841685e0f10bd5f9f8b2cee0b6af9871.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Business Management in the Built Environment STRATEGY Stuart Tennant Presentation 2011

Business Management in the Built Environment Presentation Content Strategy Management Strategy in Practice A Model of Strategy Process Auditing Environmental Factors The Competitive Environment Organisational Structure The Built Environment Summary

Business Management in the Built Environment Strategy Management: Primary Task: to match the organisations capabilities with opportunities and threats in the environment to achieve competitive advantage.
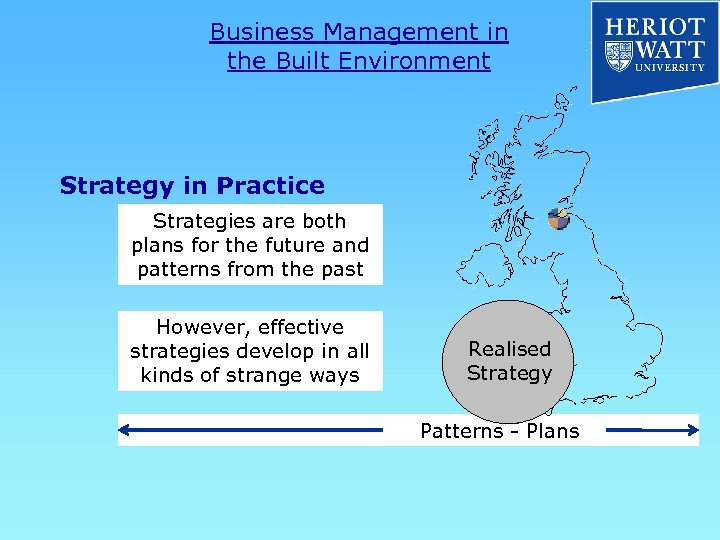
Business Management in the Built Environment Strategy in Practice Strategies are both plans for the future and patterns from the past However, effective strategies develop in all kinds of strange ways Realised Strategy Patterns - Plans
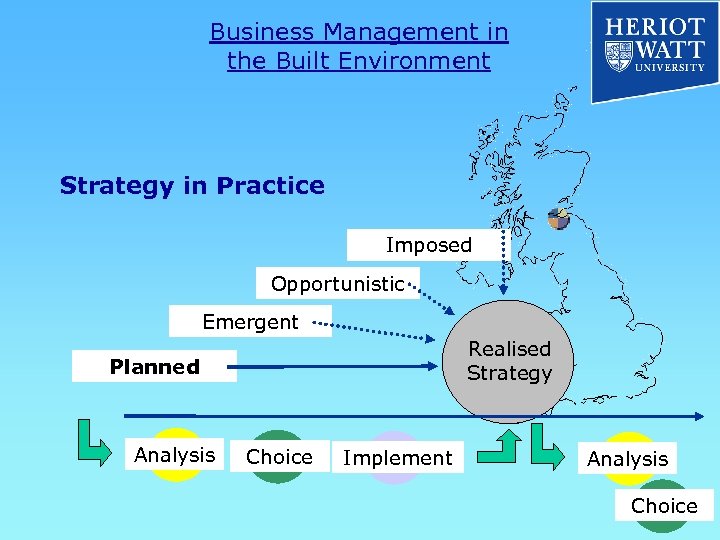
Business Management in the Built Environment Strategy in Practice Imposed Opportunistic Emergent Realised Strategy Planned Analysis Choice Implement Analysis Choice
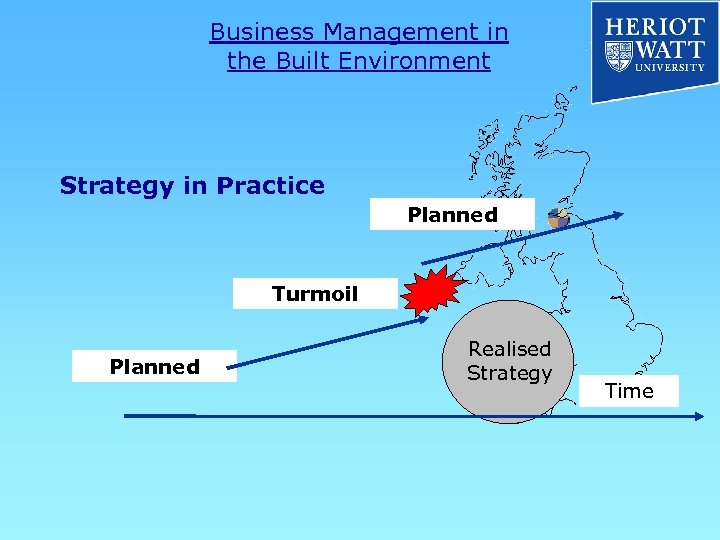
Business Management in the Built Environment Strategy in Practice Planned Turmoil Planned Realised Strategy Time
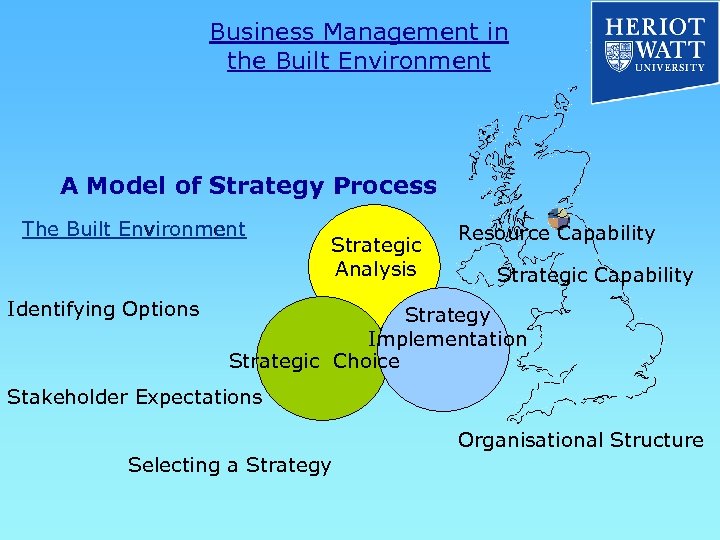
Business Management in the Built Environment A Model of Strategy Process The Built Environment Identifying Options Strategic Analysis Resource Capability Strategic Capability Strategy Implementation Strategic Choice Stakeholder Expectations Organisational Structure Selecting a Strategy
