05f91a99dfe3f636e55478400dadd67b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

CABIN CREW HUMAN FACTORS TRAINING IN MALAYSIA AIRLINES • AZIZ AL RAHIM HUSSIN • 22 APRIL 2008

MALAYSIA AIRLINES • Has over 450 flight departure a day flying to more than 100 destinations spanning across six continents. • It has a fleet of 83 aircraft ranging from B 737 to B 747 • IOSA registered airline • Awards – World Best Cabin Staff 2007 – Skytrax UK, 5 Star airline

MALAYSIA AIRLINES CABIN CREW DEMOGRAPHIC • Total cabin crew strength - 4171 • Malaysian Crew - 4005 • Foreign Crew – 166 – Japanese, Indian, Chinese, Korean, South African and Indonesian • Fleet configuration – Wide body (A 330/B 777/B 744) – Dual Fleet (B 737/A 330)

CABIN CREW HUMAN FACTORS TRAINING Aim & Objectives • To prevent Incident/Accident • Reduce risk in Cabin Operations • To use CRM knowledge, skills and attitudes (KSA) – Creating awareness of the effect of Human Factors elements in Cabin Operations – Application of CRM Knowledge in workplace – Creating positive Safety Attitude
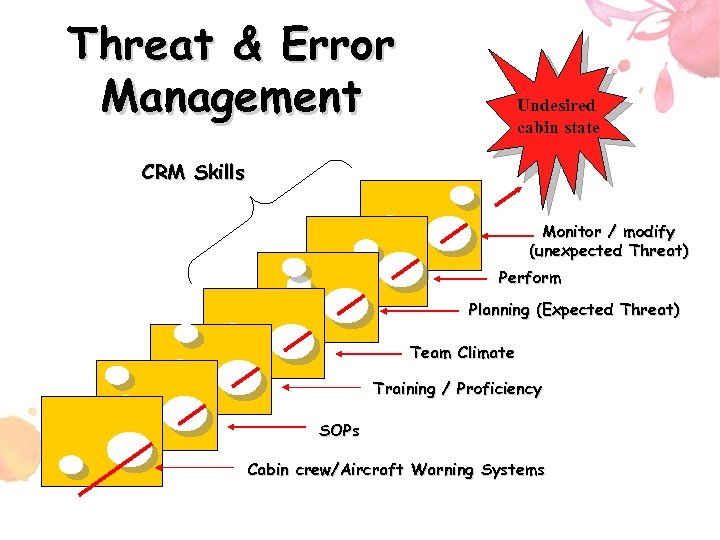
Threat & Error Management Undesired cabin state CRM Skills Monitor / modify (unexpected Threat) Perform Planning (Expected Threat) Team Climate Training / Proficiency SOPs Cabin crew/Aircraft Warning Systems

FRAMEWORK OF HUMAN FACTORS H S L L E
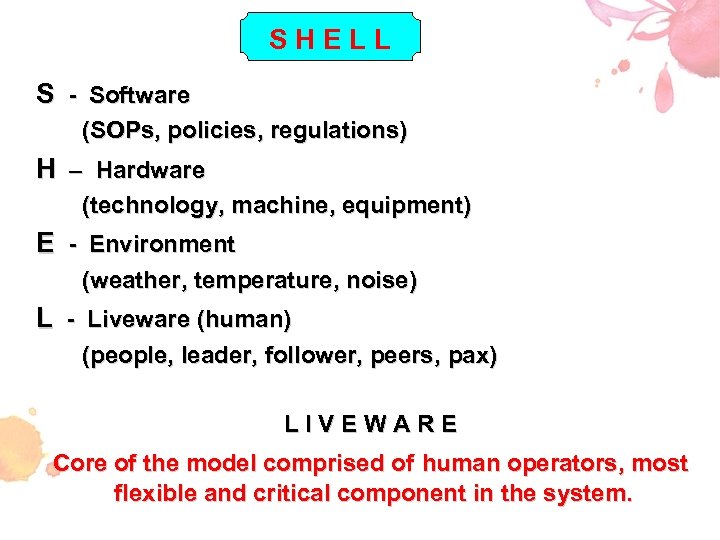
SHELL S - Software (SOPs, policies, regulations) H – Hardware (technology, machine, equipment) E - Environment (weather, temperature, noise) L - Liveware (human) (people, leader, follower, peers, pax) LIVEWARE Core of the model comprised of human operators, most flexible and critical component in the system.

