82b37a59c05b87db701e0cd0a3602523.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 115

Business tools Change Management Team Development

Business tools Agenda Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools “It should be borne in mind that there is nothing more difficult to arrange, more doubtful of success, and more dangerous to carry through than initiating changes. . . The innovator makes enemies of all those who prospered under the old order and only lukewarm support is forthcoming from those who would prosper under the new” Ø SOURCE: NICCOLO MACHIAVELLI (1469 -1527) The challenge of change

Business tools Contracting Template One What do I expect of you? Ø Facilitator Ø Manager Ø Fellow participants

Business tools Contracting Template Two What do I think you expect of me? Ø Facilitator Ø Manager Ø Fellow participants

Business tools Ground Rules What behaviours are going to help us achieve our objectives and to meet our mutual expectations?

Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools Team development is. . . Working with a group/team to assist them to work more effectively as a whole
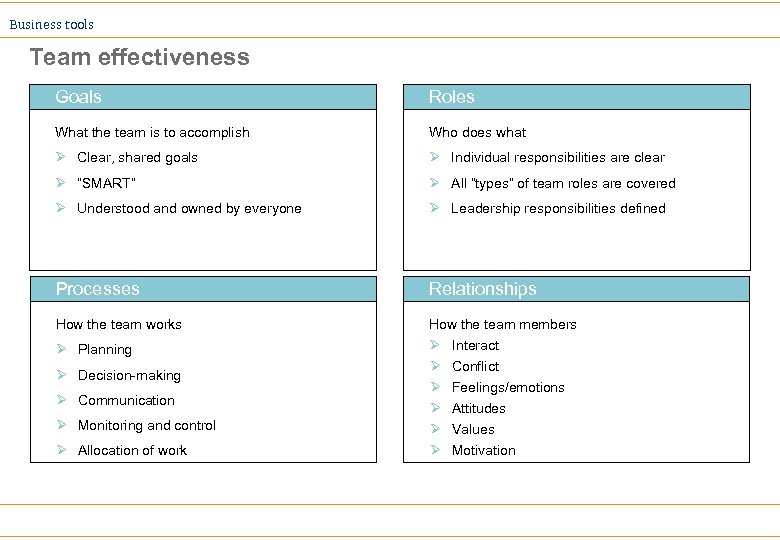
Business tools Team effectiveness Goals Roles What the team is to accomplish Who does what Ø Clear, shared goals Ø Individual responsibilities are clear Ø “SMART” Ø All “types” of team roles are covered Ø Understood and owned by everyone Ø Leadership responsibilities defined Processes Relationships How the team works How the team members Ø Planning Ø Ø Ø Ø Decision-making Ø Communication Ø Monitoring and control Ø Allocation of work Interact Conflict Feelings/emotions Attitudes Values Motivation

Business tools A hierarchy of team effectiveness Environmental factors Goals Roles Processes Relationships

Business tools Stages of team development Output Performing Forming Norming Storming Mourning Time

Business tools Stages of team development Stage Characterised by Attempt to identify tasks and how group will accomplish them Decisions on type of information required Ø Hesitant participation Ø Discussion of symptoms or problems peripheral to the tasks Ø Storming Ø Ø Forming Minimal task accomplishment Ø Personal agendas uppermost Ø Experimentation Ø Infighting, defensiveness and competition Ø Dispute about focus/priorities Ø Resistance to task demands because they interfere with personal needs Ø Polarisation of team members Ø Minimal task accomplishment Ø High energy or withdrawal
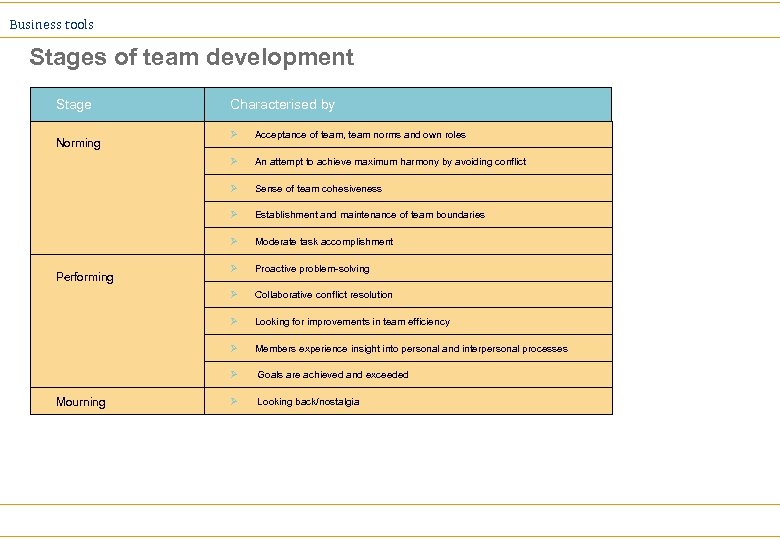
Business tools Stages of team development Stage Characterised by An attempt to achieve maximum harmony by avoiding conflict Sense of team cohesiveness Ø Establishment and maintenance of team boundaries Ø Moderate task accomplishment Ø Proactive problem-solving Ø Collaborative conflict resolution Ø Looking for improvements in team efficiency Ø Members experience insight into personal and interpersonal processes Ø Mourning Acceptance of team, team norms and own roles Ø Performing Ø Ø Norming Goals are achieved and exceeded Ø Looking back/nostalgia

Business tools Team performance links Development Stage Forming + Storming + Norming + Performing Team Concerns Goals + Roles + Processes + Relationships ?

Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools Agree sub-team mission statement What are we here to do? One sentence to describe the ”raison d’être” of the sub-team; what it does and wants to do; the boundaries of its activities; the main beneficiaries, stakeholders, customers, etc

Business tools Agree strategic objectives What are our key objectives? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Broad statements of strategic intent, focusing on desired outcomes. Exclude measures, and activities. 4 -6 maximum

Business tools Define strategic objectives Strategic Objective 1 (etc) Description (emotional, gut-feel) Measures (indicators of achievement in ST, MT, LT)

Business tools Now undertake two exercises Ø (Brief) paper review, gallery-style Ø Review feedback from ä Key player survey ä Customer survey Ø Then go back into sub-teams Ø In terms of our objectives ä What have we got right? ä What have we got wrong? ä What have we missed? ä What should we do differently? Ø In plenary answer the same question for the change management team as a whole. Who else has responsibilities and what are the respective roles. Introduce Accountability charting

