9f349ec4e8227fdf5e303e88b73c38a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Business Management in the Built Environment ADAPTED FROM Dr. Scott Fernie ‘S SLIDES AND LESSON BMBE/L 7/2017 1

Business Management in the Built Environment Forms of governance : a)Market orientation b)Hierarchy orientation c) Network structure BMBE/L 7/2017 2
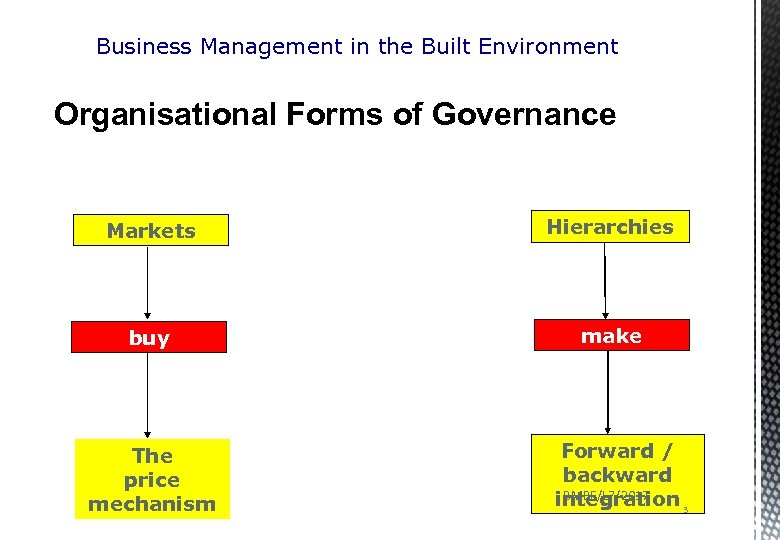
Business Management in the Built Environment Organisational Forms of Governance Markets Hierarchies buy make The price mechanism Forward / backward BMBE/L 7/2017 integration 3
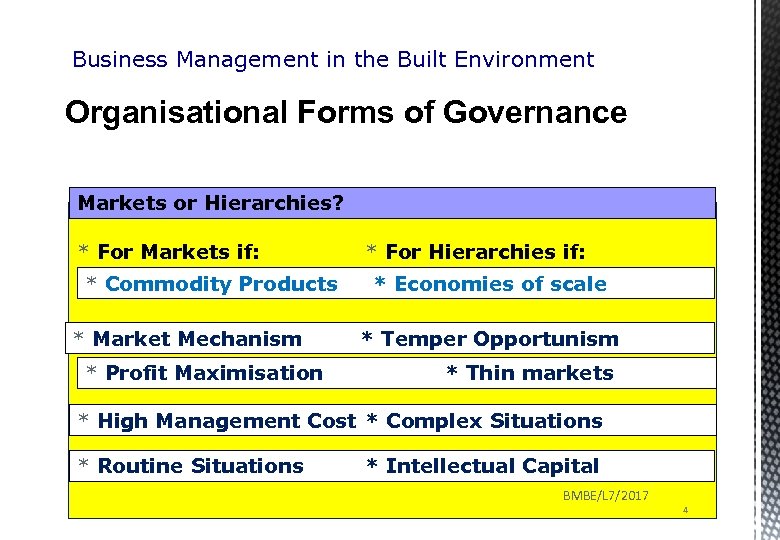
Business Management in the Built Environment Organisational Forms of Governance Markets or Hierarchies? * For Markets if: * Commodity Products * Market Mechanism * Profit Maximisation * For Hierarchies if: * Economies of scale * Temper Opportunism * Thin markets * High Management Cost * Complex Situations * Routine Situations * Intellectual Capital BMBE/L 7/2017 4
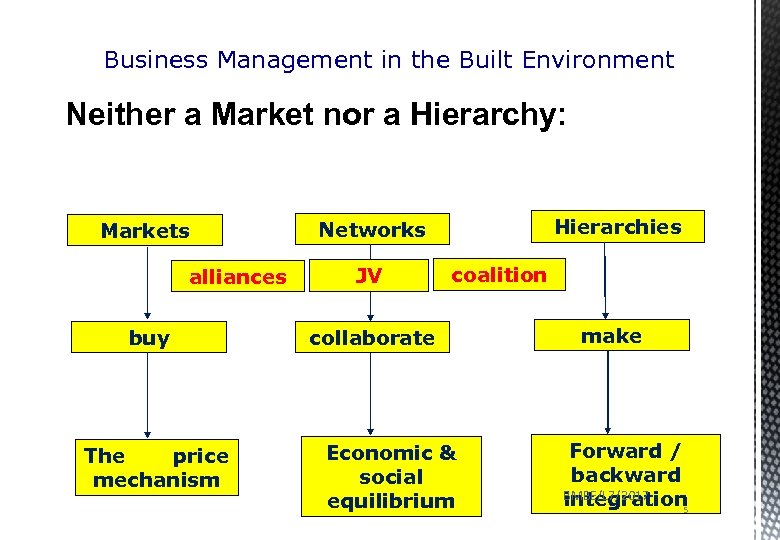
Business Management in the Built Environment Neither a Market nor a Hierarchy: Markets alliances buy The price mechanism Hierarchies Networks JV coalition collaborate Economic & social equilibrium make Forward / backward BMBE/L 7/2017 integration 5

Business Management in the Built Environment Networks and Competition Traditionally, collaboration by firms has been frowned upon by economists as the basis for monopolies and cartels. However the fashion for alliances and network collaborations seems to be generating sophisticated new ways to compete and additional sources of advantage over traditional firms BMBE/L 7/2017 6

