f31953cc328adbfcd33a33e5d2dab5ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

by R. Chidambaram Principal Scientific Adviser to the Govt. of India th Talk in INFN, Frascati Italy, 16 March, 2009 ,

The many Paths to Energy Security The Nuclear Path I have been saying for 2 decades now: “Nuclear Energy is an inevitable option to satisfy India’s future energy needs” The Renewable Path “Today, America faces grave challenges in the field of energy – from the gathering storm of global warming to a dangerous addiction to oil that jeopardizes our national and economic security…. An energy future based on abundant and clean renewable resources is not only urgently needed, but achievable” And then, of course, Efficiency
The Fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) concluded from direct observations of changes in temperature, sea level, and snow cover in the northern hemisphere during 1850 to the present, that the warming of the earth’s climate system is unequivocal. The global atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases (GHG) has increased from a pre-industrial value of about 280 ppm to 379 ppm in 2005. Multi model averages show that the temperature changes between 2090 -2099 relative to 19801999 will range from 1. 1 to 6. 4°C and sea level rise from 0. 18 to 0. 59 meters. This large uncertainly derives partly from the modeling uncertainties and partly from the uncertainties in the global energy use scenario.

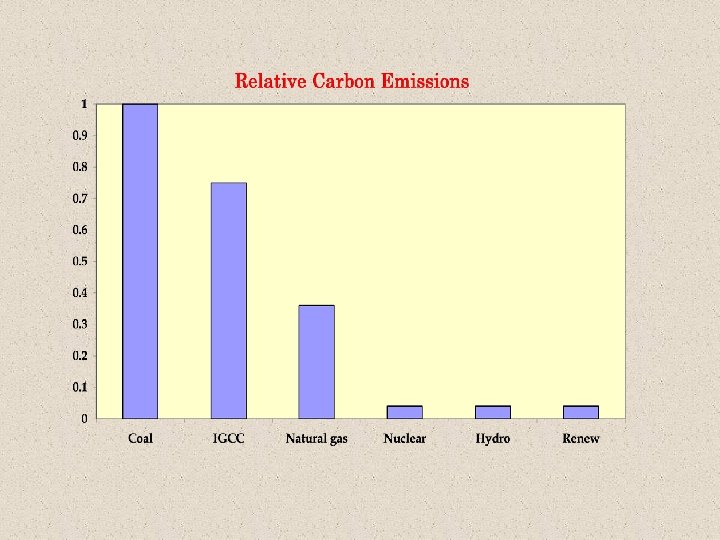
From the point of view of India, The mitigation technologies to counter the Climate Change Threat (nuclear, renewables, efficiency), coincide with the technologies we need to counter the depletion of fossil fuels. The drive towards nuclear in India (and China) is because of surging energy demand while the nuclear renaissance in the developed countries is also driven substantially by the climate change threat.
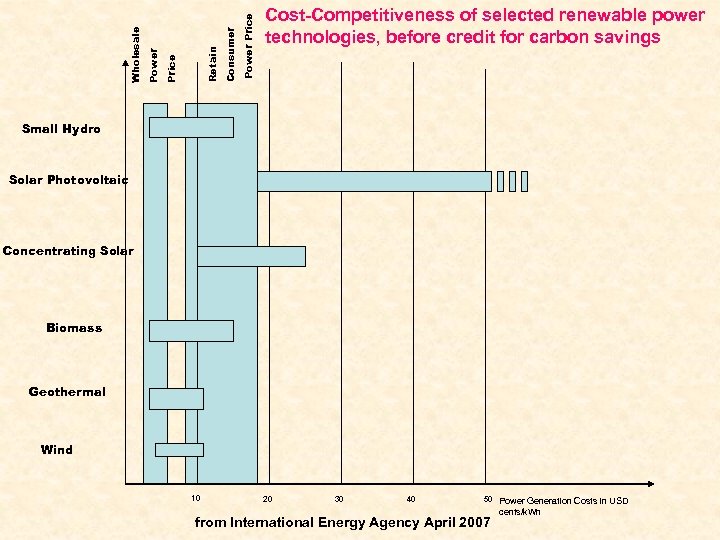
Power Price Consumer Retain Price Power Wholesale Cost-Competitiveness of selected renewable power technologies, before credit for carbon savings Small Hydro Solar Photovoltaic Concentrating Solar Biomass Geothermal Wind 10 20 30 40 50 Power Generation Costs in USD from International Energy Agency April 2007 cents/k. Wh

