sem_1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING AN INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING AS A BUSINESS MANAGEMENT TOOL THEME 1

LEARNING OBJECTIVES - The nature of business and accounting. Financial and management accounting. - Definition, functions and role of environmental accounting. - Functions and role of environmental accounting. The scope of environment accounting. - Basic dimensions of environmental accounting. - Structural elements of environmental accounting. - Forms of environmental accounting.

THE NATURE OF BUSINESS AND ACCOUNTING A business is an organization in which basic resources (inputs), such as materials and labor, are assembled and processed to provide goods and services (outputs) to customers. The objective of most businesses is to earn a profit. Profit is the difference between the amounts received from customers for goods or services and the amounts paid for the inputs used to provide the goods or services.

THE NATURE OF BUSINESS AND ACCOUNTING Three types of businesses : Service business: provide services • Wizz Air – transportation services • The Walt Disney Company (entertainment services) Merchandising business: sell products they purchase from other businesses to customers. • Wall-Mart (general merchandise) • Amazon. com (Internet books, music, video) Manufacturing businesses: change basic inputs into products that are sold to customers. • Ford Motor Co. (cars, trucks, vans) • Dell Inc. (personal computers).

WHAT IS THE ROLE OF ACCOUNTING IN BUSINESS? Do you think Google has been a successful company? Does it make money?

MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING (FA) (MA) AND FINANCIAL Financial Accounting is mainly designed to satisfy the information needs of external stakeholders, such as investors, tax authorities and creditors, all of whom have a strong interest in receiving accurate, standardized information about an organization’s financial performance. FA focuses on several types of financial information. An organization’s financial statements provide information on annual revenues and expenditures in an Income Statement (which also may be known as an Income & Expenditure Account or a Profit & Loss Account). The Balance Sheet reports assets, liabilities and equity at a specified date. In addition, the financial statements include a Cash Flow Statement. Thus, FA activities include data collection, account balancing, auditing of the financial statements and external reporting.

MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING (FA) (MA) AND FINANCIAL Management Accounting primarily focuses on satisfying the information needs of internal management. Although there accepted good practices in the realm of MA, these practices are generally not regulated by law. Each organization can determine which MA practices and information are best suited to its organizational goals and culture. MA focuses on both monetary and non-monetary information (for example, cost drivers such as labor hours and quantities of raw materials purchased) that inform management decisions and activities such as planning and budgeting, ensuring efficient use of resources, performance measurement and formulation of business policy and strategy. The collective goal of all this is to create, protect and increase value for an organization’s stakeholders. Thus, MA activities include data collection as well as routine and more strategic analysis of the data via various techniques (such as capital investment appraisal) designed to address specific management needs.
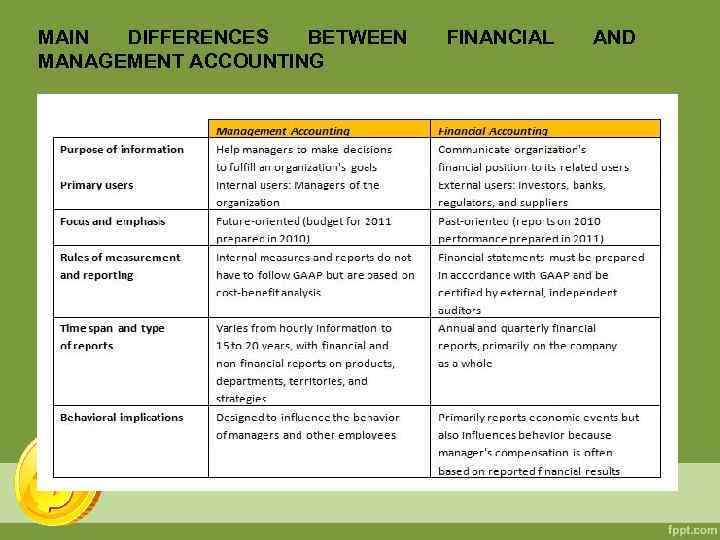
MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING FINANCIAL AND