Business Management in the Built Environment Networks and Competition Flexible capabilities: equipped to assemble diverse / unique, set of capabilities. Specialisation: networks can benefit from a division of specialisation Learning: New alliances – new learning capabilities Increased options: Networks can be a rich source of strategic options BMBE/L 7/2017 7

Question for discussion Critically explore the various types of complexity that a manager will undoubtedly encounter in developing strategy within a construction company BMBE/L 7/2017 8
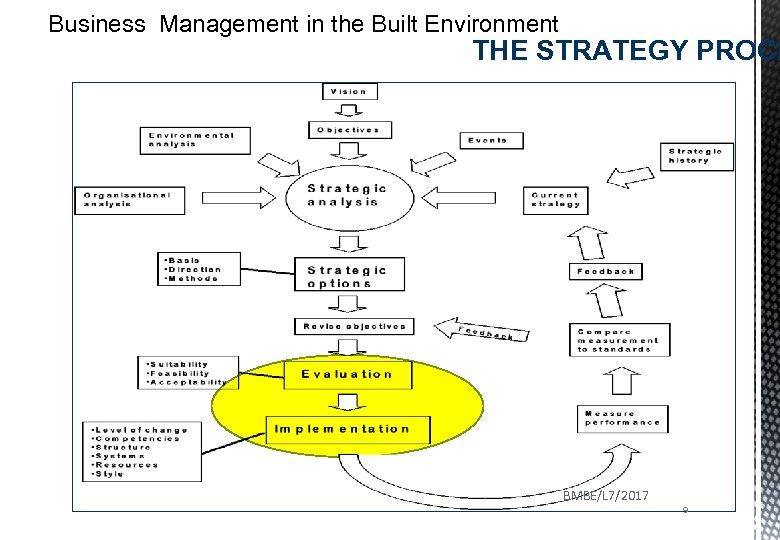
Business Management in the Built Environment THE STRATEGY PROCE BMBE/L 7/2017 9

Business Management in the Built Environment §“Organisations fail to implement more than 70 percent of their new strategic initiatives” (Miller 2002) §What are the obstacles? §Can you describe a theoretical model? §What are the connections between schools of thought and implementation BMBE/L 7/2017 10
Business Management in the Built Environment “ Implementation It can be much easier to think of a good strategy than it is to implement it” (Woolridge and Floyd 1990) “Without successful implementation, a strategy is but a fantasy” (Kast and Rosenzweig 1985) This is the same as our new year BMBE/L 7/2017 resolutions! 11

