467b3e200c4e84a2a70547989a4f10fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 91
Business System Requirement Analysis (BSRA) (Business Process Redesign) NY DAMA 2012 Presented by: Arvind D. Shah, Managing Principal Performance Development Corporation Princeton, NJ 08540 (609)443 -1226 ads 1@perfdev. com www. perfdev. com 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 1 pdc

History of Accomplishments Performance Development Corporation (PDC) is recognized internationally for assisting hundreds of clients in achieving business benefits from advanced technologies. PDC has made significant contributions through a series of notable accomplishments including: Model Driven Enterprise Information Integration (2005) CRM article published in the Journal of International Institute of CRM (UK) (2003) Business Process Redesign Handbook (1997) Introduced comprehensive Change Management seminar and methodology(1994) Integrated Business Reengineering, Total Quality Management, and Information Engineering methodologies (1991) Information Strategy Planning Handbook (1990) The Management Handbook for Information and End User Computing (1988) Relational Development Environment Guide (1987) Started the industry-leading Data Base Newsletter (1979) Developed Data Administration concept (1976) Developed Service Analysis - a methodology for defining end user requirements (1975) 5/9/12 Published Comparative Analysis of Data Base Management Systems (1973) Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 2 pdc

Mission Enable our customers to clarify and/or achieve their business goals through the gainful use of knowledge, technology and change methods and techniques. PDC helps its clients accelerate their move to new business environments through knowledge and technology enabled management. We assist clients as they seek to clarify and implement business strategy in advanced technology environments. We help management ensure that the business drives the process and that technology provides practical value within a changing organizational culture. Technology Enabler and Driver New Business Environment e c an t sis s A C D P Old Business Environment Empowered Management 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 3 pdc
Partial Client List Manufacturing Financial /Insurance Abitibi-Price(Canada) ALCOA Ciba-Geigy EBSCO Eli Lilly and Company FMC Corporation General Motors Hallmark Cards IBM Iron Ore Company(Canada) Lockheed Merck and Company Nycomed(Norway) Philip Morris Toshiba(Japan) United Biscuits (UK) Weyerhaeuser Abbey National Bank(UK) American Express Bank of America Bank of Delaware Blue Cross/Blue Shield Dow Jones Fireman's Fund Insurance JCPenny Life Johnson and Higgins Kemper Insurance Providian Insurance Transamerica Insurance UNUM Insurance USF&G Utilities AT&T Boston Edison Carolina Power and Light GTE National Fuel Gas Nebraska Public Power District NYNEX Oglethorpe Power Southern California Gas Southwestern Bell Telephone United Telephone 5/9/12 Federal, State, Local Government Atomic Energy (UK) Belmont County, OH Calgary(Canada) City Canada Post (Canada) Delaware Department of Finance Montgomery County, MD New Hampshire Dept. HHS New Jersey Motor Vehicle Services New Jersey OTIS South Dakota Dept. of Transportation Wisconsin Dept. of Transportation US Agency International Development US Central Intelligence Agency US Department of Energy US Naval Facilities Engineering Petroleum Exxon Getty - Texaco Indian Oil (India) Mobil Oil Norsk-Hydro (Norway) Shell Oil Sun Oil Retail Compucenter(Brazil) Giant Foods Sainsbury(UK) Thorn-EMI(UK) Venture Stores Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Transportation Leaseway Mayflower Education Cornell University Duke University of Michigan National Education Association Service American Bible Society CH 2 M Hill Young & Rubicam (UK) 4 pdc

Consulting Services Our scope of consulting and education services is in a constant state of evolution due to the introduction of new management techniques and advanced technologies and their proven viability in the marketplace. PDC currently provides consulting, education and placement expertise in the following areas: Management • Business Process Reengineering • Customer Relations Management • Information Strategy Planning • Enterprise Architecture Planning • Visioning and Managing Change • Data Management/governance • Disaster Contingency Planning Technology • IT Restructuring • Technology Architectures and Selection • Business Area Analysis • Process/Data Modeling • IRM for Emerging Technologies • Data Warehousing • Internet/Intranet/Extranet Implementation • Turnkey Systems • Project Management • E-Commerce Development • Offshore Development • Quality Assurance Professional Services • Executive Search • Permanent Recruiting • Contract Services 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 5 pdc

Education Services Effective on-site education course offerings have always been a top priority at PDC. Thousands of individuals have attended our seminars, normally offered in one, two and three day formats. These may be condensed to short management presentations. Our current course titles include: Business Reengineering (2 days) Provides an intensive, management-oriented overview based on extensive experience and the dramatic results achieved. Business Process Redesign (3 days) Shows how to redesign business processes to increase profits, productivity, competitiveness and customer service. Information Strategy Planning (3 days) Describes managing business success through defining organization information needs and priorities in a structured manner. Business System Requirements Analysis (3 days) Shows how to analyze business requirements using data modeling, process modeling, and information engineering techniques. Managing the Data Warehouse Commitment (2 days) Illustrates business driven approaches to utilizing information assets. Change Management (3 days) Shows how to integrate change in people, systems and structures. Information Resource Management (2 days) Illustrates how to use Data Sharing and Data Availability to accomplish the business improvement objectives. Data Modeling (2 days) Explains different levels of Data Modeling that play an important role during the Planning (ISP), Analysis (BAA) and Design (BSD) phases. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 6 pdc

Arvind D. Shah Managing Principal Mr. Shah is a Managing Principal of Performance Development Corporation and is known internationally as a speaker and authority. Mr. Shah has over thirty years of broad experience, assisting and leading efforts in Strategic Planning, Change Management, Business Reengineering, Information Engineering, Information Strategy Planning, Data Administration, Data Warehousing, and Project Management for major corporations worldwide. His consulting has involved virtually all facets of business and government in a broad range of applications. Mr. Shah's principal interests have been focused on the end user and managerial aspects of Information Technology. He developed PDC’s approach to blending Business Reengineering, Total Quality Management (TQM) and Information Engineering. He has also developed management principles to integrate the front end Internet and client/server environments with the back end mainframe computing. Prior to joining PDC, Mr. Shah was with Dow Chemical, General Electric, Exxon and Corning Glass. He was responsible for project management and design, development and implementation of IT applications in the areas of customer service, finance and accounting, sales order processing and invoicing, inventory management, facilities planning, management information, profit planning, sales forecasting, and material management systems. He has extensive experience with decision support systems and data warehousing. His experience includes: Business Reengineering • Developed a Business Process Redesign Methodology that blended Business Reengineering, TQM, and Information Engineering. Applied Business Reengineering techniques to significantly reduce the Procurement Cycle for parts and equipment in a Mining organization. • Decreased the Order Processing and Billing cycle from seven days to one half day through Business Reengineering for a large Textile company. Guided a major Insurance company in the area of Claims Processing, reducing manpower by 60% while increasing customer service and responsiveness with an overall payback completed in less than two years. • Headed a project to develop a business reengineering strategy development project for a technology service company. The deliverables included a plan that blended Business Reengineering and Information Engineering. • Assisted a major pharmaceutical firm in reengineering their sales force consisting of 2000 sales persons. The team consisted of the client as well as consultant staff. Information Engineering Mr. Shah has directed or assisted over 100 projects involving Information Strategy Plans (ISP’s), Business Area Analysis (BAA), Data Warehouse, Information Resource Management and other aspects of planning, design and implementation of information systems for major Fortune 1000 size commercial organizations and government agencies. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 7 pdc