Solar Power Global production of Solar Photovoltaics (PV) cells increased 51% in 2007 to 3, 733 Megawatts. Europe – led by Germany – surpassed Japan in solar cell manufacturing (1, 063 MW) in 2007. Germany remained the world leader in Solar PV installations, accounting for almost half the world total in 2007. Spain ranked second…. As in Germany, the Spanish market is driven by a strong guaranteed price for PV electricity…. . China raced past the U. S. for PV cell manufacturing (for 2006) …. Most PV cells made in China are exported to Europe. Worldwatch Institute, May 14, 2008 The cost is still high. The Central Government in India offers a generation-based incentive upto Rs. 12 (25 U. S. cents) per k. Wh unit to private sector players for setting up grid-interactive solar plants of a capacity of one MW and above. Out of 9147 MW Grid-Interactive power added from renewables in the last 5 years, wind power accounted for 7273 MW. There is a ‘Indian National Solar Mission’ proposed in the National Action Plan on Climate Change.

After extensive experimental work and computer simulations got done by a Working Group set up by PSA’s Office, during the last three years, starting with the technology developed by BHEL over the past two decades, the feasibility of IGCC process for high ash Indian coal has been established. This leads to cleaner and more efficient use of coal. BHEL and APGENCO have signed an agreement recently to set up a 125 MW plant at Vijayawada using IGCC technology

Ø Three-stage Nuclear Power Programme (Sustainable Development of Nuclear Energy would inevitably require closing the nuclear fuel cycle. The same limited amount of uranium has a 600 – times higher energy potential, if the fuel cycle is closed with thorium). Ø Spin-offs in Agriculture, Medicine and Industry (In India, nuclear technology has acted as a catalyst for nucleating many other high technologies from parallel processing supercomputers to welding) Ø Development of Major Facilities for Research (research reactors, particle accelerators, synchrotron radiation sources, superconducting tokamak, advanced instrumentation)
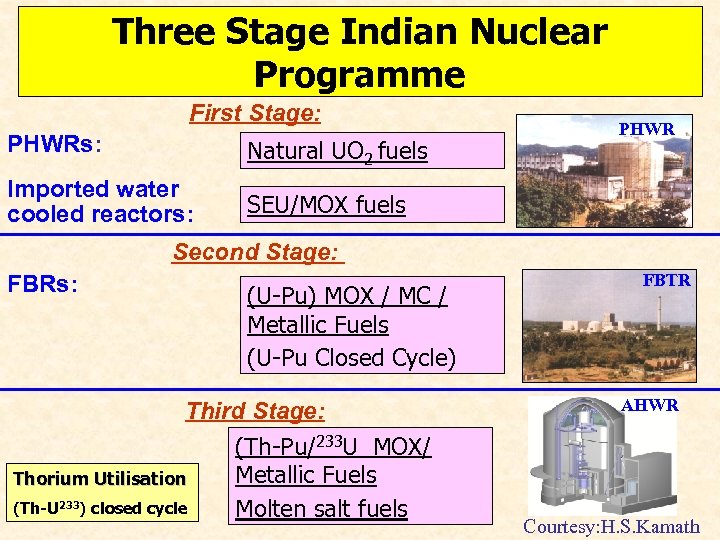
Three Stage Indian Nuclear Programme First Stage: PHWRs: Natural UO 2 fuels Imported water cooled reactors: PHWR SEU/MOX fuels Second Stage: FBRs: (U-Pu) MOX / MC / Metallic Fuels (U-Pu Closed Cycle) Third Stage: (Th-Pu/233 U MOX/ Metallic Fuels Thorium Utilisation (Th-U 233) closed cycle Molten salt fuels FBTR AHWR Courtesy: H. S. Kamath