Business Management in the Built Environment Implementation – what could be easier §“Organisations fail to implement more than 70 percent of their new strategic initiatives” (Miller 2002) §What are the obstacles? §Take 10 minutes to make a list of reasons §You could think about why you fail to implement your own plans and relate these to construction organisations BMBE/L 7/2017 12

Business Management in the Built Environment 1. Focus on formulation rather than implementation – Do you ever spend time planning and forget about implementing study plans? 2. The models of implementation are too complex (Okumus 2003) BMBE/L 7/2017 13
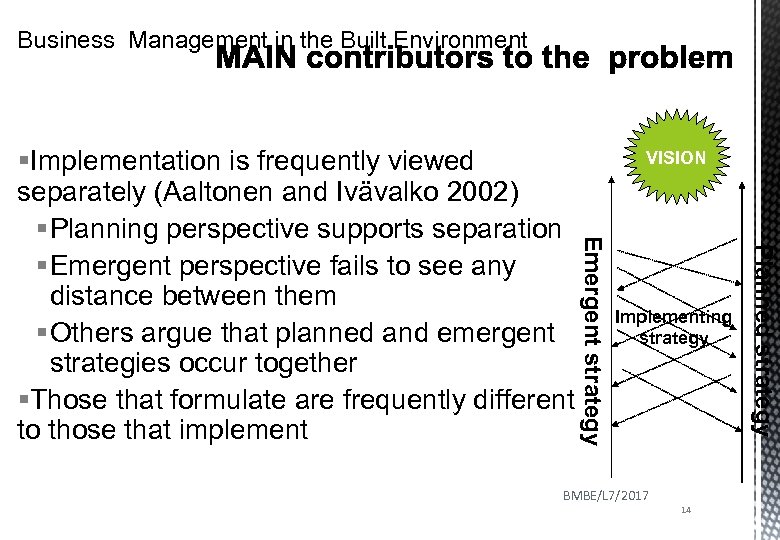
Business Management in the Built Environment VISION Implementing strategy BMBE/L 7/2017 14 Planned strategy Emergent strategy §Implementation is frequently viewed separately (Aaltonen and Ivävalko 2002) § Planning perspective supports separation § Emergent perspective fails to see any distance between them § Others argue that planned and emergent strategies occur together §Those that formulate are frequently different to those that implement

Business Management in the Built Environment §Ultimately change involves people and thus it is NOT a simple linear, predictable process § It simply IS NOT easy to control people § Strategy does not resonate with practitioners § We are challengers and questioners of change § We represent barriers and resistance to change § We also provide opportunities to change § ‘All progress is made through the unreasonable man!’ § We are also the implementers of change § Change may also be implemented by unreasonable man BMBE/L 7/2017 15