Reengineering of the Information Technology Services (IS) Function Guided the restructuring of the IS Function for a strategic business unit of a Fortune 1000 sizes global telecommunications firm. The objective was to prepare for planned business reengineering projects. Assisted a division of a major Pharmaceutical company in the reorganization of its IS function. The objective was to build systems using Information Engineering and Client Server Technologies. Directed a project which involved restructuring the IS function of a Public Utility company. The objective was to transform the IS organization into a mature organization capable of capitalizing on new technologies while being responsive to business needs. The impetus was to incorporate Planning, Business Reengineering and TQM in all their projects. Clients Served AT&T Nebraska Public Power District National Fuel Gas Eli Lilly Capital Holdings/National Liberty National Fuel Gas Navy Federal Credit Union Rodale Press Southwestern Bell Unionmutual Insurance Co. CH 2 M Hill, Inc. Getty/Texaco Oil State of Delaware Naval Facilities Engineering Command United Biscuits (UK) Venture Stores GTE AP Technoglass Thorn EMI (UK) State of New Jersey FMC University of Michigan Iron Ore (Canada) Toshiba (Japan) National Computer Center (Brazil) Nycomed (Norway) Education • BS, Electrical Engineering, University of Bombay • MS, Electrical Engineering, Ohio State University • MBA, Information Systems, College of William and Mary Publications Co-authored the following books: The Management Handbook for Information Center and End User Computing, published in 1988 by QED Information Sciences The Information Strategy Planning Handbook, published in 1990 by Performance Development Corporation The Business Process Redesign Methodology Handbook published in 1999 by Performance Development Corporation 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 8 pdc
Business Systems Requirement Analysis (Systematically integrating process, data and business rules) As the bridge from Planning to Design, Business System Requirement Analysis (BSRA) builds upon the results of Enterprise Architecture or Information Strategy Planning to document business system requirements. To be successful, you need a comprehensive methodology which is flexible as well as replicable in addition to modeling tools and techniques. A BSRA project is usually initiated from two sources. It could come from systems planning or be initiated to address a specific business need. In either case it is important that current processes and data sources are analyzed and business rules are extracted and documented. Equally important is to improve process in order to solve the current system problems and take advantage of the new system features. No project can succeed if business analysts did not participate in the business system requirements analysis. The data gathering, validation and approval are key steps for delivering a system that meets business needs. The project must have milestones at which point senior management is involved in decision making. This presentation includes the discussion of the methodology that evolved over 30 years of PDC’s consulting experience. The methodology integrates the aspects of enterprise architecture, information engineering and business process as well as quality management. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 9 pdc
Business System Requirement Analysis (BSRA) 1. The BSRA Methodology 2. How to plan and scope the project for on-time delivery of quality results 3. How to gather and document Requirements 4. How to integrate Process and Data 5. How to redesign processes BSRA 6. How to blend Quality Management 7. How to develop a transition plan 8. How to get management and users involved 9. How to apply this approach to Data Management Processes 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 10 pdc
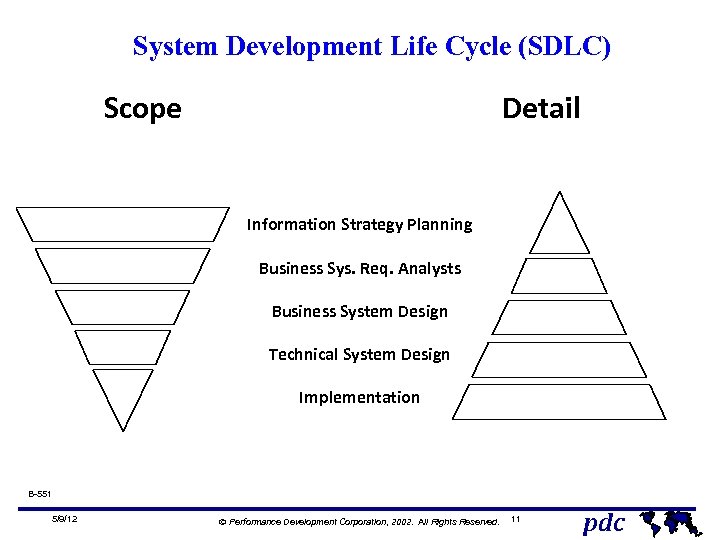
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Scope Detail Information Strategy Planning Business Sys. Req. Analysts Business System Design Technical System Design Implementation B-551 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 11 pdc
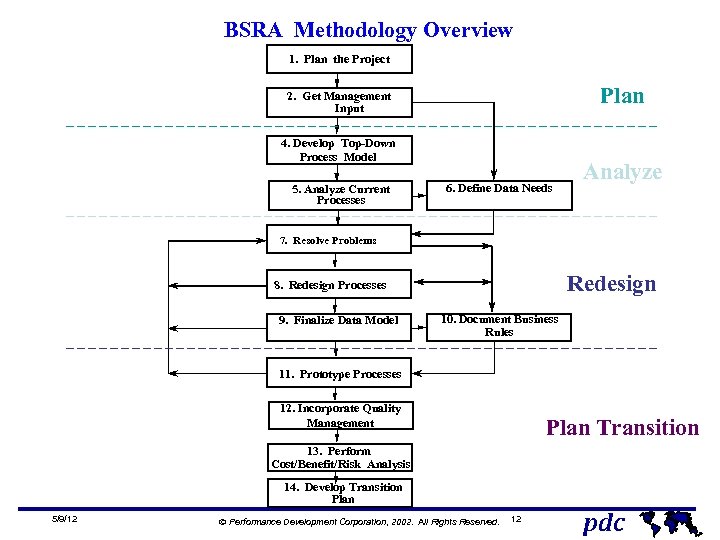
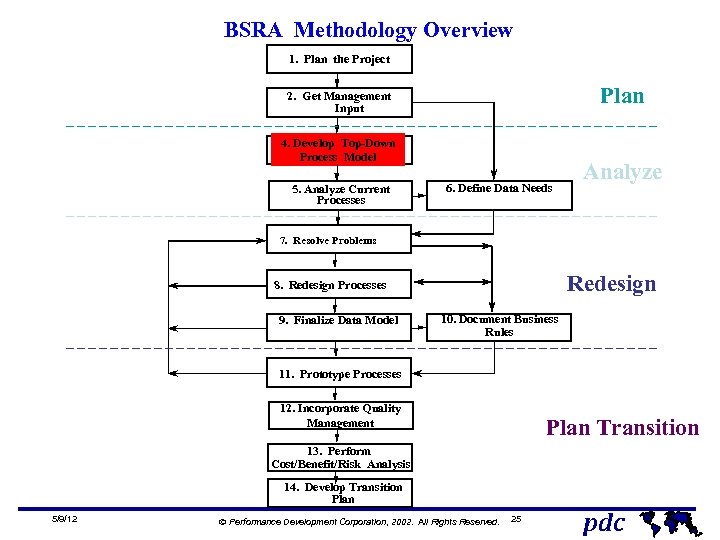
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 12 pdc
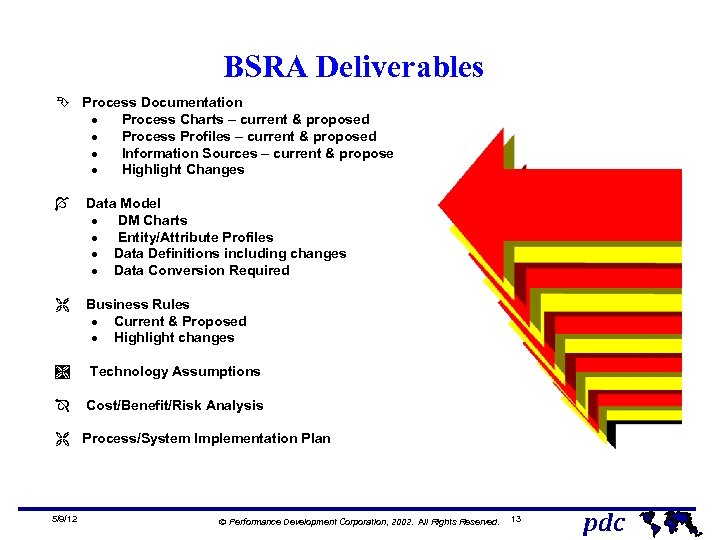
BSRA Deliverables Ê Process Documentation · Process Charts – current & proposed · Process Profiles – current & proposed · Information Sources – current & propose · Highlight Changes Í Data Model · DM Charts · Entity/Attribute Profiles · Data Definitions including changes · Data Conversion Required Ë Business Rules · Current & Proposed · Highlight changes Ì Technology Assumptions Î Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis Ë Process/System Implementation Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 13 pdc
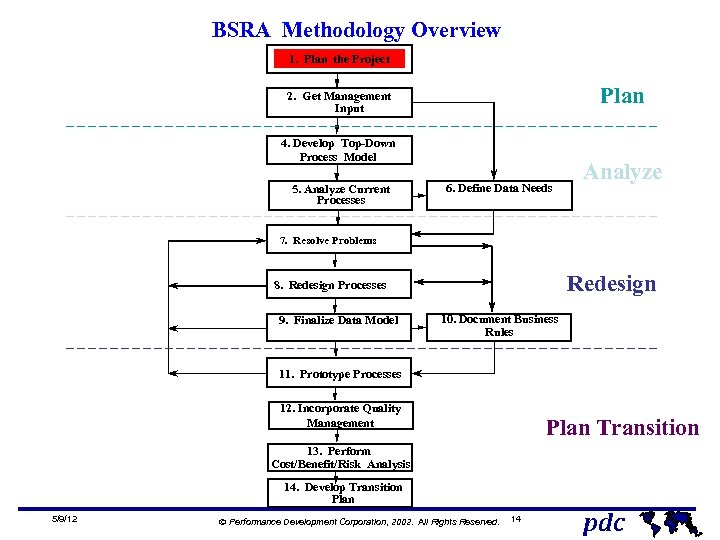
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 14 pdc

Task 1. Plan the Redesign Project Subtasks 1. 1 Define/refine project scope 1. 2 Select project team 1. 3 Secure Facilities 1. 4 Develop project schedule 1. 5 Allocate resources 1. 6 Define deliverables 1. 7 Prepare documentation system 1. 8 Obtain management approval 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 15 pdc
Importance of Scoping u Puts fence around project u Sets Stakeholder expectations u Data Self-sufficiency u Size selected will be appropriate u Timeframe is defined 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 16 pdc
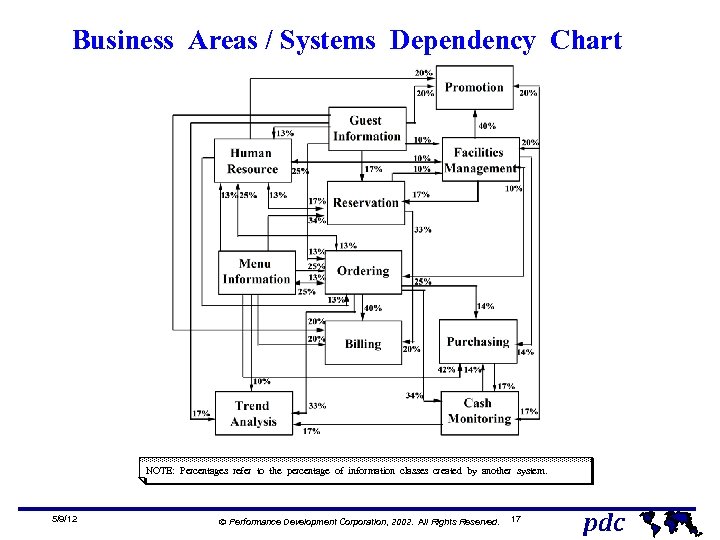
Business Areas / Systems Dependency Chart NOTE: Percentages refer to the percentage of information classes created by another system. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 17 pdc
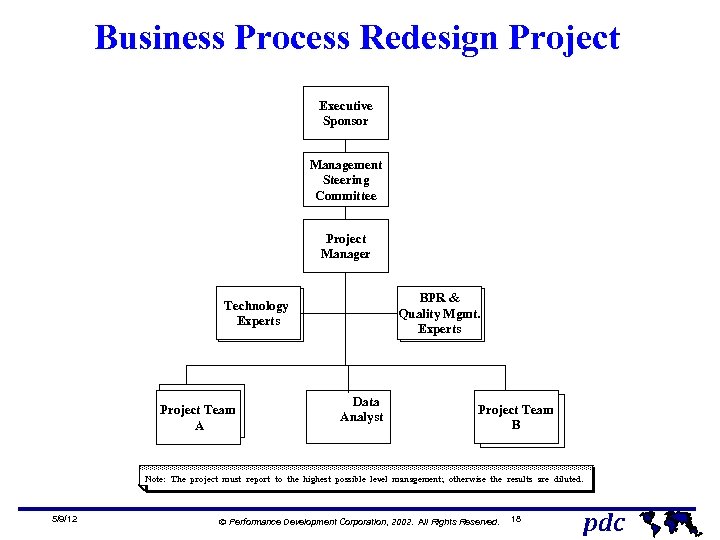
Business Process Redesign Project Executive Sponsor Management Steering Committee Project Manager BPR & Quality Mgmt. Experts Technology Experts Project Team A Data Analyst Project Team B Note: The project must report to the highest possible level management; otherwise the results are diluted. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 18 pdc

Who Gets What Kind of Education and Training? • Management and Client – One-two hour overviews – Brief education at milestone meetings • Project Team – Team-building training in the beginning – Three day workshop training – Periodic reinforcement training at beginning of each major task • Client Representatives – Four hour overview – Brief training when needed • Documentor(s) – One day documentation training and methodology review 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 19 pdc

Interview Estimating 2 hours for preparation 2 hours for interview 2 hours for debriefing/documentation 6 hours q For every interview hour, provide two hours for preparation and review. q Immediate documentation after interview is recommended. q In cases where travel is involved, concentrated period of interviewing must be followed by appropriate time for documentation and cleanup. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 20 pdc