Business tools Accountability Charting Ø Most common forms: ä Responsibility chart ä Inter-accountability chart ä RACI chart
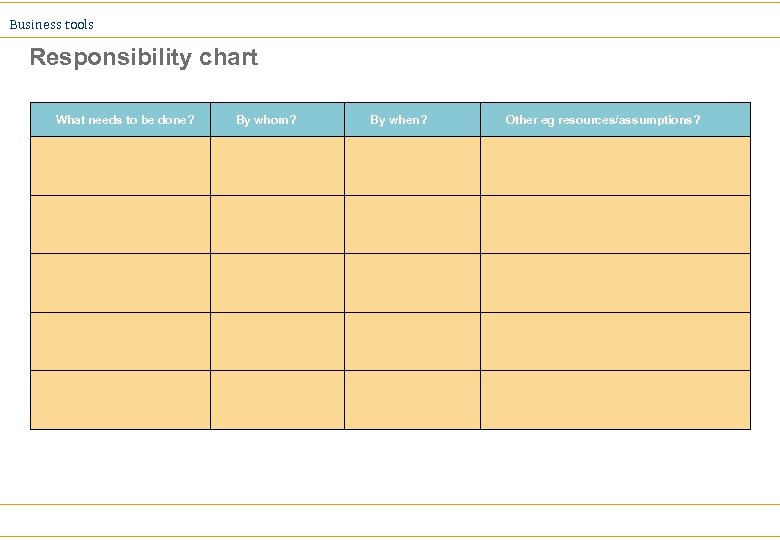
Business tools Responsibility chart What needs to be done? By whom? By when? Other eg resources/assumptions?
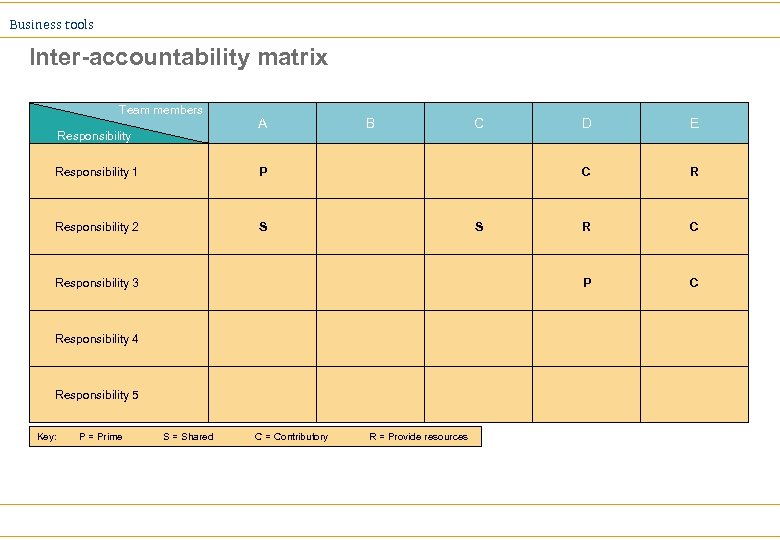
Business tools Inter-accountability matrix Team members A Responsibility 1 S Responsibility 3 Responsibility 4 Responsibility 5 Key: P = Prime S = Shared C = Contributory R = Provide resources E C S C P Responsibility 2 B D R R C P Responsibility C
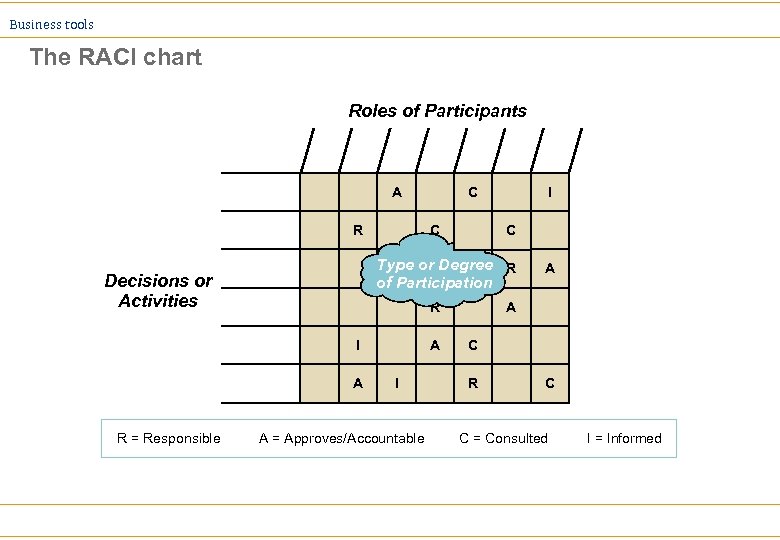
Business tools The RACI chart Roles of Participants A R C I C Type or. I Degree R C of Participation Decisions or Activities R I A R = Responsible C A I A = Approves/Accountable A A C R C C = Consulted I = Informed
Business tools Establishing a sense of urgency and creating a vision

Business tools From ‘As Is’ to ‘To Be’ Present State Desired State

Business tools The change process and the transition state Present State Transition State Typical characteristics of the transition state Ø Low stability Ø High emotional stress Ø High, often undirected energy Ø Control becomes a major issue Ø Past patterns of behaviour become highly valued Ø Conflict may increase Desired State

Business tools Comfort Zone Growth Pain Risk Challenge Excitement Self Esteem Opportunity Comfort Zone Fear Danger Change Progress

Business tools Breaking the habit - The formula for initiating change Dx. V x. P>C D = Dissatisfaction V = Vision of the future P = Practical first steps to change C = The perceived cost (material, psychological) of change

Business tools For change to be initiated successfully, all of the elements must be present , or else. . . D + V + P = Dysfunction D + V + P = Ulcers D + V + P = Short term interest D + V + P = Academic theory D + V + P = Hope D + V + P = Advocacy D + V + P = Success

Business tools Urgency and Vision Ø How is FATP doing? Ø What is the implications? Ø What should/can we do?

Business tools Objectives Ø To optimise the performance of the change management team by: ä Updating on FATP and reviewing feedback ä Confirming scope, objectives etc and roles in delivering the change ä Discussing the principles of effective change ä Reviewing change tools/techniques ä Identifying ways to improve team effectiveness Ø Output ä Individual, sub-team and change team plans

Business tools Agenda Day 1 Day 2 Ø Introduction Ø Working Together Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Review of Day 1 ä Input and Exercises on change agent skills Ø Prioritising and Planning ä Individual, sub-team and change team plans
Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools Learning from Kotter’s experience Error Eight steps to transformation Ø Not establishing a great enough sense of urgent No 1 Establish a sense of urgency Ø Not creating a powerful enough guiding coalition No 2 Form a guiding coalition Ø Lacking a vision No 3 Create a vision Ø Under-communicating by a factor of ten No 4 Communicate the vision Ø Not removing obstacles to the new vision No 5 Empower others to act of the vision Ø Not systematically planning for and creating short term wins No 6 Plan and create short term wins Ø Declaring victory too soon No 7 Consolidate improvement and produce still more change Ø Not anchoring changes in the culture of the business No 8 Institutionalise new approaches

Business tools Forming a guiding coalition (and managing different roles in change)

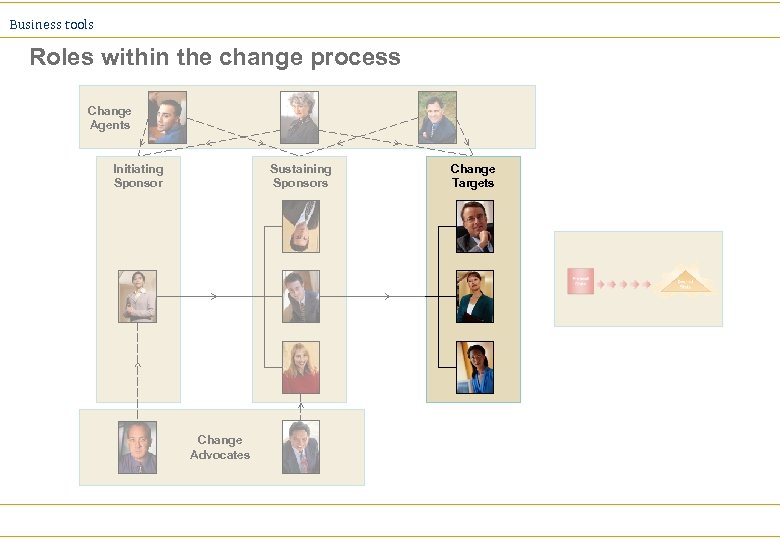
Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets

Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets

Business tools Advocate Ø Wants the change, but needs sponsorship to initiate it Ø Is seen to support the change Ø Is respected (in the appropriate places) Ø Can lead the way in adopting the changed situation/approach Established members of an organisation may initially be strong opponents but make the best advocates if you can convert them. They may have to be your first targets
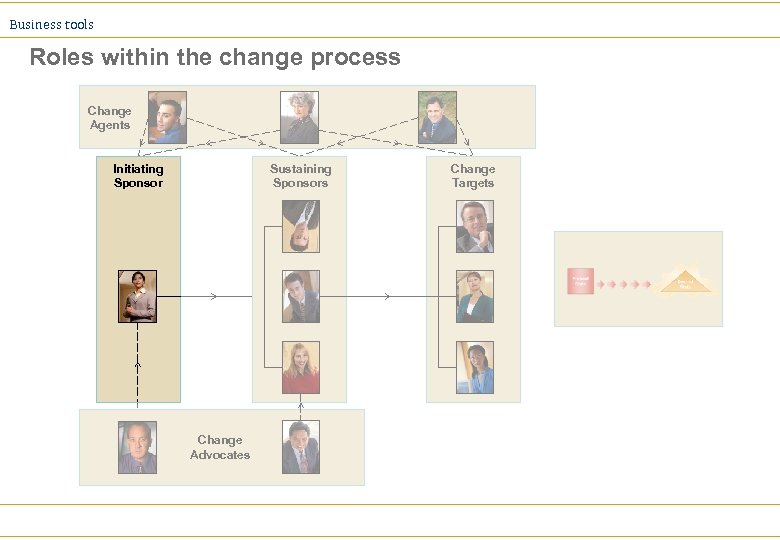
Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets

Business tools Initiating sponsor Ø Gives the project ‘legitimacy’ Ø Must have the necessary seniority Ø Must want the change and be seen to want the change Ø May not play a day to day part but must be available to provide support and backing when needed Initiating sponsors will need to provide leadership throughout the project, not only at the launch

Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets

Business tools Sustaining sponsor Ø Provide day to day management backing for specific activity Ø Must want the change and be seen to want the change Ø Must have clear, agreed and measurable targets Sponsorship must cascade throughout the organisation to avoid ‘black holes’ developing where change momentum is lost
Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets

Business tools Target Ø Is someone who will have to change Ø Is probably already too busy Ø May not be aware of the change that is needed Ø May not want it anyway. . . Almost everybody involved will be a target at some point even if they then take on another role

Business tools Roles within the change process Change Agents Initiating Sponsor Sustaining Sponsors Change Advocates Change Targets
Business tools Change agent Ø Have to facilitate the changes (do the training, hold the workshops, produce the material etc) Ø Must have a sustaining sponsor who ‘lends’ their authority Ø Must want the change, be seen to want the change and model the new behaviours Ø Must have clear, agreed and measurable targets Becoming a change agent, particularly in the initial stages of the project, can be difficult and support is essential

Business tools The change agent’s dilemma. . . Ø The sponsor needs to make his/her commitment clear to the target (ie “I’m behind this 150%”) Ø Sponsorship cannot be delegated to agents Ø Agents cannot legitimise change Ø Only sponsors can legitimise change . . . is the sponsor’s challenge

Business tools Principles of sponsorship Ø Sponsorship is critical to successful change Ø Sponsorship cannot be delegated to agents Ø “Initiating” and “Sustaining” sponsors must never attempt to fulfill each other’s functions Ø Cascading sponsorship must be established and maintained Ø Weak sponsors must be educated or replaced, or failure is inevitable

Business tools A guiding coalition, and roles in change Ø How is FATP doing? Ø What are the implications? Ø What should/can we do?

Business tools Communicating the vision and building commitment

Business tools Commitment Phase VIII. Internalisation VII. Institutionalisation Commitment Threshold VI. Adoption Acceptance Phase V. Installation IV. Positive perception Disposition Threshold III. Understand the change II. Awareness of the change I. Contact Unawareness Confusion Negative perception Decision not to attempt/support installation Change aborted after initial after extensive utilisation Time Ø SOURCE: Preparation Phase Degree of support for the change The path to commitment
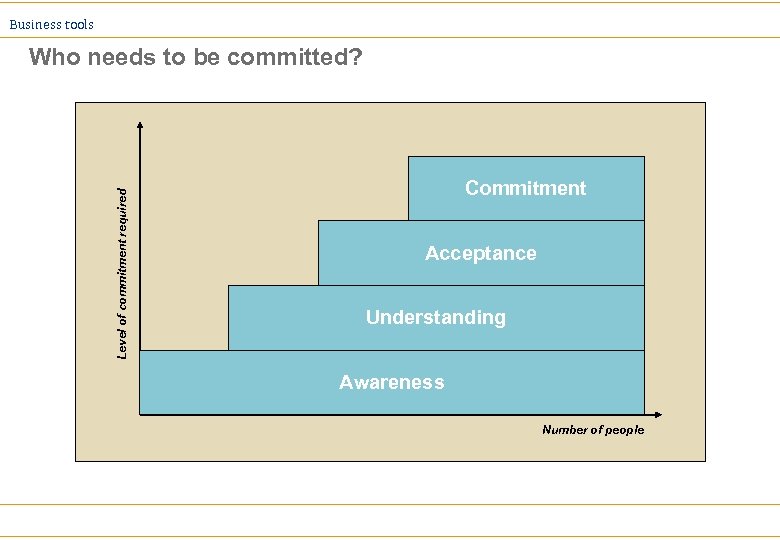
Business tools Level of commitment required Who needs to be committed? Commitment Acceptance Understanding Awareness Number of people
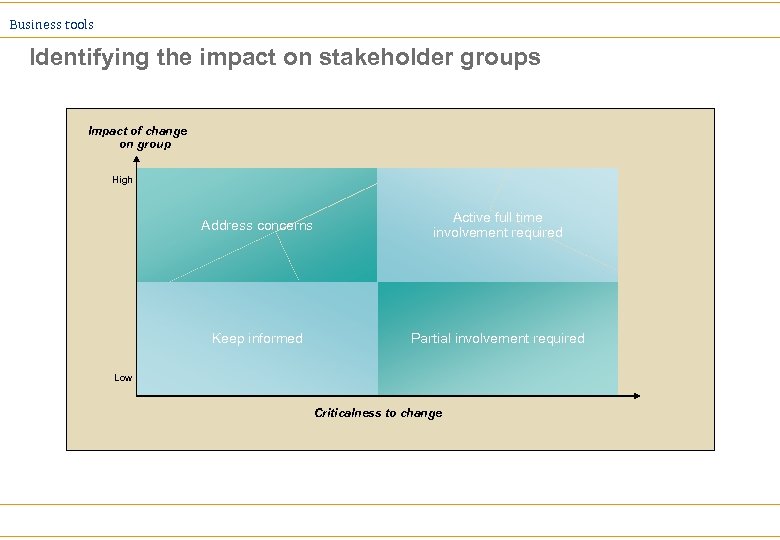
Business tools Identifying the impact on stakeholder groups Impact of change on group High Address concerns Active full time involvement required Keep informed Partial involvement required Low Criticalness to change

Business tools Tailoring the communication effort Level of commitment required Commitment Acceptance Understanding Awareness Quad 1 2 3 4 Number of people

Business tools Communicating the vision and building commitment Ø How is FATP doing? Ø What are the implications? Ø What should/can we do?

