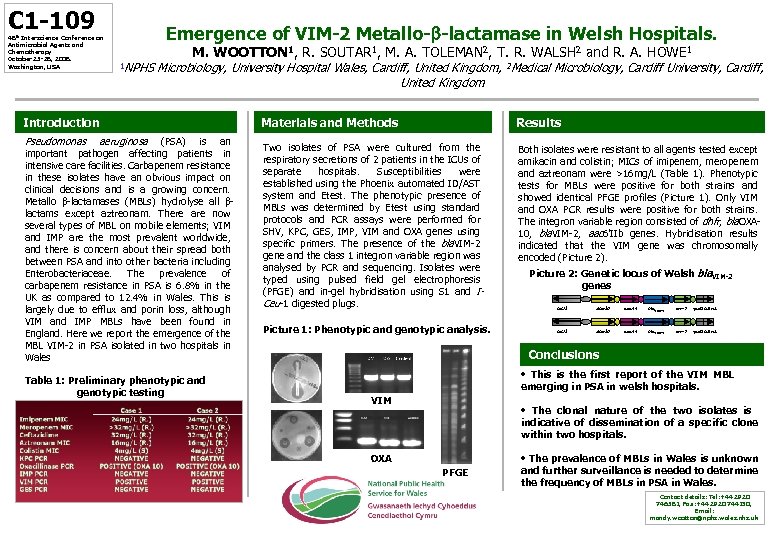
 C 1 -109 48 th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy October 25 -28, 2008. Washington, USA Emergence of VIM-2 Metallo- -lactamase in Welsh Hospitals. M. WOOTTON 1, R. SOUTAR 1, M. A. TOLEMAN 2, T. R. WALSH 2 and R. A. HOWE 1 1 NPHS Microbiology, University Hospital Wales, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2 Medical Microbiology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom Introduction Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PSA) is an important pathogen affecting patients in intensive care facilities. Carbapenem resistance in these isolates have an obvious impact on clinical decisions and is a growing concern. Metallo β-lactamases (MBLs) hydrolyse all βlactams except aztreonam. There are now several types of MBL on mobile elements; VIM and IMP are the most prevalent worldwide, and there is concern about their spread both between PSA and into other bacteria including Enterobacteriaceae. The prevalence of carbapenem resistance in PSA is 6. 8% in the UK as compared to 12. 4% in Wales. This is largely due to efflux and porin loss, although VIM and IMP MBLs have been found in England. Here we report the emergence of the MBL VIM-2 in PSA isolated in two hospitals in Wales Table 1: Preliminary phenotypic and genotypic testing Materials and Methods Results Two isolates of PSA were cultured from the respiratory secretions of 2 patients in the ICUs of separate hospitals. Susceptibilities were established using the Phoenix automated ID/AST system and Etest. The phenotypic presence of GI= Glycopeptide determined by Etest using standard MBLs was intermediate protocols and PCR assays were performed for SHV, KPC, GES, IMP, VIM and OXA genes using specific primers. The presence of the bla. VIM-2 gene and the class 1 integron variable region was analysed by PCR and sequencing. Isolates were typed using pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and in-gel hybridisation using S 1 and ICeu-1 digested plugs. Both isolates were resistant to all agents tested except amikacin and colistin; MICs of imipenem, meropenem and aztreonam were >16 mg/L (Table 1). Phenotypic tests for MBLs were positive for both strains and showed identical PFGE profiles (Picture 1). Only VIM and OXA PCR results were positive for both strains. The integron variable region consisted of dhfr, bla. OXA 10, bla. VIM-2, aac 6’IIb genes. Hybridisation results indicated that the VIM gene was chromosomally encoded (Picture 2). a Picture 1: Phenotypic and genotypic analysis. Picture 2: Genetic locus of Welsh bla. VIM-2 genes int. I 1 oxa-10 aac. A 4 bla. VIM-2 arr-2 qac. EΔ 1/sul Conclusions • This is the first report of the VIM MBL emerging in PSA in welsh hospitals. VIM • The clonal nature of the two isolates is indicative of dissemination of a specific clone within two hospitals. OXA PFGE • The prevalence of MBLs in Wales is unknown and further surveillance is needed to determine the frequency of MBLs in PSA in Wales. Contact details: Tel: +44 2920 746581, Fax: +44 2920 744130, Email: mandy. wootton@nphs. wales. nhs. uk
C 1 -109 48 th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy October 25 -28, 2008. Washington, USA Emergence of VIM-2 Metallo- -lactamase in Welsh Hospitals. M. WOOTTON 1, R. SOUTAR 1, M. A. TOLEMAN 2, T. R. WALSH 2 and R. A. HOWE 1 1 NPHS Microbiology, University Hospital Wales, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2 Medical Microbiology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom Introduction Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PSA) is an important pathogen affecting patients in intensive care facilities. Carbapenem resistance in these isolates have an obvious impact on clinical decisions and is a growing concern. Metallo β-lactamases (MBLs) hydrolyse all βlactams except aztreonam. There are now several types of MBL on mobile elements; VIM and IMP are the most prevalent worldwide, and there is concern about their spread both between PSA and into other bacteria including Enterobacteriaceae. The prevalence of carbapenem resistance in PSA is 6. 8% in the UK as compared to 12. 4% in Wales. This is largely due to efflux and porin loss, although VIM and IMP MBLs have been found in England. Here we report the emergence of the MBL VIM-2 in PSA isolated in two hospitals in Wales Table 1: Preliminary phenotypic and genotypic testing Materials and Methods Results Two isolates of PSA were cultured from the respiratory secretions of 2 patients in the ICUs of separate hospitals. Susceptibilities were established using the Phoenix automated ID/AST system and Etest. The phenotypic presence of GI= Glycopeptide determined by Etest using standard MBLs was intermediate protocols and PCR assays were performed for SHV, KPC, GES, IMP, VIM and OXA genes using specific primers. The presence of the bla. VIM-2 gene and the class 1 integron variable region was analysed by PCR and sequencing. Isolates were typed using pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and in-gel hybridisation using S 1 and ICeu-1 digested plugs. Both isolates were resistant to all agents tested except amikacin and colistin; MICs of imipenem, meropenem and aztreonam were >16 mg/L (Table 1). Phenotypic tests for MBLs were positive for both strains and showed identical PFGE profiles (Picture 1). Only VIM and OXA PCR results were positive for both strains. The integron variable region consisted of dhfr, bla. OXA 10, bla. VIM-2, aac 6’IIb genes. Hybridisation results indicated that the VIM gene was chromosomally encoded (Picture 2). a Picture 1: Phenotypic and genotypic analysis. Picture 2: Genetic locus of Welsh bla. VIM-2 genes int. I 1 oxa-10 aac. A 4 bla. VIM-2 arr-2 qac. EΔ 1/sul Conclusions • This is the first report of the VIM MBL emerging in PSA in welsh hospitals. VIM • The clonal nature of the two isolates is indicative of dissemination of a specific clone within two hospitals. OXA PFGE • The prevalence of MBLs in Wales is unknown and further surveillance is needed to determine the frequency of MBLs in PSA in Wales. Contact details: Tel: +44 2920 746581, Fax: +44 2920 744130, Email: mandy. wootton@nphs. wales. nhs. uk