Focus Group Session Estimating + Usually 1/2 or 1 day session. + 6 - 12 participants. + Limited to single topic. + 1/2 day session will require 1/2 day preparation and documentation. + Focus group technique approximately 30% faster than interviewing. + Focus group sessions allow all interested partners to build consensus on models and issues, so less time is required for cleanup and integration. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 21 pdc
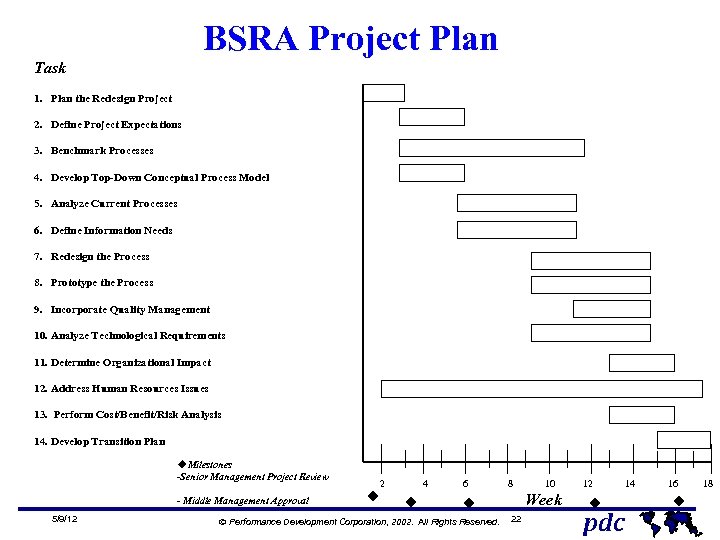
BSRA Project Plan Task 1. Plan the Redesign Project 2. Define Project Expectations 3. Benchmark Processes 4. Develop Top-Down Conceptual Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Information Needs 7. Redesign the Process 8. Prototype the Process 9. Incorporate Quality Management 10. Analyze Technological Requirements 11. Determine Organizational Impact 12. Address Human Resources Issues 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan u. Milestones -Senior Management Project Review - Middle Management Approval 5/9/12 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 u u u Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Week 22 u pdc u
Documentation System & Process & Data & Business Rules & Systems/technology & Problems/solutions & Data gathering & Communication requirements Remember a fool is still a fool with a tool 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 23 pdc

Project Initiation Management Role o Initiate commitment o Continue education o Combine with overview session o Ask for frequent participation o Solicit departmental support while seeking approval o Announcement of project from Chief Executive Officer 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 24 pdc
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 25 pdc

Process Definition A collection of prescribed activities, which, when performed, add value to product or service • Produces distinct deliverable whose quality can be measured • Has a beginning and end • Usually repetitive • At high level is cross functional • At low level is within a function 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 26 pdc
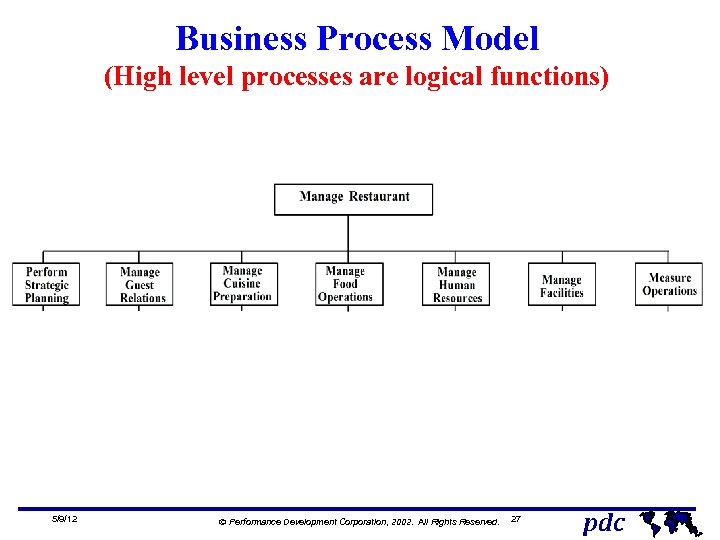
Business Process Model (High level processes are logical functions) 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 27 pdc
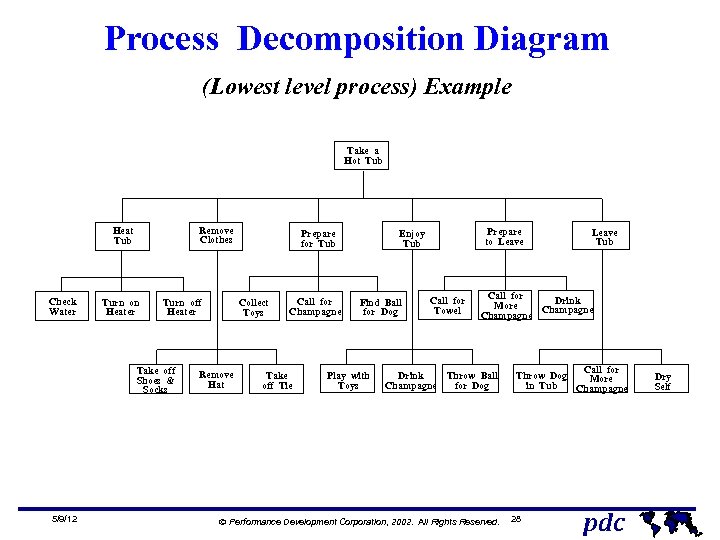
Process Decomposition Diagram (Lowest level process) Example Take a Hot Tub Remove Clothes Heat Tub Check Water Turn on Heater Turn off Heater Take off Shoes & Socks 5/9/12 Prepare for Tub Collect Toys Remove Hat Call for Champagne Take off Tie Prepare to Leave Enjoy Tub Find Ball for Dog Play with Toys Call for Towel Drink Champagne Leave Tub Call for Drink More Champagne Throw Ball for Dog Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Call for Throw Dog More in Tub Champagne 28 pdc Dry Self

Process Profile Content • Objective • Description -------------------[ Stakeholder [ Deliverable/Output [ Trigger [ Input [ Quality Criteria [ Value Added [ Information Needed [ Organizations (participating) [ Frequency [ Volume [ Availability (response time) [ Related Process -Prerequisite -Post-requisite [ Tasks [ Problems [ Current system support Some of these will be developed during project 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 29 pdc
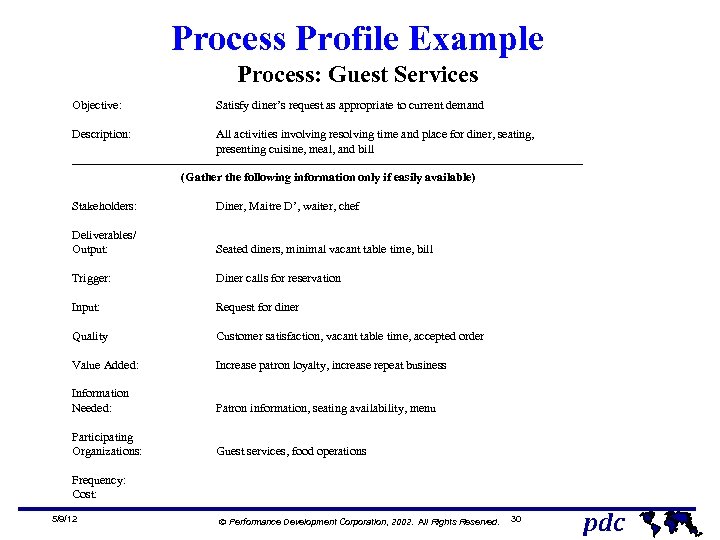
Process Profile Example Process: Guest Services Objective: Satisfy diner’s request as appropriate to current demand Description: All activities involving resolving time and place for diner, seating, presenting cuisine, meal, and bill ----------------------------------------------------------------(Gather the following information only if easily available) Stakeholders: Diner, Maitre D’, waiter, chef Deliverables/ Output: Seated diners, minimal vacant table time, bill Trigger: Diner calls for reservation Input: Request for diner Quality Customer satisfaction, vacant table time, accepted order Value Added: Increase patron loyalty, increase repeat business Information Needed: Patron information, seating availability, menu Participating Organizations: Guest services, food operations Frequency: Cost: 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 30 pdc
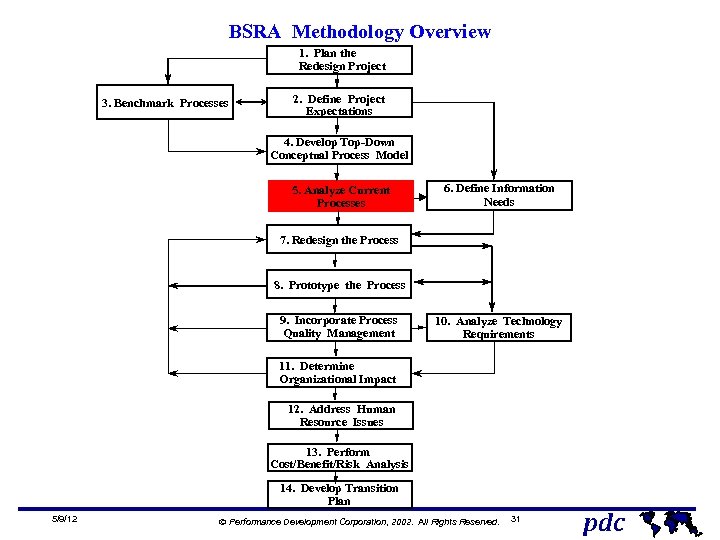
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Redesign Project 3. Benchmark Processes 2. Define Project Expectations 4. Develop Top-Down Conceptual Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Information Needs 7. Redesign the Process 8. Prototype the Process 9. Incorporate Process Quality Management 10. Analyze Technology Requirements 11. Determine Organizational Impact 12. Address Human Resource Issues 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 31 pdc
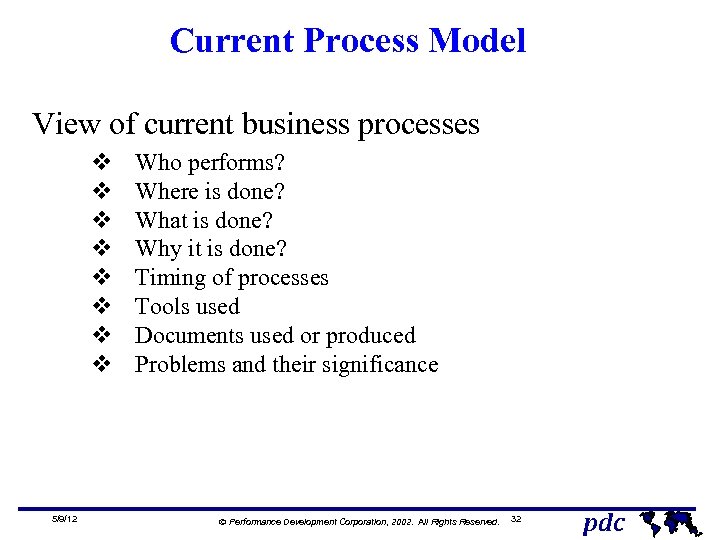
Current Process Model View of current business processes v v v v 5/9/12 Who performs? Where is done? What is done? Why it is done? Timing of processes Tools used Documents used or produced Problems and their significance Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 32 pdc
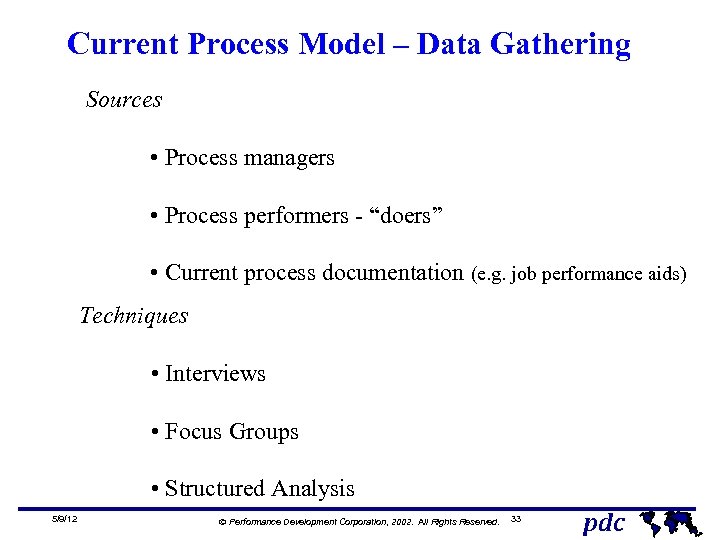
Current Process Model – Data Gathering Sources • Process managers • Process performers - “doers” • Current process documentation (e. g. job performance aids) Techniques • Interviews • Focus Groups • Structured Analysis 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 33 pdc
Document Current Processes Data Gathering Steps • Summarize major activities performed by interviewee: • Capture the process flow involved • List all the activities and repeat to confirm your understanding • Review each activity in detail: • Concentrate on the data sources used • Ask for copies of each source • Mark on the source documents the data used • Discuss any data source not yet accounted for: • For reports, concentrate on usages • Watch for information exchanges by telephone/email • Ask about problems; Invite suggestions for improvements 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 34 pdc