International Conference on "Fifty Years of Nuclear Power – the next Fifty years" APSARA REACTOR. BARC, India Date of Criticality, August 4, 1956. First Nuclear Reactor in Asia Moscow & Obninsk 27 June – 2 July 2004 In Celebration of the golden jubilee of going into operation of the first electric power generating reactor in the world on June 27, 1954 at Obninsk. This reactor AM-1 was a 5 MW graphitemoderated and water cooled reactor. India commissioned its first research reactor Apsara in 1956

PFBR Construction Phase Launched q PROTOTYPE FAST BREEDER REACTOR of 500 MWe has been designed by IGCAR. q A new Public Sector Company BHAVINI has launched construction of this reactor on 23 rd October 2004 q Fabrication of large sized components such as Safety vessel and Main vessel in progress. PFBR Safety Vessel fabrication under progress 29/5/06 - 01/06/06 Construction site of PFBR Construction under progress Courtesy: H. S. Kamath 12

Advanced Heavy Water Reactor AHWR is a vertical pressure tube type, boiling light water cooled and heavy water moderated reactor using 233 U-Th MOX and Pu-Th MOX fuel. Major Design Objectives • Power output – 300 MWe with 500 m 3/d of desalinated water. • A large fraction (65%) of power from thorium. • Extensive deployment of passive safety features – 3 days grace period, and no impact in public domain • Design life of 100 years. • Easily replaceable channels. coolant • Feb. 2007 – AERB completes prelicensing safety appraisal of AHWR • April 2008 – AHWR critical facility commissioned • International recognition as an innovative Design Courtesy: R. K. Sinha
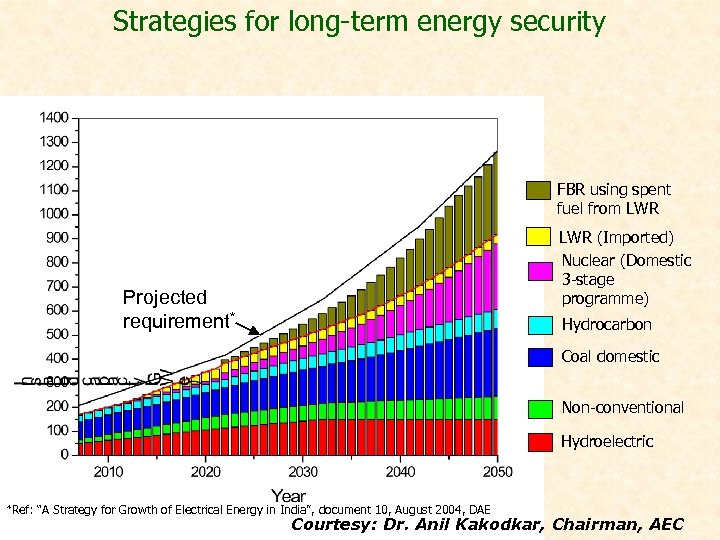
Strategies for long-term energy security FBR using spent fuel from LWR (Imported) Nuclear (Domestic 3 -stage programme) Projected requirement* Hydrocarbon Coal domestic Non-conventional Hydroelectric *Ref: “A Strategy for Growth of Electrical Energy in India”, document 10, August 2004, DAE Courtesy: Dr. Anil Kakodkar, Chairman, AEC
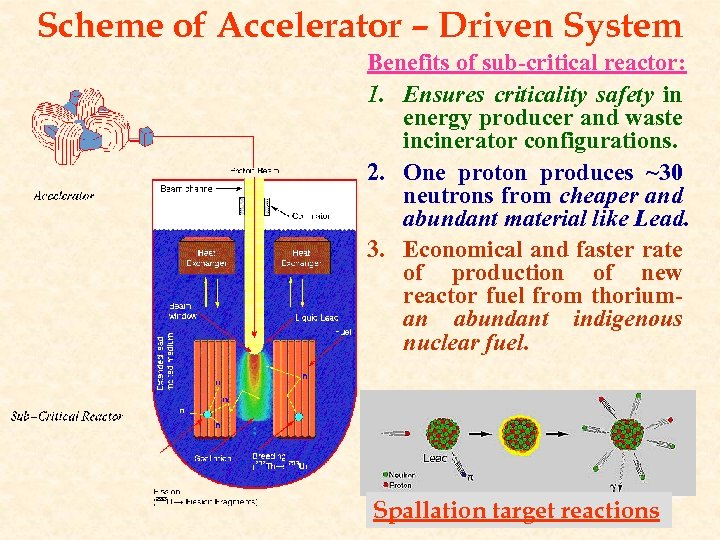
Scheme of Accelerator – Driven System Benefits of sub-critical reactor: 1. Ensures criticality safety in energy producer and waste incinerator configurations. 2. One proton produces ~30 neutrons from cheaper and abundant material like Lead. 3. Economical and faster rate of production of new reactor fuel from thoriuman abundant indigenous nuclear fuel. Spallation target reactions

