ce0a7943c82204a9973249b4b65ec54a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Business Plan The Business Plan BU 113: Foundations of Business Administration

Memorable statistics n New business startups each year: 600, 000 -650, 000 n Business failures each year: 500, 000 -600, 000

Reasons for Failure and Success of Businesses Failure due to 1. Managerial incompetence or inexperience 2. Neglect 3. Weak control systems 4. Insufficient capital Success due to 1. Hard work, drive, and dedication 2. Market demand for product/service 3. Managerial competence 4. Luck

The Process, the Plan, and BU 113 n Idea n Test n Plan n Execute n Evaluate

What is a Business Plan? n n n n n Blueprint of your business Written plan detailing operational and financial aspects of your company Explanation of the business concept Analysis of the market Presentation of the strategy Outline of projected development of the business Definition of capital needs of the business Projection of financial performance Presentation of management’s credentials/positions

Who needs a Business Plan? n n n Business associates: Bankers: Other investors: Management: Potential employees: n n n Direction and purpose Financing Funding for growth Internal plans Join the company?

Concerns of Investors n How are you unique? Proprietary technology ¨ Unique product ¨ n Management track record Great ideas won’t go anywhere without good management. ¨ Depth of management ¨ n Rate of Return High risk requires potential for high return ¨ Where on the growth curve is the business? ¨ Are financial projections reasonable? ¨ n Exit Strategy How to get out with mega profit (go public, sell out) ¨ When? ¨

Cover Page Company XYZ February, 201_ Business Plan Copy Number 5 This document contains confidential and proprietary information belonging exclusively to XYZ Company. John Smith Chief Executive Officer 123 Executive Drive Maple Valley, VT 55555 (802)555 -555 Company Headquarters This is a business plan. It does not imply an offering of securities.

Business Plan—Format & Components n n Cover Page Table of Contents (with page numbers) Your company’s mission statement The business: ¨ Management: Management Structure/Background ¨ Marketing Plan ¨ Financial Plan ¨ Supporting documents n n n Revised resumes Company logo Organization chart Power. Point slides in handout form List of all shareholders and their investment

Mission Statement n n Brief description of a company’s fundamental purpose. Answers the questions: ¨ Why do we exist? ¨ What do we hope to achieve in the future? May include target markets, key products/services, focus on profitability/growth and major values. May refer to certain stakeholder groups.

Mission -- Examples n n “It is the mission of Saint Michael’s College to contribute through higher education to the enhancement of the human person and to the advancement of human culture in the light of the Catholic faith. ” (SMC Facts) “The Home Depot’s values guide the beliefs and actions of all associates on a daily basis. Our values are the fabric of the Company’s unique culture and are central to our success. In fact, they are our competitive advantage in the marketplace. Associate pride and our “orangeblooded” entrepreneurial spirit are distinctive hallmarks of our culture. ” 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Taking care of our people Giving back to our communities Doing the right thing Excellent customer service Creating shareholder value Building strong relationships Entrepreneurial spirit Respect for all people Source: Home Depot – Our Company – Values

Components of the Plan: Management n n n Type of organization / form of business ownership / Background Organization chart Management team Roles in the business ¨ Experience ¨ Skills Marketing ¨ Supporting documents: Manager 1 Resumes ¨ XYZ Company General Manager Finance Manager Marketing Manager 2

Components of the Plan: Marketing n Product / Service ¨ ¨ n Key characteristics, uniqueness Picture, design / model Suppliers Amount of inventory to be ordered Target market Who will want this product and why? How company will meet customer needs and wants ¨ Economic / social / cultural and demographic characteristics ¨ How large is the target market? ¨ ¨

Components of the Plan: Marketing (cont’d) n Competitive Environment Competitors – Who? ¨ Competitors’ Strengths ¨ Competitors’ Weaknesses ¨
Components of the Plan: Marketing (cont’d) n Price ¨ Pricing n strategy vs. competition Promotion ¨ Promotional n strategy: developing demand for product Place / distribution ¨ Getting the product from production to the consumer