Document Current Processes Data Gathering Suggestions • Use top-down conceptual model and profile from Task 4 as guideline and verification of completeness. • Don’t take anything for granted; there is no such thing as a bad question. • Keep the interview on track. Ask an appropriate question when you think the interviewee is going off the subject. • Don’t fill out forms in front of users. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 35 pdc
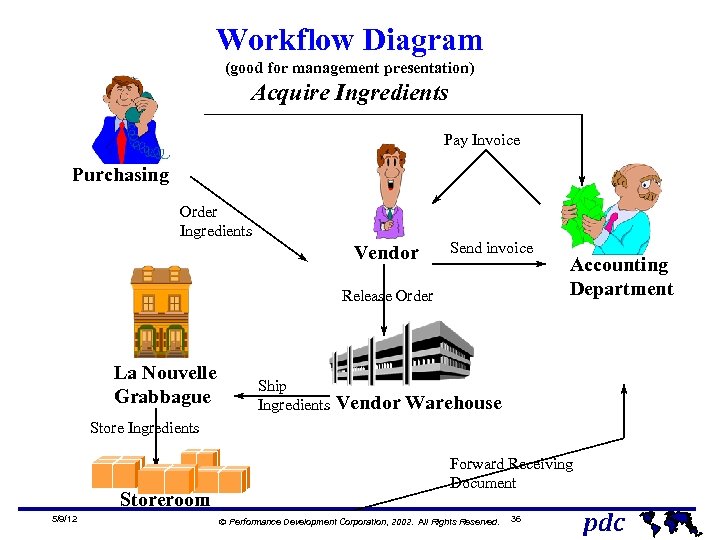
Workflow Diagram (good for management presentation) Acquire Ingredients Pay Invoice Purchasing Order Ingredients Vendor Send invoice Release Order La Nouvelle Grabbague Ship Ingredients Accounting Department Vendor Warehouse Store Ingredients Storeroom 5/9/12 Forward Receiving Document Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 36 pdc
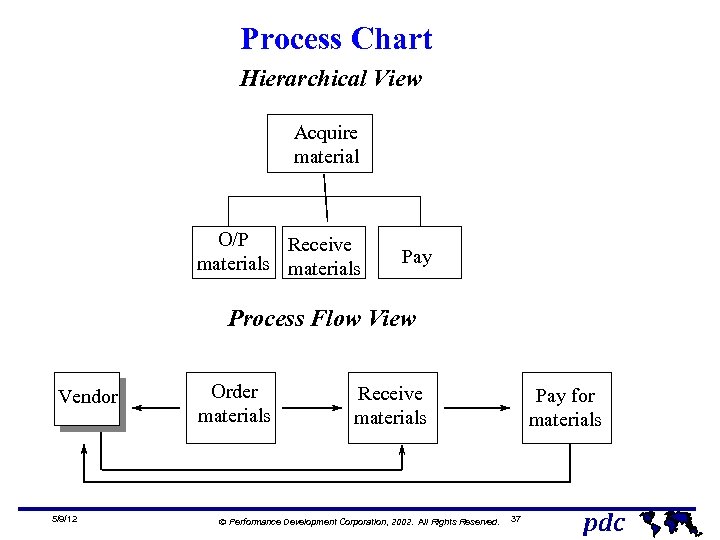
Process Chart Hierarchical View Acquire material O/P Receive materials Pay Process Flow View Vendor 5/9/12 Order materials Receive materials Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Pay for materials 37 pdc
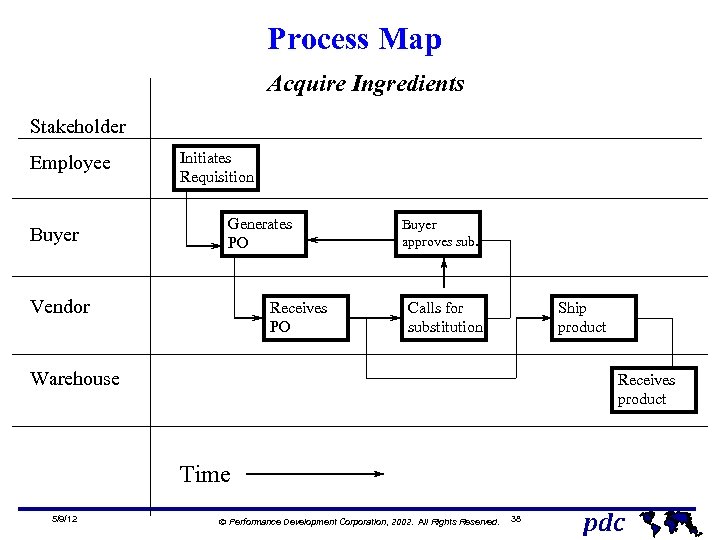
Process Map Acquire Ingredients Stakeholder Employee Buyer Initiates Requisition Generates PO Vendor Receives PO Buyer approves sub. Calls for substitution Ship product Warehouse Receives product Time 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 38 pdc
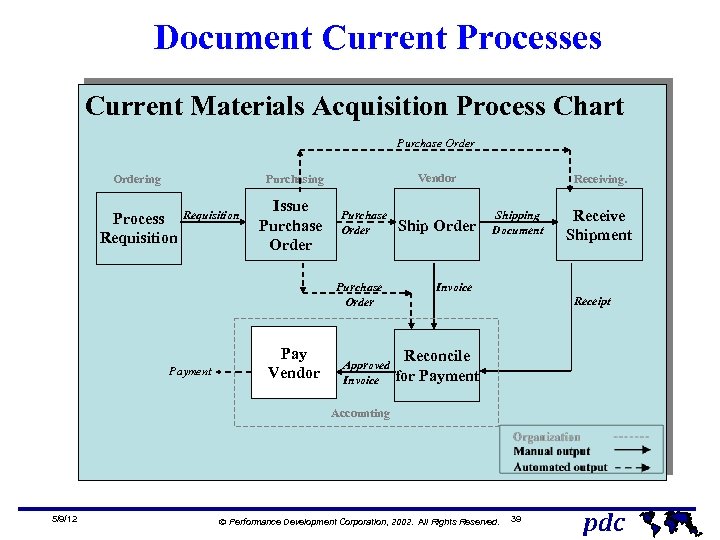
Document Current Processes Current Materials Acquisition Process Chart Purchase Ordering Vendor Purchasing Process Requisition Issue Purchase Order Payment Pay Vendor Approved Invoice Ship Order Receiving. Shipping Document Receive Shipment Invoice Receipt Reconcile for Payment Accounting 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 39 pdc
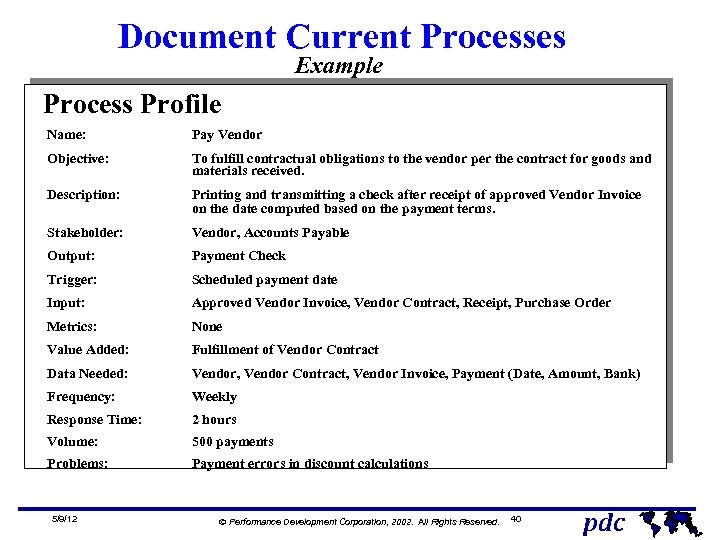
Document Current Processes Example Process Profile Name: Pay Vendor Objective: To fulfill contractual obligations to the vendor per the contract for goods and materials received. Description: Printing and transmitting a check after receipt of approved Vendor Invoice on the date computed based on the payment terms. Stakeholder: Vendor, Accounts Payable Output: Payment Check Trigger: Scheduled payment date Input: Approved Vendor Invoice, Vendor Contract, Receipt, Purchase Order Metrics: None Value Added: Fulfillment of Vendor Contract Data Needed: Vendor, Vendor Contract, Vendor Invoice, Payment (Date, Amount, Bank) Frequency: Weekly Response Time: 2 hours Volume: 500 payments Problems: Payment errors in discount calculations 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 40 pdc
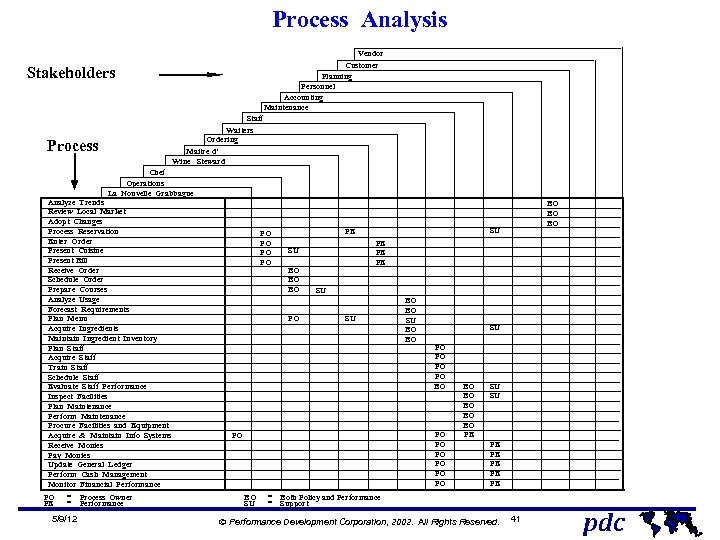
Process Analysis Vendor Customer Planning Personnel Accounting Maintenance Stakeholders Staff Waiters Ordering Maitre d' Wine Steward Chef Operations La Nouvelle Grabbague Analyze Trends Review Local Market Adopt Changes Process Reservation Enter Order Present Cuisine Present Bill Receive Order Schedule Order Prepare Courses Analyze Usage Forecast Requirements Plan Menu Acquire Ingredients Maintain Ingredient Inventory Plan Staff Acquire Staff Train Staff Schedule Staff Evaluate Staff Performance Inspect Facilities Plan Maintenance Perform Maintenance Procure Facilities and Equipment Acquire & Maintain Info Systems Receive Monies Pay Monies Update General Ledger Perform Cash Management Monitor Financial Performance PO PE = Process Owner = Performance 5/9/12 PO PO BO SU BO BO BO PO SU PE SU PE PE PE BO BO SU BO BO PO PO BO PO PO PO BO BO BO PE SU SU SU PE PE PE BO BO BO = Both Policy and Performance = Support Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 41 pdc © Process

