468e4e1c1d8480fad0c2536a5fbdee79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

BUSINESS ORGANISATIONS: THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Topics Covered • Introduction to business • Purpose of a business organisation – Vision and Mission. • Strategic Direction of the Organisation: Industries and Markets • How Businesses Create Value • How the Business Organisation Operates: The Role of Management and Corporate Culture • Aligning the Business Model with the Value Proposition • Conclusions Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Key Concepts • Introduction to Business? The Business Organisation as a Transformation System Enterprise and 2009. See; Worthington and Britton, its Business Environment © Goodfellow
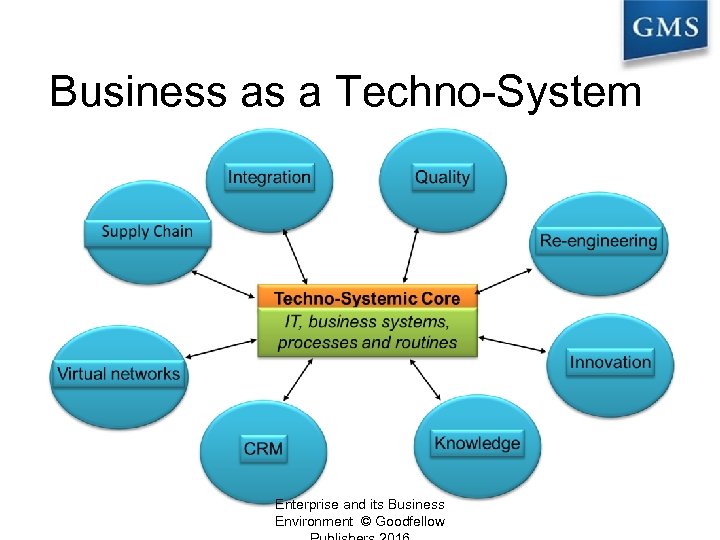
Business as a Techno-System Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
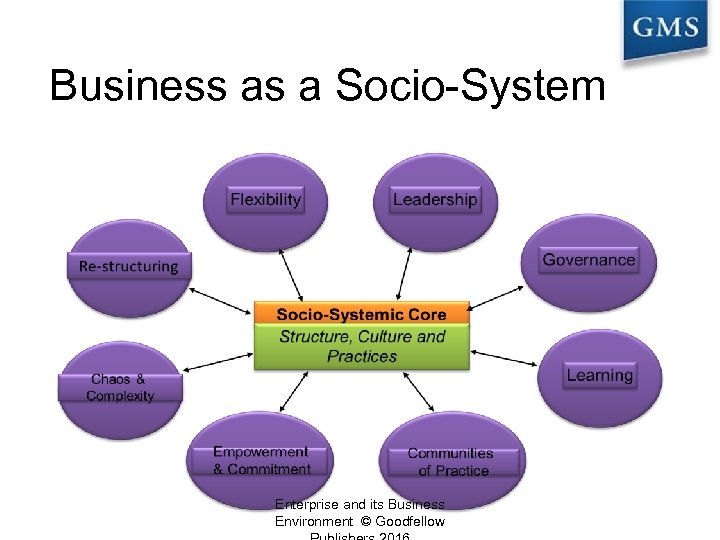
Business as a Socio-System Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Delivering Strategy Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Introduction to Business • What is an Industry & What is a Market? Communication Goods/service Industry Market (a collection of sellers) (a collection of buyers) Money Information Note: We Might Call this Process - Trade; Commerce; Exchange (See; Kotler, 2007) Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Introduction to Business • Marketing…. What is it? • What is the Difference Between Sales & Marketing? • Note Down Your Answers!! • You Can Discuss Questions with those Sitting Around You… • Be Prepared To Give Feedback. . . Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Definitions of Marketing • Kotler (2000); • “Satisfying human wants and needs at a profit” (Kotler, 2000) • Chartered Institute of Marketing (CIM); • Marketing as a management process: “which identifies, anticipates and supplies consumer requirements efficiently and effectively” • Peter Drucker (1999): • “Because the purpose of business is to create and keep customers, it only has two central functions - marketing and innovation. The basic function of marketing is to attract and retain customers at a profit” • A Marriage of Philosophy & Economics • The philosophy of customer satisfaction • Economics of supply and