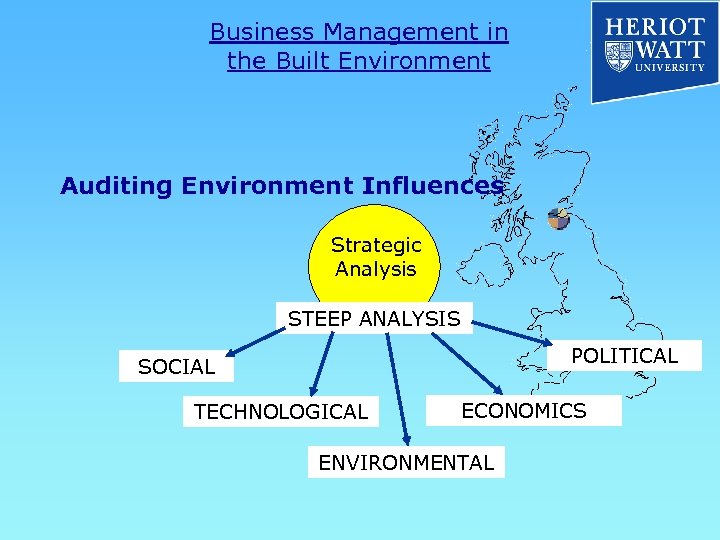
Business Management in the Built Environment Auditing Environment Influences Strategic Analysis STEEP ANALYSIS POLITICAL SOCIAL TECHNOLOGICAL ECONOMICS ENVIRONMENTAL
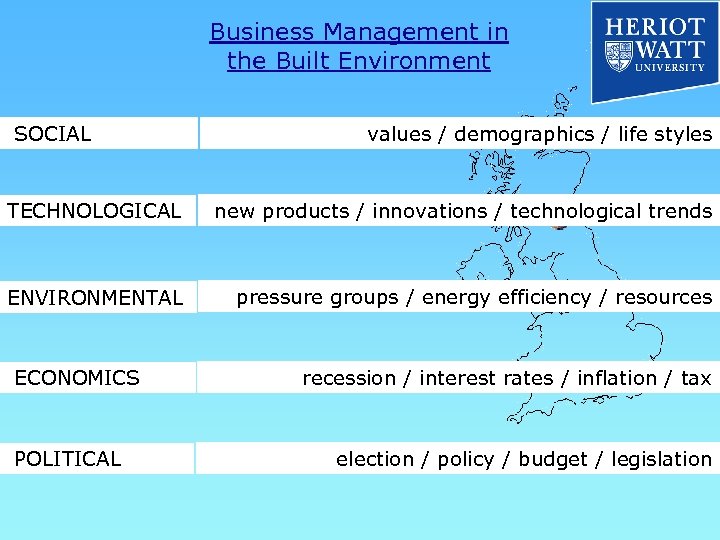
Business Management in the Built Environment SOCIAL values / demographics / life styles TECHNOLOGICAL new products / innovations / technological trends ENVIRONMENTAL pressure groups / energy efficiency / resources ECONOMICS POLITICAL recession / interest rates / inflation / tax election / policy / budget / legislation

Business Management in the Built Environment Auditing Environment Influences Strategic Analysis STEEP ANALYSIS When Should STEEP be used? § Times of Uncertainty § Times of Information Overload § Times of Disorganization

Business Management in the Built Environment Auditing Environment Influences Strategic Analysis STEEP ANALYSIS 1. Comprehend the element of the environment 2. Assess interrelationships between trends 3. Relate trends to issues 4. Forecast the future direction of issues 5. Derive implications

Business Management in the Built Environment Auditing the Built Environment SOCIAL Strategic Analysis Affordable Housing POLITICAL PFI / PPP ENVIRONMENTAL TECHNOLOGICAL Systems Building ECONOMICS Waste Management Recession
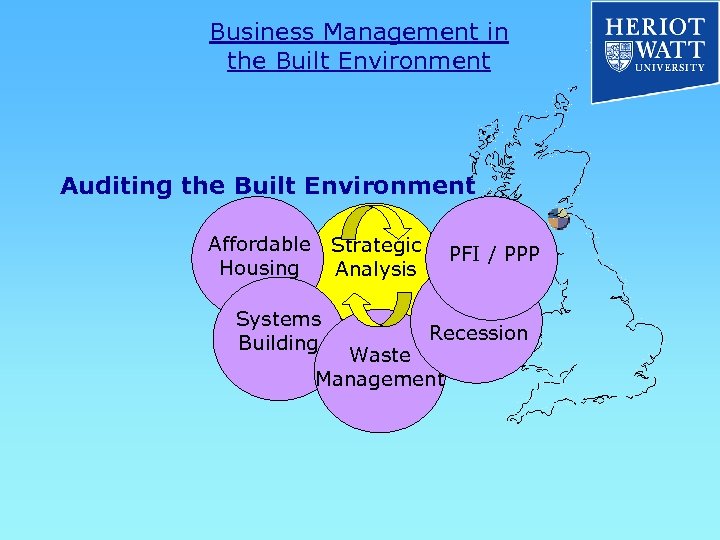