Business tools Empowering others to act on the vision, and managing resistance
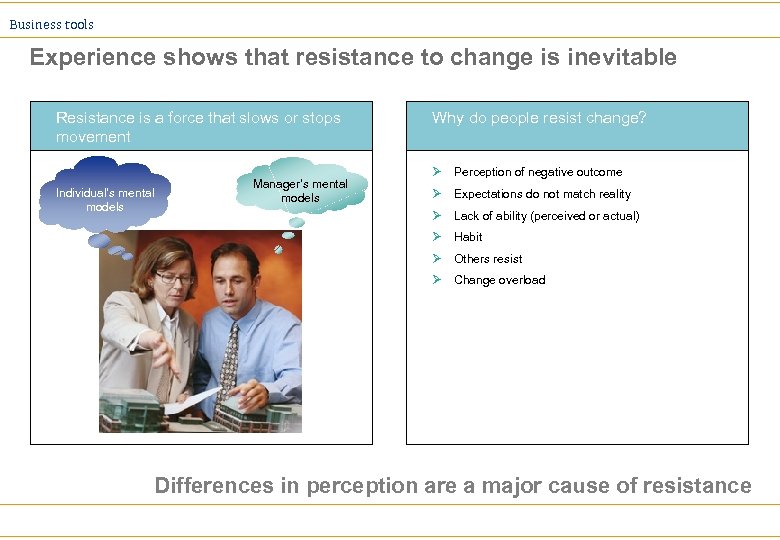
Business tools Experience shows that resistance to change is inevitable Resistance is a force that slows or stops movement Individual’s mental models Manager’s mental models Why do people resist change? Ø Perception of negative outcome Ø Expectations do not match reality Ø Lack of ability (perceived or actual) Ø Habit Ø Others resist Ø Change overload Differences in perception are a major cause of resistance

Business tools Dysfunction occurs because of the aggregate impact of several changes Assimilation Points Used Macro 1000 Organisational 900 Micro 800 700 600 800 points Bereavement 700 points Divorce 500 550 points Service Culture 400 points OCP 300 200 points Laser 100 75 points Prince William 100 points The Euro 400 points BSC 100 points I-buy Examples of multiple changes that require assimilation effort
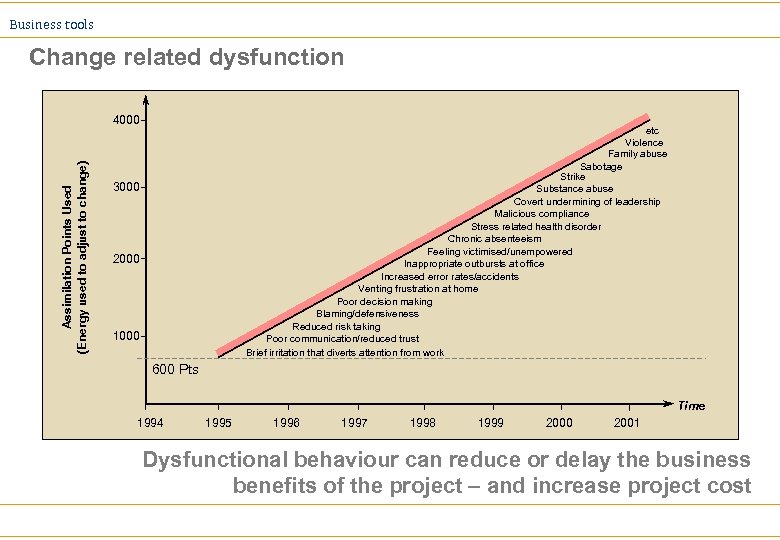
Business tools Change related dysfunction Assimilation Points Used (Energy used to adjust to change) 4000 etc Violence Family abuse Sabotage Strike Substance abuse Covert undermining of leadership Malicious compliance Stress related health disorder Chronic absenteeism Feeling victimised/unempowered Inappropriate outbursts at office Increased error rates/accidents Venting frustration at home Poor decision making Blaming/defensiveness Reduced risk taking Poor communication/reduced trust Brief irritation that diverts attention from work 3000 2000 1000 600 Pts Time 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 Dysfunctional behaviour can reduce or delay the business benefits of the project – and increase project cost

Business tools Emotional response to negative change Active Adjustment Emotional response Anger Bargaining Depression Time Ø Elisabeth Kubler-Ross Shock Passive Testing Denial Stability

Business tools When a change is perceived as positive Pessimism Opting Out Informed Pessimism (Doubt) 3. Hopeful Realism (Hope) 4. 1. Uninformed Optimism (Certainty) Informed Optimism (Confidence) 5. Completion (Satisfaction) Ø Daryl Connor 2.
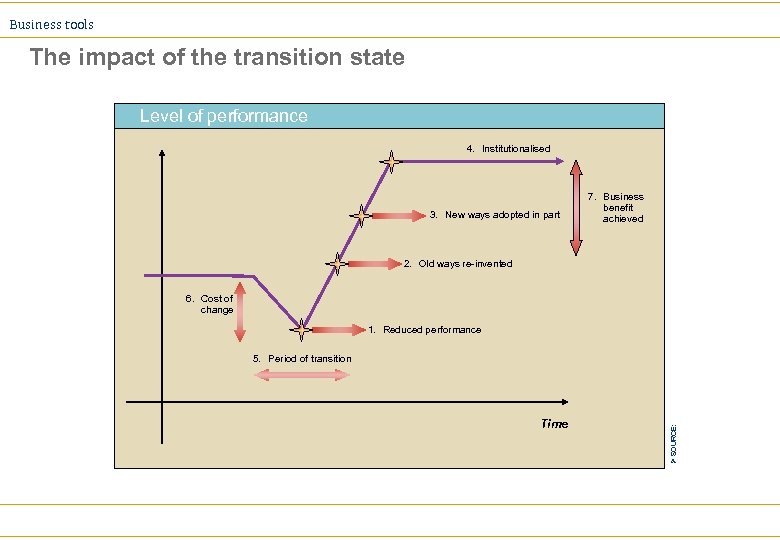
Business tools The impact of the transition state Level of performance 4. Institutionalised 3. New ways adopted in part 7. Business benefit achieved 2. Old ways re-invented 6. Cost of change 1. Reduced performance Time Ø SOURCE: 5. Period of transition
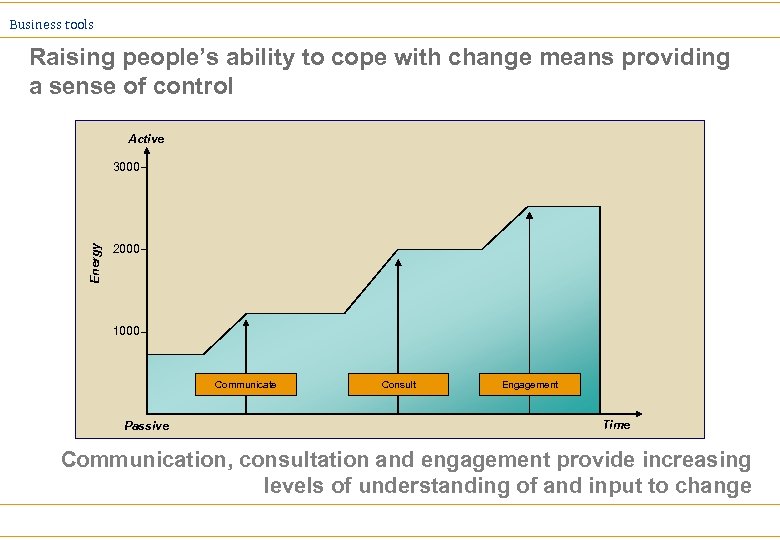
Business tools Raising people’s ability to cope with change means providing a sense of control Active Energy 3000 2000 1000 Communicate Passive Consult Engagement Time Communication, consultation and engagement provide increasing levels of understanding of and input to change

