B.Eng1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 200

Business English Lessons 1: adam Shuaibu

Course outline Greetings and Introductions Words of Appreciation

Introducing yourself and other people ¡ What are they doing? Introductions and greetings ¡ How are they doing? shake hands, smile, make eyecontact, bend body, exchange business card ¡ What are they saying? Glad to meet you

Greetings in English Speaker A: --- Hi ! (greeting) My name is/ I am Anna. ( presenting one’s name) Nice to meet you. (showing willingness for the meeting) Speaker B: ---Nice to meet you, too! (responding with showing happiness) My name is/ I am Lena. ( presenting one’s name )

Ways to greet each other Hello, …/ Hi, … Good morning! (afternoon, evening) How do you do? /How are you? Good/Nice/Glad/Pleased to see/meet you! What a pleasant surprise! How are you? - Fine, thanks. And you? How have you been? - Very well. And you?

Responses to greetings Fine, thank you. And you? Very well, thanks. And you? Not too bad, thanks. All right, thanks. Same as usual. Not very well,I’m afraid. Can’t complain.

Introducing oneself May I introduce myself? My name’s…. . Let me introduce myself. My name’s …. I’d like to introduce myself. I’m …. I don’t think we’ve met. I’m ….

Introducing someone else May I introduce…. . ? This is …. Have you met … ? I’d like you to meet …. I want you to meet ….
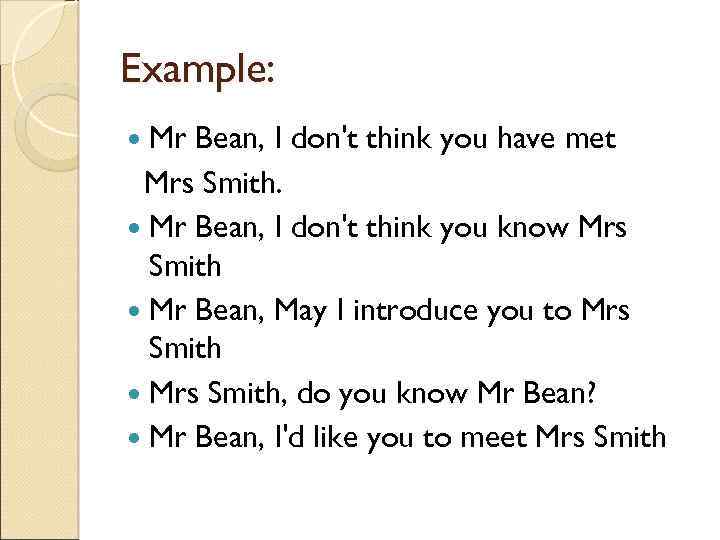
Example: Mr Bean, I don't think you have met Mrs Smith. Mr Bean, I don't think you know Mrs Smith Mr Bean, May I introduce you to Mrs Smith, do you know Mr Bean? Mr Bean, I'd like you to meet Mrs Smith

Words of Appreciation Thanks. Thank you. Thanks a lot. Thank you very much indeed. It was very kind of you. I appreciate your help. You’ve been very helpful.

Thanking someone who tries to help Thanks anyway. Thank you for (looking). Thanks for (trying). It doesn’t matter. Thanks. Never mind. Thanks

Responding to thanks ◦ You’re welcome. (US) ◦ Not at all. (formal, UK) ◦ Don’t mention it. ◦ (It’s) my pleasure. ◦ It was nothing. ◦ That’s alright/OK. ◦ No problem. ◦ Any time.

Good-byes Good bye/ Bye/ I’ll say good bye/ See you later/ See you soon. I must/(have to) go now. I (really) must be going. I’m afraid I’ve got to go. It’s getting (very/ rather) late. They’re calling my flight. I’ve got some things to prepare for …. I want to get away before the traffic gets too bad. I’ve enjoyed talking to you. It’s been (most) interesting talking to you. It’s been a very useful meeting/ nice afternoon. Thanks for everything. Thank you for (all) your help. Thank you for coming.

Have a good/ safe trip/ flight. - Thank you … (same to you). Have a good weekend. - Same to you. Enjoy the rest of your stay. - Same to you. It was nice meeting you. - I really enjoyed meeting you, too. I hope to see you again. - I hope so, too. See you on the 13 th. - See you. I look forward to our next meeting. I look forward to seeing you again. I look forward to seeing you when you’re next in Moscow.

Making contact Mind if I join you? Excuse me, you must be …. Excuse me, have we met? I really enjoyed your talk this morning. Are you giving a talk? Excuse me, are you Mrs … ? - Yes, that’s right. Hello, you must be Mrs …. You are Mrs …, aren’t you?