Business Management in the Built Environment Auditing the Built Environment Affordable Housing Strategic Analysis Systems Building PFI / PPP Recession Waste Management
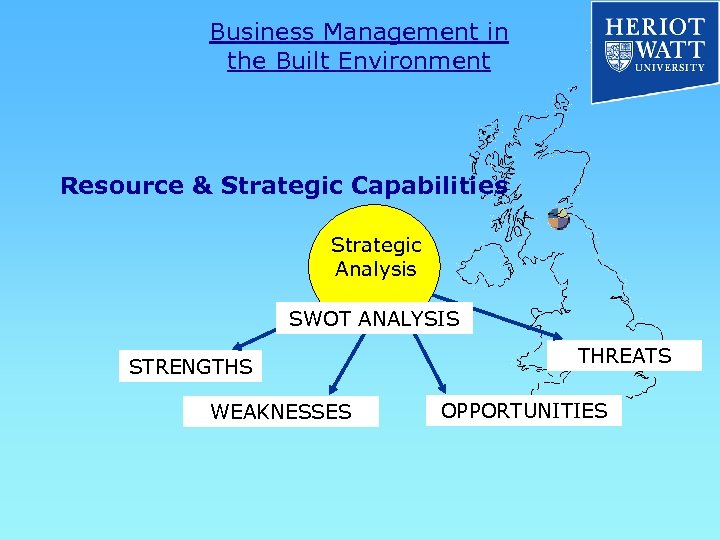
Business Management in the Built Environment Resource & Strategic Capabilities Strategic Analysis SWOT ANALYSIS STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES THREATS OPPORTUNITIES
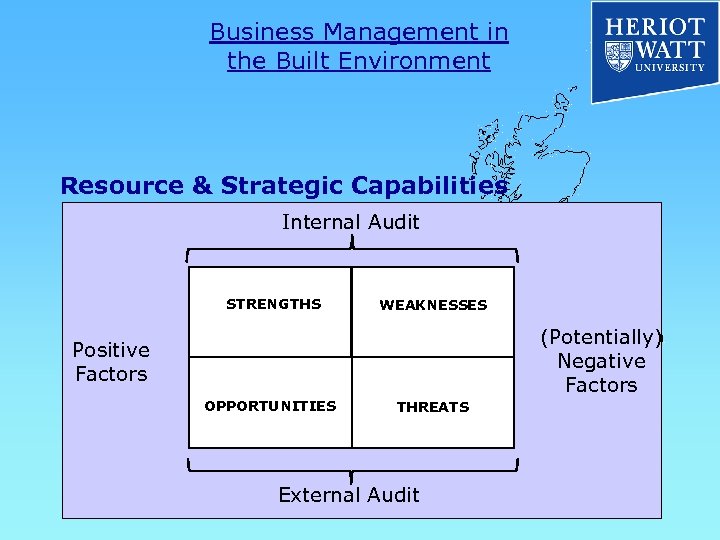
Business Management in the Built Environment Resource & Strategic Capabilities Internal Audit STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES (Potentially) Negative Factors Positive Factors OPPORTUNITIES THREATS External Audit
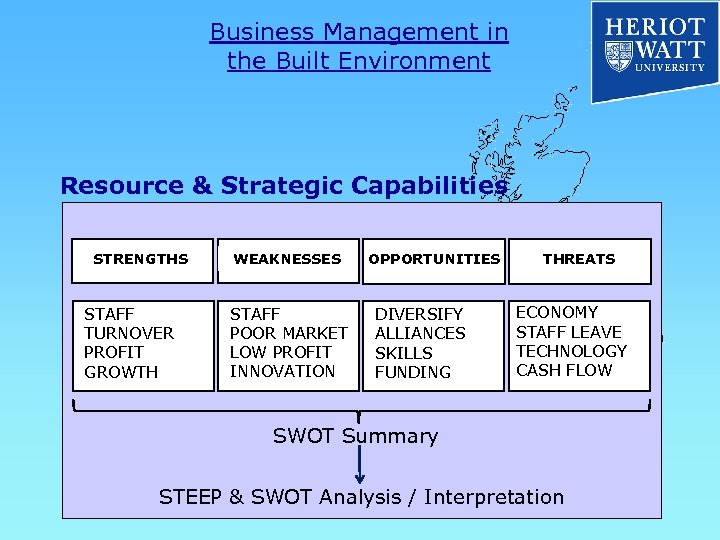
Business Management in the Built Environment Resource & Strategic Capabilities STRENGTHS STAFF TURNOVER PROFIT GROWTH WEAKNESSES STAFF POOR MARKET LOW PROFIT INNOVATION OPPORTUNITIES DIVERSIFY ALLIANCES SKILLS FUNDING THREATS ECONOMY STAFF LEAVE TECHNOLOGY CASH FLOW SWOT Summary STEEP & SWOT Analysis / Interpretation

Business Management in the Built Environment STEEP & SWOT Analysis & Interpretation STEEP & SWOT Analysis / Interpretation Use in conjunction with other techniques Porter’s Five Forces Porter’s Generic Strategies Boston Consulting Group Matrix Diversification Analysis
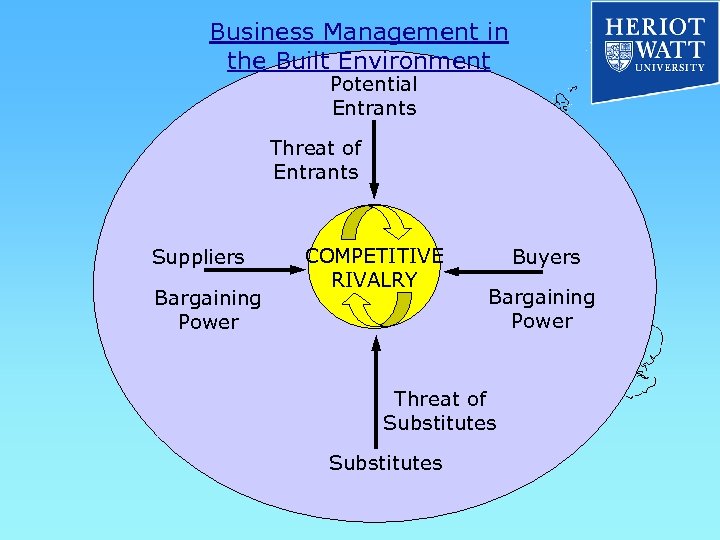
Business Management in the Built Environment Potential Entrants Threat of Entrants Suppliers Bargaining Power COMPETITIVE RIVALRY Buyers Bargaining Power Threat of Substitutes
