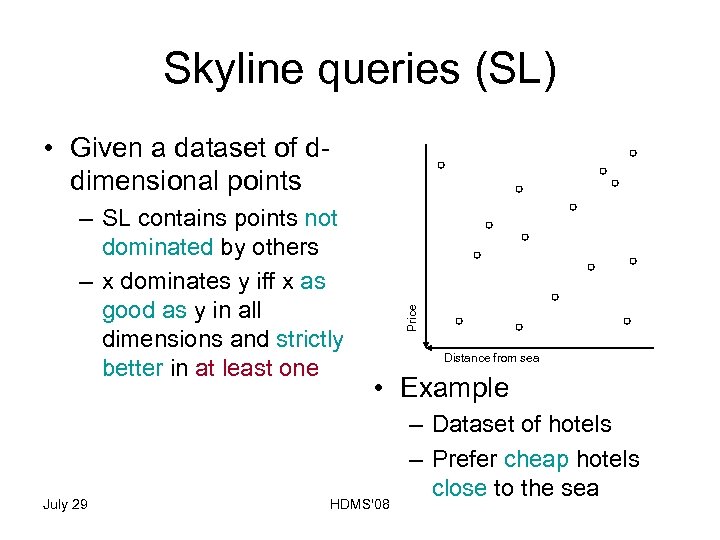 Skyline queries (SL) – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one July 29 Price • Given a dataset of ddimensional points Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
Skyline queries (SL) – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one July 29 Price • Given a dataset of ddimensional points Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
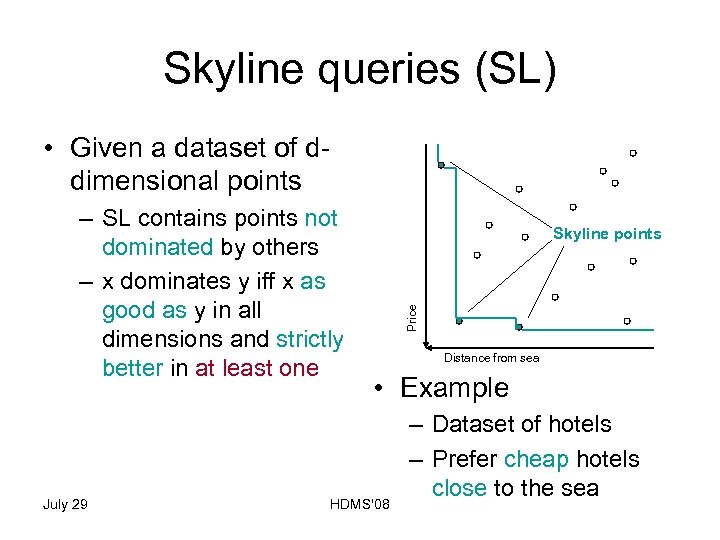 Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
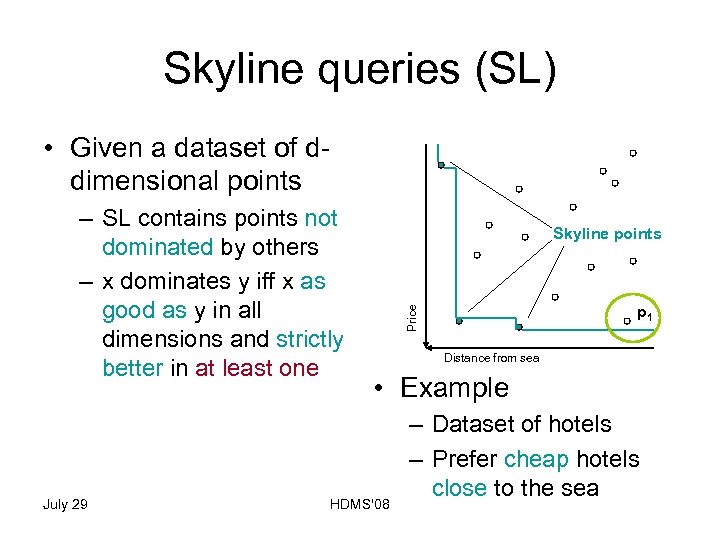 Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points p 1 Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points p 1 Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
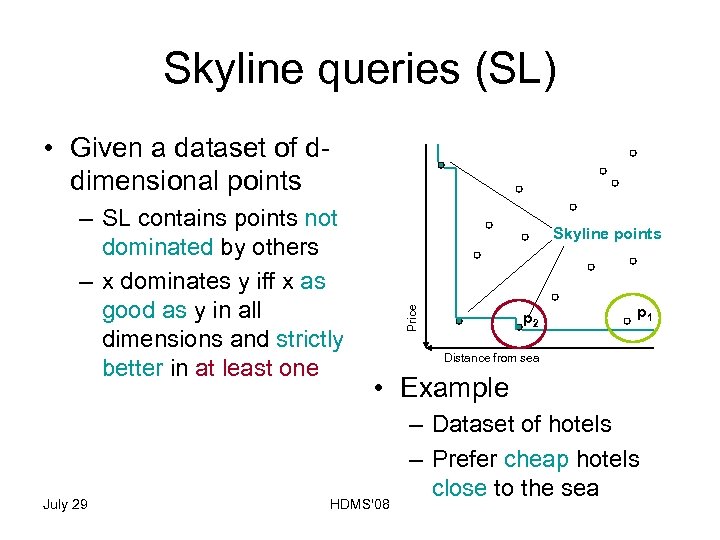 Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one p 2 p 1 Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
Skyline queries (SL) • Given a dataset of ddimensional points July 29 Skyline points Price – SL contains points not dominated by others – x dominates y iff x as good as y in all dimensions and strictly better in at least one p 2 p 1 Distance from sea • Example HDMS'08 – Dataset of hotels – Prefer cheap hotels close to the sea
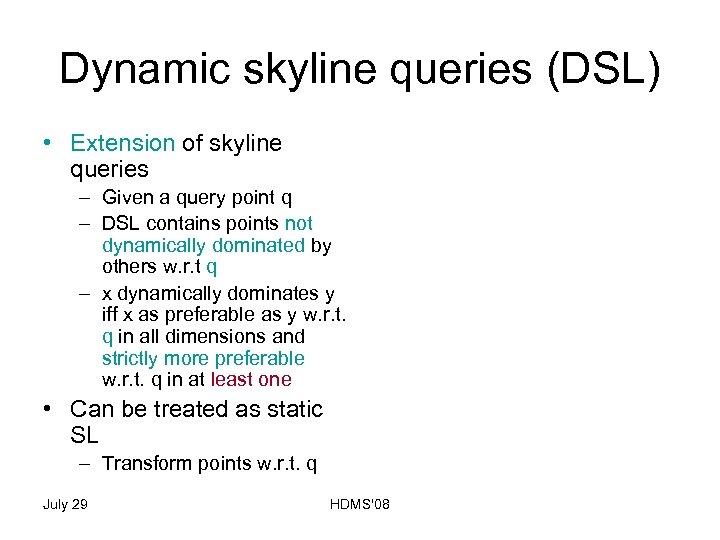 Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one • Can be treated as static SL – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one • Can be treated as static SL – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
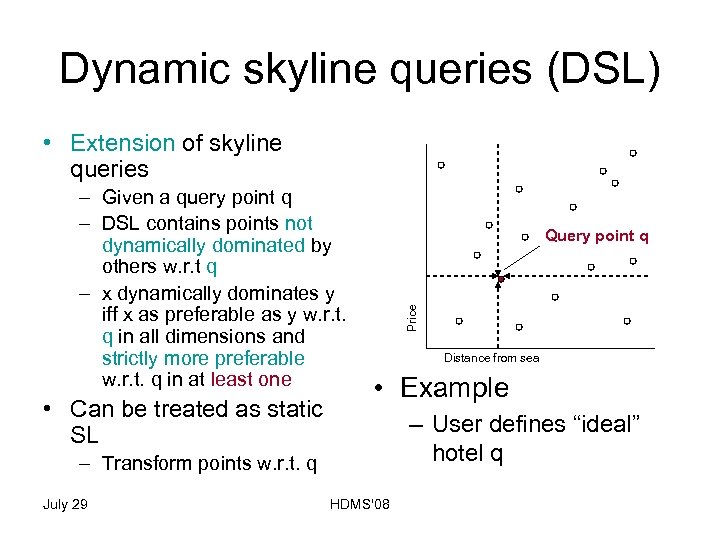 Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries • Can be treated as static SL Query point q Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries • Can be treated as static SL Query point q Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
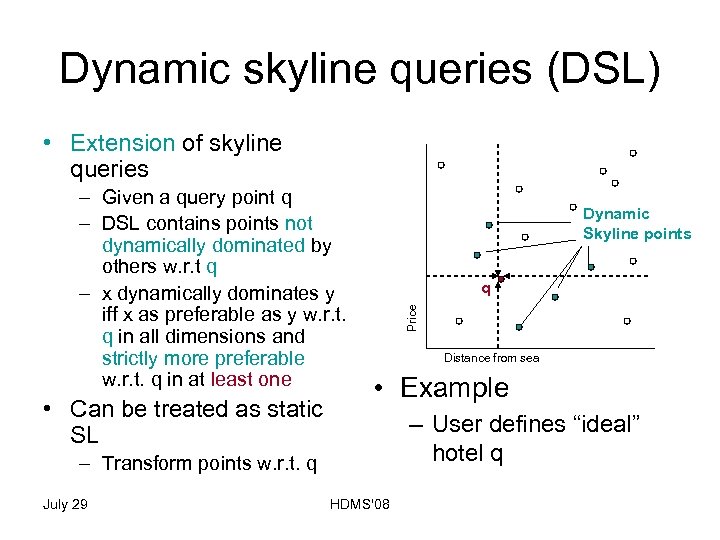 Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries • Can be treated as static SL Dynamic Skyline points q Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries • Can be treated as static SL Dynamic Skyline points q Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 HDMS'08
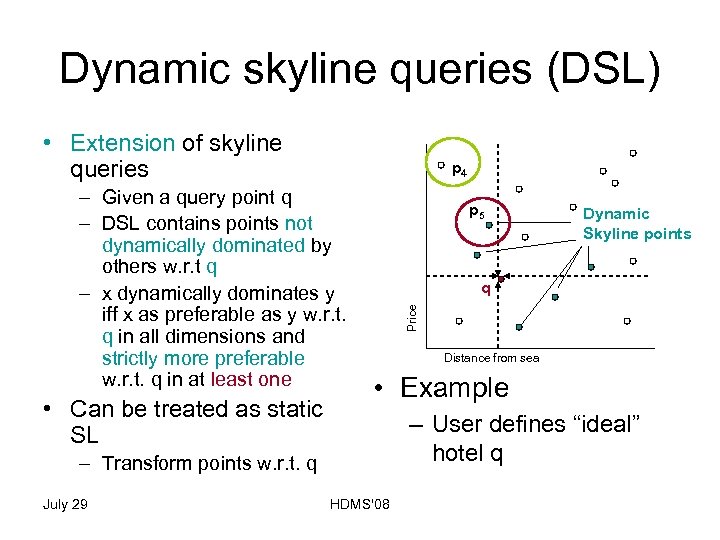 Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries p 4 • Can be treated as static SL p 5 q Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 Dynamic Skyline points Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one HDMS'08