CABIN CREW HUMAN FACTORS TRAINING • To improve the working environment for cabin crews and all those associated with cabin operations. • The emphasis is placed on the nontechnical aspects of Flight and Cabin Crew performance.

HISTORY OF MH CRM TRAINING • First CRM started in year 1992 – Joint training by Flight Crew and cabin crew, Dispatcher and ground staff. – 2 nd generation and continue to evolve • Joint CRM recurrent training in 1999 – 1 day joint training – 4 th generation • Split in year 2002 – Introduction of Threat & Error management – 6 th generation

TYPE OF CRM TRAINING • CRM Initial – Mandatory for all new cabin crew – 1 day basic training covering all main topics – Topics covered in CRM Initial • • • Culture Teamwork Communication Situational Awareness/Stress Problem Solving Decision Making (PSDM) In addition to the above, we include module on Financial Defense – To inform crew on the potential stress arise from financial problem.

TYPE OF CRM TRAINING – Why Culture in CRM Training? • Multi racial and multi national crew • Application of Geoff Hofstede’s Culture four dimension: – – Individualism/Collectivism Masculinity/Femininity Uncertainty Avoidance Power Distance • Culture Familiarization Course – For all foreign crew prior to operations – 1 day training on understanding Culture differences in Malaysia

TYPE OF CRM TRAINING • CRM Recurrent – Mandatory for all cabin crew – 1 day training, conducted annually. – revised to every two years (dispensation from DCA(M) and meeting IOSA requirement). – Latest generation of CRM (Threat & Error Management (TEM))

OPERATIONALIZING CRM TRAINING • Safety Emergency Procedures Training Practical Drill – Joint training between Flight Crew and cabin crew – Application of CRM values in handling normal/abnormal situation – E. g Bomb threat management, fire fighting on board, evacuation drill etc.

FULL CRM TRAINING • CRM – All Cabin crew, priority for supervisory – Cover all CRM elements including the Threat and Error Management (TEM) – Full 3 days program – Joint training between Flight Crew, Cabin Crew, Dispatcher and operations staff. • INTEGRATED HUMAN FACTORS – Operations Division Personnel : • • • Airport Operations Engineering & Maintenance Security Inflight Services/ Catering Cargo

SOURCE OF CRM MODULES • Guideline from Human Factors Digest No 15 and Human Factors Training Manual DOC 9683. • Recent development in MAS/industry – Cabin event – Cabin crew error – Passenger events

SOURCE OF CRM MODULES • Safety issues worldwide • Top 10 reported cabin events from cabin crew voyage report, Hazard Report and MAS Confidential Human Factors Incident Reporting (CHIRP) and Air Safety Report (ASR) • Lesson learnt from internal and external Safety Investigation.

WHERE DO WE STAND • MH CRM – Asiana Airlines – Jet Airways – Air Asia – Royal Malaysian Air Force – Myanmar Airways

CONCLUSION • Objective – Accident/Incident prevention • History – Started in 1992 and we continue to evolve • Type of CRM Training – Initial – Recurrent – Full CRM training • Source – Human Factors Digest No 15 and Human Factors Training Manual DOC 9683. – Recent Development in MAS and aviation ndustry • What make our CRM unique is that we include Lesson Learnt from own and others incident/accident.

Thank you
05f91a99dfe3f636e55478400dadd67b.ppt