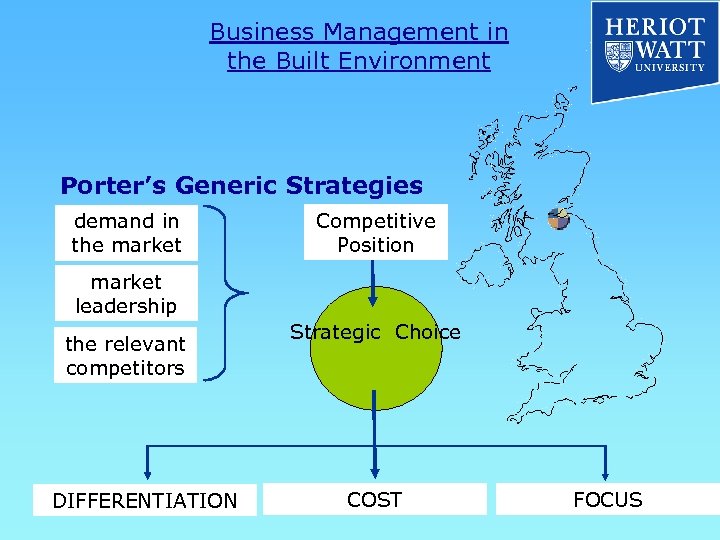
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies demand in the market Competitive Position market leadership the relevant competitors DIFFERENTIATION Strategic Choice COST FOCUS

Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies Competitive Forces: § Drive down costs while maintaining average quality Cost Leadership / Cost Focus § Differentiate product or service in ways that are valued by the customer Broad Differentiation / Differentiation Focus
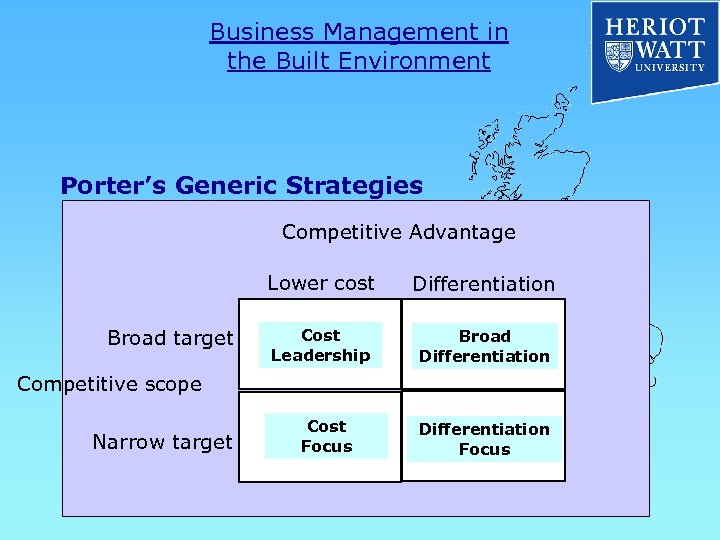
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies Competitive Advantage Lower cost Broad target Differentiation Cost Leadership Broad Differentiation Competitive scope Narrow target Cost Focus Differentiation Focus
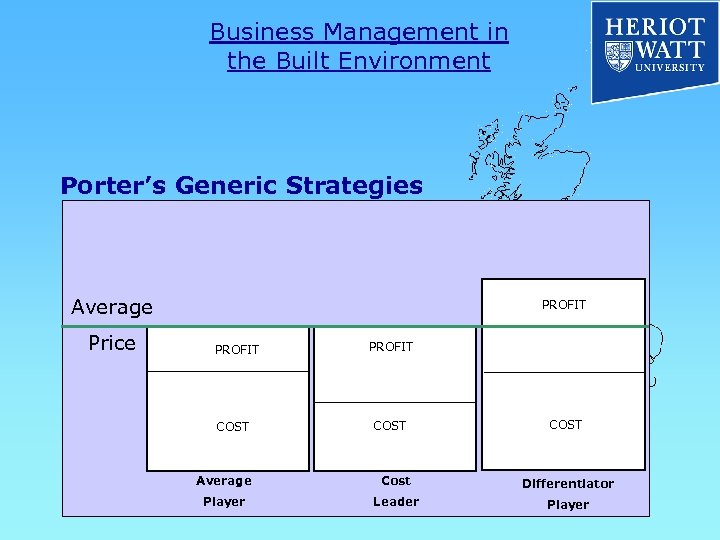
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies Average Price PROFIT COST Average Cost Differentiator Player Leader Player
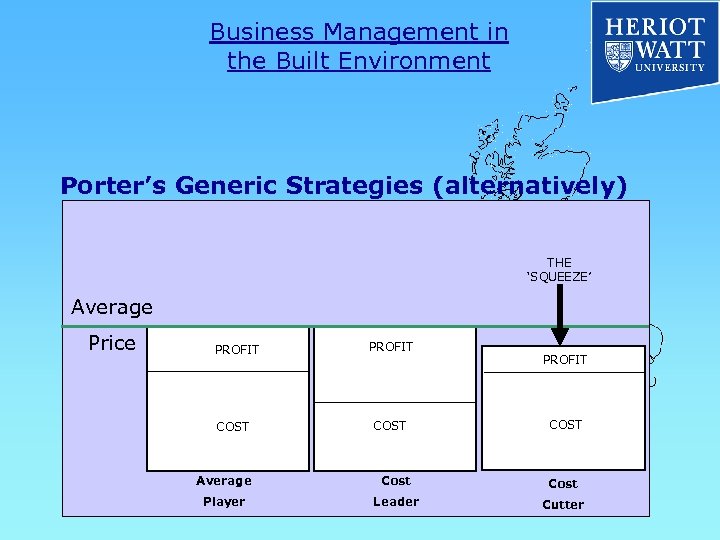
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies (alternatively) THE ‘SQUEEZE’ Average Price PROFIT COST Average Cost Player Leader Cutter
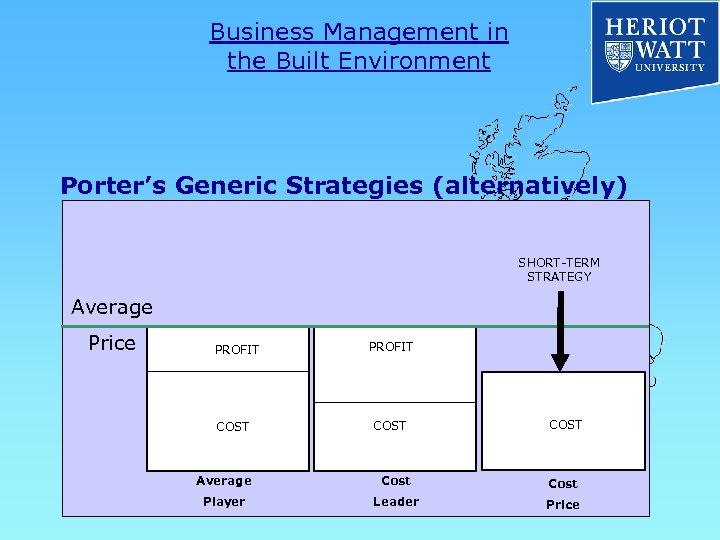
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies (alternatively) SHORT-TERM STRATEGY Average Price PROFIT COST Average Cost Player Leader Price
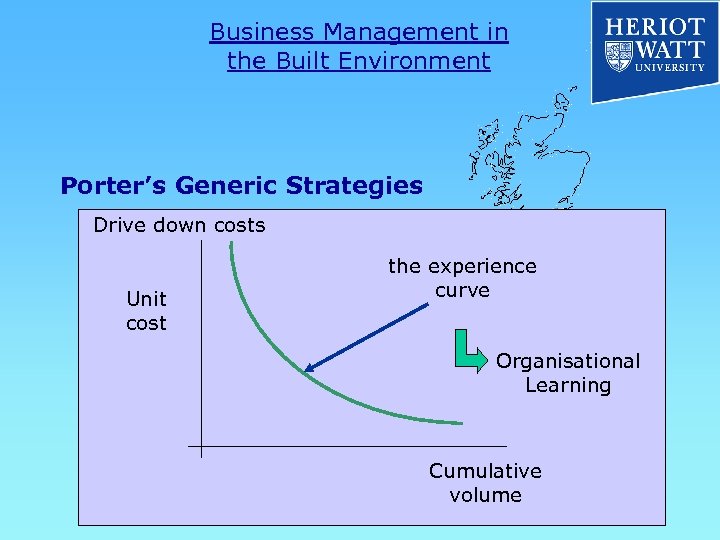
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies Drive down costs Unit cost the experience curve Organisational Learning Cumulative volume