Dynamic skyline queries (DSL) • Extension of skyline queries p 4 • Can be treated as static SL p 5 q Distance from sea • Example – User defines “ideal” hotel q – Transform points w. r. t. q July 29 Dynamic Skyline points Price – Given a query point q – DSL contains points not dynamically dominated by others w. r. t q – x dynamically dominates y iff x as preferable as y w. r. t. q in all dimensions and strictly more preferable w. r. t. q in at least one HDMS'08
 Intuition (1) • Traditional SL algorithms need to run anew for each DSL query • Our idea – Exploit results from past queries to reduce processing cost for future DSL queries – Cache past queries – Decide which queries in cache are useful July 29 HDMS'08
Intuition (1) • Traditional SL algorithms need to run anew for each DSL query • Our idea – Exploit results from past queries to reduce processing cost for future DSL queries – Cache past queries – Decide which queries in cache are useful July 29 HDMS'08
 Price Intuition (2) Distance from sea July 29 HDMS'08
Price Intuition (2) Distance from sea July 29 HDMS'08
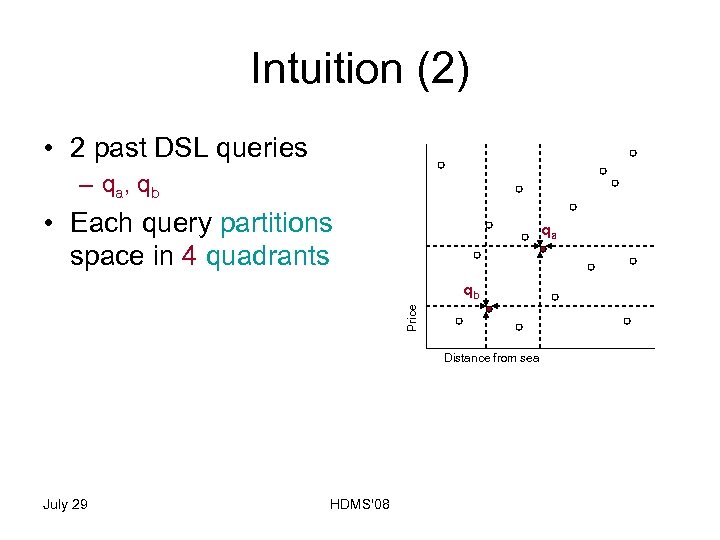 Intuition (2) • 2 past DSL queries – q a, q b • Each query partitions space in 4 quadrants qa Price qb Distance from sea July 29 HDMS'08
Intuition (2) • 2 past DSL queries – q a, q b • Each query partitions space in 4 quadrants qa Price qb Distance from sea July 29 HDMS'08
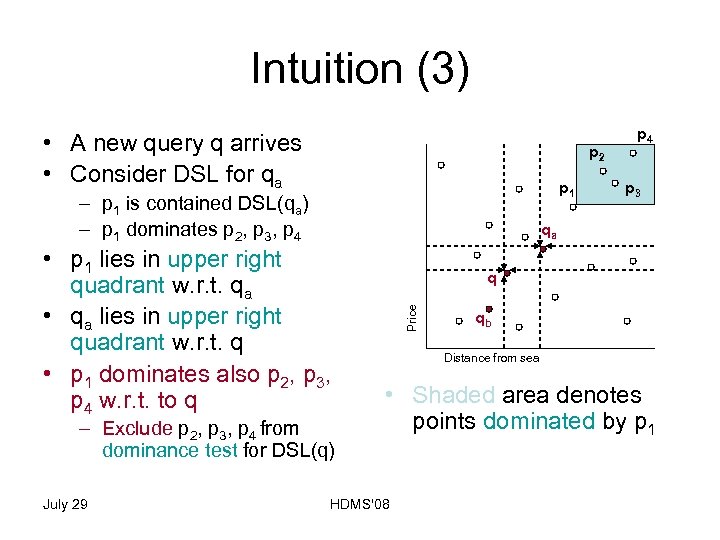 Intuition (3) • A new query q arrives • Consider DSL for qa p 2 p 1 – p 1 is contained DSL(qa) – p 1 dominates p 2, p 3, p 4 p 3 qa – Exclude p 2, p 3, p 4 from dominance test for DSL(q) q Price • p 1 lies in upper right quadrant w. r. t. qa • qa lies in upper right quadrant w. r. t. q • p 1 dominates also p 2, p 3, p 4 w. r. t. to q July 29 p 4 qb Distance from sea • Shaded area denotes points dominated by p 1 HDMS'08
Intuition (3) • A new query q arrives • Consider DSL for qa p 2 p 1 – p 1 is contained DSL(qa) – p 1 dominates p 2, p 3, p 4 p 3 qa – Exclude p 2, p 3, p 4 from dominance test for DSL(q) q Price • p 1 lies in upper right quadrant w. r. t. qa • qa lies in upper right quadrant w. r. t. q • p 1 dominates also p 2, p 3, p 4 w. r. t. to q July 29 p 4 qb Distance from sea • Shaded area denotes points dominated by p 1 HDMS'08