Business Management in the Built Environment • Weak management roles in implementation • A lack of communication • Lacking commitment to the strategy • Unaware or lack of understanding of strategy • Unaligned organisational systems and resources • Poor coordination and sharing of responsibilities • Inadequate capabilities and training provided • Competing activities diverted attention away from Taken from Aaltonen implementation and Ivävalko (2002) and Al-Ghamdi (1998) BMBE/L 7/2017 16

Business Management in the Built Environment • Uncontrollable environmental factors • Formulators walk away from implementation!! • Formulators and/or implementers left the company • Leadership necessary was absent during implementation • Underestimation of resources required to carry through implementation • Control and monitoring systems inadequate • Lack of definition of key tasks and activities Taken from Aaltonen and Ivävalko (2002) and Al-Ghamdi (1998) BMBE/L 7/2017 17

Business Management in the Built Environment • To identify what requires to be changed • To consider what is required to make change happen • To monitor what actually changes • To consider the context within which change will occur • To formulate and execute a plan/process for change • To monitor and react to implementation (Pettigrew 1987) BMBE/L 7/2017 18
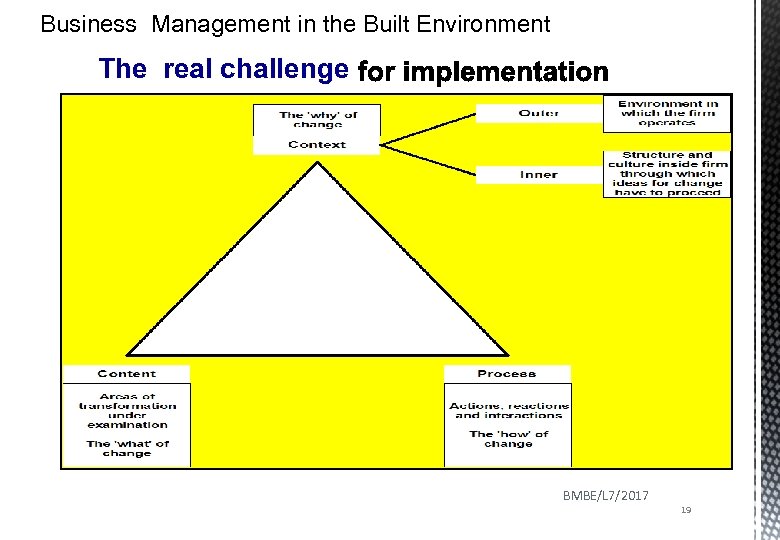