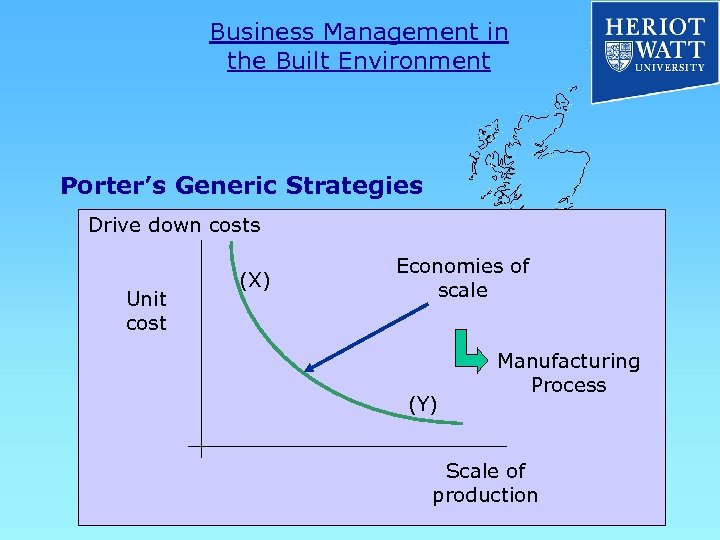
Business Management in the Built Environment Porter’s Generic Strategies Drive down costs Unit cost (X) Economies of scale (Y) Manufacturing Process Scale of production
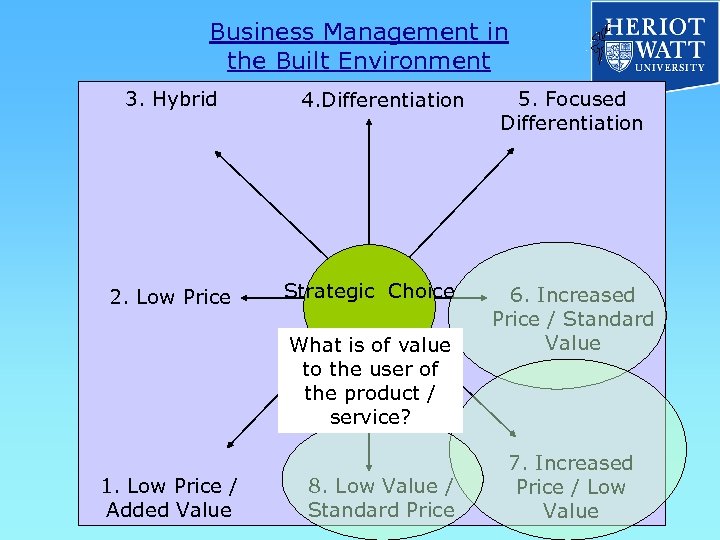
Business Management in the Built Environment 3. Hybrid 2. Low Price 4. Differentiation Strategic Choice What is of value to the user of the product / service? 1. Low Price / Added Value 8. Low Value / Standard Price 5. Focused Differentiation 6. Increased Price / Standard Value 7. Increased Price / Low Value
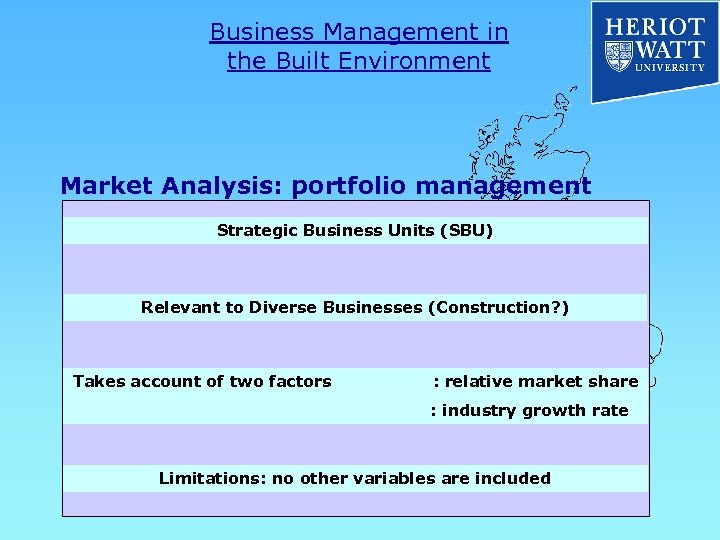
Business Management in the Built Environment Market Analysis: portfolio management Strategic Business Units (SBU) Relevant to Diverse Businesses (Construction? ) Takes account of two factors : relative market share : industry growth rate Limitations: no other variables are included

Business Management in the Built Environment Market Analysis: the growth / share matrix Theoretically offer the best profit & growth Low growth in a poor market / weakness Profits best utilised elsewhere Requires large investment for development
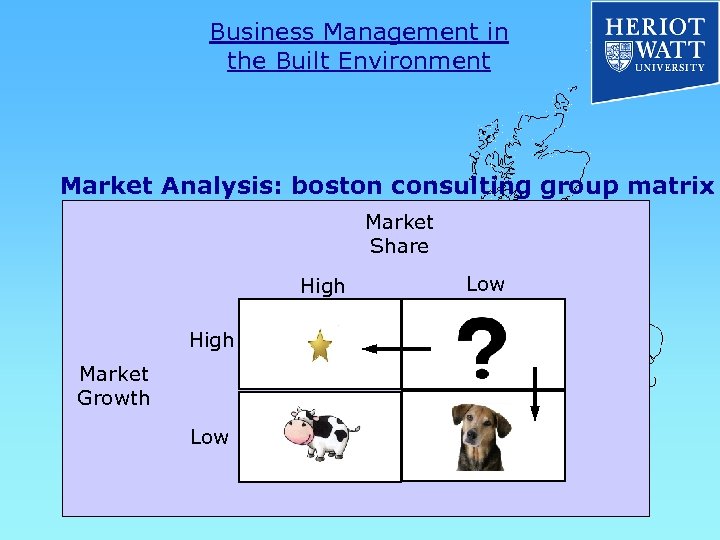
Business Management in the Built Environment Market Analysis: boston consulting group matrix Market Share High Market Growth Low
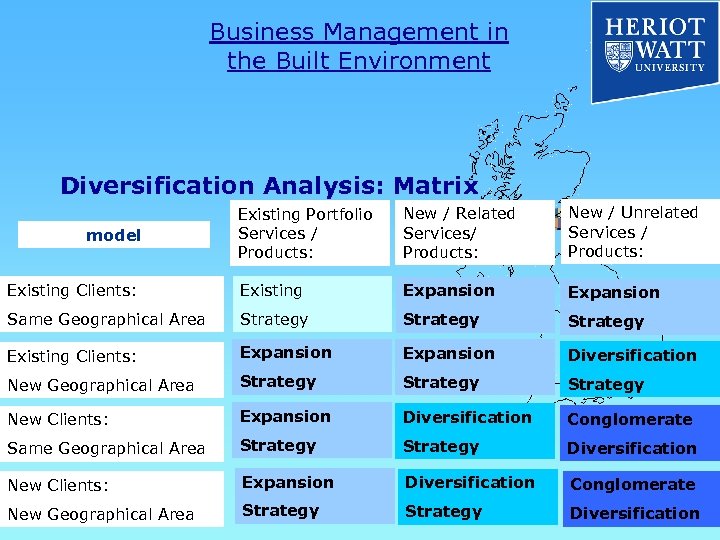