Financial Plan BU 113: Foundations of Business Administration

Purpose—Financial Plan Determine feasibility of business n Determine capital needed to start business n Estimate return to shareholders n

Capital Needed to Start Business q Determine total amount of capital needed to start the business q Do you need to: Buy equipment? § Buy product/raw materials for product to sell? (Include in product cost: transportation & packaging) § Buy supplies for advertising § Pay sales taxes? §

Financing Sources: How to Raise Money Sources: Selling stock or borrowing money q Stock sales: 25 cents/share q Inside shareholders (management team). What percent of company do you want to own? § Outside shareholders (sell to others at marketplace) § You must offer at least 20 shares to outside shareholders. § Specify what percent ownership 1 share represents § o EX: If you plan to sell 100 total shares to management and outsiders, 1 share = 1% ownership in the company.

Financing Sources: Examples Sale of Product n Capital needed: $100 o Outside 20 shares: Sale of Service n No capital needed o (20 shares X $. 25/share = $5) = 5% o Inside 380 shares (20 shares X $. 25/share = $5) = 20% o Total Raised: $100 = 100% o Total Shares Issued: 400 shares Inside 80 shares (more/less) (80 shares X $. 25/share = $20) = 80% ( $95 / $. 25 per share = 380 shares): (380 shares X $. 25/share = $95) = 95% o Outside 20 shares (minimum): o Total Raised: $25 = 100% o Total Shares Issued: 100 shares

Projected Income Statement Sales = Number of units of product/service expected to be sold per week X sales price Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) = number of units of product expected to be sold each week X cost to buy including taxes, shipping, etc. (no COGS with a service) Less: Advertising and other expenses = actual amount expected to be spent during a particular week Less: n Taxes = 10% of profit before taxes (EBT) Note: You cannot pay management wages.
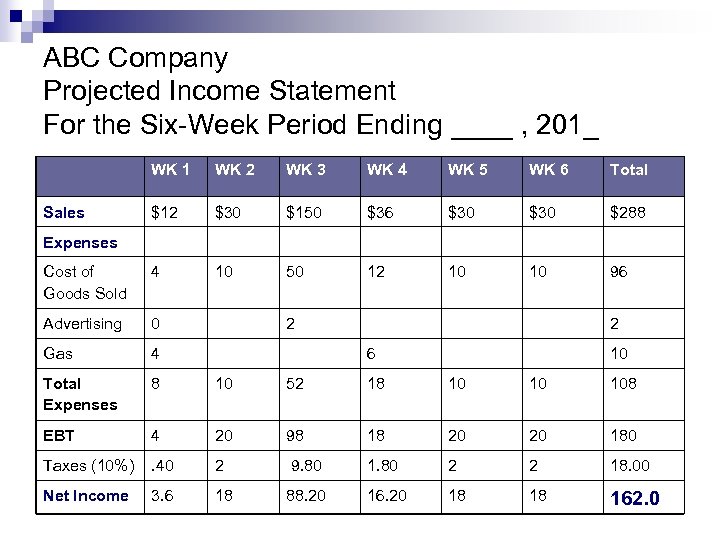
ABC Company Projected Income Statement For the Six-Week Period Ending ____ , 201_ WK 1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4 WK 5 WK 6 Total $12 $30 $150 $36 $30 $288 Cost of Goods Sold 4 10 50 12 10 10 96 Advertising 0 Gas 4 Total Expenses 8 10 52 18 10 10 108 EBT 4 20 98 18 20 20 180 Taxes (10%) . 40 2 9. 80 1. 80 2 2 18. 00 Net Income 3. 6 18 88. 20 16. 20 18 18 162. 0 Sales Expenses 2 2 6 10
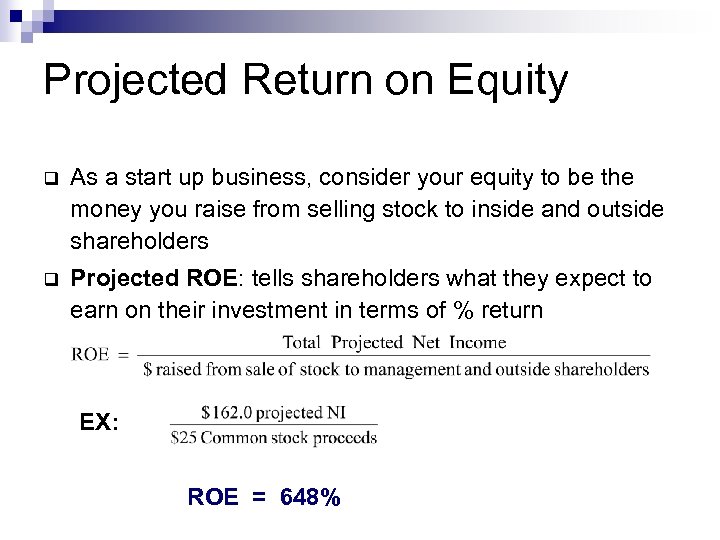
Projected Return on Equity q As a start up business, consider your equity to be the money you raise from selling stock to inside and outside shareholders q Projected ROE: tells shareholders what they expect to earn on their investment in terms of % return EX: ROE = 648%