 Contribution in brief • Caching past DSL queries cannot reduce processing cost for future ones – We need more information about dominance relationships • Introduce orthant skylines (OSL) and examine their relationship with DSL • Extend Bitmap algorithm to compute OSL in parallel with DSL • Cache OSL to enhance DSL queries evaluation – Present 3 cache replacement policies • LRU, LFU, LPP • Experimental evaluation of caching mechanism July 29 HDMS'08
Contribution in brief • Caching past DSL queries cannot reduce processing cost for future ones – We need more information about dominance relationships • Introduce orthant skylines (OSL) and examine their relationship with DSL • Extend Bitmap algorithm to compute OSL in parallel with DSL • Cache OSL to enhance DSL queries evaluation – Present 3 cache replacement policies • LRU, LFU, LPP • Experimental evaluation of caching mechanism July 29 HDMS'08
 Related work • Non-indexed methods – – Block-Nested Loops (Bn. L) Bitmap Multidimensional Divide and Conquer (Dn. C) Sort First Scan (SFS) • Index-based methods – B-tree • sort points according to the lowest valued coordinate – R-tree • Nearest neighbor based (NN) • Branch and bound (BBS) July 29 HDMS'08
Related work • Non-indexed methods – – Block-Nested Loops (Bn. L) Bitmap Multidimensional Divide and Conquer (Dn. C) Sort First Scan (SFS) • Index-based methods – B-tree • sort points according to the lowest valued coordinate – R-tree • Nearest neighbor based (NN) • Branch and bound (BBS) July 29 HDMS'08
 Related work • Non-indexed methods – – Block-Nested Loops (Bn. L) Bitmap Multidimensional Divide and Conquer (Dn. C) Sort First Scan (SFS) • Index-based methods – B-tree • sort points according to the lowest valued coordinate – R-tree • Nearest neighbor based (NN) • Branch and bound (BBS) July 29 HDMS'08
Related work • Non-indexed methods – – Block-Nested Loops (Bn. L) Bitmap Multidimensional Divide and Conquer (Dn. C) Sort First Scan (SFS) • Index-based methods – B-tree • sort points according to the lowest valued coordinate – R-tree • Nearest neighbor based (NN) • Branch and bound (BBS) July 29 HDMS'08
 Bitmap • Bn. L variant • Suitable for domains with low cardinality and discrete • In brief – Computes a bitmap representation of the points in the dataset – Examines each point separately (dominance test) • Checks whether it is contained in the skyline or not • Exploits fast bitwise operations OR/AND July 29 HDMS'08