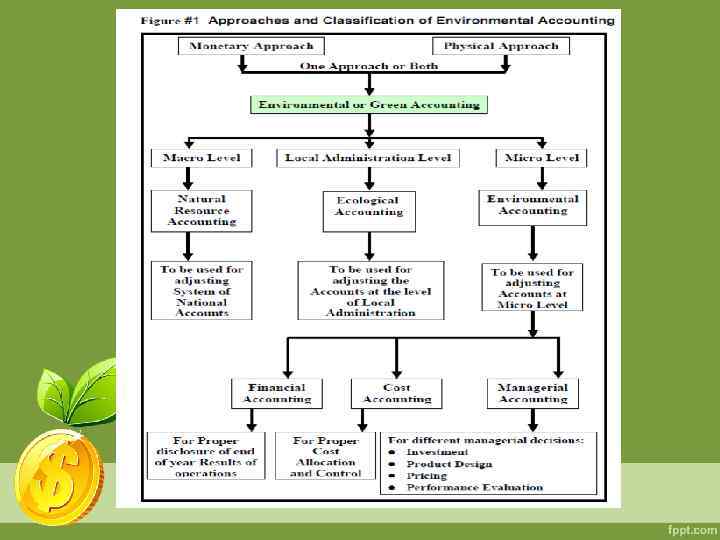
GREEN ACCOUNTING = ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING Green Accounting is a general term where it may mean Environmental, Ecological or Natural Resource Accounting. Needless to say that Environmental Accounting is also a general term which may mean the integration of environmental dimension into the macro or micro level despite that it is more applicable to the latter level. However, the four main terms mentioned overlap with each other.

GREEN ACCOUNTING = ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING Environmental Accounting At micro level it means the entire domain of accounting for the environment including: financial accounting, reporting and auditing, and environmental management accounting. Environmental Financial Accounting aims to the true disclosure in the financial statements in the end of period. That is, include environmental dimension in the published sheets of operations. Environmental Management Accounting means the management of environmental and economic performance through the development and implementation of appropriate environment related accounting systems and practices. While this may include reporting and auditing in some companies, environmental management accounting typically involves life-cycle costing, benefits assessment, and strategic planning for environmental management.

GREEN ACCOUNTING = ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING Environmental Cost Accounting deals with environmental costs in order to reach the full cost accounting. i. e. the identification, evaluation, and allocation of conventional costs, environmental costs, and social costs to processes, products, activities, or budgets. According to the polluter pays principle (PPP)(2) each polluter has to pay for the costs for dealing with the pollution resulting from his operation. Failure to bear these costs by the polluter will mean that some other party (a third party) will have to shoulder them - external environmental costs.

GREEN ACCOUNTING = ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING Environmental costs are expenditures incurred to prevent, contain, or remove environmental contamination. Environmental costs are often hard to define from a business stand point. In the past 10 years they are more likely to be qualified as a subset of the costs of operating a business. When substances are released into the air, water or land, the resulting pollution used to be considered a social cost, an externality. The term environmental cost has at least two major dimensions: (1) It can refer solely to costs that directly impact "private costs"; (2) It also can include the costs to individuals, society, and the environment for which a company is not accountable "social costs".

GREEN ACCOUNTING = ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING Ecological Accounting In many cases, the term Ecological Accounting is used to refer to the preparation of accounts according to physical data only. In addition, Ecological accounting is the type of Environmental Accounting. In this respect, Ecological accounting is mainly used to prepare an asset management plans at local administration level. Such plans provide a tool to evaluate the condition and life cycle of any particular physical asset. Natural Resource Accounting The term natural resource accounting is called after inclusion of environmental aspects into the system of national accounts(1). Where emphasis is given to natural assets, deterioration in its quality… in order to get an environmentally adjusted economic indicators such as environmental gross national Income.