demand Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Key Concepts • What is the Difference Between Sales & Marketing? • Sales Assumes a Product - Marketing Does Not!!! • Marketing Starts Before the Product is Ever Produced - it Starts with Needs & Wants! • It is Used to Evaluate the Scale, Extent & Salient Characteristics of Demand & How the Product Can Be Flexed to Meet Them… • Levitt (1960) “Selling Focuses on the Needs of the Seller; Marketing on the Needs of the Buyer” Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
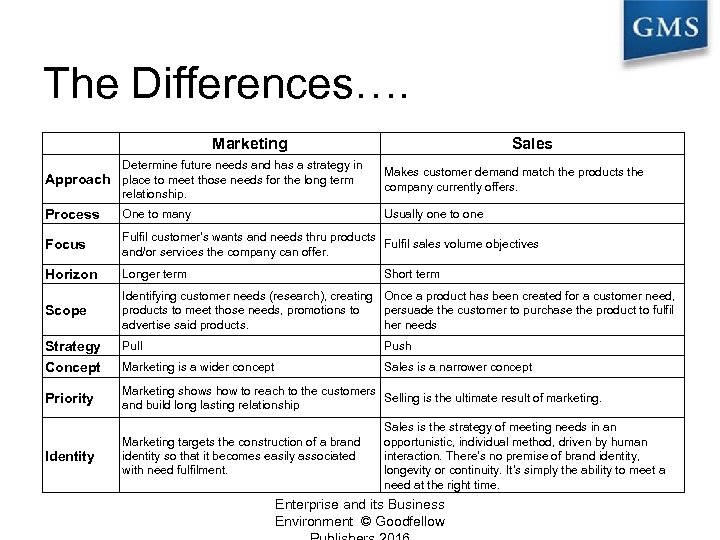
The Differences…. Marketing Sales Determine future needs and has a strategy in Approach place to meet those needs for the long term relationship. Makes customer demand match the products the company currently offers. Process One to many Usually one to one Focus Fulfil customer's wants and needs thru products Fulfil sales volume objectives and/or services the company can offer. Horizon Longer term Scope Identifying customer needs (research), creating Once a product has been created for a customer need, products to meet those needs, promotions to persuade the customer to purchase the product to fulfil advertise said products. her needs Strategy Concept Priority Identity Short term Pull Push Marketing is a wider concept Sales is a narrower concept Marketing shows how to reach to the customers Selling is the ultimate result of marketing. and build long lasting relationship Marketing targets the construction of a brand identity so that it becomes easily associated with need fulfilment. Sales is the strategy of meeting needs in an opportunistic, individual method, driven by human interaction. There's no premise of brand identity, longevity or continuity. It's simply the ability to meet a need at the right time. Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Sales V’s Marketing Focus Product Means Ends Selling & Profits Through Promoting Sales Volume (A) The Selling Concept Customer Needs Integrated Marketing Profits Through Customer Satisfaction (B) The Marketing Concept See; Kotler: 2000 Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
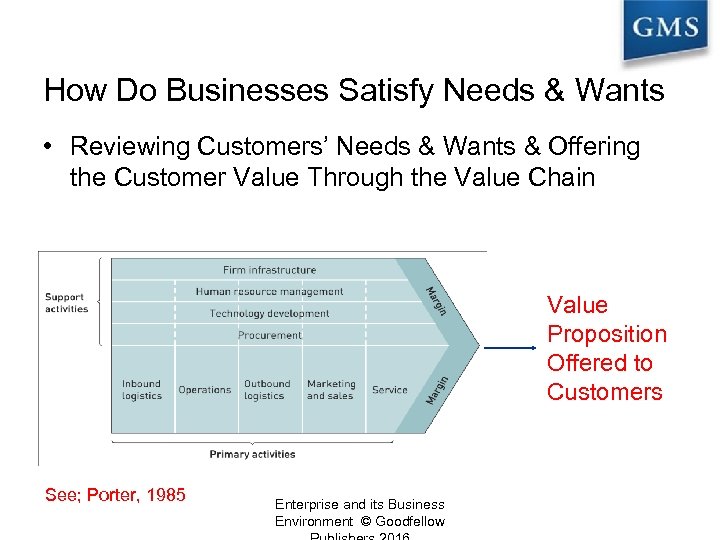