Business Management in the Built Environment Diversification Analysis: Matrix Existing Portfolio Services / Products: New / Related Services/ Products: New / Unrelated Services / Products: Existing Clients: Existing Expansion Same Geographical Area Strategy Existing Clients: Expansion Diversification New Geographical Area Strategy New Clients: Expansion Diversification Conglomerate Same Geographical Area Strategy Diversification New Clients: Expansion Diversification Conglomerate New Geographical Area Strategy Diversification model

Business Management in the Built Environment Organisational Structure “Structure follows Strategy” Chandler, 1962. Strategy Implementation

Business Management in the Built Environment Organisational Forms of Governance Markets Hierarchies buy make The price mechanism Forward / backward integration

Business Management in the Built Environment Organisational Forms of Governance Markets or Hierarchies? * For Markets if: * For Hierarchies if: * Commodity Products * Economies of scale * Market Mechanism * Temper Opportunism * Profit Maximisation * Thin markets * High Management Cost * Complex Situations * Routine Situations * Intellectual Capital
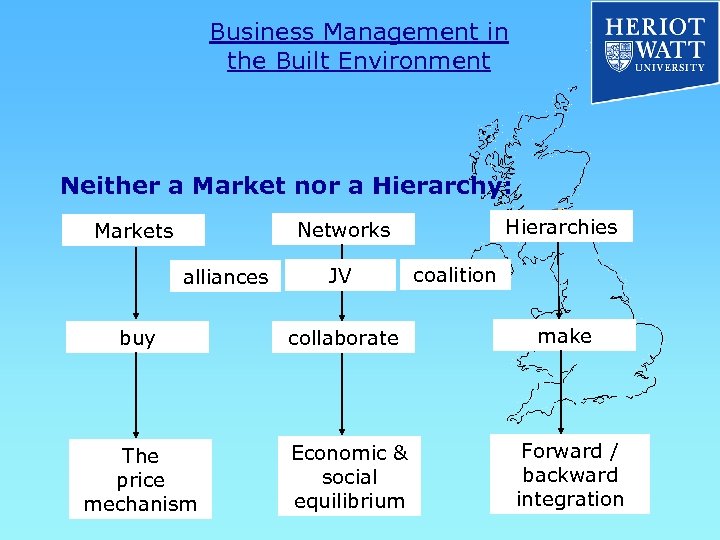
Business Management in the Built Environment Neither a Market nor a Hierarchy: Hierarchies Networks Markets alliances JV coalition buy collaborate make The price mechanism Economic & social equilibrium Forward / backward integration