Business tools People react to change by. . . Ø Adopting coping responses Ø Assimilating change – up to their personal capacity at the time Ø If overloaded: demonstrating dysfunctional behaviour Ø Resisting How can we help people through change? Ø By raising their ability to cope Ø By surfacing and addressing resistance

Business tools The importance of surfacing resistance early Ø Resistance to change We need to surface resistance early so that people Ø Ø Fully understand the consequences of decisions Learn to accept these consequences and become resolute Resistance Dangerous Ideal Implement Time Ignored or suppressed resistance is likely to surface at a high pressure point in the programme
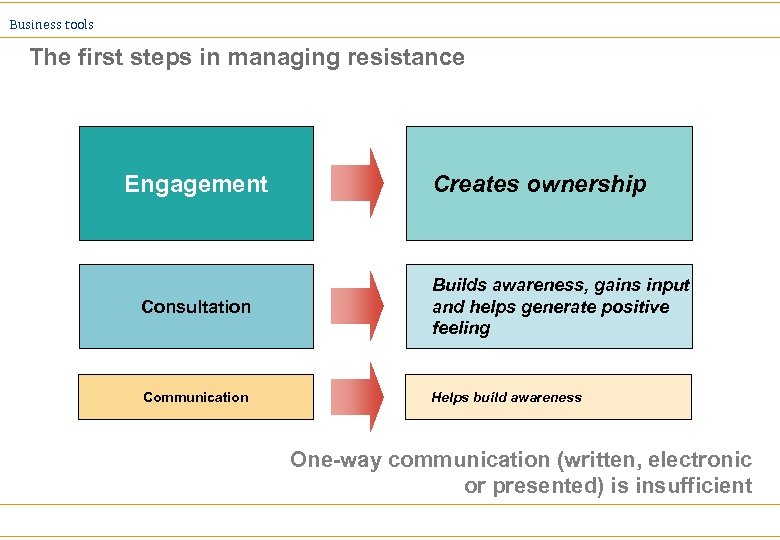
Business tools The first steps in managing resistance Engagement Creates ownership Consultation Builds awareness, gains input and helps generate positive feeling Communication Helps build awareness One-way communication (written, electronic or presented) is insufficient
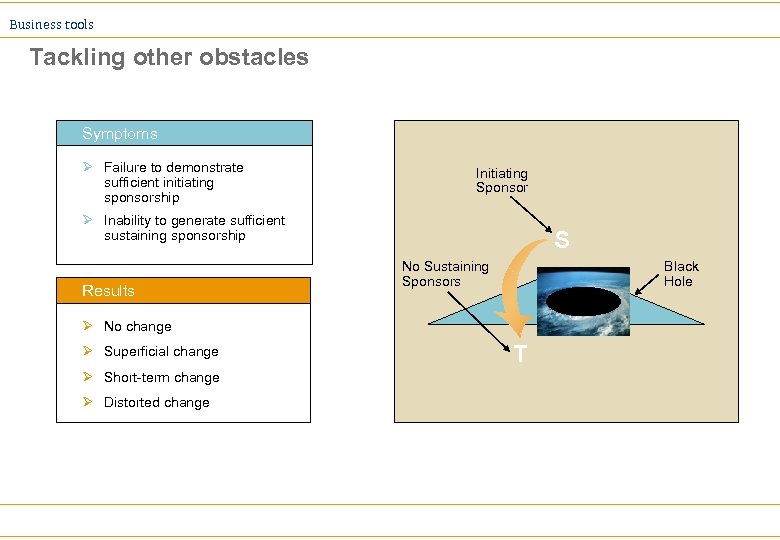
Business tools Tackling other obstacles Symptoms Ø Failure to demonstrate sufficient initiating sponsorship Initiating Sponsor Ø Inability to generate sufficient sustaining sponsorship Results S No Sustaining Sponsors Black Hole Ø No change Ø Superficial change Ø Short-term change Ø Distorted change T

Business tools Institutionalising new approaches

Business tools “Change the change, change the culture, or prepare to fail!” Current Culture Introducing a change that is radically different from the existing culture is difficult to achieve Attempts to introduce changes that are generally consistent with the current culture are usually successful Belief Behaviours Assumptions “Change the change, change the culture, or prepare to fail!”
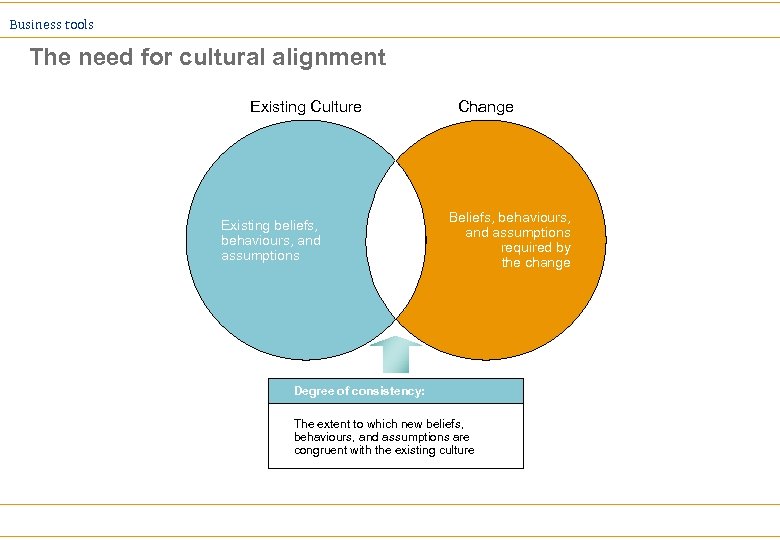
Business tools The need for cultural alignment Existing Culture Existing beliefs, behaviours, and assumptions Change Beliefs, behaviours, and assumptions required by the change Degree of consistency: The extent to which new beliefs, behaviours, and assumptions are congruent with the existing culture

Business tools Building the capacity for continuous change Present State Desired State Capacity for change