ORGANIZATION, GEOGRAPHIC AND GEOPOLITICAL LEVELS At the organization level, EA takes place in the context of both management accounting (assessment of an organization’s expenditures on pollution control equipment; revenues from recycled materials; annual monetary savings from new energy-efficient equipment) and financial accounting (evaluation and reporting of the organization’s current environment-related liabilities). At the geographic and geopolitical levels, EA information is collected, typically by government, to assess the health of a particular ecosystem (such as a watershed), a particular political entity (such as a nation) or even the entire world.
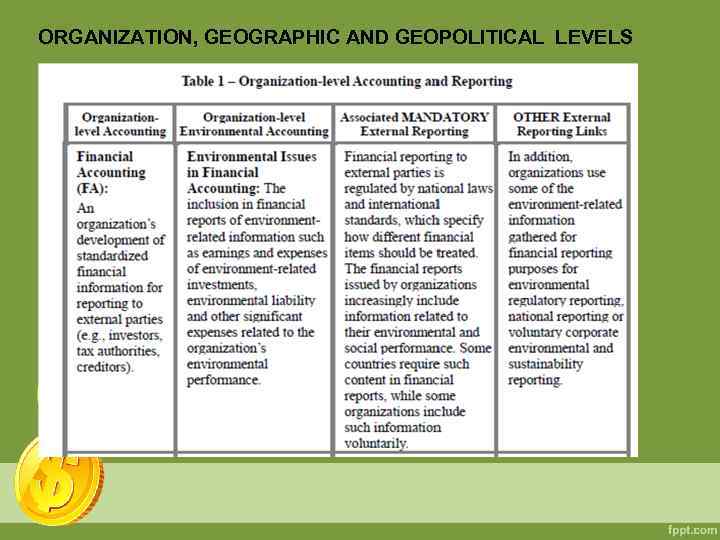
ORGANIZATION, GEOGRAPHIC AND GEOPOLITICAL LEVELS
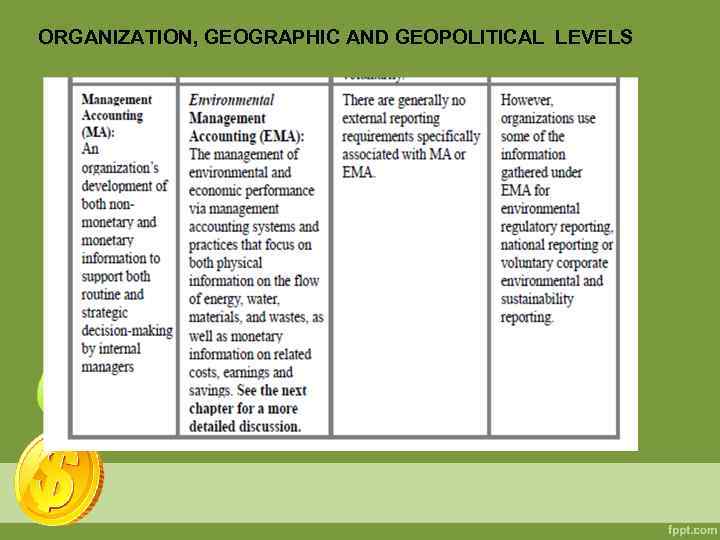
ORGANIZATION, GEOGRAPHIC AND GEOPOLITICAL LEVELS
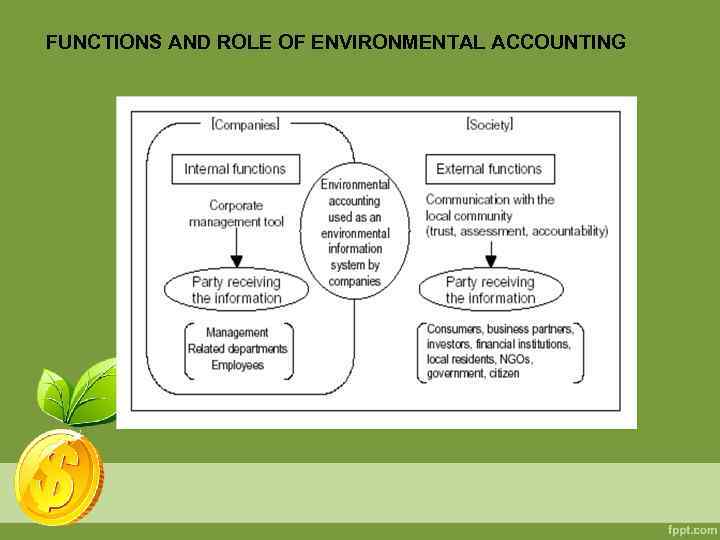
FUNCTIONS AND ROLE OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING

BASIC DIMENSIONS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING (1) Relevance (2) Reliability a. Faithful Representation b. Substance Over Form c. Neutrality d. Completeness e. Prudence (3) Understandability (4) Comparability (5) Verifiability

SCOPE OF ENVIRONMENT ACCOUNTING 1. From Internal point of view investment made by the corporate sector for minimization of losses to environment. It includes investment made into the environment saving equipment devices. This type of accounting is easy as money measurement is possible. 2. From external point of view all types of loss are indirectly due to business operation/activities. It mainly includes:

a. Degradation and destruction like soil erosion, loss of bio diversity, air pollution, water pollution, voice pollution, problem of solid waste, coastal & marine pollution. b. Depletion of nonrenewable natural resources i. e. loss emerged due to over exploitation of nonrenewable natural resources like minerals, water, gas, etc. c. Deforestation and Land uses. This type of accounting is not easy, as losses to environment cannot be measured exactly in monetary value. Further, it is very hard to decide that how much loss was occurred to the environment due to a particular industry. For this purpose approx. idea can be given or other measurement of loss like quantity of non-renewable natural re-sources used, how much Sq. meter area deforested and total area used for business purpose including residential quarters area for employees etc. , how much solid waste produced by the factory, how much wasteful air pass through chimney in air and what types of elements are included in a standard quantity of wasteful air, type and degree of noise made by the factory, etc. can be used.
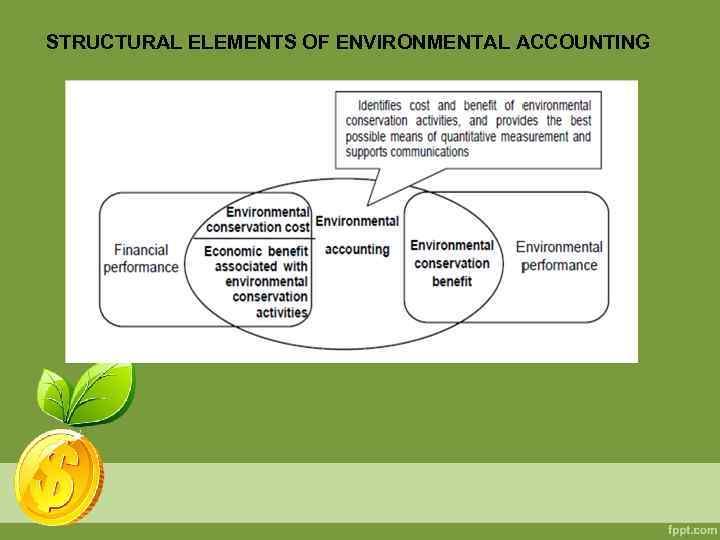
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING
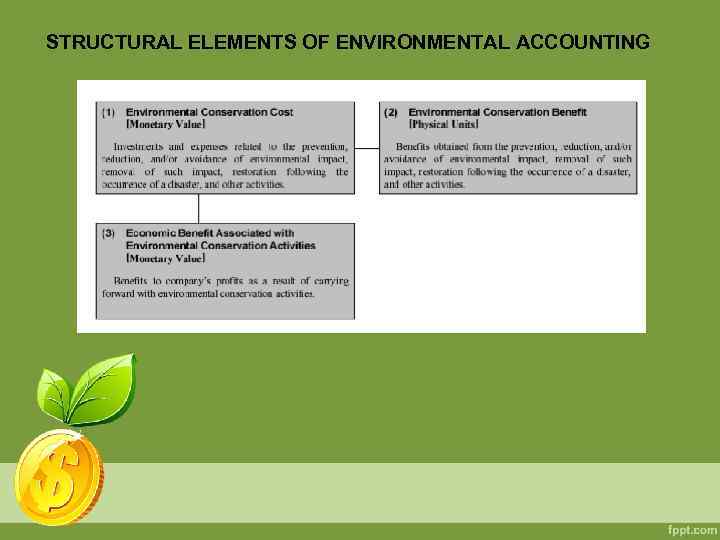
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING

STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING The quantitative and qualitative information for each component factor

FORMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING 1. Environmental Management Accounting (EMA): Management accounting with a particular focus on material and energy flow information and environmental cost information. This type of accounting can be further classified in the following subsystems: a) Segment Environmental Accounting: This is an internal environmental accounting tool to select an investment activity, or a project, related to environmental conservation from among all processes of operations, and to evaluate environmental effects for a certain period. b) Eco Balance Environmental Accounting: This is an internal environmental accounting tool to support PDCA for sustainable environmental management activities. c) Corporate Environmental Accounting: This is a tool to inform the public of relevant information compiled in accordance with the Environmental Accounting. It should be called as Corporate Environmental Reporting. For this purpose the cost and effect (in quantity and monetary value) of its environmental conservation activities are used

FORMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING 2. Environmental Financial Accounting (EFA): Financial Accounting with a particular focus on reporting environmental liability costs and other significant environmental costs. 3. Environmental National Accounting (ENA): National Level Accounting with a particular focus on natural resources stocks & flows, environmental costs & externality costs etc.

LIMITATIONS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING EA suffers from various serious limitations as follows: 1. There is no standard accounting method. 2. Comparison between two firms or countries is not possible if method of accounting is different which is quite obvious 3. Input for EA is not easily available because costs and benefits relevant to the environment are not easily measurable. 4. Many business and the Government organizations even large and well managed ones don’t adequately track the use of energy and material or the cost of inefficient materials use, waste management and related issue. Many organizations, therefore, significantly underestimate the cost of poor environment performance to their organization.

LIMITATIONS OF ENVIRONMENTAL ACCOUNTING 5. It mainly considers the cost internal to the company and excludes cost to society. 6. EA is a long-term process. Therefore, to draw a conclusion with help of it is not easy. 7. EA cannot work independently. It should be integrated with the financial accounting, which is not easy. 8. EA must be analyzed along with other aspects of accounting. Because costs and benefits related to the environment itself depend upon the results of the financial accounting, management accounting, cost accounting, tax accounting, national accounting, etc. 9. The user of information contained in the EA needs adequate knowledge of the process of EA as well as rules and regulations prevailing in that country either directly or indirectly related to environmental aspects.

HOME TASK Questions 1. Describe the purpose of environmental accounting and explain its role in business and society. 2. What is a place of environmental accounting within the financial and management accounting? 3. Who are the primary users of environmental accounting information? 4. Why should organizations (or accountants) care about environmental issues? 5. Why Do Environmental Accounting? 6. Describe approaches and classification of environmental accounting. 7. What are environmental issues in financial and management accounting? 8. What are main functions of the EA? 9. What are structural elements of the EA? 10. What are forms of the environmental accounting?

THANK YOU!
sem_1.ppt