Business Management in the Built Environment Networks and Competition Traditionally, collaboration by firms has been frowned upon by economists as the basis However the fashion for monopolies and cartels. alliances and network collaborations seems to be generating sophisticated new ways to compete and additional sources of advantage over traditional firms
Business Management in the Built Environment Networks and Competition Flexible capabilities: equipped to assemble diverse / unique, set of capabilities. Specialisation: networks can benefit from a division of specialisation Learning: New alliances – new learning capabilities Increased options: Networks can be a rich source of strategic options
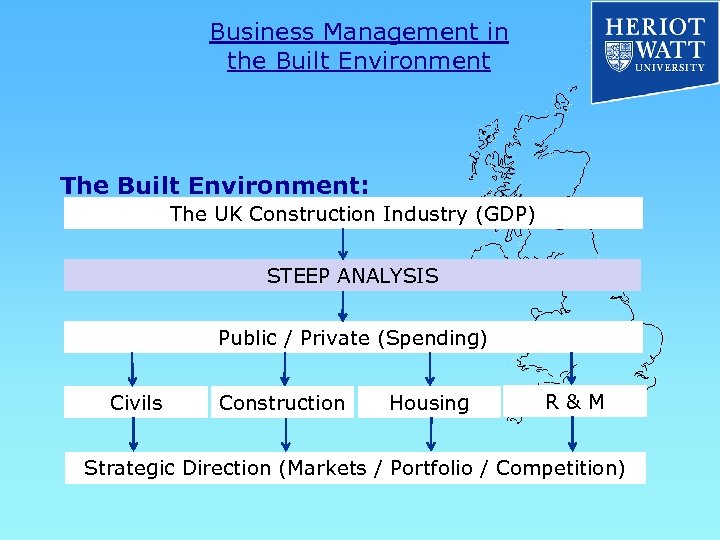
Business Management in the Built Environment The Built Environment: The UK Construction Industry (GDP) STEEP ANALYSIS Public / Private (Spending) Civils Construction Housing R&M Strategic Direction (Markets / Portfolio / Competition)
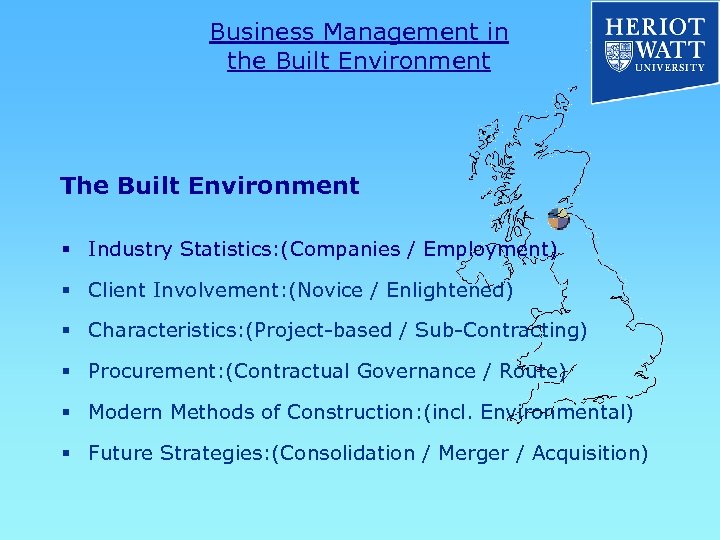
Business Management in the Built Environment The Built Environment § Industry Statistics: (Companies / Employment) § Client Involvement: (Novice / Enlightened) § Characteristics: (Project-based / Sub-Contracting) § Procurement: (Contractual Governance / Route) § Modern Methods of Construction: (incl. Environmental) § Future Strategies: (Consolidation / Merger / Acquisition)
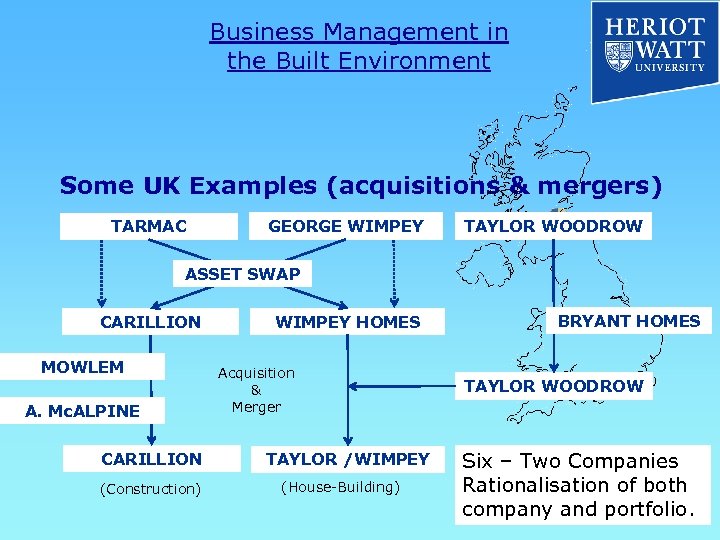
Business Management in the Built Environment Some UK Examples (acquisitions & mergers) TARMAC GEORGE WIMPEY TAYLOR WOODROW ASSET SWAP CARILLION MOWLEM A. Mc. ALPINE CARILLION (Construction) WIMPEY HOMES Acquisition & Merger TAYLOR /WIMPEY (House-Building) BRYANT HOMES TAYLOR WOODROW Six – Two Companies Rationalisation of both company and portfolio.