How Do Businesses Satisfy Needs & Wants? • Reviewing Customers’ Needs & Wants & Offering the Customer Value Through the Value Chain The Value Chain within an Organisation Value Proposition Offered to Customers See; Porter, 1985 Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
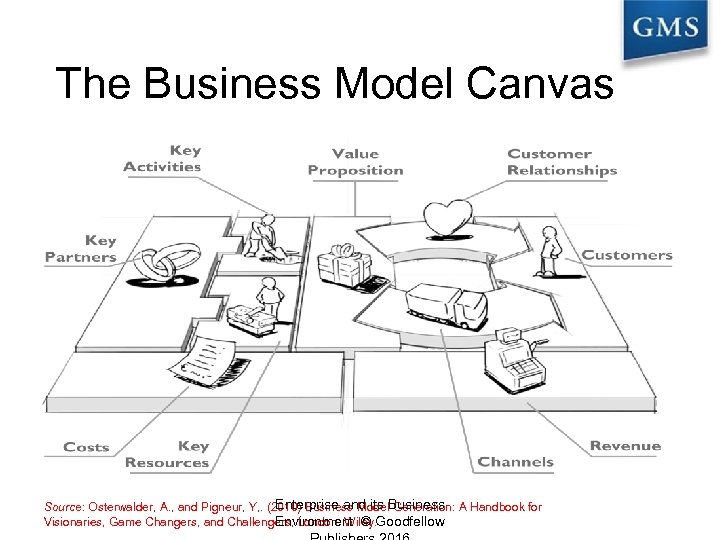
The Business Model Canvas Enterprise and its Generation: Source: Osterwalder, A. , and Pigneur, Y, . (2010) Business Model. Business A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers, London: Wiley. Goodfellow Environment ©
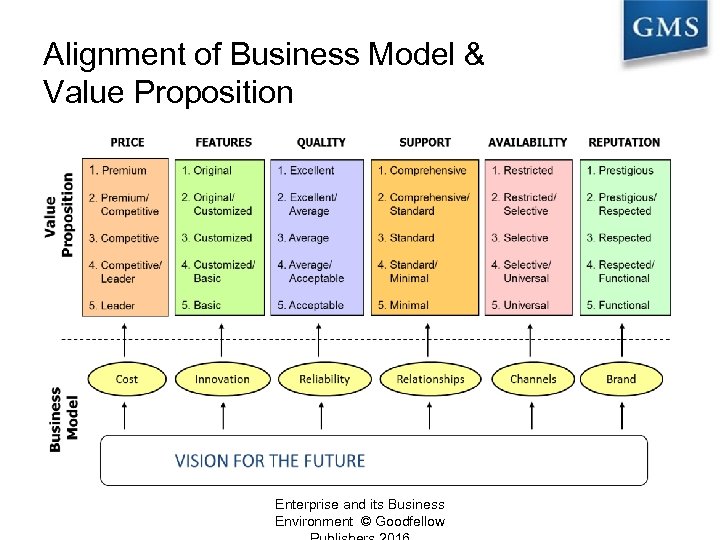
Alignment of Business Model & Value Proposition Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

The Elements of Managing this Process Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

The Importance of Management • Its About Adding Value to Resources To Survive!!! ◦ Everyone Manages Part of that Value-adding Process ◦ Ryannair – A Group of Entrepreneurs Saw an Opportunity in The Market & Created an Organisation to Take Advantage of it – Can You Name Any Others? ◦ They Bring Together Resources & Transform them into a Product/Service that they Provide to Customers ◦ Worked Out What Customers’ Value: ◦ Cost Rather Than Luxury & Delivered This (Their Unique Value Proposition) ◦ Carried 65 Million Passengers 2009 Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Systems Approach to Management Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
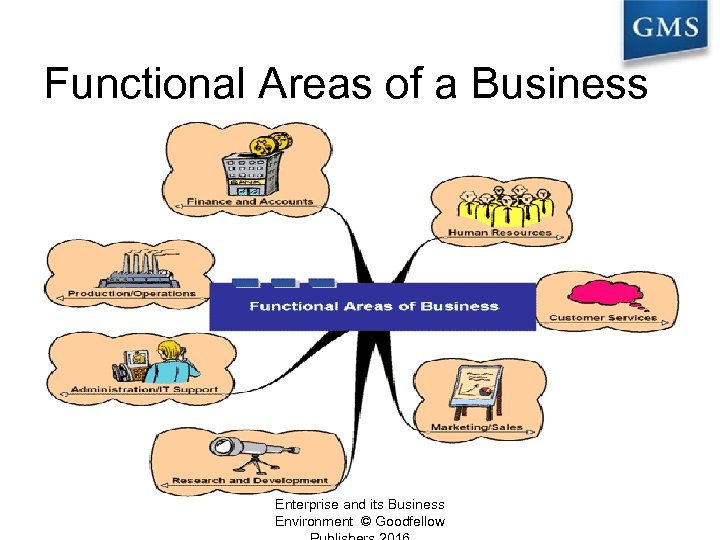
Functional Areas of a Business Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Figure 1. 1: Managing Organisation & Environment Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
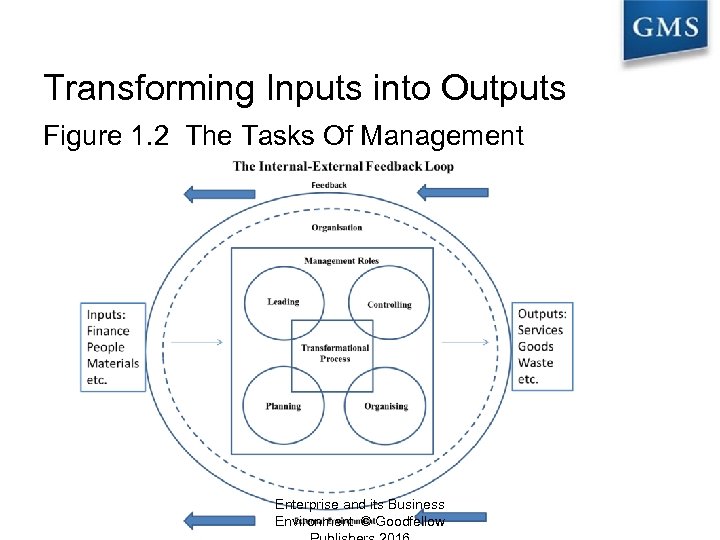
Transforming Inputs into Outputs Figure 1. 2 The Tasks Of Management Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Management & Organisation • A World of Managed Organisations on Which We Depend – Supermarkets, Retailers, E-tailers… • Management is to Create Organisations that Work – That Add Value to Resources they Use • “Value” Is Subjective – Value to A May Be Waste to B • What Types of Value People Who Buy the Following Brands of Jeans Are Looking for From the Product • Prada Jeans • Next Jeans • Tesco Jeans Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