Steady State Superconducting Tokamak India has now joined ITER co-operative programme Courtesy : P. K. Kaw

Energy very similar to INDUS-II 63 Indian proposals for beamtime have been accepted after review jointly by DST, India and Sincrotrone, Italy. 62 co-authored research papers. Many projects on structure-based drug-design.

Indigenous: INDUS-2 AT RRCATIndore Access to outside SRS’s through DST in project mode, building and owning beam line instrument powder, surface diffraction (Photon Factory, Tsukuba); building beam-line instrument in collaboration - macromolecule crystallogrphy & high pressure diffraction (ELETTRA, Trieste); buying access to beam-line instrument – macromolecular crystallography beam line at ESRF, Grenoble (by DBT); discussion on access to the new SRS PETRA 3 at Hamburg by paying for building and maintaining one beam line. (by DST).

“U-TURN FOR NUCLEAR OPPONENTS” In a landmark article for the left-leaning Independent newspaper. New Statesman Writer Mark Lynas said the anti-nuclear campaigns of the past “will come to be seen as an enormous mistake for which the Earth’s climate is now paying the price”. Stephen Tindale(who ran the UK branch of Greenpeace from 2000 to 2005 told the newspaper, “It was like a kind of religious conversion. Being anti-nuclear was an essential part of being an environmentalist for a long time. “He now claims that ‘It’s actually quite widespread, now, this view that nuclear power is not ideal but it’s better than climate change. ” Tindale’s announcements echo that of Patrik Moore, one of the Canadian founders of Greenpeace. Moore now advocates the use of nuclear power and large hydro for low-carbon power generation… 23 February 2009 – World Nuclear News. James Lovelock, Eminent Environmental Scientist and proponent of the Gaia Hypothesis, was the earliest to this U-turn in 2004. To reverse a longstanding (extreme) position requires high-integrity and character.

Italian nuclear moved forward at summit 24 February 2009, World Nuclear News The 27 th Franco-Italian summit saw delegations of ministers from both sides (conclude) a new agreement on cooperation in nuclear energy – Electricite` de France and Enel partnership to conduct feasibility studies towards “at least four EPRS in Italy”. The Step is among the biggest that Italy has so far taken towards a re-employment of nuclear energy, …. (after) Silvio Berlusconi’s Forza Italia party put a return to nuclear energy in its manifesto.