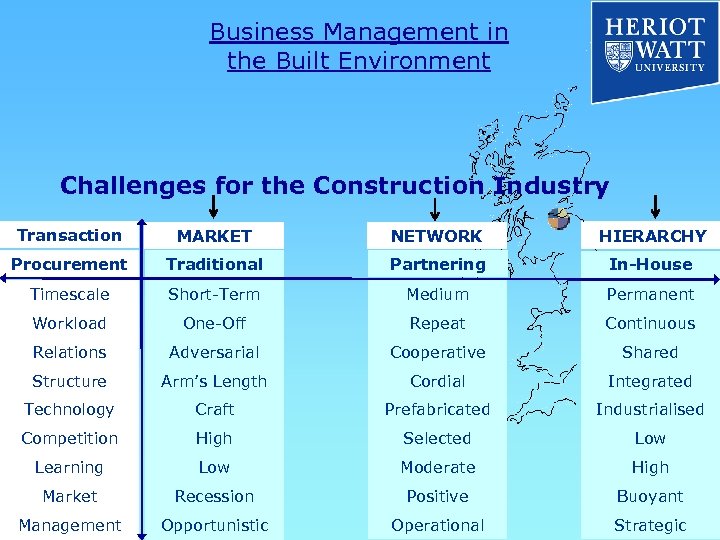
Business Management in the Built Environment Challenges for the Construction Industry Transaction MARKET BUY NETWORK MAKE HIERARCHY Procurement Traditional Partnering In-House Timescale Short-Term Medium Permanent Workload One-Off Repeat Continuous Relations Adversarial Cooperative Shared Structure Arm’s Length Cordial Integrated Technology Craft Prefabricated Industrialised Competition High Selected Low Learning Low Moderate High Market Recession Positive Buoyant Management Opportunistic Operational Strategic
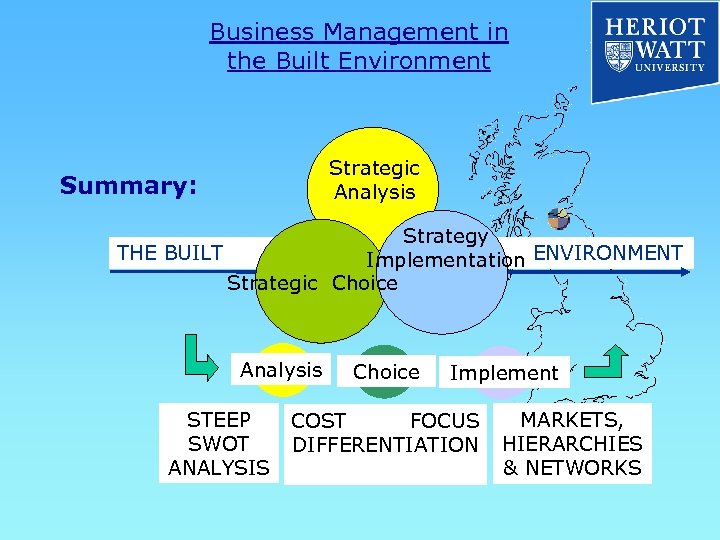
Business Management in the Built Environment Strategic Analysis Summary: Strategy THE BUILT Implementation ENVIRONMENT Strategic Choice Analysis STEEP SWOT ANALYSIS Choice Implement COST FOCUS DIFFERENTIATION MARKETS, HIERARCHIES & NETWORKS

Business Management in the Built Environment Recommended Reading: Mintzberg, H. (1987) Crafting strategy. Harvard Business Review, 65 (5) pp. 66 – 75.

Business Management in the Built Environment Further Reading: Johnston, G. and Scholes, K. (1993) Exploring Corporate Strategy: text and case studies. Prentice Hall, London. Newcombe, R. , Langford, D. and Fellows, R. (1990) Construction Management 1 Organisational Systems. Mitchell, London. Thank You
841685e0f10bd5f9f8b2cee0b6af9871.ppt