Business tools Detecting the culture Ø What do leaders measure, reward, control? Ø Leaders’ reaction to critical incidents Ø Who are the role models? Ø Criteria for recruitment, promotion, retirement and departure Ø Formal and informal socialisation: rituals and rites of passage Ø Stories and myths about key people and events Ø Organisation and physical design Ed Schein
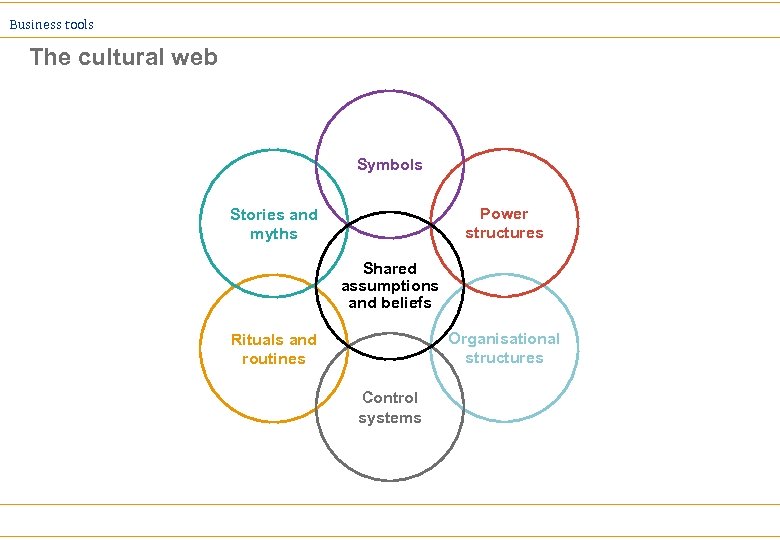
Business tools The cultural web Symbols Power structures Stories and myths Shared assumptions and beliefs Organisational structures Rituals and routines Control systems

Business tools The individual mindset – the building block of culture Skill Knowledge Social role Values Self image Personality traits Motivation

Business tools The levers of change Skills and behaviour Leadership Ø FACT Ø Finance Forum Ø Customer focus Ø Competencies for new processes Mindset Vision ‘New World’ Process and systems Ø Leapfrog Ø Laser Ø GSTP Organisatio n Structure Ø OCP Performance Review Results HR Processes

Business tools Institutionalise new approaches Ø How is FATP doing? Ø What are the implications? Ø What should/can we do?
Business tools Review of Day 1
Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools Mapping Your Interactions

Business tools Change Team Map - Bubble Chart Ø Identify a significant change that you are involved in Ø List all the people who have an impact on that change (formally and informally). Name individuals rather than job titles or depts Ø In the centre of a blank page, write your name and a brief description of your responsibility for the change Ø Draw circles for each of the people listed in step 2. Represent how closely or frequently you work with each person by how closely you draw their circle Ø Represent the importance of each relationship by the thickness of the line and the nature of the flow of information with arrows
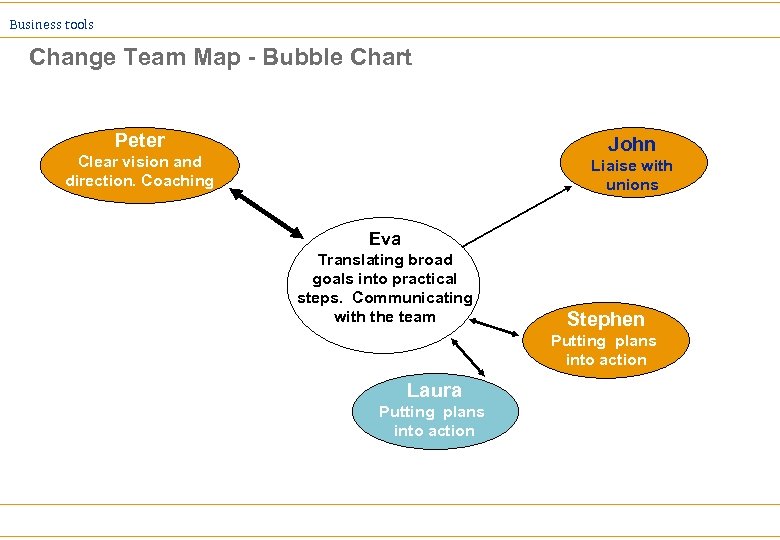
Business tools Change Team Map - Bubble Chart Peter John Clear vision and direction. Coaching Liaise with unions Eva Translating broad goals into practical steps. Communicating with the team Stephen Putting plans into action Laura Putting plans into action
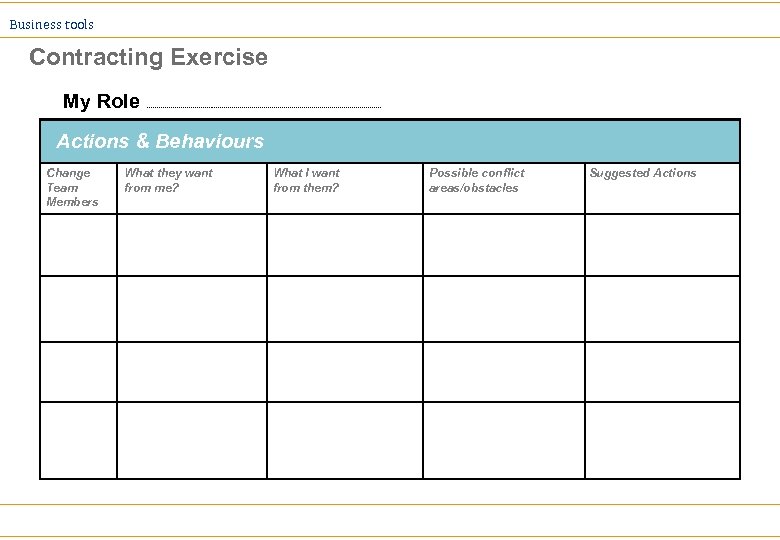
Business tools Contracting Exercise My Role Actions & Behaviours Change Team Members What they want from me? What I want from them? Possible conflict areas/obstacles Suggested Actions

Business tools The Change Agent Role and Skills

Business tools The role of the change agent The change agent is the essential link between the sponsor, who legitimises the change, and the targets, who actually change. Therefore change agent skills are critical to successful implementations In addition to “technical” knowledge and skills in their specialist area, change agents must be able to apply a wide range if interpersonal skills, based on what is increasingly be called “emotional intelligence” The foundation of emotional intelligence is self-awareness

Business tools etc Confronting Conflict Resolution Coaching Feedback Influencing Listening Emotional intelligence