Keeping the conversation going What do you do, by the way? What do you do for a living? What line of business are you in? How are you enjoying the conference? Do you know many people here? Where are you from? Do you often travel to ……? Have you been here before? Is this your first visit to ……? How long are you going to stay? Can I get you a drink? So, where are you staying?

Where do you work? I work at…(name of the Company): KFC I work for… (company/famous person): Mr. … I work in…(place): in an office, school, factory I work in…(city/country): in Moscow, in France I work in…(department/general area): in sales, human resources/finance, consulting, etc. I work with…(computers, children, etc) I’m responsible for…

If there are people who are different in ages, sex, positions and etc, you Introduce the visited one to the visiting one first. Introduce the junior positioned one to the senior one first. Introduce the younger one to the elder one first. Introduce the male to the female first. After conducting introduction, the introducer usually should find an excuse as to leave the new acquaintances to chat.

Getting away If you’ll excuse me, I have to make a phone call. If you’ll excuse me, I must just go and say hello to someone. Would you excuse me a moment? I’ll be right back.

Practice with partners as you are at a business meeting, where you are strangers to each other.

Task 1: Situation one: Suppose you are Mrs Anna from England. You have never been to ABC conference before. Introduce yourself formally to the receptionist. Situation two: Suppose you are Mrs Lena from Chicago. You came to the annual conference of ABC Company last year and met many friends at this year’s meeting. Greet the receptionist.

Task 2 Situation : Introduce Ms/Mr Smith to your sales manager, Ms/Mr Richards who is from Sydney. Ms/Mr Smith is from Hong. Kong and works for the Shanghai Bank.

Steps: greeting---responding to greeting--introducing other people---giving information about other people---the other two introducing each other

Invitations. I was wondering if you would like to join us for a meal. Perhaps you would like to have dinner at my home. Perhaps you would like to come round for a meal. We wanted to invite you to dinner. I thought you might like to try some of our local cuisine. There’s a really nice place just a few minutes from here/ round the corner/ down the road. There’s a pretty good place you might like which specializes in fish. There’s a great new place with a fantastic view of the city.

Accepting That’s very kind of you. Thank you for inviting me. I’d like that very much. I’d be delighted to come. Thank you. That’d be very nice. I’ll look forward to it. Yes, please. Thanks. That’s/ What a good idea. That sounds good/ fun.

Setting the details What time should I come? Where shall we meet? Shall I pick you up? What time/ Where shall I pick you up? Shall we meet at half past seven? Say at half past seven.

Declining Thank you very much, but I’m afraid I can’t come. That’s very kind of you, : Unfortunately, I have arranged something else. but I won’t be here tomorrow. unfortunately I’m busy on Tuesday. Thanks, but I won’t be able to make it then.

LESSON 2 Telephoning and Voice message

Telephone conversation. Introducing yourself Good morning, Anna. (How can I help you? ) Hello, the ABC company. Anna Vladmirovna speaking. (What can I do for you? ) Hello, this is … from …. Hello, my name’s …. I’m calling from ….

Asking for the caller’s name Who’s calling, please? Can I have your name, please?

Saying who you want Can I have the accounts department? I’d like to speak to …. Could I speak to …, please? Is … there, please? I’m calling about ….

Responding I’ll put you through/ connect you. Hold the line, please. I’m sorry he/ she is not available. I’m afraid he/ she’s busy at the moment. I’m afraid he/ she’s away/ not in at the moment/ in a meeting.

Reason for calling I’m calling/ringing to …. I’d like to …. I need some information about ….

Leaving and taking a message Can I leave a message? Can I take a message? Would you like to leave a message? Please tell him/ her …. Could you ask him/ her to call me? Could you tell him/ her I called?

Asking for repetition I’m sorry, but I didn’t catch your name/ your number. Sorry, I didn’t hear that. Could you repeat it, please? Could you say it again? I’m afraid I didn’t understand. Could you spell that, please? Could you speak up?

TELEPHONE NUMBERS 543 476 706 - five four three four seven six seven oh (zero) six 234 226 589 - two three four two (double two) six five eight nine

Important phrasal verbs call back/ ring back cut off get through speak up hang up hold on pick up put through

Leaving Voice message. Have you ever left a message on a voice mail in English? Are Do you able to receive messages? you know how to leave a message? What are things that you say when you leave a message?