Bitmap • Bn. L variant • Suitable for domains with low cardinality and discrete • In brief – Computes a bitmap representation of the points in the dataset – Examines each point separately (dominance test) • Checks whether it is contained in the skyline or not • Exploits fast bitwise operations OR/AND July 29 HDMS'08
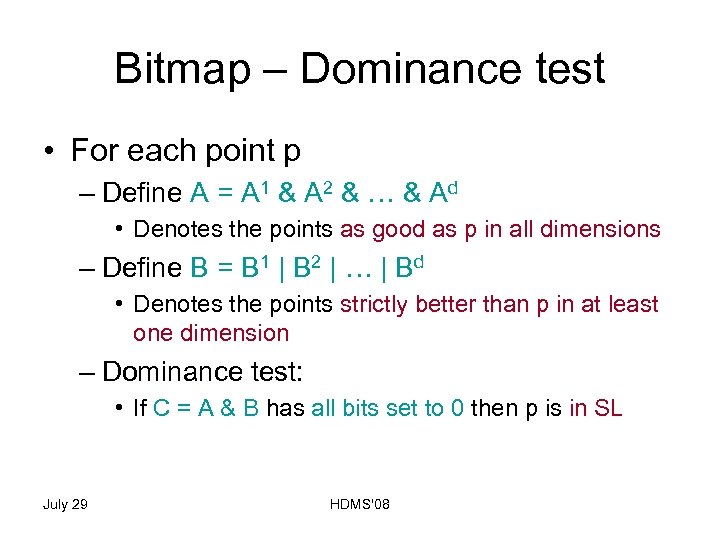 Bitmap – Dominance test • For each point p – Define A = A 1 & A 2 & … & Ad • Denotes the points as good as p in all dimensions – Define B = B 1 | B 2 | … | Bd • Denotes the points strictly better than p in at least one dimension – Dominance test: • If C = A & B has all bits set to 0 then p is in SL July 29 HDMS'08
Bitmap – Dominance test • For each point p – Define A = A 1 & A 2 & … & Ad • Denotes the points as good as p in all dimensions – Define B = B 1 | B 2 | … | Bd • Denotes the points strictly better than p in at least one dimension – Dominance test: • If C = A & B has all bits set to 0 then p is in SL July 29 HDMS'08
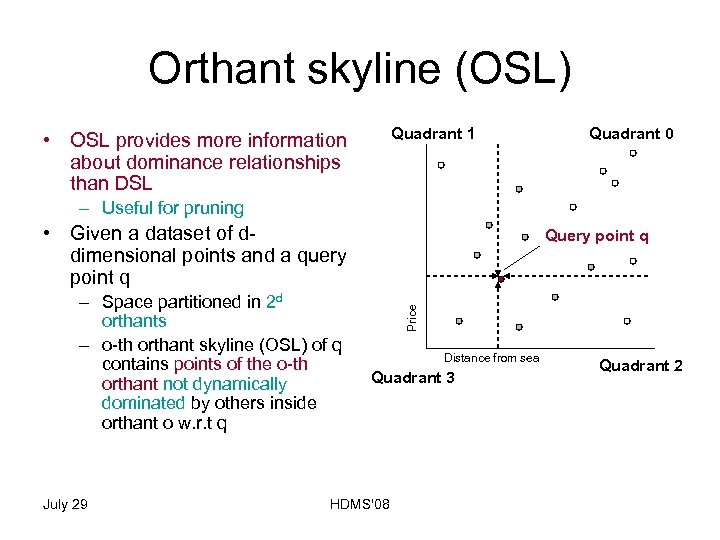
 Orthant skyline (OSL) • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q July 29 HDMS'08
Orthant skyline (OSL) • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q July 29 HDMS'08
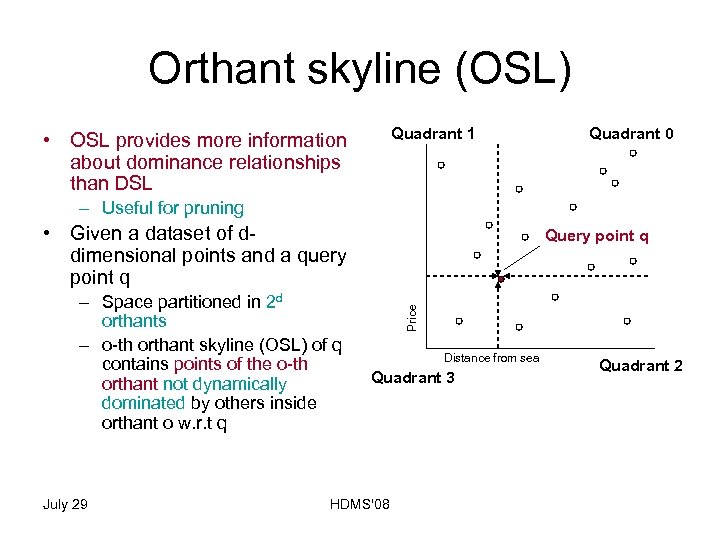 Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q July 29 Price – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q July 29 Price – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
 Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q July 29 Price – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q July 29 Price – Space partitioned in 2 d orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
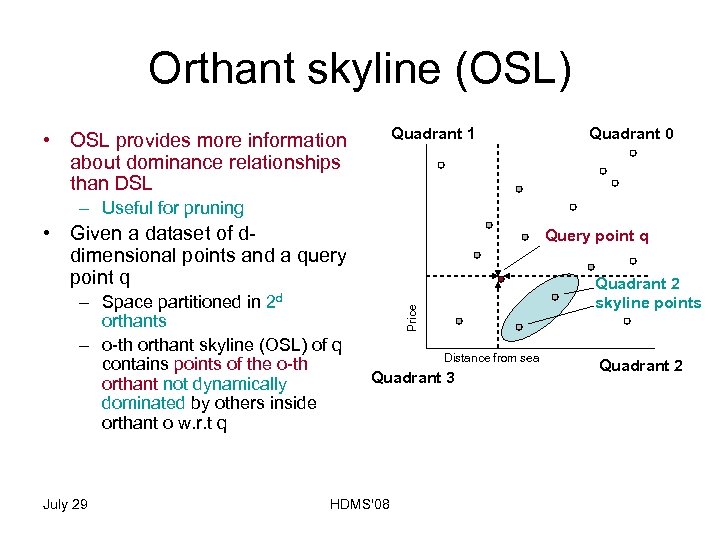 Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q – Space partitioned in orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q July 29 Quadrant 2 skyline points Price 2 d Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
Orthant skyline (OSL) Quadrant 1 • OSL provides more information about dominance relationships than DSL Quadrant 0 – Useful for pruning • Given a dataset of ddimensional points and a query point q – Space partitioned in orthants – o-th orthant skyline (OSL) of q contains points of the o-th orthant not dynamically dominated by others inside orthant o w. r. t q Query point q July 29 Quadrant 2 skyline points Price 2 d Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
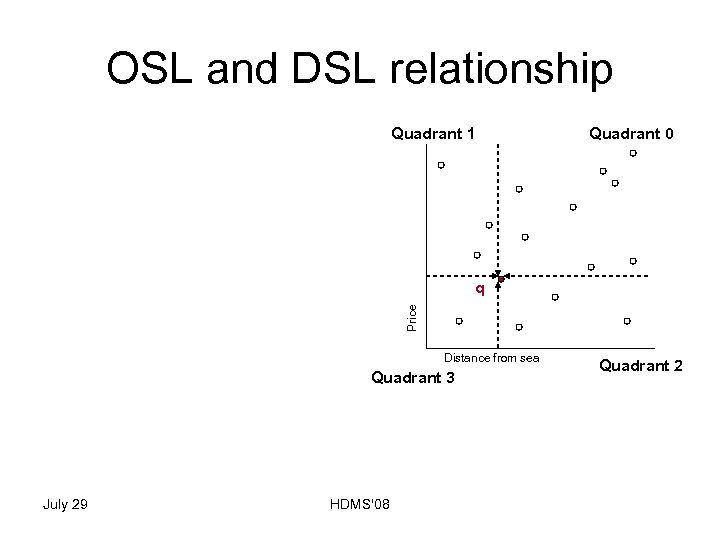 OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
 OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
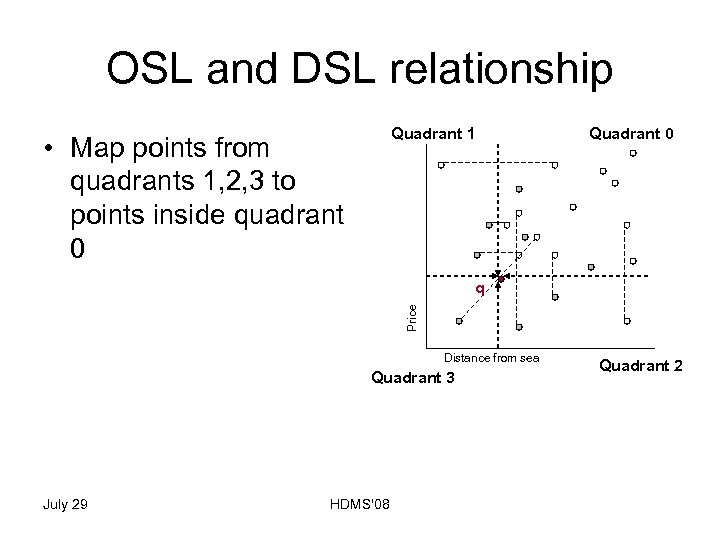 OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
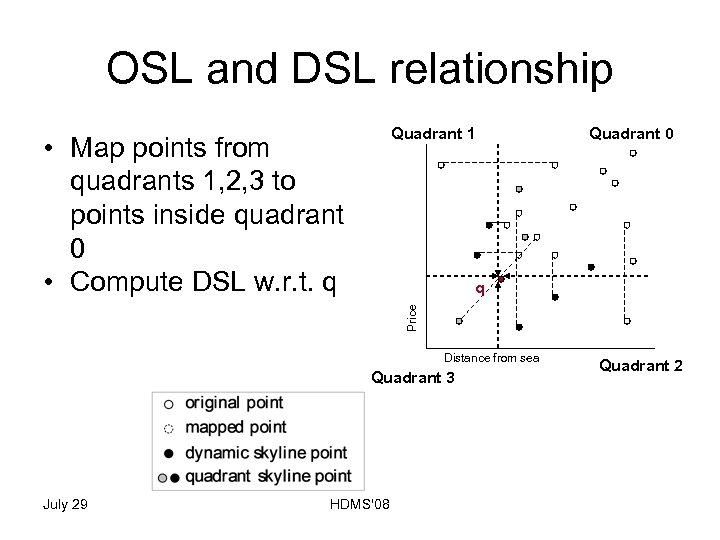 OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship Quadrant 1 • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q Quadrant 0 Price q Distance from sea Quadrant 3 July 29 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
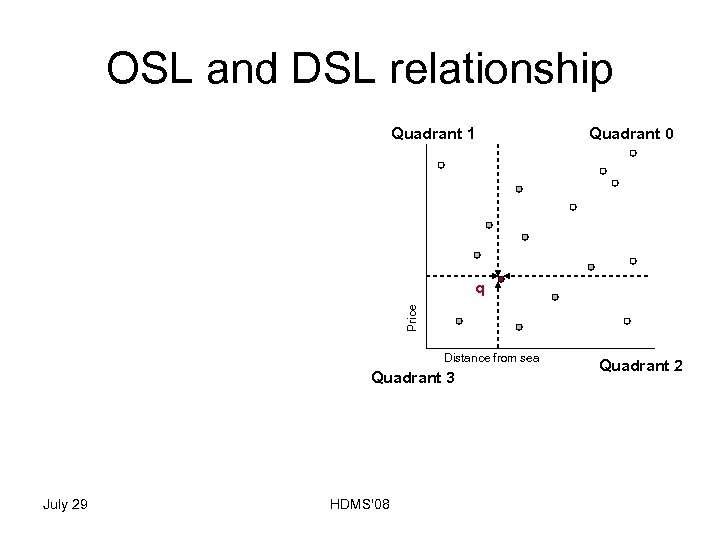
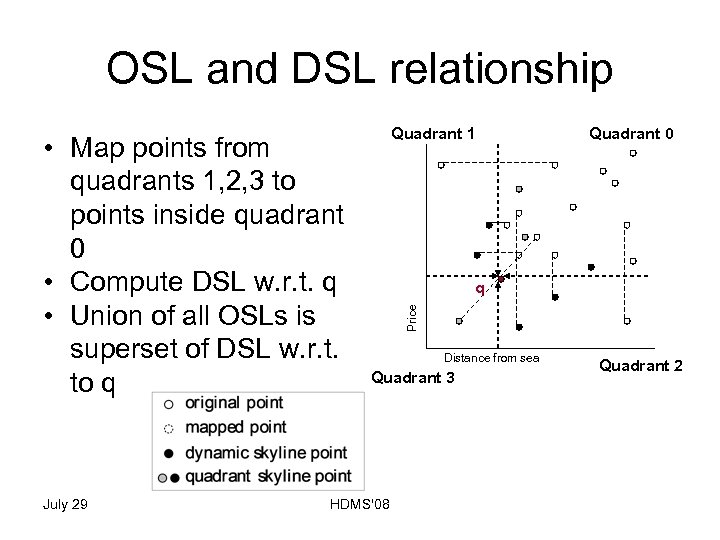 OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
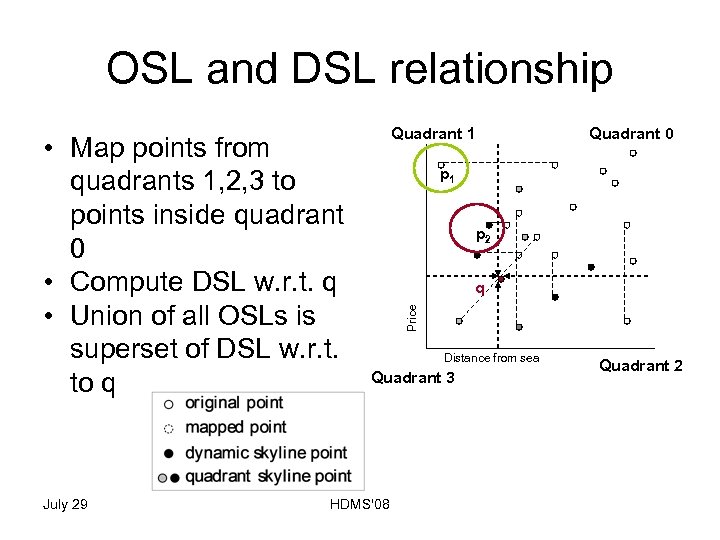 OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 p 1 p 2 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 p 1 p 2 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
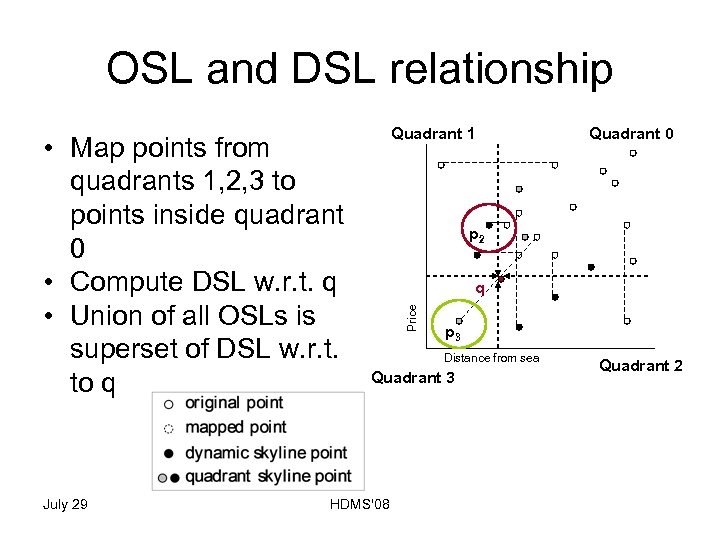 OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 p 2 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 p 3 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
OSL and DSL relationship July 29 Quadrant 0 p 2 q Price • Map points from quadrants 1, 2, 3 to points inside quadrant 0 • Compute DSL w. r. t. q • Union of all OSLs is superset of DSL w. r. t. to q Quadrant 1 p 3 Distance from sea Quadrant 3 HDMS'08 Quadrant 2
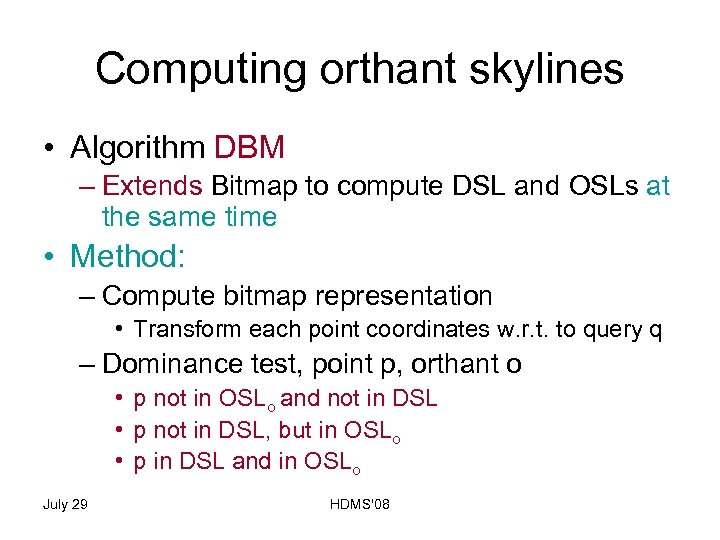 Computing orthant skylines • Algorithm DBM – Extends Bitmap to compute DSL and OSLs at the same time • Method: – Compute bitmap representation • Transform each point coordinates w. r. t. to query q – Dominance test, point p, orthant o • p not in OSLo and not in DSL • p not in DSL, but in OSLo • p in DSL and in OSLo July 29 HDMS'08
Computing orthant skylines • Algorithm DBM – Extends Bitmap to compute DSL and OSLs at the same time • Method: – Compute bitmap representation • Transform each point coordinates w. r. t. to query q – Dominance test, point p, orthant o • p not in OSLo and not in DSL • p not in DSL, but in OSLo • p in DSL and in OSLo July 29 HDMS'08
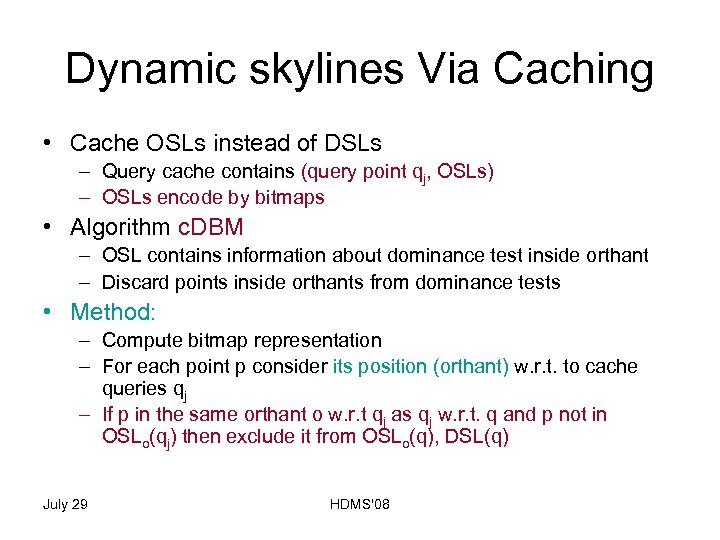 Dynamic skylines Via Caching • Cache OSLs instead of DSLs – Query cache contains (query point qj, OSLs) – OSLs encode by bitmaps • Algorithm c. DBM – OSL contains information about dominance test inside orthant – Discard points inside orthants from dominance tests • Method: – Compute bitmap representation – For each point p consider its position (orthant) w. r. t. to cache queries qj – If p in the same orthant o w. r. t qj as qj w. r. t. q and p not in OSLo(qj) then exclude it from OSLo(q), DSL(q) July 29 HDMS'08