Business Management in the Built Environment The real challenge BMBE/L 7/2017 19
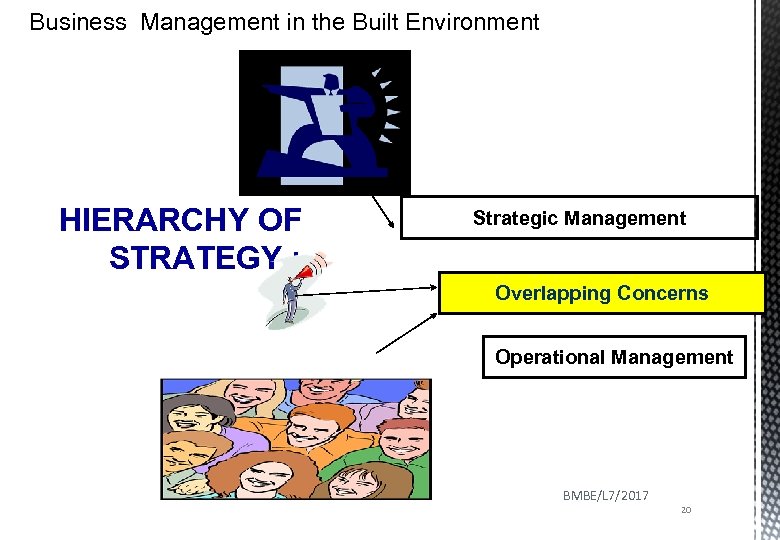
Business Management in the Built Environment HIERARCHY OF STRATEGY : Strategic Management Overlapping Concerns Operational Management BMBE/L 7/2017 20
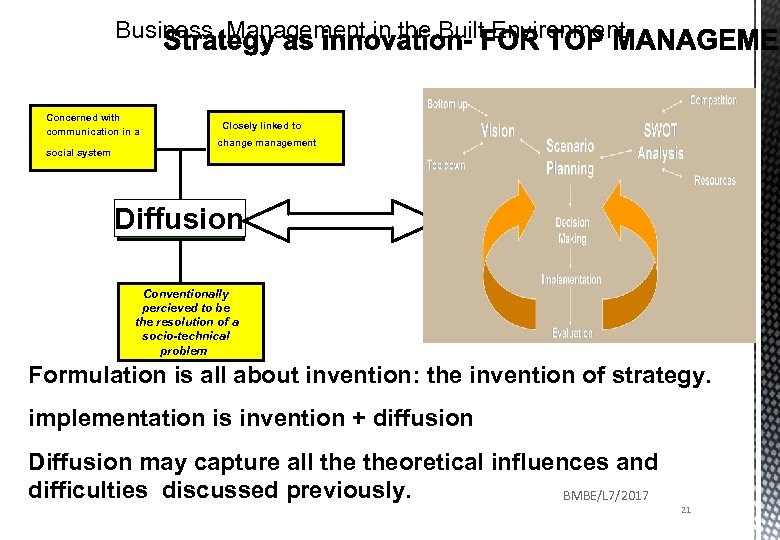
Business Management in the Built Environment Concerned with communication in a social system Closely linked to change management Diffusion Conventionally percieved to be the resolution of a socio-technical problem Formulation is all about invention: the invention of strategy. implementation is invention + diffusion Diffusion may capture all theoretical influences and difficulties discussed previously. BMBE/L 7/2017 21
Business Management in the Built Environment Mckinsey 7 -s model BMBE/L 7/2017 22
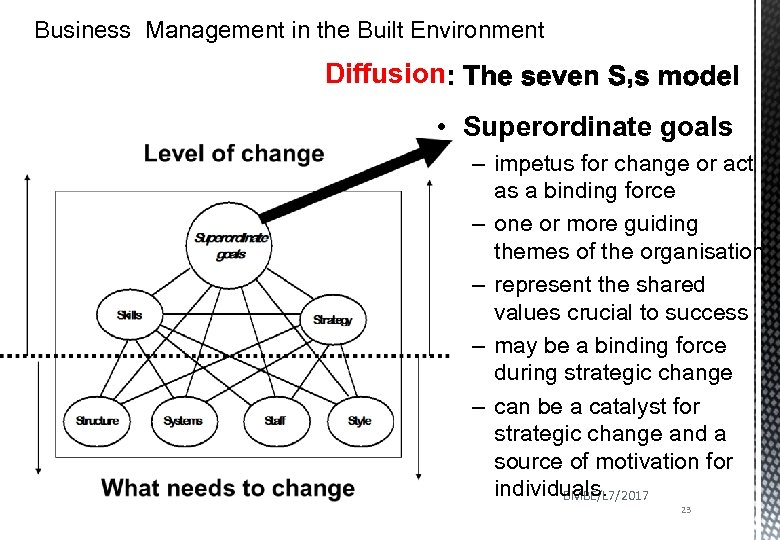
Business Management in the Built Environment Diffusion • Superordinate goals – impetus for change or act as a binding force – one or more guiding themes of the organisation – represent the shared values crucial to success – may be a binding force during strategic change – can be a catalyst for strategic change and a source of motivation for individuals. BMBE/L 7/2017 23
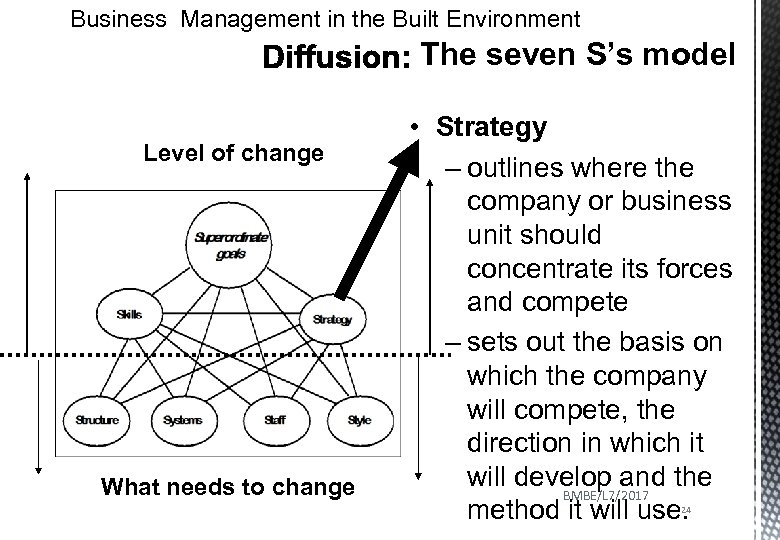
Business Management in the Built Environment The seven S’s model Level of change What needs to change • Strategy – outlines where the company or business unit should concentrate its forces and compete – sets out the basis on which the company will compete, the direction in which it will develop and the BMBE/L 7/2017 method it will use. 24