How to Use Process/Organization Matrix • Customize to suit your needs • The following cell values might make more sense in your business P = Who is accountable for this process Whose head will be on the block if this process fails S = Who supports or participates in the process A = Who reviews or approves CD = Who is the direct customer for this process CI = 5/9/12 Who is the indirect customer for this process Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 42 pdc
Identification of Problems • Solicit problems/issues process • Identify the stakeholders impacted by the problem • Associate with processes • Associate with goals • Quantify the impact of problem • Identify the nature of problem • Data-oriented • System limitation • Human-oriented • Store in repository • Assign team responsibility 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 43 pdc
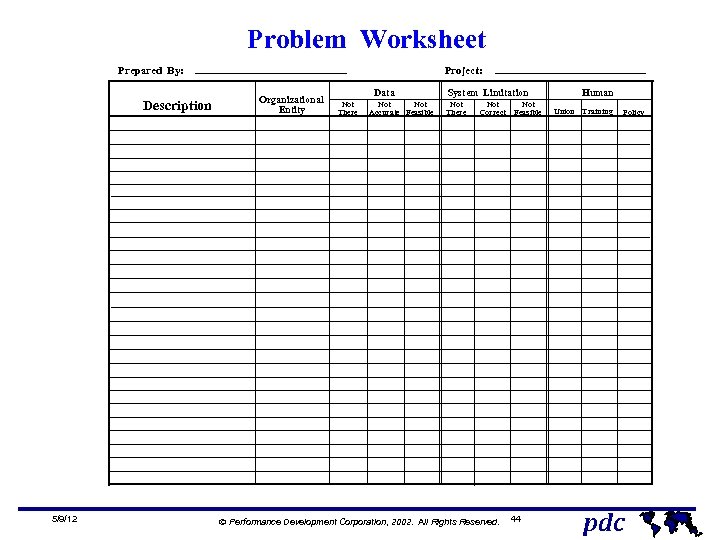
Problem Worksheet Prepared By: Description 5/9/12 Project: Organizational Entity Data Not There Not Accurate Feasible System Limitation Not There Not Correct Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Not Feasible 44 Human Union Training Policy pdc

5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. pdc
Inventory of Current Systems • Existing business systems, automated and manual • Organizational responsibilities • Current files/databases • Systems under development • Technology platforms • Measures of satisfaction/effectiveness 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 46 pdc
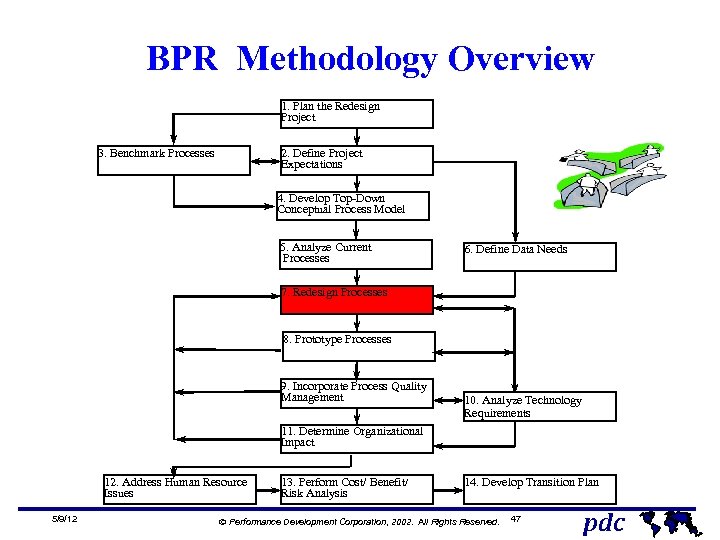
BPR Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Redesign Project 3. Benchmark Processes 2. Define Project Expectations 4. Develop Top-Down Conceptual Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs 7. Redesign Processes 8. Prototype Processes 9. Incorporate Process Quality Management 10. Analyze Technology Requirements 11. Determine Organizational Impact 12. Address Human Resource Issues 5/9/12 13. Perform Cost/ Benefit / Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 47 pdc
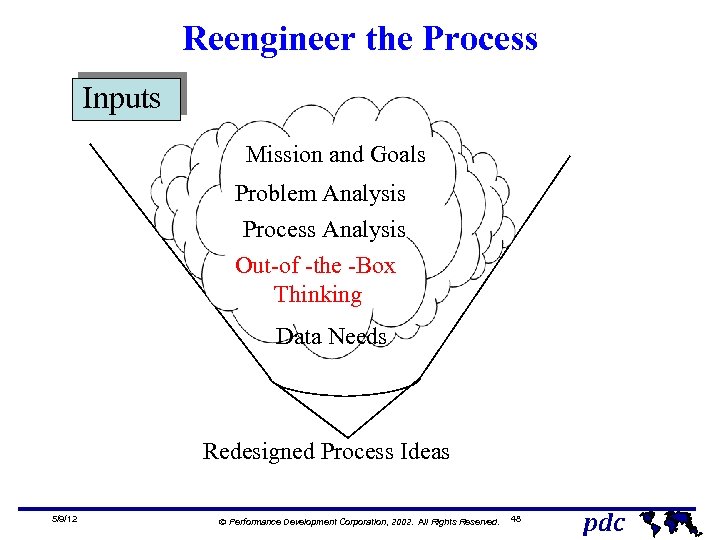
Reengineer the Process Inputs Mission and Goals Problem Analysis Process Analysis Data Needs Out-of -the -Box Thinking Data Needs Redesigned Process Ideas 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 48 pdc