Voice message steps Who is calling? Hello/good day Mr. …this is/I’m/my name is…. From…. (place of work) Why are you calling? I’m calling about/with regards to/in relations to…. . When can they call you back? . . You can call/reach me any day after 5 pm How can they reach you? . . . You can call/reach me at (802)555 -5555 Look forward to talking to you Bye.
![Business voicemail greetings Hi, you’ve reached [your name] of [your business]. I’m sorry that Business voicemail greetings Hi, you’ve reached [your name] of [your business]. I’m sorry that](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-40.jpg)
Business voicemail greetings Hi, you’ve reached [your name] of [your business]. I’m sorry that I’m not available to answer your call at the present time. Please leave your name, number and a quick message at the tone and I’ll forward your message to the appropriate person. Hi this is [your name], I’m either away from my desk or on the phone, please leave your name and number along with a short message and I’ll be sure to get back to you. Hello, you have reached the office of [your name]; I will be out of my office starting on [date] and will be returning on [date]. You can call me when I return or leave a brief message. If this is an emergency I can be reached on my cell, which is [your number].

LESSON 3 Business Meetings

Definition of meeting A meeting is a gathering of two or more people that has been convened for the purpose of achieving a common goal through verbal interaction, such as sharing information or reaching agreement. Meetings may occur face to face or virtually, as mediated by communications technology, such as a telephone conference call or a videoconference.

Meeting protocol The traditional greeting among British managers is a light but firm handshake accompanied by a polite greeting. In general, British people are more reserved than continental Europeans and you should refrain from physical contact apart from the initial handshake. Smiling, on the other hand, particularly at the initial stage of an encounter is considered an expression of positive intentions. Sometimes at the start of a meeting, with many attendees, the chairperson will arrange to go around the table, with each person introducing themselves, with their name and job title, and if external to the organisation, the company they represent.

Types of Meetings Ø Formal Meetings Statutory Meetings One-on-One Extraordinary General Meetings “EGM” Team Meeting Annual General Meetings “AGM” Ø Informal Informational Meeting

Informal Meetings An informal meeting is any meeting that isn't highly structured and doesn't have a specific length, scope or other rigid component such as minutes. If a small problem has arisen on a business project, it is often more efficient to address the issue right away with an informal meeting where only the affected personnel are involved. An informal meeting may also be preferred when there is no specific topic in mind, but brainstorming or discussion of broad matters is needed.

One-on-One This is a type of informal meeting where just two people meet. This may be to discuss business ideas or it may be between an off the record discussion between a manager and a staff member to discuss their experiences in the workplace, or any troubles they may be having which could affect their work.

Team Meeting: This is an informal meeting where a project team joins together to discuss their project and any issues which may be related to it. These meetings may be called suddenly if issues arise during the course of a project.

Informational Meeting This is a meeting where large groups of people join together to receive an instruction or piece of information from their manager. They may also receive news about the company via this type of meeting.

Formal Meetings A formal meeting is a pre-planned gathering of two or more people who have assembled for the purpose of achieving a common goal through verbal interaction. Formal meetings are characterised by their predetermined topics, a set of objectives and formal notices. These meetings are held at a specific time, at a defined place and according to an agreed agenda. Formal meetings are typically lead by a chairperson with the discussions and agreements recorded in a written form known as minutes. A formal meetings is also known as a board meeting, a committee meeting, a caucus meeting, a conclave, a congress, a council meeting, a stockholders meeting as summit meeting or a symposium.

Statutory meeting This is the first meeting of the shareholder’s of a company. It is a mandatory general meeting of the members of a company which is required to be held within certain prescribed period of time. Applicability to certain Companies: Every company limited by shares, and every company limited by guarantee and having a share capital. Private Companies are not required to hold any such meeting.

Time Limit for holding Statutory Meeting All companies that are required to hold Statutory Meeting, shall hold the meeting within a period of not less than 1 month nor more than 6 months from the date at which the company is entitled to commence business. Frequency of holding statutory meeting: Statutory meeting is held once in a lifetime of a company.

Statutory Report: Board of directors to forward it at least 21 days before the meeting. Every member should receive the copy. Notice of meeting to clearly indicate the word “statutory meeting”. Matters/Agendas at the statutory meeting: Generally, the agenda of a statutory meeting is only to consider and adopt the Statutory Report, but the members of the company present at the meeting shall be at liberty to discuss any matter relating to the formation of the company or arising out of the statutory report, whether previous notice has been given or not.