Business tools Differential responses to change Ø A key factor in the application of change agent skills is the ability to understand the other persons “frame of reference” Ø One useful way of categorising frames of reference is to understands the degree to which the other person is primarily a: ä An intuitor ä A thinker ä A feeler ä A sensor
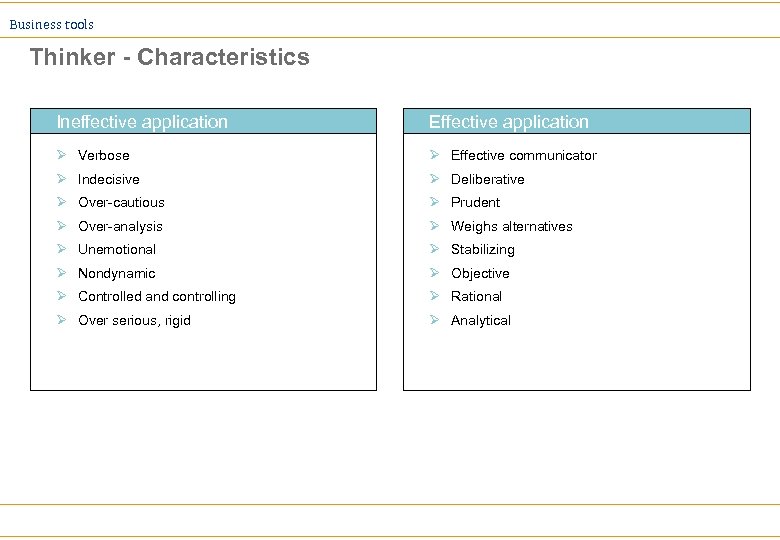
Business tools Thinker - Characteristics Ineffective application Effective application Ø Verbose Ø Effective communicator Ø Indecisive Ø Deliberative Ø Over-cautious Ø Prudent Ø Over-analysis Ø Weighs alternatives Ø Unemotional Ø Stabilizing Ø Nondynamic Ø Objective Ø Controlled and controlling Ø Rational Ø Over serious, rigid Ø Analytical

Business tools Thinker - Behaviours Typically: Under Stress: Ø Works in a steady, tenacious manner Ø Can be overly cautious – to the point of indecision Ø Relies upon observation and rational principles (logic) Ø Avoids emotionalism Ø Is sceptical towards novel departures form what’s been proven out in the past Ø Is sceptical of own initial reactions and those of others until tested analysed Ø Prefers to “sleep” on new ideas before making a commitment Ø Avoids being swept away by needs of the moment or emotional fervour Ø Is likely to appear rigid and insecure Ø Is concerned with correctness at the expense of timely exploitation of opportunities Ø Appears emotionally “out of touch”, task oriented Ø Is at times unwilling to depart from established methods and routines

Business tools Sensor - Characteristics Ineffectiveness application Effective Application Ø Doesn’t see long range Ø Pragmatic Ø Status seeking, self-involved Ø Assertive, directional Ø Acts first, then thinks Ø Results-oriented Ø Lacks trust in others Ø Objective – bases opinions on what he or she actually sees Ø Domineering Ø Arrogant Ø Competitive Ø Confident

Business tools Sensor - Behaviours Typically: Under Stress: Ø Is a doer, moves ahead resourcefully, seems to move mountains Ø Is somewhat impatient acts impulsively, and likes short-term results but lacks long-range vision Ø Thrives on working on a variety of project tasks at once Ø Has an incredible ability to get things done Ø Is overreactive to diverse opinions that represent resistance for caution and movement Ø Will commit to things only after he or she thinks it’s likely to work Ø Has a tendency to ride roughshod over feelings of others Ø Must be able to understand relate to proposed action to his or her direct experience or finds it difficult to proceed Ø Is likely to construe loyalty as a degree to which other agree with or help him or her Ø Learns best by doing, not by theoretically or conceptually analysing the situation Ø Is direct and decisive Ø Relieves anxiety by acting Ø Is well organised, pragmatic, hard-driving Ø Imposes high standards for self and others Ø May demonstrate “tunnel vision”

Business tools Intuitor - Characteristics Ineffective application Effective application Ø Unrealistic Ø Original Ø “far out” Ø Imaginative Ø Fantasy-bound Ø Creative Ø Scattered Ø Broad-gauged Ø Devious Ø Charismatic Ø Out of touch Ø Idealistic Ø Dogmatic Ø Intellectually tenacious Ø impractical Ø ideological

Business tools Intuitor - Behaviours Typically: Under Stress: Ø Is a fast, deep thinker Ø May be seen by others as detached or overly intellectualised Ø Questions him or herself and others, therefore doesn’t take things for granted Ø Seems at times to know things before others Ø Resents being hemmed in or required to operate in a well-defined manner Ø Enjoys creating own structure out of disorder Ø Cuts through traditional thought and able to see profitable new directions and solutions Ø Is concerned with the big picture Ø Can be impatient – irritated with other who demand detail Ø Can be more concerned with developing ideas than putting them into practical use Ø At times, uncompromising and impractical Ø More concerned with development and defence of ideas than in translating them into more visible forms or trying to adapt them to the suggestions of others Ø Avoids the tedious, nitty-gritty details
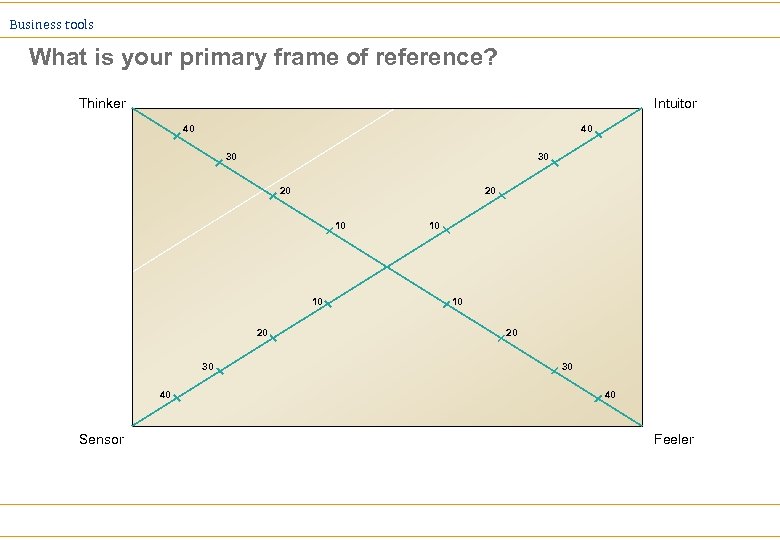
Business tools What is your primary frame of reference? Thinker Intuitor 40 40 30 30 20 20 10 10 20 30 40 Sensor 10 10 20 30 40 Feeler

Business tools Focus on Listening
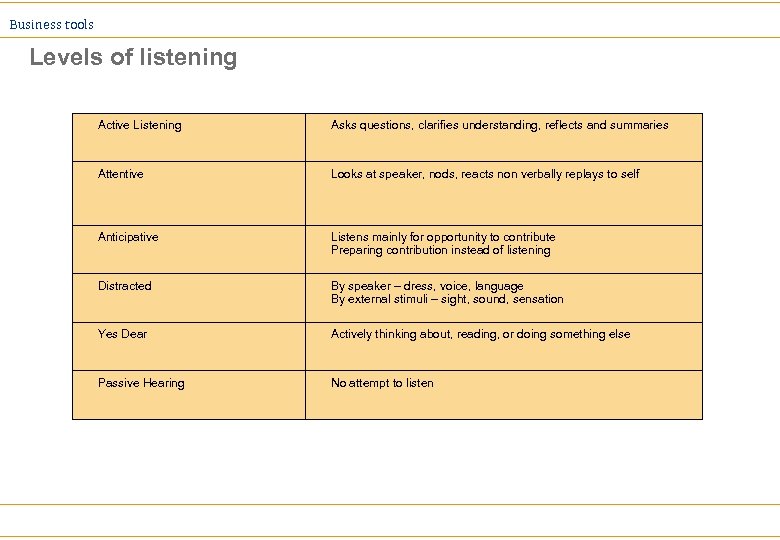
Business tools Levels of listening Active Listening Asks questions, clarifies understanding, reflects and summaries Attentive Looks at speaker, nods, reacts non verbally replays to self Anticipative Listens mainly for opportunity to contribute Preparing contribution instead of listening Distracted By speaker – dress, voice, language By external stimuli – sight, sound, sensation Yes Dear Actively thinking about, reading, or doing something else Passive Hearing No attempt to listen

Business tools Active listening Ø Communicates to the other person that they are heard and understood Ø Recognises the feelings that underlie what is being said Ø Makes the other person feel accepted as a person by the listener

Business tools Active listening: How would you respond ? “I feel frustrated that I don’t have the resources I need to do my job”

Business tools Active listening - Why is it Difficult? Ø What are the barriers to being an effective listener?

