butadine styrene.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 11

Butadiene styrene rubber Kubeeva. R. E Cht – 13 -6 ka 2

Contents: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction Discovery Production IR-spectroscopy Application Advantages and disadvantages Conclution Reference 2
Introduction • Butadiene-styrene rubbers - group -1, 3 butadiene polymerization products of styrene or methyl styrene and the most common type of general purpose rubbers, whose synthesis is carried out in an emulsion free radical mechanism. • SCS are non-crystallizable copolymers irregular structure with a statistical distribution of monomer units. • About 30% of isolated styrene units, approximately 40% are located pair wise • 80% of the butadiene units of the polymer chains are attached in position 1, 4, mainly in the trans form (about 70%), about 20% in the attached position 1, 2. • A variety of styrene-butadiene rubbers are styrene-amethyl styrene rubbers (SKMS), are characterized by similar structures and properties. 3

Discovery • Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is one of the most versatile polymer rubber compounds. It consists of the organic compound styrene and the chemical butadiene, with the amount of butadiene SBR is a replacement for natural rubber. • It was originally developed prior to World War II in Germany by chemist Walter Bock. Industrial manufacture began during World War , and was used extensively by the U. S. • Synthetic Rubber Program to produce Government Rubber. Styrene (GR-S); • This compound is produced either through ionic polymerization of a solution or as an emulsion through free radical polymerization. • this product was first developed in the 1930 s by I. G. Farbenindustrie in Germany. • It was created through an emulsion procedure that used polymerization as the means of producing a material that had a low reaction viscosity but had all the attributes of natural rubber. • It was very cost-effective and was used to stretch dwindling natural rubber resources, especially in tire manufacturing at a time when tires were made of solid rubber. . 4
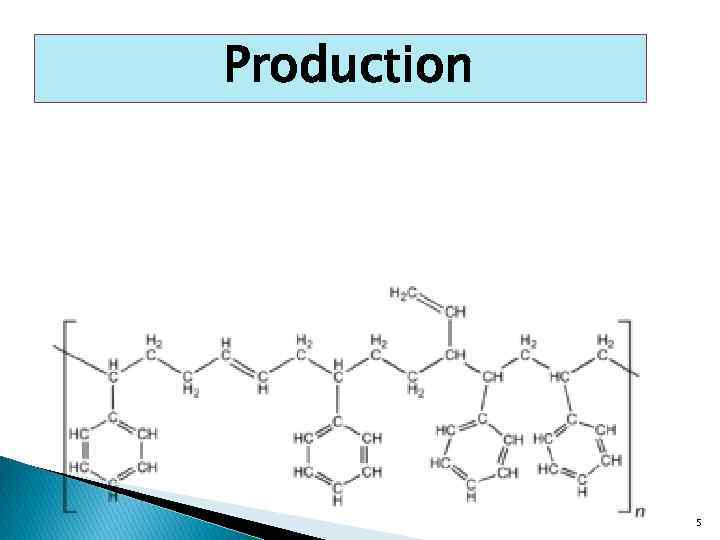
Production 5

Properties • This type of rubber is usually very weak unless reinforcing fillers are incorporated. With suitable fillers, this becomes a strong rubber • It has similar chemical and physical properties like natural rubber • It has better abrasion resistance • It has poorer fatigue resistance • Heat resistance is better than natural rubber • Low temperature flexibility and tensile strength are less than that of natural rubber Dangers Use of these gloves when working 6
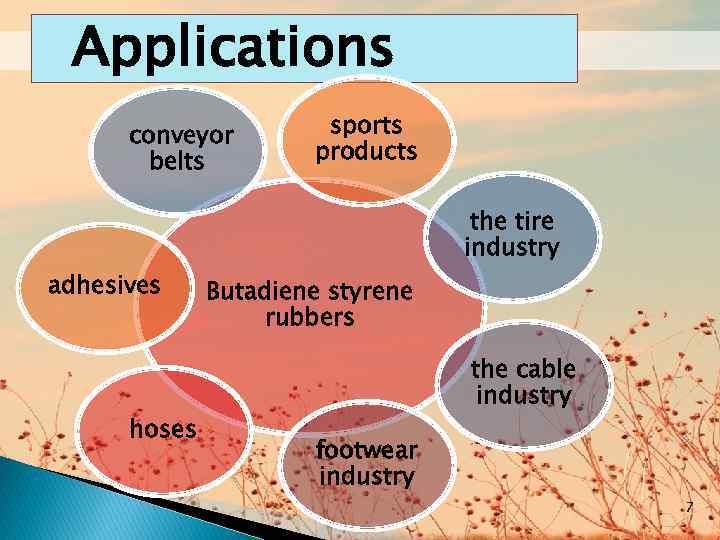
Applications conveyor belts sports products the tire industry adhesives hoses Butadiene styrene rubbers the cable industry footwear industry 7
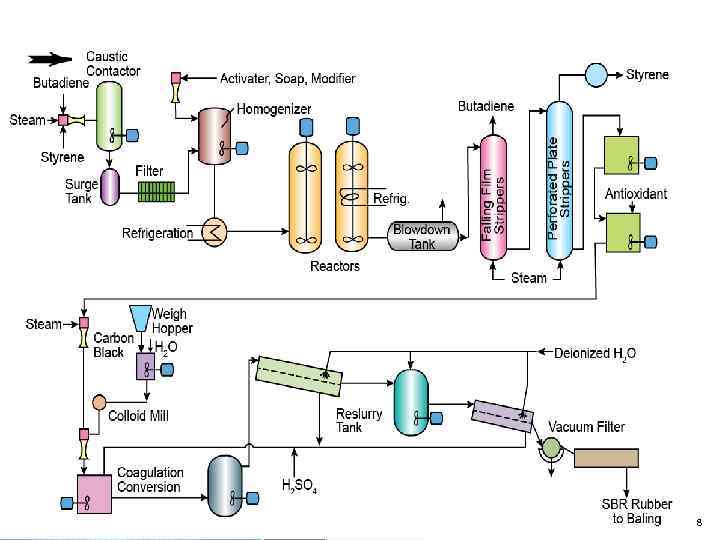
8

Advantages • High-strength, tear strength, elasticity and durability. Disadvantages • • 9

Conclusion • Styrene-butadiene rubber is one of the most common commercially available general-purpose rubbers and is available in a wide range and large volume. • Distribution of butadiene and styrene in the macromolecule polymer - irregular, statistically. • Production of styrene-butadiene rubber may be conducted either in solution or in emulsion. 10

References 1. 2. 3. 4. MERL - Rubber Selection Guide AAA Acme Rubber Co - Nitrile Rubber http: //www. dsm. com/en_US/html/dfi/acn_production. htm http: //www. ec. gc. ca/substances/ese/eng/psap/final/public/buta diene. cfm 5. Brydson J. A. , Rubber chemistry, L, 1978 6. Wood L. A. , «Rubber Chem. and Technol. » , 1976, V. 49, № 2, p. 189– 99 7. Каучуки синтетические бутадиен-метилстирольный CKMC-30 APKM-I 5 и бутадиен-стирольный СКС-30 АРКМ-8. Технические условия. ГОСТ 11138– 78. Государственный комитет СССР по стандартам: Москва, 1978. 11
butadine styrene.pptx