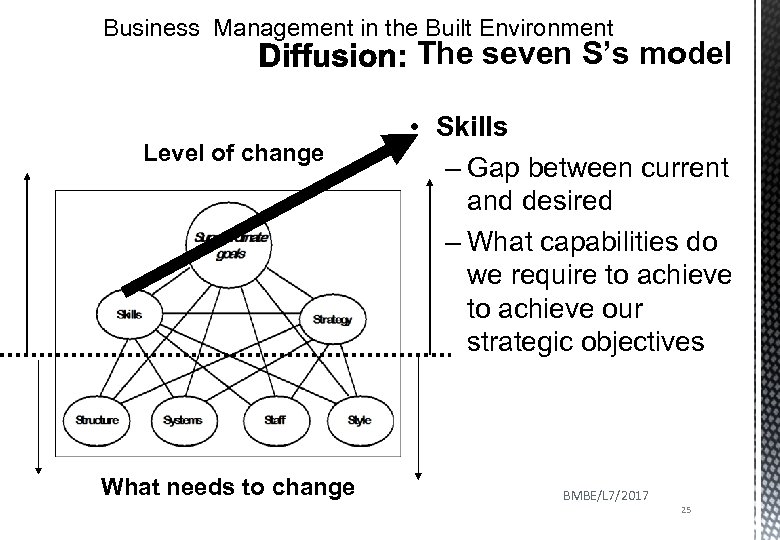
Business Management in the Built Environment The seven S’s model Level of change What needs to change • Skills – Gap between current and desired – What capabilities do we require to achieve our strategic objectives BMBE/L 7/2017 25

Business Management in the Built Environment What levels are there? §Three primary “S’s” determine level of change § Continuation. Additional resources, new skills and unfamiliar tasks are not required § Routine. A small refinement on continuation. Additional resources may be required in the short term § Limited Change. Additional resources required, but it does not require any major organisational change. § Radical change. Involves major change within the organisation. Numerous changes in the organisation’s structure, systems, staff and management styles. BMBE/L 7/2017 § Organisational redirection. Major changes in terms of the industry in which the 26
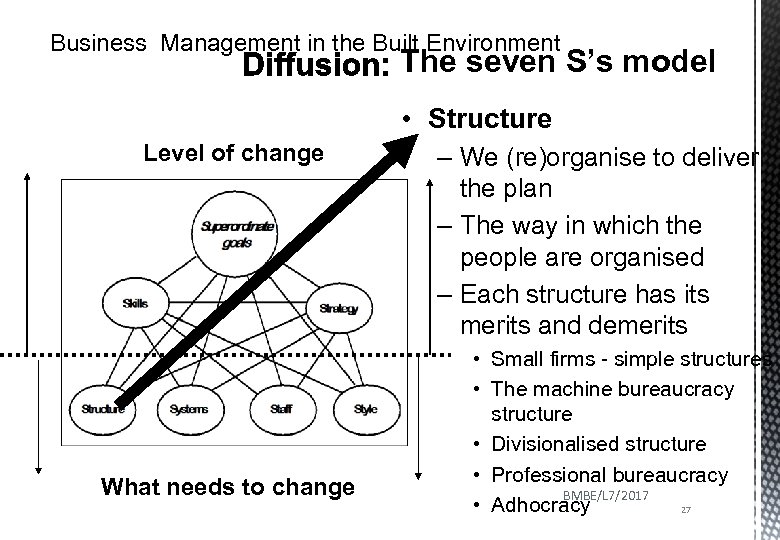
Business Management in the Built Environment The seven S’s model • Structure Level of change What needs to change – We (re)organise to deliver the plan – The way in which the people are organised – Each structure has its merits and demerits • Small firms - simple structures • The machine bureaucracy structure • Divisionalised structure • Professional bureaucracy BMBE/L 7/2017 • Adhocracy 27