People Define it in Different Ways • Zeithaml (1988) Found Four Main Definitions: • 1 Value is Low Price • 2 Value is Whatever I Want in a Product • 3 Value is the Quality I Get for the Price I Pay • 4 Value is What I Get for What I Give Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Other Functions of Organisations • Create Value, Wealth & Human Well-Being • Articulate & Implement Ideals • Gain Power to Protect Sectional Interests • Give People Work, Status, Social Contact • Enrich Directors & Senior Managers Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Specialised Areas of Management • General Management • Functions • Line • Staff • Project • Hierarchies • • Performing Direct Operations Managing Staff on Direct Operations Managing Managers Managing the Business Managers Add Value By Influencing Others Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Influencing Through the Process of Managing • Rosemary Stewart – Interrupted, Fragmented, Diverse • Mintzberg – Ten Management Roles, In Three Groups • Informational • Monitor, Disseminator, Spokesperson • Interpersonal • Figurehead, Leader, Liaison • Decisional • Entrepreneur, Disturbance Handler, Resource Allocator, Negotiator Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Roles & Performance (Luthans, 1988) • Those Who Achieved Promotion • Spent More Time Networking & Politicking • Those Who Were Effective • Spent More Time on Communications And HRM (Managing the Human Side) • Manager as Networker, Politician Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Influencing Through the Tasks of Managing • Planning – Overall Direction of Work • Organising – Allocating Resources, Time, Effort • Leading – Generating Effort & Commitment Towards Objectives • Controlling – Monitor Progress, Compare With Plan, Adjust if Needed Apply to All Kinds of Tasks (Incl. Study); & Are Done Iteratively Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Influencing Through Shaping the Context • Internal – Elements of the Organisation – The Immediate Context of Managing • External – Micro & Macro Environment Historical – Past, Present & Future Events • These Interact with Each Other • People Interpret their Context • Work Within it or Act to Change it in Some Way • People Interpret New Context, Work Within it, or Seek to Change it… Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Critical Thinking • Effective Managers Have Developed the Skills of Critical Thinking, Whose Components Are: • Identifying & Challenging Assumptions • Recognising the Importance of Context • Imagining & Exploring Alternatives • Seeing Limitations Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