Liquidating Dividend q Liquidating Dividend to be paid at end of semester q Different from a regular dividend real companies pay q = Distribution of all the cash of the company after payment of all liabilities. q Purpose: to close the business down q Liquidating Dividend Per Share = [Ending cash (= $ from sale of stock to managers and outsiders + Net Income) - Liabilities (including taxes payable)] divided by total # Shares outstanding

Supporting documents n List of Shareholders: Attach a table with the information about your shareholders’ investment, for both management and outside shareholders. ¨ ¨ n name contact information number of shares invested percent ownership in the company based on the number of shares owned Revised resume of each manager Company logo Power. Point slides in handout form (6 slides per page)
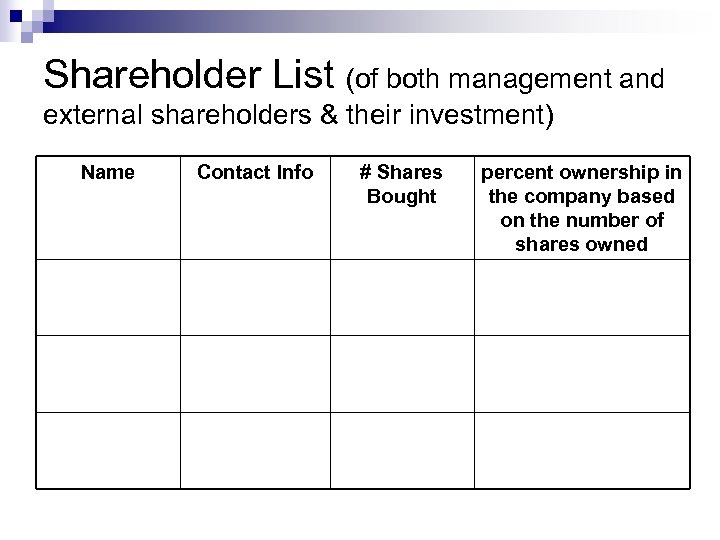
Shareholder List (of both management and external shareholders & their investment) Name Contact Info # Shares Bought percent ownership in the company based on the number of shares owned

Key Success Factors – from BU 113 groups 2010 1. “Organization is vital. ” ¨ 2. 3. Regular meetings, showing up with work completed, earning group’s trust 5. Using meeting time well; balance of centralized and decentralized decision-making 6. strong / “forceful” communication with customers; self-motivation / dedication to contribute, clear directions Cooperation/ communication/respect ¨ Management ¨ Motivation / Leadership ¨ maintaining record of inventory, sales, customer info, money collected Promptness/responsibility /accountability ¨ 4. Open-mindedness, problemsolving meetings on short notice, preparation/ understanding concepts & expectations, teamwork Small inventory
ce0a7943c82204a9973249b4b65ec54a.ppt