Do you want to just redesign or reengineer the process? 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 49 pdc
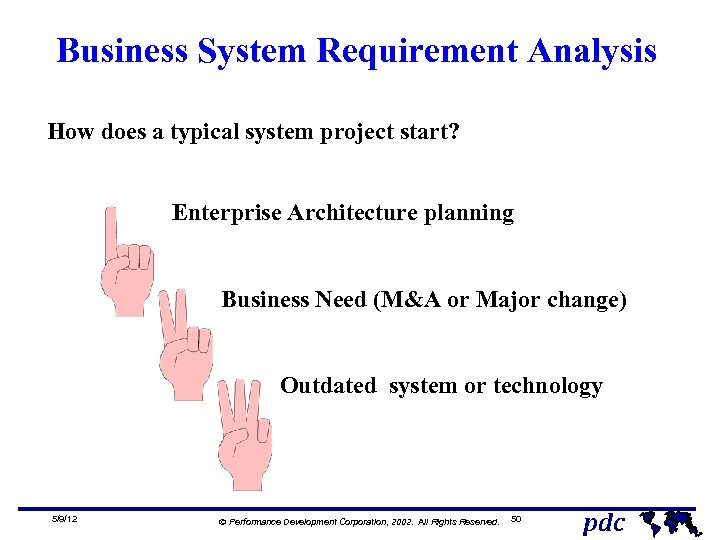
Business System Requirement Analysis How does a typical system project start? Enterprise Architecture planning 5/9/12 Business Need (M&A or Major change) Outdated system or technology Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 50 pdc
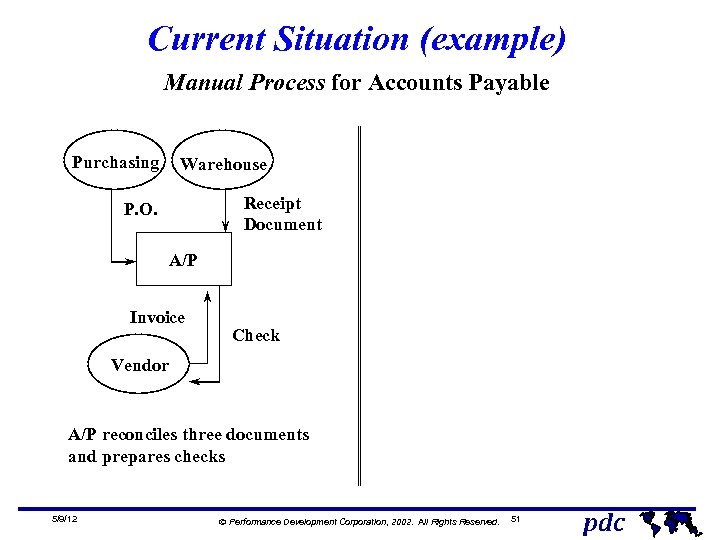
Current Situation (example) Manual Process for Accounts Payable Purchasing Warehouse Receipt Document P. O. A/P Invoice Check Vendor A/P reconciles three documents and prepares checks 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 51 pdc
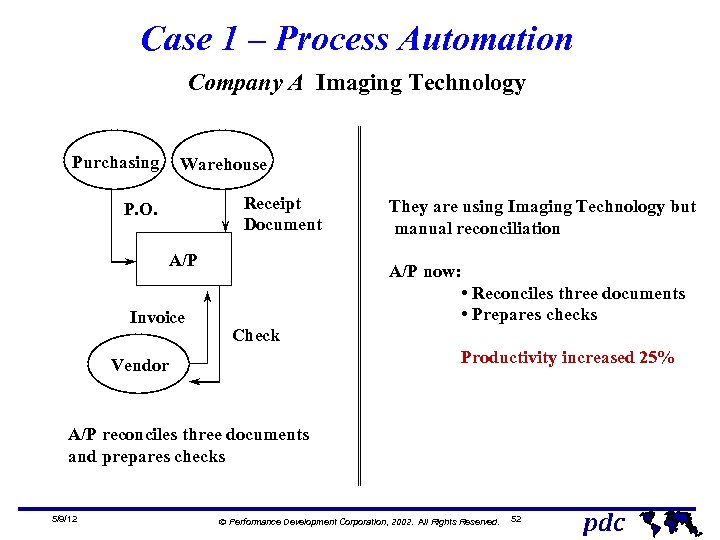
Case 1 – Process Automation Company A Imaging Technology Purchasing Warehouse Receipt Document P. O. A/P Invoice They are using Imaging Technology but manual reconciliation A/P now: • Reconciles three documents • Prepares checks Check Productivity increased 25% Vendor A/P reconciles three documents and prepares checks 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 52 pdc
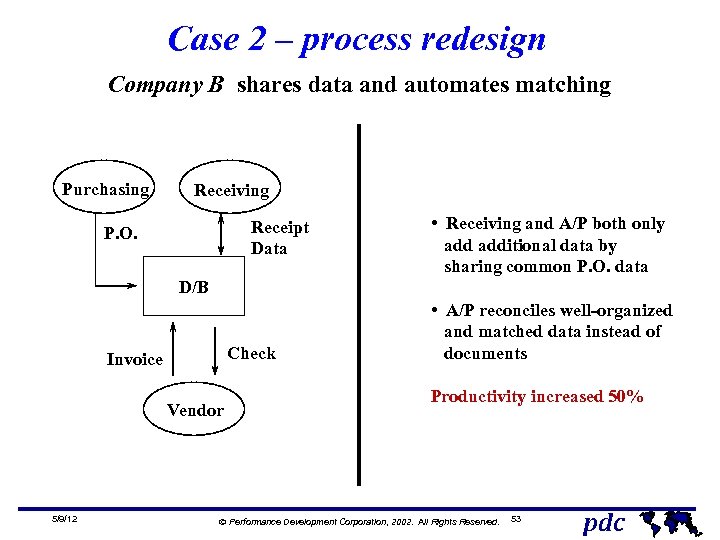
Case 2 – process redesign Company B shares data and automates matching Purchasing Receiving Receipt Data P. O. • Receiving and A/P both only additional data by sharing common P. O. data D/B Check Invoice Vendor 5/9/12 • A/P reconciles well-organized and matched data instead of documents Productivity increased 50% Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 53 pdc
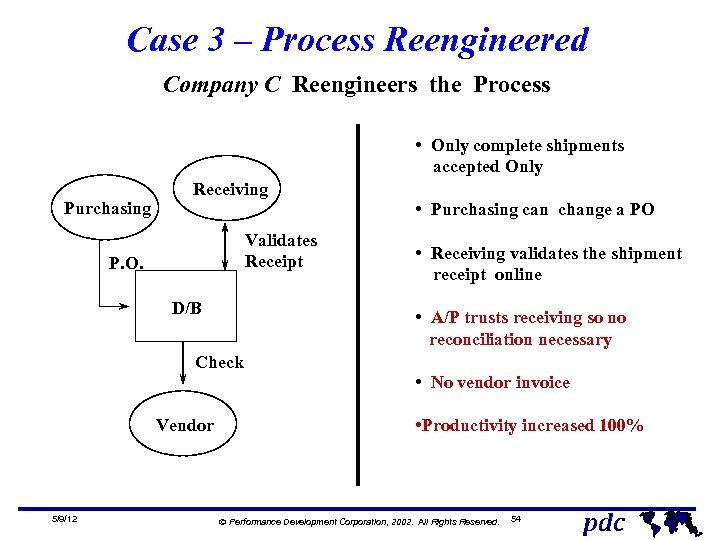
Case 3 – Process Reengineered Company C Reengineers the Process • Only complete shipments accepted Only Purchasing Receiving Validates Receipt P. O. D/B • Purchasing can change a PO • Receiving validates the shipment receipt online • A/P trusts receiving so no reconciliation necessary Check • No vendor invoice Vendor 5/9/12 • Productivity increased 100% Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 54 pdc
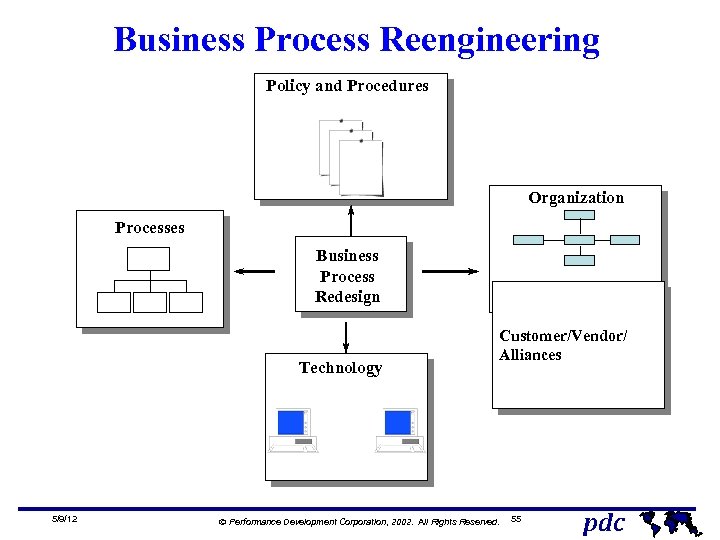
Business Process Reengineering Policy and Procedures Organization Processes Business Process Redesign Technology 5/9/12 Customer/Vendor/ Alliances Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 55 pdc
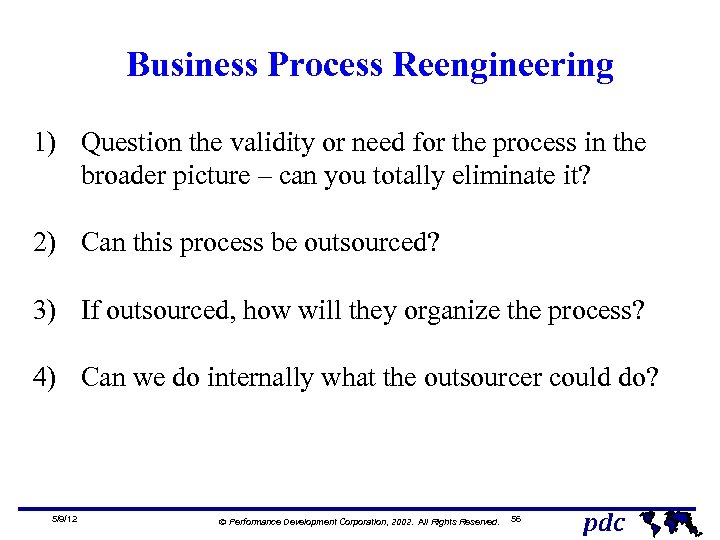
Business Process Reengineering 1) Question the validity or need for the process in the broader picture – can you totally eliminate it? 2) Can this process be outsourced? 3) If outsourced, how will they organize the process? 4) Can we do internally what the outsourcer could do? 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 56 pdc
Refine Process Using Redesign Principles · Question the validity of the process · Ensure that all the problems are addressed · Can you do the whole process in one step? · Capitalize on data sharing · Eliminate non-value-added processes. · Re-sequence or use parallel processes to improve performance. · Eliminate handoffs (Combine processes. ) · Replace a specialist’s function so that non-specialists can handle it with automated decision making business rules. The specialist only handles exceptions. · Replace all pre-approvals after-the fact reporting · Replace after-the-fact reconciliation with front-end edits, validation, and quality checks. · Explore new technologies 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 57 pdc
Capitalize on Data Sharing Steps Eliminate redundant data entry and storage Maximize data sharing with internal and external stakeholders Refine process design based on data sharing 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 58 pdc
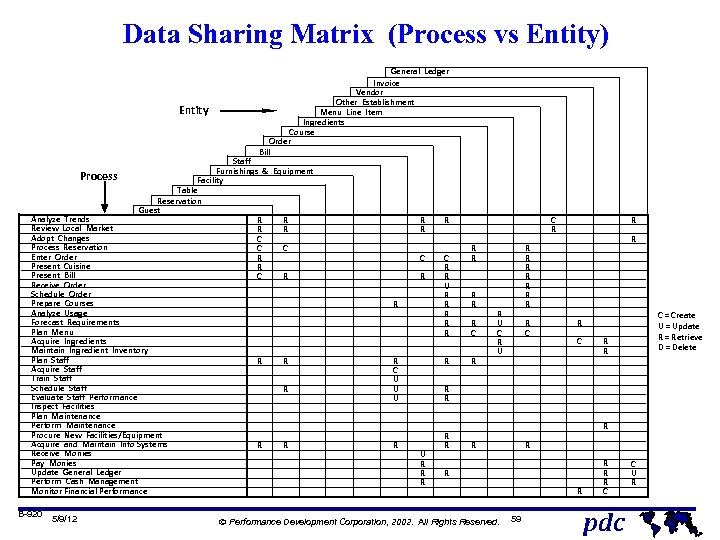
Data Sharing Matrix (Process vs Entity) Entity Process Staff Furnishings & Equipment Facility Table Reservation Guest R R C C C R R C R Analyze Trends Review Local Market Adopt Changes Process Reservation Enter Order Present Cuisine Present Bill Receive Order Schedule Order Prepare Courses Analyze Usage Forecast Requirements Plan Menu Acquire Ingredients Maintain Ingredient Inventory Plan Staff Acquire Staff Train Staff Schedule Staff Evaluate Staff Performance Inspect Facilities Plan Maintenance Perform Maintenance Procure New Facilities/Equipment Acquire and Maintain Info Systems Receive Monies Pay Monies Update General Ledger Perform Cash Management Monitor Financial Performance B-920 5/9/12 General Ledger Invoice Vendor Other Establishment Menu Line Item Ingredients Course Order Bill R R C R R R R C U U U R C R R U R R R C R R R U C R U R C C = Create U = Update R = Retrieve D = Delete R C R R U R R R R R Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. R 59 R R R C pdc C U R