“Expanded use of nuclear technologies offers immense potential to meet important development needs. In fact, to satisfy energy demands and to mitigate threat of climate change – two of the 21 st century’s greatest challenges – there are major opportunities for expansion of nuclear energy in those countries that choose to have it”. from Report prepared by an independent Commission at the request of the Director General of the International Atomic Energy Agency - 2008

§ The use of uranium in the once-through mode will enable the use of only a small fraction of the available uranium resource. § Fast reactors used in the closed fuel cycle mode provide the option for the full exploitation of the natural resources. This is further enhanced by inclusion of Thorium in the closed nuclear fuel cycle. § The closed fuel cycle, in comparison to the once-through cycle, reduces the volumes of waste requiring treatment and disposal. § With the closed fuel cycle, Nuclear is near-Renewable. § Then there is Nuclear Fusion.
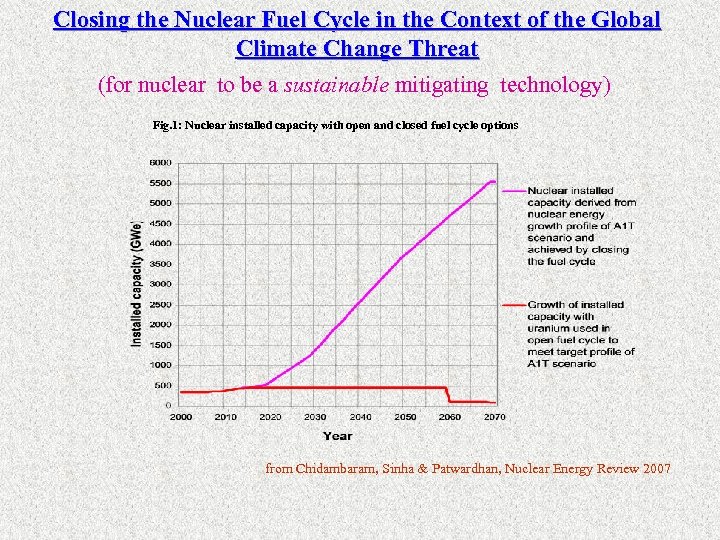