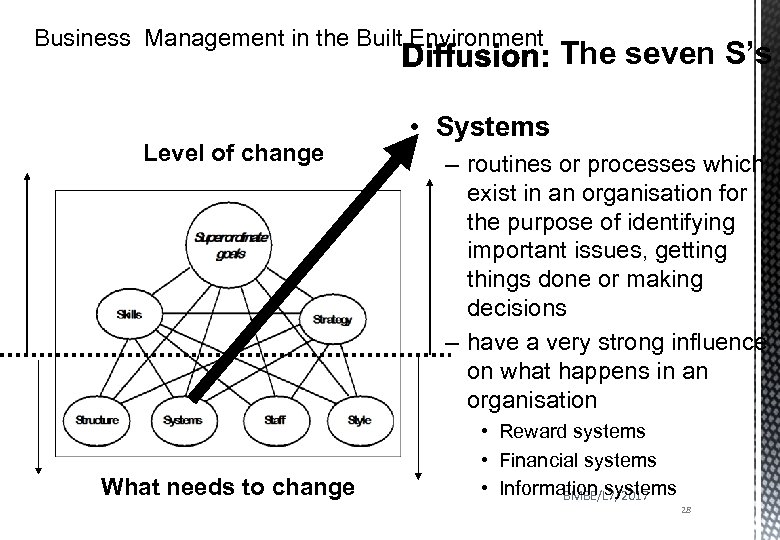
Business Management in the Built Environment Level of change What needs to change The seven S’s • Systems – routines or processes which exist in an organisation for the purpose of identifying important issues, getting things done or making decisions – have a very strong influence on what happens in an organisation • Reward systems • Financial systems • Information systems BMBE/L 7/2017 28
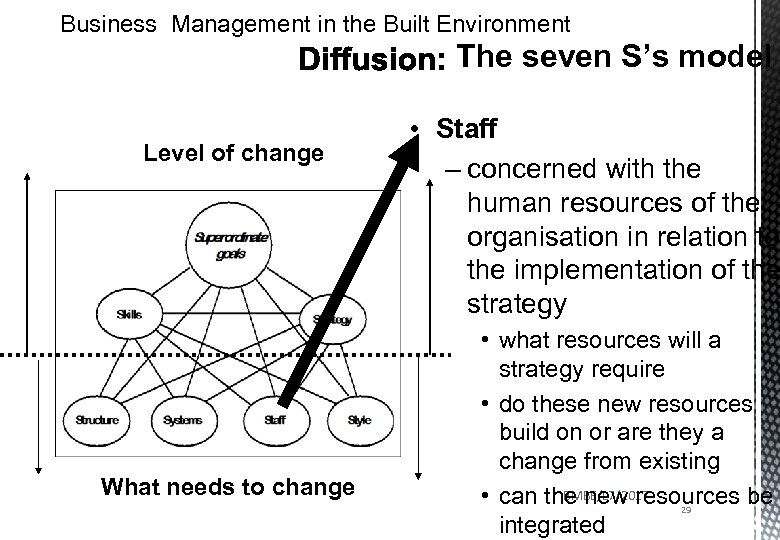
Business Management in the Built Environment The seven S’s model Level of change What needs to change • Staff – concerned with the human resources of the organisation in relation to the implementation of the strategy • what resources will a strategy require • do these new resources build on or are they a change from existing BMBE/L 7/2017 • can the new resources be 29 integrated
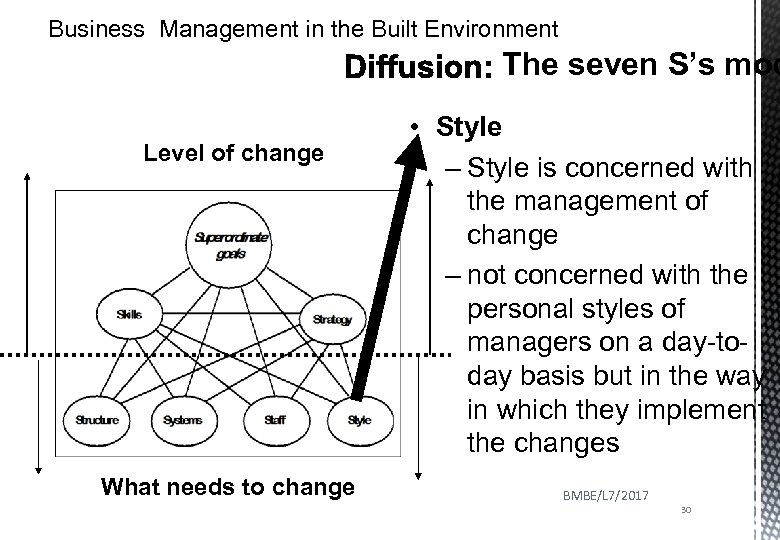
Business Management in the Built Environment The seven S’s mod Level of change What needs to change • Style – Style is concerned with the management of change – not concerned with the personal styles of managers on a day-today basis but in the way in which they implement the changes BMBE/L 7/2017 30
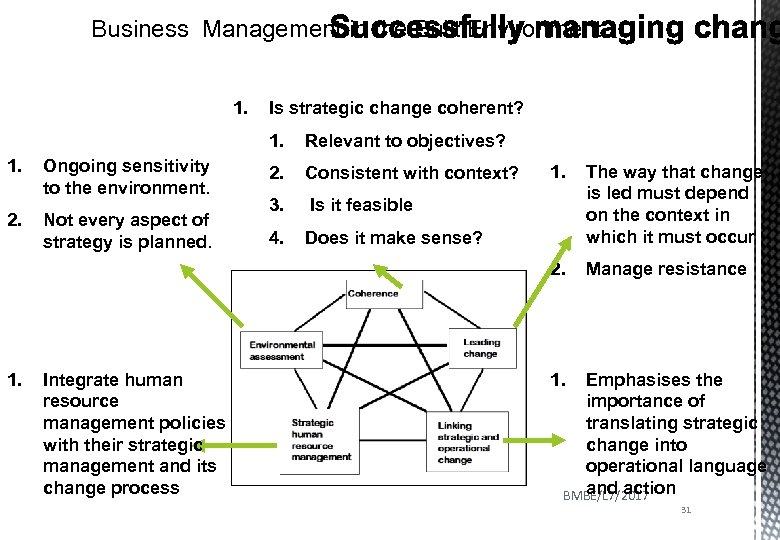
Business Management in the Built Environment 1. Is strategic change coherent? 1. 1. Relevant to objectives? Ongoing sensitivity to the environment. 2. Consistent with context? Not every aspect of strategy is planned. 3. Is it feasible 4. Does it make sense? 1. Integrate human resource management policies with their strategic management and its change process The way that change is led must depend on the context in which it must occur 2. 1. Manage resistance 1. Emphasises the importance of translating strategic change into operational language and action BMBE/L 7/2017 31

Business Management in the Built Environment Question for thought: In the context of a built environment organisation, critically examine and discuss typical problems encountered when implementing a strategy and how these could be addressed. BMBE/L 7/2017 32

Business Management in the Built Environment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cole, G. A. (1997) Strategic Management, Continuum, London Woolridge, B. , Floyd, S. W. (1990) Bridging the gap between strategy and operations: the implications of middle management involvement in strategy, The Annual International Conference of the Strategic Management Society Proceedings, Stockholm. Al-Ghamdi, S. M. (1998) Obstacles to successful implementation of strategic decisions: the British experience, European Business Review, 98(6) 322 -327 Aaltonen, P. , Ivävalko, H. (2002) Implementing strategies successfully, Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 13(6), 415 -418 Pettigrew, A. M. (1987). "Context and action in the transformation of the firm. " Journal of Management Studies, 24, 649 -670. BMBE/L 7/2017 33
9f349ec4e8227fdf5e303e88b73c38a8.ppt