3d3b6df8cf4bd59d38c5a569e7289e40.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

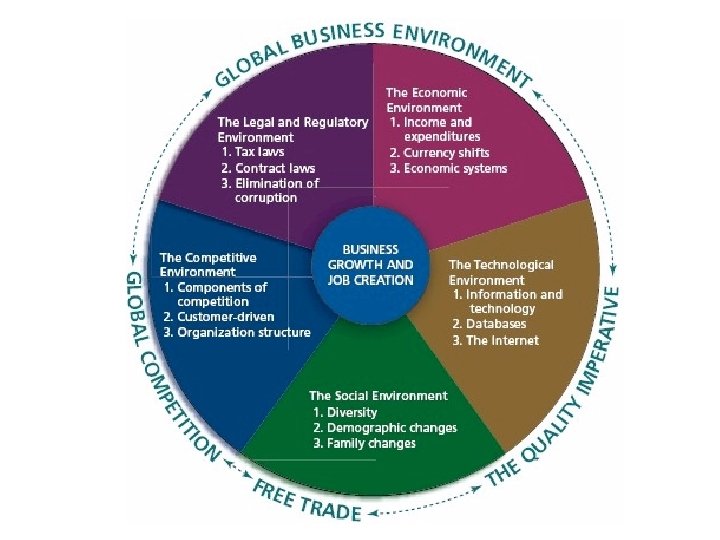
Business Environment The business environment consists of the surrounding factors that either help or hinder the development of businesses. © 2010 Mc. Graw-Hill Ryerson Limited Slides by Professor Tim Richardson of the School of Marketing and e. Business, Seneca College and the Dept. of Management, University of Toronto (UTSC)
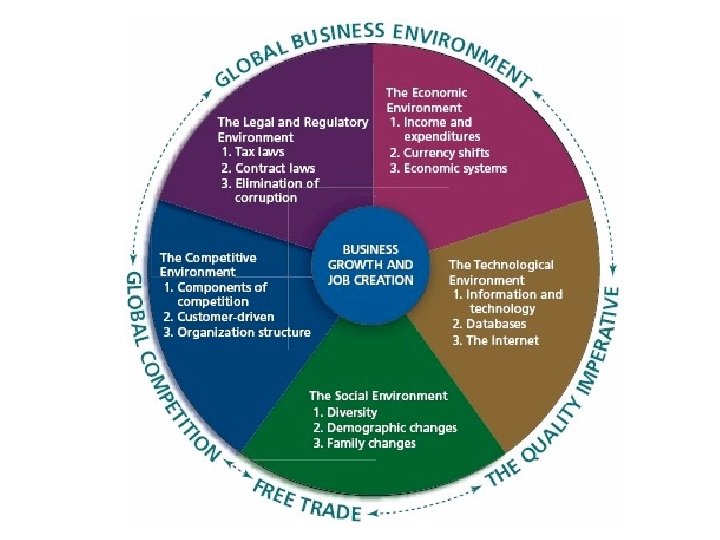

Legal and Regulatory Environment People are willing to start new businesses if they believe that the risk of losing their money isn’t too great. Part of that decision is affected by how governments work with businesses. • Freedom of ownership • Contract laws • Elimination of corruption Chapter 1 Slide 3

Legal and Regulatory Environment • Governments can do a lot to lessen the risk of starting and running a business through laws • examples of laws include the Canada Small Business Financing Act, the Consumer Packaging and Labelling Act, and the Trade Unions Act. Chapter 1 Slide 4

Economic Environment • The economic environment looks at income, expenditures, and resources that affect the cost of running a business. • Businesses review the results of major economic indicators such as consumer spending, employment levels, and productivity. • • Tradable currency Minimum taxes and regulation Imports and exports Employment levels and productivity Chapter 1 Slide 5

