
By Perederiy Nadia

Credit risk is risk due to uncertainty in a counterparty’s (also called an obligor’s or credit’s) ability to meet its financial obligations.

In assessing credit risk from a single counterparty, an institution must consider three issues: 1. default probability 2. credit exposure 3. recovery rate

For loans to individuals or small businesses, credit quality is typically assessed through a process of credit scoring.

The term credit analysis is used to describe any process for assessing the credit quality of a counterparty.

Credit rating agencies

Exhibit 1 indicates the system of credit ratings employed by Standard & Poor’s. Other systems are similar.

Credit risk modeling is a concept that broadly encompasses any algorithm-based methods of assessing credit risk.

Credit risk modeling include: supplanting traditional credit analysis; being used by financial engineers to value credit derivatives; and being extended as portfolio credit risk measures used to analyze the credit risk of entire portfolios of obligations to support securitization, risk management or regulatory purposes.
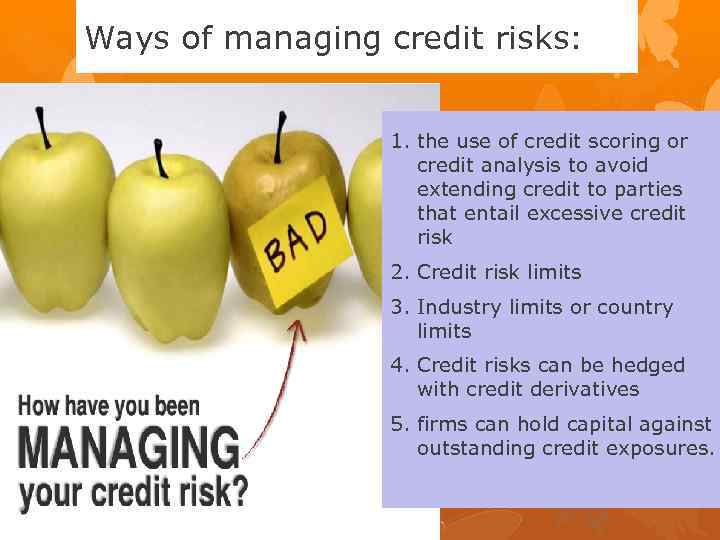
Ways of managing credit risks: 1. the use of credit scoring or credit analysis to avoid extending credit to parties that entail excessive credit risk 2. Credit risk limits 3. Industry limits or country limits 4. Credit risks can be hedged with credit derivatives 5. firms can hold capital against outstanding credit exposures.

Thank you for your attention!