Ensure Problem Resolution Steps • Review problem analysis summary from Task 5 • Add any problems which may be created by the new design • Resolve the problems and refine the processes 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 60 pdc
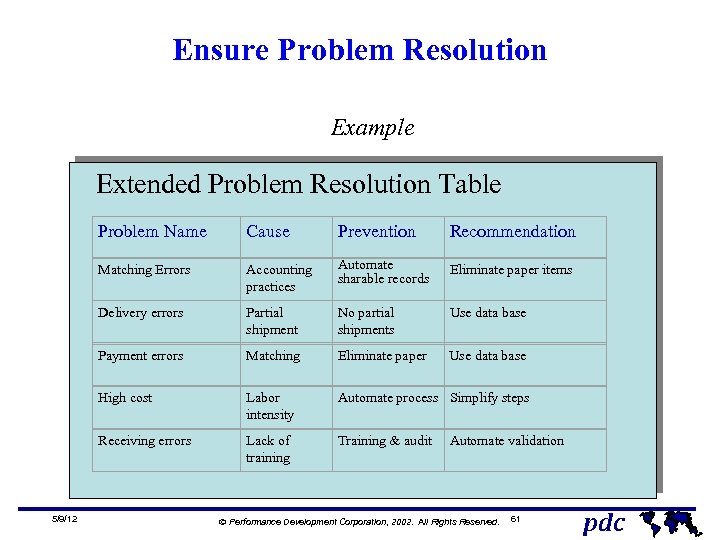
Ensure Problem Resolution Example Extended Problem Resolution Table Problem Name Recommendation Accounting practices Automate sharable records Eliminate paper items Delivery errors Partial shipment No partial shipments Use data base Payment errors Matching Eliminate paper Use data base High cost Labor intensity Automate process Simplify steps Receiving errors 5/9/12 Prevention Matching Errors Cause Lack of training Training & audit Automate validation Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 61 pdc
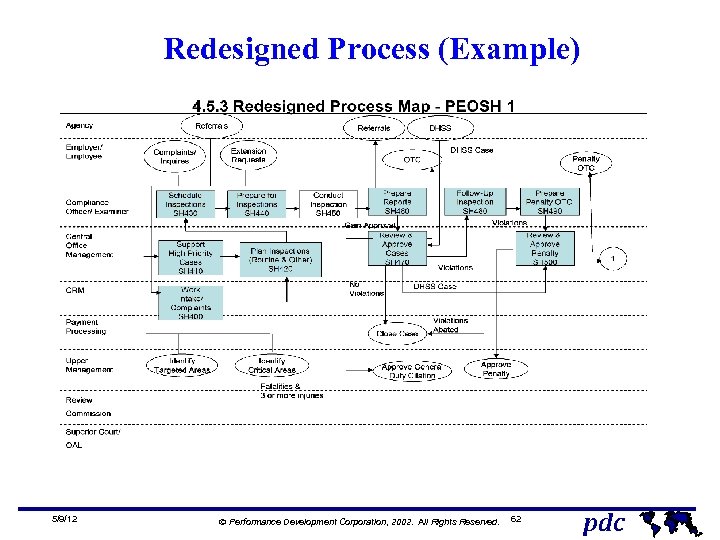
Redesigned Process (Example) 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 62 pdc
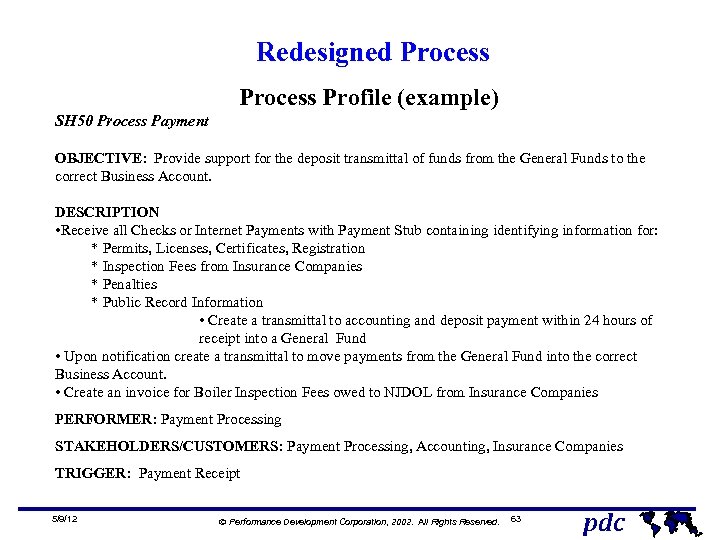
Redesigned Process Profile (example) SH 50 Process Payment OBJECTIVE: Provide support for the deposit transmittal of funds from the General Funds to the correct Business Account. DESCRIPTION • Receive all Checks or Internet Payments with Payment Stub containing identifying information for: * Permits, Licenses, Certificates, Registration * Inspection Fees from Insurance Companies * Penalties * Public Record Information • Create a transmittal to accounting and deposit payment within 24 hours of receipt into a General Fund • Upon notification create a transmittal to move payments from the General Fund into the correct Business Account. • Create an invoice for Boiler Inspection Fees owed to NJDOL from Insurance Companies PERFORMER: Payment Processing STAKEHOLDERS/CUSTOMERS: Payment Processing, Accounting, Insurance Companies TRIGGER: Payment Receipt 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 63 pdc
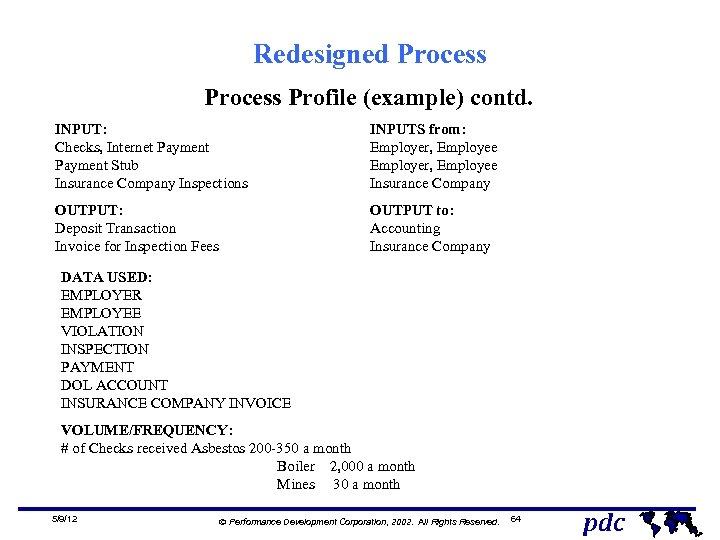
Redesigned Process Profile (example) contd. INPUT: Checks, Internet Payment Stub Insurance Company Inspections OUTPUT: Deposit Transaction Invoice for Inspection Fees INPUTS from: Employer, Employee Insurance Company OUTPUT to: Accounting Insurance Company DATA USED: EMPLOYER EMPLOYEE VIOLATION INSPECTION PAYMENT DOL ACCOUNT INSURANCE COMPANY INVOICE VOLUME/FREQUENCY: # of Checks received Asbestos 200 -350 a month Boiler 2, 000 a month Mines 30 a month 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 64 pdc

Documenting the Process Profile (example) contd. BUSINESS SYSTEMS MODULES: Payment Processing Document Management Case Tracking/Workflow Management POTENTIAL TECHNOLOGY: Web Document Management RELATED PROCESSES: To: SH 40 Issue Permits, Licenses, and Certificates QUALITY METRICS: • % Checks deposited within 24 hours BASELINE PROCESS REFERENCE: 12. 4. 1. 5 Manage Collection of Fees 13. 4. 2. 4 Manage Collection of Fees 14. 4. 2. 7 Manage Collection of Fees SIGNIFICANT CHANGES: (Will guide business rules) • The most significant change in this area is the centralization of Payment Processing and the implementation of Payment Stubs for all Fees and Penalties • Tighter controls will ensure Checks are processed within 24 hours • All payments will be made via Certified Check or Credit Card Payment on the internet. An interface to the Accounting System will provide better control over transactions processed 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 65 pdc
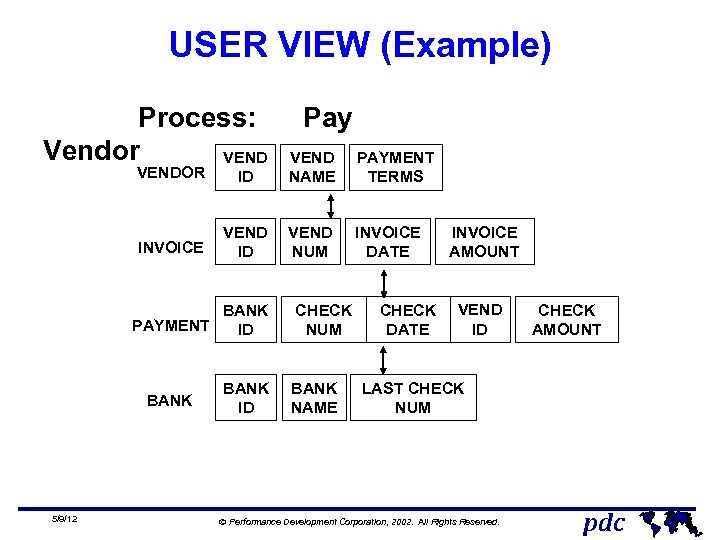
USER VIEW (Example) Process: Pay Vendor VEND PAYMENT VENDOR ID NAME TERMS INVOICE VEND ID VEND NUM INVOICE DATE BANK PAYMENT ID BANK 5/9/12 BANK ID CHECK NUM BANK NAME CHECK DATE INVOICE AMOUNT VEND ID CHECK AMOUNT LAST CHECK NUM Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. pdc
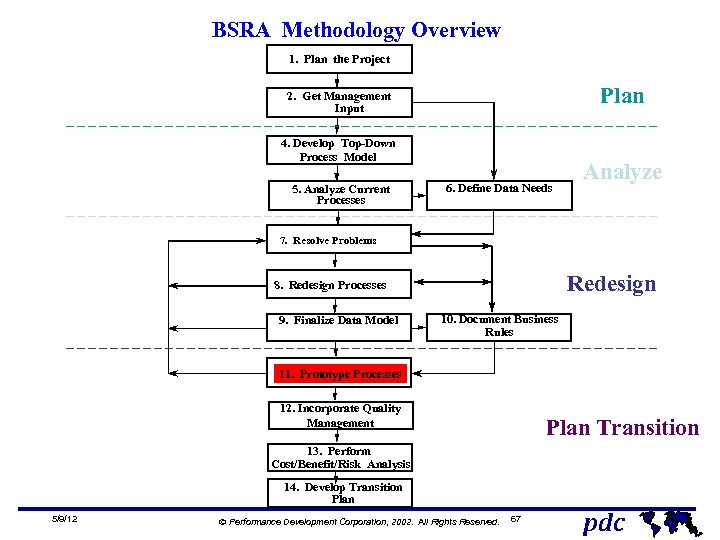
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 67 pdc