Dynamic skylines Via Caching • Cache OSLs instead of DSLs – Query cache contains (query point qj, OSLs) – OSLs encode by bitmaps • Algorithm c. DBM – OSL contains information about dominance test inside orthant – Discard points inside orthants from dominance tests • Method: – Compute bitmap representation – For each point p consider its position (orthant) w. r. t. to cache queries qj – If p in the same orthant o w. r. t qj as qj w. r. t. q and p not in OSLo(qj) then exclude it from OSLo(q), DSL(q) July 29 HDMS'08
 Cache Replacement Policies • General idea – Limited cache space – Identify least useful query point in cache – Replace it with new one July 29 HDMS'08
Cache Replacement Policies • General idea – Limited cache space – Identify least useful query point in cache – Replace it with new one July 29 HDMS'08
 Usage-based policies • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08
Usage-based policies • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08
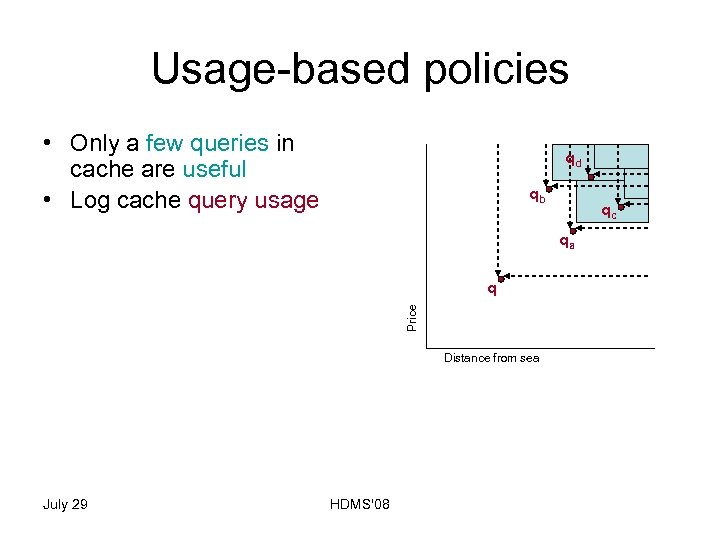 Usage-based policies • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
Usage-based policies • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
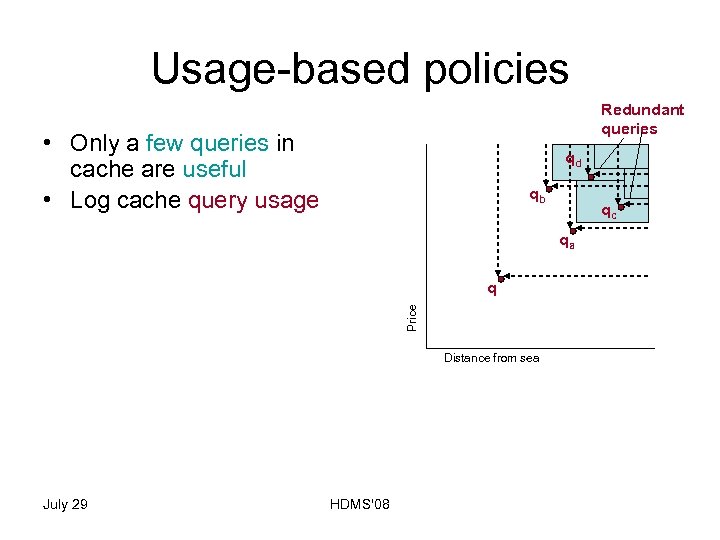 Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query point cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
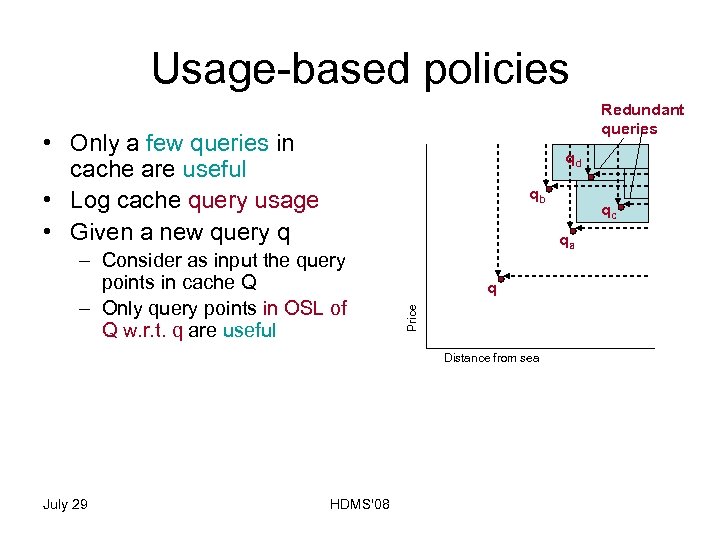 Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query points in cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query points in cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
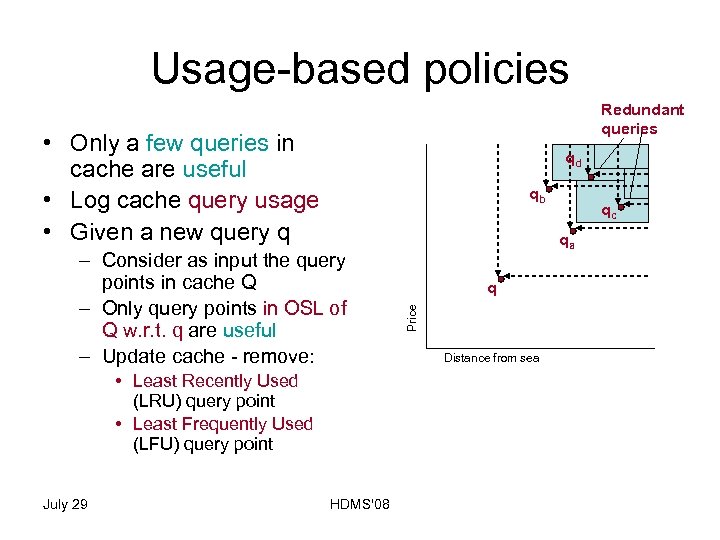 Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query points in cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
Usage-based policies Redundant queries • Only a few queries in cache are useful • Log cache query usage • Given a new query q qd qb • Least Recently Used (LRU) query point • Least Frequently Used (LFU) query point July 29 HDMS'08 qa q Price – Consider as input the query points in cache Q – Only query points in OSL of Q w. r. t. q are useful – Update cache - remove: qc Distance from sea
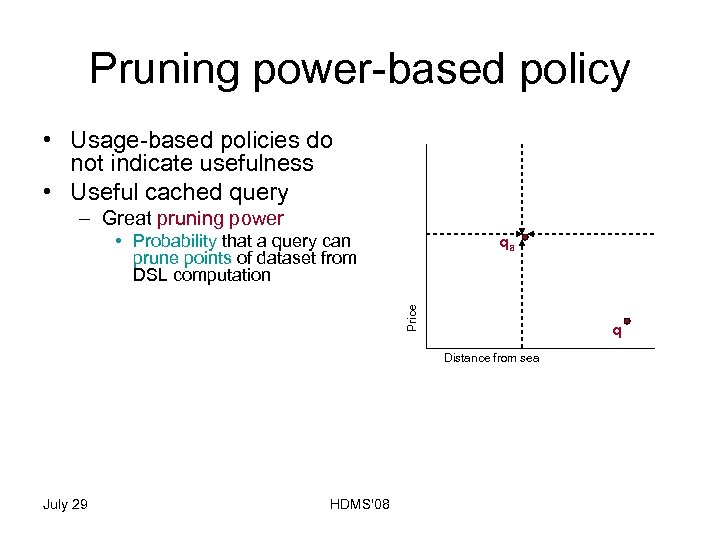 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 Price – Depends on qa q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 Price – Depends on qa q Distance from sea