Business tools Active listening - Two Facets Level 1 - Drawing out information Ø Ø Paying attention Questioning Probing Encouraging Level 2 - Communicating understanding Ø Ø Feeding back what has been heard Reflecting implications Acknowledging feelings Probing
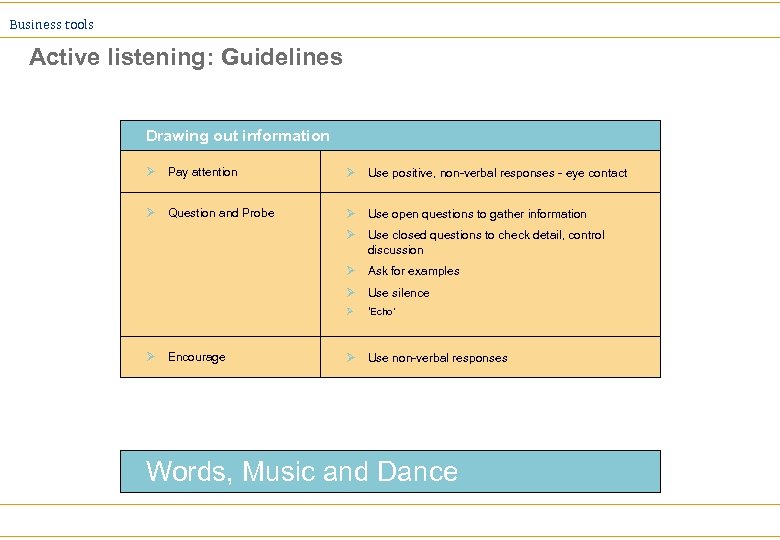
Business tools Active listening: Guidelines Drawing out information Ø Pay attention Ø Use positive, non-verbal responses - eye contact Ø Question and Probe Ø Use open questions to gather information Ø Use closed questions to check detail, control discussion Ø Ask for examples Use non-verbal responses Ø Use silence Ø Ø Encourage ‘Echo’ Ø Use non-verbal responses Words, Music and Dance
Business tools Active Listening: Guidelines Communicate understanding Ø Feedback - what has been heard/ ä “As I understand it. . . ” Ø Reflect implication ä ‘so that may mean’ Ø Acknowledge feelings ä ‘that must have been hard’ Ø Probe more ä ‘how did that make you feel? ’ paraphrase

Business tools Active listening exercise Ø In triads comprising one speaker, one listener and one observer: Ø Speaker: Talk about a change you have been involved with that went well or poorly Ø The listener is to use active listening skills to develop their understanding of the situation the speaker found themselves in Ø At the end, the listener is to feed back a summary of what has been said and their perceptions of the speakers feelings Ø The observer manages the time and feedback process

Business tools Summary Ø Active listening is a critical skill effective two-way communication performance in any situation Ø Active listening is easy to understand what active listening is, but difficult to do in “real life”. It takes conscious effort and practice Ø The rewards are greater clarity of understanding and commitment for all

Business tools Summary: Key elements in the change process Synergistic Relationship Present State D i s s a f a c t i s f a c t i o n Transition risk factors Sponsor Commitment Agent Skills Mindset Cultural Alignment Plan Time Target Resistance V i s i o n Desired State

Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Ø Review and Next Steps

Business tools Team and individual action plans

Business tools Change team action plans
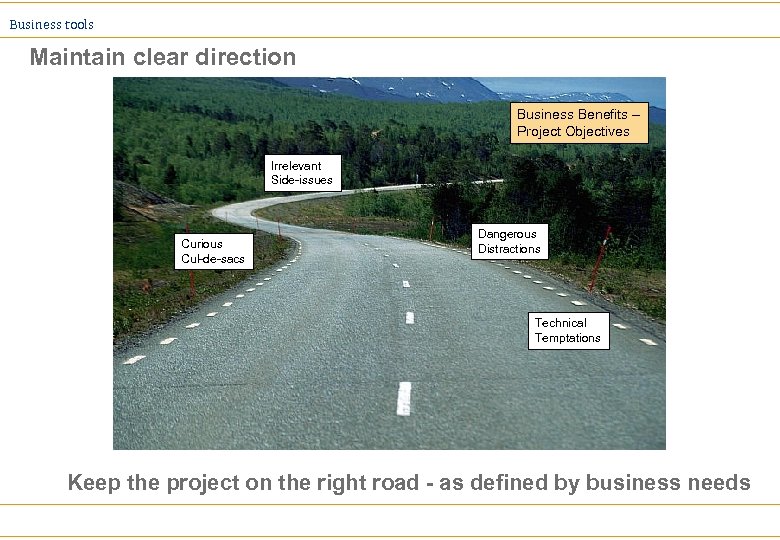
Business tools Maintain clear direction Business Benefits – Project Objectives Irrelevant Side-issues Curious Cul-de-sacs Dangerous Distractions Technical Temptations Keep the project on the right road - as defined by business needs

Business tools What is a Plan? Ø What are we doing? - it re-states the objectives Ø How are we doing it ? - it outlines our strategy Ø What does this involve? - it identifies activities Ø When will we do these? - it specifies a schedule Ø Who is doing what? - it defines responsibilities and organisation Ø How much will it cost? - it includes cost estimates Ø What if things change? - it defines control processes Ø How do I understand it? - it is simple, structured, and up-to-date

Business tools A project management plan Business needs and project objectives Organisation Time Scope (Work Breakdown) Resources HL HH LL LH Costs Risks A project plan is not just a schedule

Business tools Typical project management plan contents Ø Project Specific 1. Introduction Background, business needs, benefits and costs 2. Terms of Reference Objectives, key deliverables, contract, constraints 3. Project Implementation Strategy 4. Risk Management 5. Project Organisation Approach, key risks, contingency plans Management and reporting structure 6. Project Control Procedures 7. Meetings Schedule Ø High level risk assessment Ø Cost schedules Documentation, routines Purpose, frequency, attendees, purpose Appendices Ø Top level plan Resources, approach, communications

Business tools Planning: group exercise
Business tools Summary Ø Always keep focused on the business objectives and benefits Ø Project planning is more than producing a schedule Ø Involvement from others during planning will produce a better result

Business tools Agenda Ø Introduction Ø Developing Team Effectiveness Ø Reviewing Team Goals Ø Delivering Business Benefits Ø Working Together Ø Prioritising and Planning Review and Next Steps Ø Review and Next Steps
Business tools Responsibility chart What needs to be done? By whom? By when? Other eg resources/assumptions?
82b37a59c05b87db701e0cd0a3602523.ppt