Economic Environment • The movement of a country’s currency relative to other currencies also pertains to this environment. • Currency movements are especially critical for countries, such as Canada, that generate a great deal of business activity from exports. Chapter 1 Slide 6
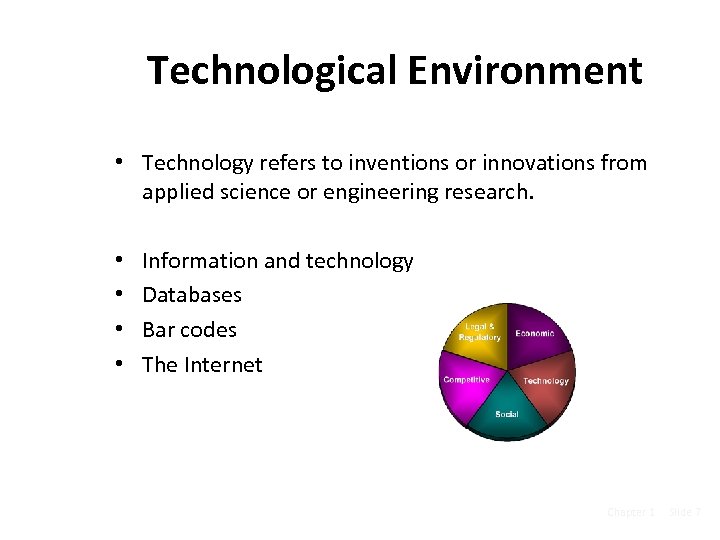
Technological Environment • Technology refers to inventions or innovations from applied science or engineering research. • • Information and technology Databases Bar codes The Internet Chapter 1 Slide 7

Technological Environment The use and application of technology affects productivity. Productivity is the amount of output you generate given the amount of input. – The more you can produce in any given period of time, the more money you are worth to companies. Chapter 1 Slide 8

Technological Environment Productivity • Effectiveness means producing the desired result. • Efficiency means producing goods and services using the least amount of resources. Chapter 1 Slide 9

Technological Environment E-commerce • There are two major types of e-commerce transactions: – business-to-consumer (B 2 C) – business-to-business (B 2 B) Chapter 1 Slide 10

Technological Environment E-commerce • B 2 G means the business that companies do with government agencies and departments to supply goods and services. • G 2 C refers to the business that government does online with people, such as renewing licences or applying for permits. Chapter 1 Slide 11

Technological Environment E-Business refers to a wide range of business activities on the web from simple posting of product photos to B 2 B marketplaces. E-commerce refers to the websites that allow transactions so that customers can buy products online. Generally speaking e-commerce is considered a subset of e-business. Chapter 1 Slide 12

Technological Environment Identity Theft • obtaining personal information about a person, such as a social insurance number and/or credit card number, and using that information for illegal purposes, such as buying things with them. See www. witiger. com/ecommerce/identitytheft. htm Chapter 1 Slide 13

Competitive Environment • All the environments are important, but the degree to which you need to deal with them depends on whether you do or do not have competition. • Customer service • Stakeholder recognition • Employee service • Concern for the environment Chapter 1 Slide 14

Competitive Environment • Competing by giving employees decisionmaking authority: empowerment. • To meet the needs of customers, firms must give their front-line workers (office clerks, front-desk clerks at hotels, salespeople, etc. ) the responsibility, authority, freedom, training, and equipment they need to respond quickly to customer requests and to make other decisions essential to producing quality goods and providing good service. Chapter 1 Slide 15

Competitive Strategies • Exceed customer expectations – Business is becoming customer-driven • Deliver faster (speed) – Service, new product introduction • Restructuring and empowerment – Responsibility, authority, autonomy, training, and equipment to front line • Concern for environment

Social Environment We’re particularly interested in the demographic trends that most affect businesses and career choices. • Demography: the statistical study of the human population with regard to its size, density, and other characteristics such as age, race, gender, and income. • Diversity • Demographic changes • Family Chapter 1 Slide 17

Social Environment The Aging Population More people are living longer due to: • better medical knowledge and technology • better health habits, including: – proper nutrition – more exercise – a reduction in the number of people who smoke Chapter 1 Slide 18

Social Environment Managing Diversity • Canada has a strong multicultural population. • Since the 1980 s, it has welcomed 5. 1 million immigrants. • Between 2001 and 2006 alone, 1. 4 million newcomers. Chapter 1 Slide 19
3d3b6df8cf4bd59d38c5a569e7289e40.ppt