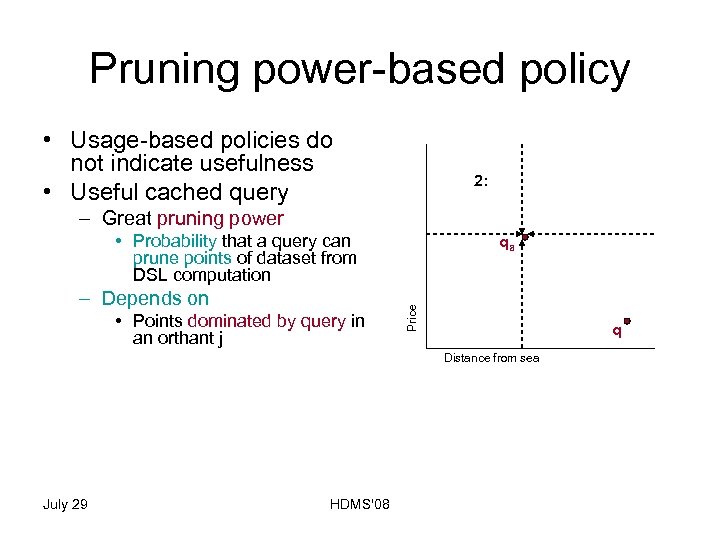 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 2 4 2: 2 4 3: 2 4 74: 2 4 q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 2 4 2: 2 4 3: 2 4 74: 2 4 q Distance from sea
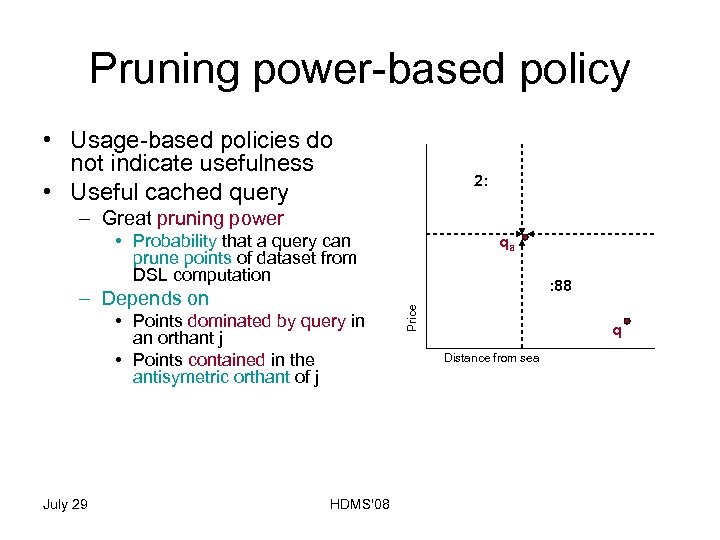 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 4 2: 3 4 3: 4 4 74: 88 4 q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 4 2: 3 4 3: 4 4 74: 88 4 q Distance from sea
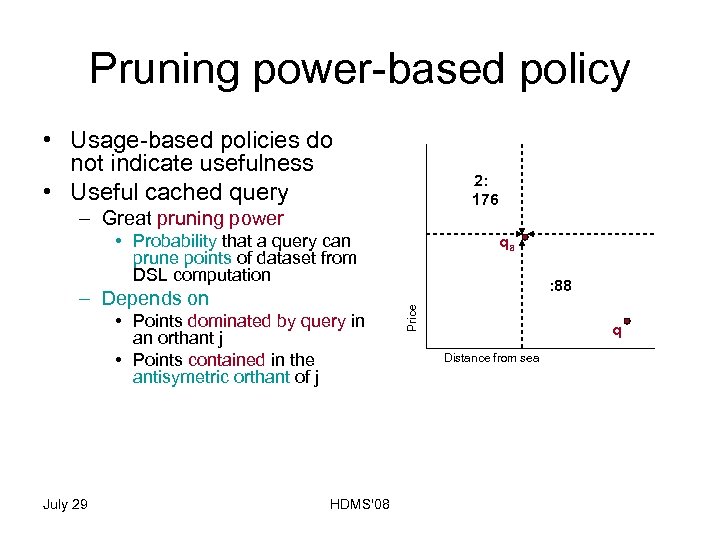 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 4 2: 3 176 3: 4 4 74: 88 4 q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 4 2: 3 176 3: 4 4 74: 88 4 q Distance from sea
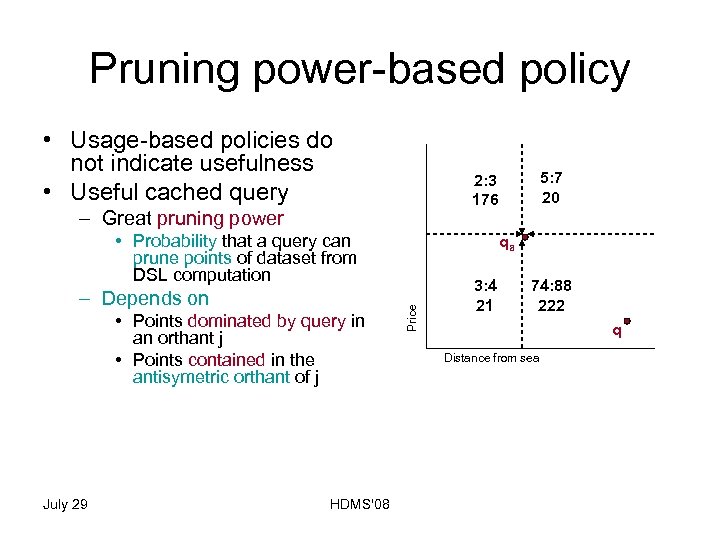 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 20 2: 3 176 3: 4 21 74: 88 222 q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 20 2: 3 176 3: 4 21 74: 88 222 q Distance from sea
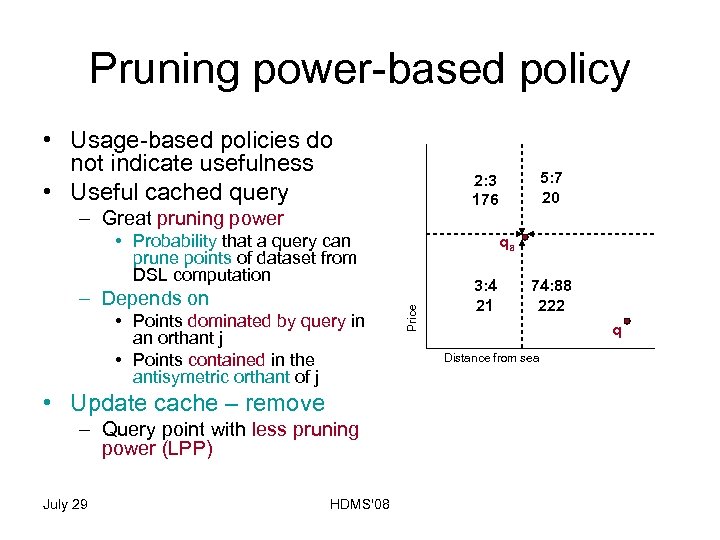 Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 20 2: 3 176 3: 4 21 74: 88 222 q Distance from sea
Pruning power-based policy • Usage-based policies do not indicate usefulness • Useful cached query – Great pruning power • Probability that a query can prune points of dataset from DSL computation • Points dominated by query in an orthant j • Points contained in the antisymetric orthant of j • Update cache – remove – Query point with less pruning power (LPP) July 29 HDMS'08 qa Price – Depends on 5: 7 20 2: 3 176 3: 4 21 74: 88 222 q Distance from sea
 Experimental Evaluation • Synthetic datasets – Distribution types • Independent, correlated, anti-correlated – Number of points N • 10 k, 20 k, 50 k, 100 k, – Dimensionality • d = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – Domain size for dimension • |D| = {10, 20, 50} • Compare – Bitmap (NO-CACHE) – c. DBM with LFU, LRU, LPP cache replacement policies – Query cache • |Q| = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50} past query points • Cache size is |Q|*N bits uncompressed July 29 HDMS'08
Experimental Evaluation • Synthetic datasets – Distribution types • Independent, correlated, anti-correlated – Number of points N • 10 k, 20 k, 50 k, 100 k, – Dimensionality • d = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6} – Domain size for dimension • |D| = {10, 20, 50} • Compare – Bitmap (NO-CACHE) – c. DBM with LFU, LRU, LPP cache replacement policies – Query cache • |Q| = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50} past query points • Cache size is |Q|*N bits uncompressed July 29 HDMS'08