Closing the Nuclear Fuel Cycle in the Context of the Global Climate Change Threat (for nuclear to be a sustainable mitigating technology) Fig. 1: Nuclear installed capacity with open and closed fuel cycle options from Chidambaram, Sinha & Patwardhan, Nuclear Energy Review 2007
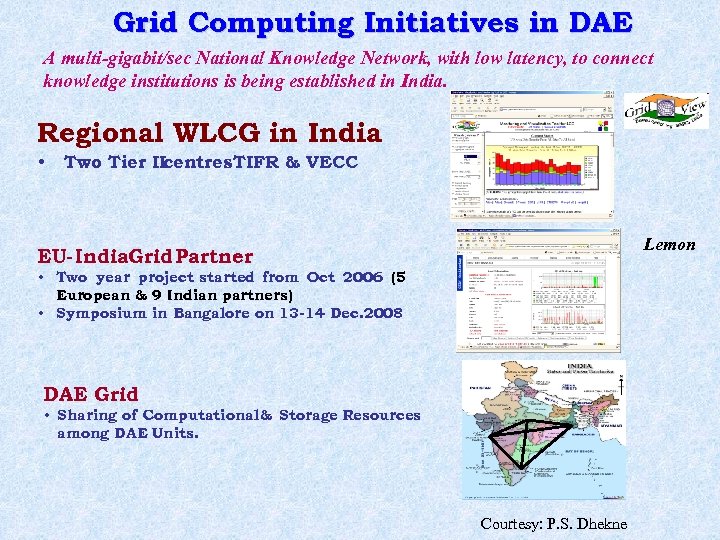
Grid Computing Initiatives in DAE A multi-gigabit/sec National Knowledge Network, with low latency, to connect knowledge institutions is being established in India. Regional WLCG in India • Two Tier II centres TIFR & VECC Lemon EU-India. Grid Partner • Two year project started from Oct 2006 (5 European & 9 Indian partners) • Symposium in Bangalore on 13 -14 Dec. 2008 DAE Grid • Sharing of Computational & Storage Resources among DAE Units. Courtesy: P. S. Dhekne
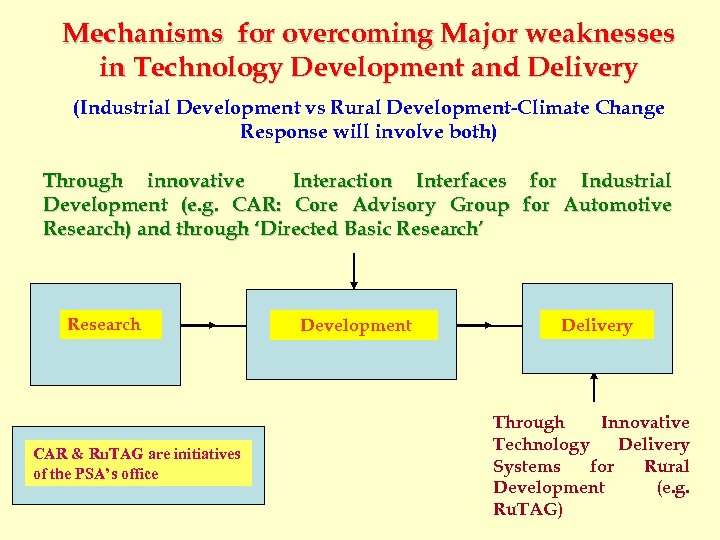
Mechanisms for overcoming Major weaknesses in Technology Development and Delivery (Industrial Development vs Rural Development-Climate Change Response will involve both) Through innovative Interaction Interfaces for Industrial Development (e. g. CAR: Core Advisory Group for Automotive Research) and through ‘Directed Basic Research’ Research CAR & Ru. TAG are initiatives of the PSA’s office Development Delivery Through Innovative Technology Delivery Systems for Rural Development (e. g. Ru. TAG)