Prototype the Process Sub-Tasks 8. 1 Develop prototypes 8. 2 Incorporate technology 8. 3 Assess feasibility of redesign process 8. 4 Determine skills required 8. 5 Review with sponsor 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 68 pdc
Prototyping What to Expect • Proof of concept Prototyping • Feedback for redesign refinement • Insight into downstream activities – Feasibility of process – Skills that may be required – Potential organizational effects 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 69 pdc
When to Prototype Drastic change 5/9/12 Complex New processes technology Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. Political situation 70 pdc
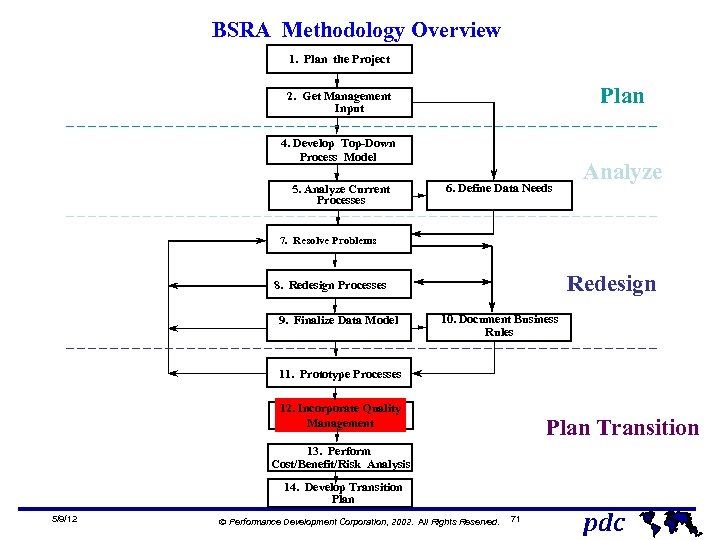
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 71 pdc
Total Quality Management TQM Mission: Continuously improve the ability to achieve the “quality” objectives for products, services, and resources 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 72 pdc

Incorporate Quality Management Tasks: • Define deliverables for a core process • Identify customers of each major process (internal/external/ultimate) • Define customers’ expectations and perception of quality • Develop metrics for quality of each deliverable • Develop metrics for internal quality objective. • Incorporate metrics as part of process • Incorporate additional entity/attributes • Develop continuous improvement mechanism • Refine process definitions/profiles 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 73 pdc
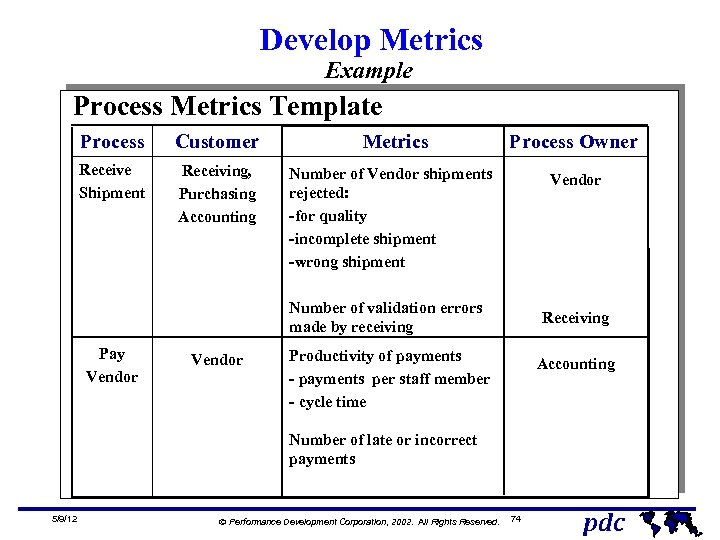
Develop Metrics Example Process Metrics Template Process Customer Metrics Process Owner Receive Shipment Receiving, Purchasing Accounting Number of Vendor shipments rejected: -for quality -incomplete shipment -wrong shipment Vendor Number of validation errors made by receiving Pay Vendor Receiving Productivity of payments - payments per staff member - cycle time Accounting Number of late or incorrect payments 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 74 pdc
Refine Data Entities and Processes Example Data Entity Refinement Template 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 75 pdc

Process Quality Management Deming’s Solution • Plan • Do • Check • Act 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 76 pdc
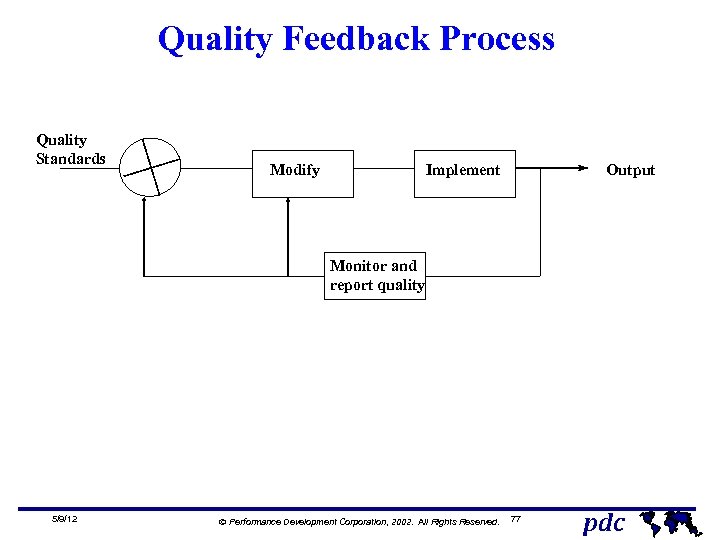
Quality Feedback Process Quality Standards Modify Implement Output Monitor and report quality 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 77 pdc
Continuous Improvement Mechanism • Apply existing continuous improvement mechanism • If Continuous Improvement mechanism does not exist in your organization, use this project to implement it • If a new effort is required, provide education and training 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 78 pdc
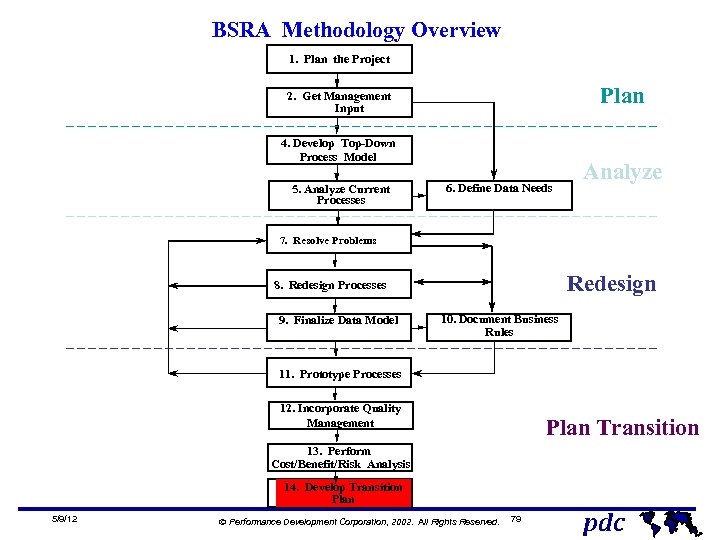
BSRA Methodology Overview 1. Plan the Project Plan 2. Get Management Input 4. Develop Top-Down Process Model 5. Analyze Current Processes 6. Define Data Needs Analyze 7. Resolve Problems Redesign 8. Redesign Processes 9. Finalize Data Model 10. Document Business Rules 11. Prototype Processes 12. Incorporate Quality Management Plan Transition 13. Perform Cost/Benefit/Risk Analysis 14. Develop Transition Plan 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 79 pdc

Analyze Technology Requirements • Assessment of hardware, software: – – New decision/business rules New internal and external users New process locations New organizational structures, procedures • “What is required”? • “Is existing technology sufficient? ” • Is new technology necessary and mature? • Any technology required for QM? 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 80 pdc

Organizational Readiness for New Technology • • • 5/9/12 Existing technological infrastructure Sophistication of current users Rate at which new technology can be absorbed Ability to conform to new standards Potential training effort Potential support effort – New roles – Continuous updating of knowledge – Continuous upgrading of skills Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 81 pdc
Organizational Change Documentation • Policies • Procedures • Responsibilities for redesigned processes – Owner – Performer – Support – Quality assurance 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 82 pdc

Organizational Changes Needed Example • Resource requirements • Organizational structure changes • Organizational responsibility changes (business rules) Relocation of 20 Full Time Equivalents from Accounting. None immediately; but may position Accounting for future combining of roles. - Receiving accepting shipments authorizes vendor payment, and Accounting no longer does manual reconciliation and focuses more on education and quality assurance for Receiving validation. - Receiving employees are empowered to accept or reject shipments and authorize payment. - Vendor must comply to new “no invoice” and shipment policy. 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 83 pdc

Developing a Transition Plan Process redesign is not complete without a detailed road map that shows how to get to the new environment • Project Implementation Schedule (next steps) • Tasks • Timing • Resources • Organization Transition Plan • New structures • New reporting relationships • Training • Technical Transition • H/W, S/W acquisition or development • Data Conversion 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 84 pdc

Potential Problems u Management acceptance and support u Stakeholder buy-in 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 85 pdc

How to get Buy-in • Executive Management – Define mission, goals, objectives, opportunities and their burning issues – 1 ½ hour Presentation – Review Redesigned processes – related to their expectations • Middle Management – – Participate in Top down Process Model Validate current environment documentation Review Redesigned processes – related to their expectations Assign priorities in the Transition Plan • User Level – 50% of the Team comes from the user side – Data Analyst is continually involved 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 86 pdc

Process Management Function Ø Establish a charter Ø Develop business reengineering and continuous improvement methodology Ø Build process management expertise Ø Develop and implement Process Ownership program Ø Standardize process documentation Ø Initiate culture change initiatives 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 87 pdc

How would you apply this to your Data Management processes? Who are the stakeholders? What are the processes required to support their needs? What data you would need support these processes? What screens and reports users will need? Who will build the system to support these needs? What quality metrics you need? How can you make your tools easy to use? Who is the Process Owner for these processes? 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 88 pdc
Lessons Learned For Business System Project 1. Project team should be comprised of: • The team must have 50% business analysts • Core team members must be full-time for the duration of the project • Average Number 4 (minimum 2, maximum 6) 2. Scope the project so that: • It takes no more than six months • Ideal three months • Average four months 3. You may select: • One or multiple related processes which has single executive or committee in charge 4. Prototype and validate feasibility of new concept 5. Do not ignore implementation risks 6. The output must include an implementable action plan 7. Use an experienced arbitrator and adviser if this is your first time 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 89 pdc

Process Reengineering - Success Factors • Strong executive sponsor • Appropriate scope – Self-sufficient data requirements – No more than four months for a given phase • No a priori constraints – Authority to question any business policy, procedure, or standard • Expand horizon to include external agents • Revolutionary thinking – “out-of-the-box”, but evolutionary implementation 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 90 pdc
Business System Requirement Analysis (BSRA) (Business Process Redesign) Thank You Presented by: Arvind D. Shah, Managing Principal Performance Development Corporation Princeton, NJ 08540 (609)443 -1226 ads 1@perfdev. com www. perfdev. com 5/9/12 Ó Performance Development Corporation, 2002. All Rights Reserved. 91 pdc
467b3e200c4e84a2a70547989a4f10fb.ppt