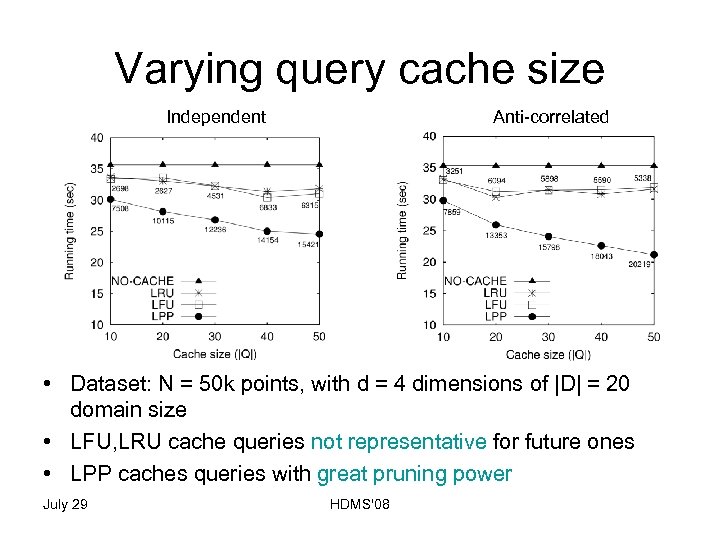 Varying query cache size Independent Anti-correlated • Dataset: N = 50 k points, with d = 4 dimensions of |D| = 20 domain size • LFU, LRU cache queries not representative for future ones • LPP caches queries with great pruning power July 29 HDMS'08
Varying query cache size Independent Anti-correlated • Dataset: N = 50 k points, with d = 4 dimensions of |D| = 20 domain size • LFU, LRU cache queries not representative for future ones • LPP caches queries with great pruning power July 29 HDMS'08
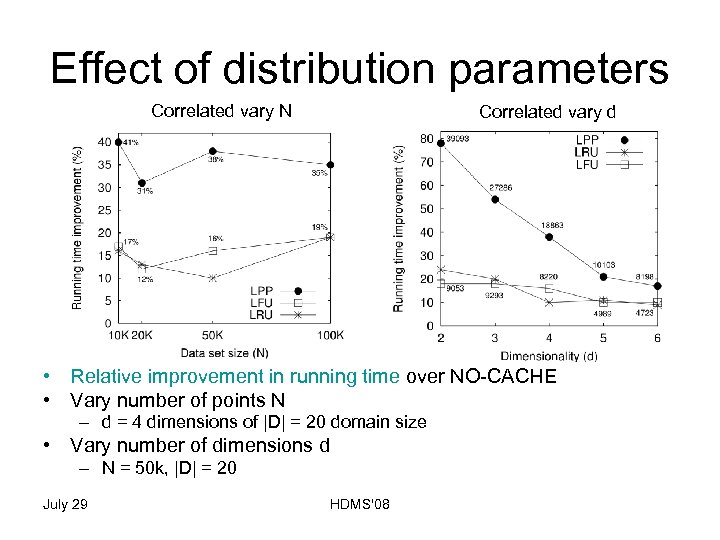 Effect of distribution parameters Correlated vary N Correlated vary d • Relative improvement in running time over NO-CACHE • Vary number of points N – d = 4 dimensions of |D| = 20 domain size • Vary number of dimensions d – N = 50 k, |D| = 20 July 29 HDMS'08
Effect of distribution parameters Correlated vary N Correlated vary d • Relative improvement in running time over NO-CACHE • Vary number of points N – d = 4 dimensions of |D| = 20 domain size • Vary number of dimensions d – N = 50 k, |D| = 20 July 29 HDMS'08
 Conclusions and Future work • Conclusions – Introduced orthant skylines (OSLs) and discussed its relationship with DSL – Extended Bitmap to compute OSLs and DSL at the same time (DBM algorithm) – Proposed caching mechanism of OSLs to reduce cost for future DSL queries • LRU, LFU, LPP cache replacement policies – Experimentally verified the efficiency of caching mechanism • Future work – Apply caching mechanism to index-based methods – Further increase pruning power of cached queries July 29 HDMS'08
Conclusions and Future work • Conclusions – Introduced orthant skylines (OSLs) and discussed its relationship with DSL – Extended Bitmap to compute OSLs and DSL at the same time (DBM algorithm) – Proposed caching mechanism of OSLs to reduce cost for future DSL queries • LRU, LFU, LPP cache replacement policies – Experimentally verified the efficiency of caching mechanism • Future work – Apply caching mechanism to index-based methods – Further increase pruning power of cached queries July 29 HDMS'08
 Questions ? July 29 HDMS'08
Questions ? July 29 HDMS'08