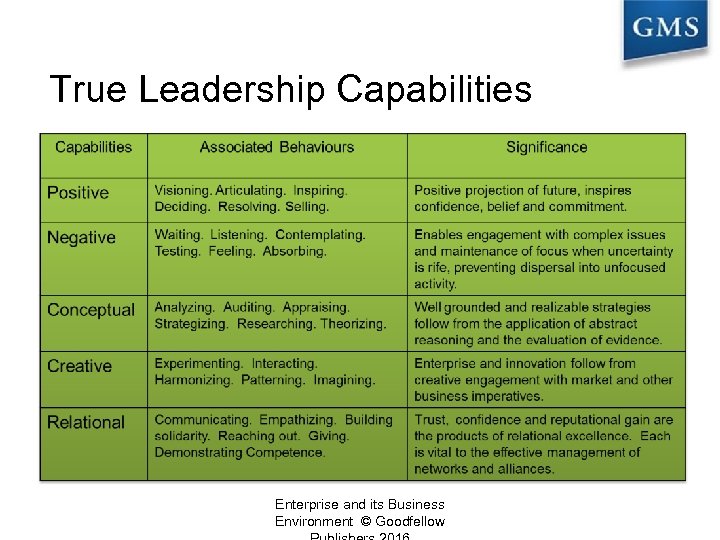
True Leadership Capabilities Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow

Conclusion • Management Role is to Add Value to Resources • Managing a General Human Activity • Scale of Responsibility for Resources Varies • Managers Aim to Influence Others Through: • Processes of Managing • Tasks of Managing • Shaping Contexts • How Well they Do Depends on Thinking Enterprise and its Business Critically Environment © Goodfellow

References • • • Boddy, D. (2002) Management an Introduction. 2 nd Edition. Essex: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Carson, D. , Cromie, S. , Mc. Gowan, P. , and Hill, J. (1995) Marketing and Entrepreneurship in SMEs An Innovative Approach. London: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Hannigan, T. (2002) Management: Concepts and Practices. 3 rd Edition. Essex: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Hellriegel, D. , Jackson, S. E. , and Slocum, J. W. (2002) Management a Competency Based Approach, 9 th Edition, Ohio: South Western. Kotler, P. , 1991. Marketing management. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Kotler, P. , Armstrong, G. , Saunders, J. and Wong, V. (2002) Principles of Marketing; Third European Edition. 3 rd Edition. London: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Mullens, L. J. (2002) Management and Organisational Behaviour. 6 th Edition. Essex: Financial Times/Prentice Hall. Palmer, A. and Hartley, B. (1996) The Business and Marketing Environment. 2 nd Edition. Berkshire: Mc. Graw Hill. Timmons, J. & and Spinelli, S. , 2007. New Venture Creation Entrepreneurship for the 21 st Century. 7 th ed. New York: Mc. Graw Hill Publishing. Luthans, F. , Welsh, D. H. B. , & Taylor, L. (1988, June). A descriptive model of managerial effectiveness. Group & Organization Studies, 13(2), 148 -162. Enterprise and its Business Environment © Goodfellow
468e4e1c1d8480fad0c2536a5fbdee79.ppt