What is ‘Directed Basic Research’ Research In its execution, and in the requirement of no other deliverablesthan knowledgegeneration, it is no different from conventional basic research. So the University academics should be comfortable with this kind of research. The selected areas are determined in a national perspective, just like in Technology. Foresight. ‘Directed’Basic Research may be in an area where the knowledgegenerationwould benefit. Indian Societyin the long term or it may be in area where the results of the , research would benefit Indian Industry or our strategic interests in the long term, particularly in cross disciplinary technology areas. From R. Chidambaram, Current Science (2007)
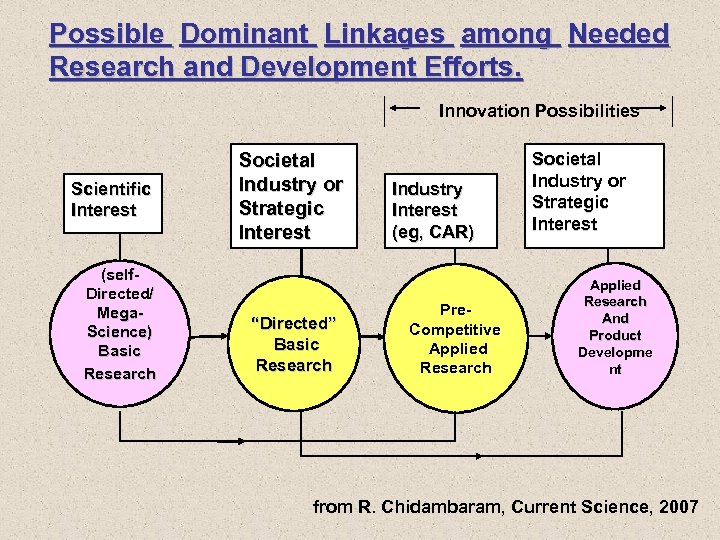
Possible Dominant Linkages among Needed Research and Development Efforts. Innovation Possibilities Scientific Interest (self. Directed/ Mega. Science) Basic Research Societal Industry or Strategic Interest “Directed” Basic Research Industry Interest (eg, CAR) Pre. Competitive Applied Research Societal Industry or Strategic Interest Applied Research And Product Developme nt from R. Chidambaram, Current Science, 2007
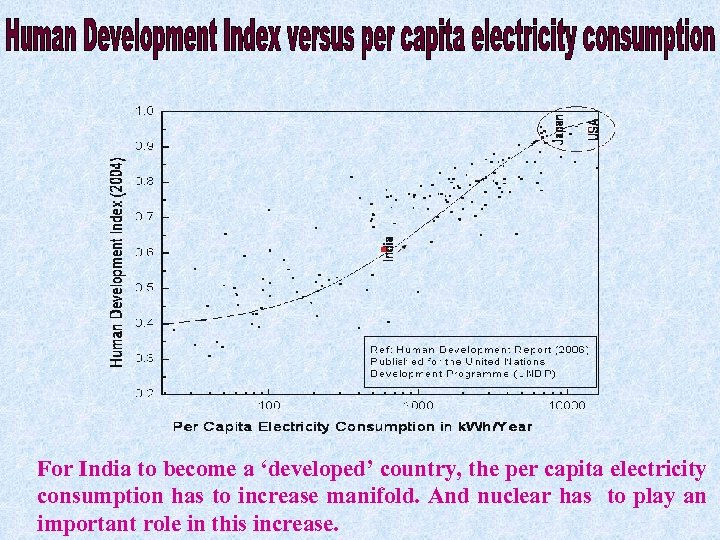
For India to become a ‘developed’ country, the per capita electricity consumption has to increase manifold. And nuclear has to play an important role in this increase.
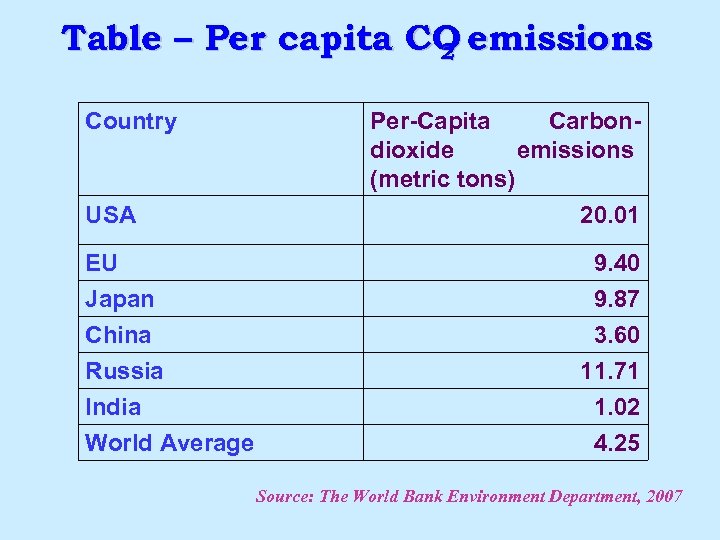
Table – Per capita CO emissions 2 Country USA EU Japan China Russia India World Average Per-Capita Carbondioxide emissions (metric tons) 20. 01 9. 40 9. 87 3. 60 11. 71 1. 02 4. 25 Source: The World Bank Environment Department, 2007

“We are determined that India’s per-capita GHG emissions are not going to exceed those of developed countries even while pursuing policies of development and economic growth”. Dr. Manmohan Singh, Prime Minister of India, at Heiligendamm. June, 2007 in

f31953cc328adbfcd33a33e5d2dab5ec.ppt