Contents of the report Total shares allotted Cash received Abstract of the receipts and payments Directors and auditors Contracts Underwriting contract Arrears of calls Commission and brokerage
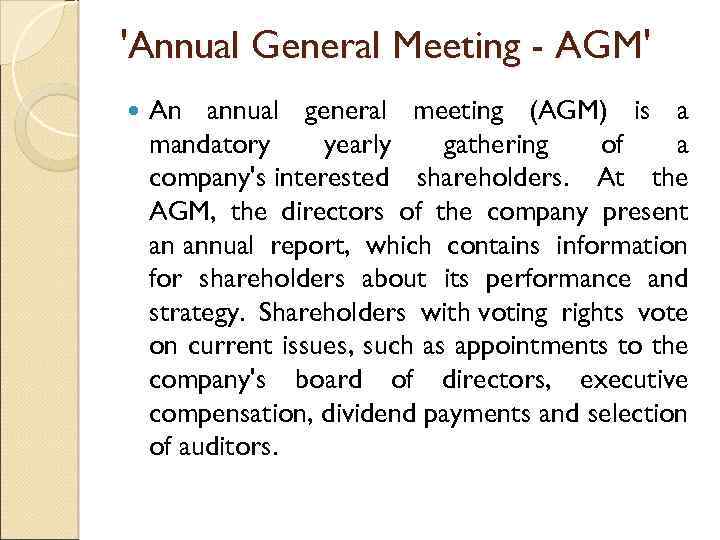
'Annual General Meeting - AGM' An annual general meeting (AGM) is a mandatory yearly gathering of a company's interested shareholders. At the AGM, the directors of the company present an annual report, which contains information for shareholders about its performance and strategy. Shareholders with voting rights vote on current issues, such as appointments to the company's board of directors, executive compensation, dividend payments and selection of auditors.

Mandatory Agenda The corporate laws that govern the company, along with its memorandum and articles of association, contain the rules governing the AGM. For example, there are provisions detailing how far in advance shareholders must be notified of where and when the AGM will be held and how to vote by proxy. In most jurisdictions, the following items, by law, must be discussed at the AGM: Minutes of previous meeting: The minutes of the previous year's AGM must be presented and approved. Financial statements: The company presents its annual financial statements to its shareholders for approval. Ratification of director's actions: The shareholders approve and ratify (or not) the decisions made by the board of directors over the previous year. This often includes the payment of a dividend. Election of the board of directors: The shareholders elect the board of directors for the upcoming year.

Extraordinary General Meeting “EGM” An extraordinary general meeting, commonly abbreviated as EGM, is a meeting of members of an organisation, shareholders of a company, or employees of an official body, which occurs at an irregular time. The term is usually used where the group would ordinarily hold an annual general meeting (AGM), but where an issue arises which requires the input of the entire membership and is too serious or urgent to wait until the next AGM. Members and/or shareholders must be informed of the purpose of the EGM so that they may attend in a position where they can discuss and exercise intelligent judgment, otherwise any resolutions passed are invalid.

Procedure: Before the EGM the board of the organisation will have agreed upon one or more resolutions that will be put to the shareholders or members for approval at the EGM. In some settings, this is known as a special general meeting or an emergency general meeting.

Meeting Notice When you need to give others a heads up about a meeting, a Notice of Meeting makes it official. A notice of meeting should contain enough information for the recipient to attend the meeting without consulting other references or documents. The notice of meeting may take the form of a memo, letter, email or in the case of a public notice, a poster.

Components of a Meeting Notice: A greeting and the formal invitation, tailored to the recipient The salient details, including date, time and place Directions to the location if it may be unfamiliar to the recipient Request for an RSVP (Répondez s'il vous plaît- meaning "Please respond") by a specific date Contact information

The Meeting Agenda The agenda is document that is circulated in advance to all prospective meeting participants and which serves the following purposes: Notice of meeting- The agenda serves as a notice of meeting if it is sent out to meeting participants in advance. List of items/topics - The agenda is a list of topics that will be discussed. The agenda enables participants to prepare in advance for the topics so that they can make a more valuable contribution. Prioritise meeting discussion - Topics that are of greatest importance should be placed first on the agenda. In this way the agenda prioritise meeting discussion time. Briefs meeting participants - If the agenda includes items with which are unfamiliar to the meeting’s participants, the agenda item should be followed by some brief information as to what the item is about. Limits discussion - The agenda helps the meeting chairperson to make best use of the time available. The agenda may have an amount of time stated for each item. Otherwise some topics may receive too much time and others too little.

Minutes of Meetings Minutes provide a record of what was said and decisions that were made in a previous meeting. The Minutes are an extremely important document and in the case of formal committee and board meetings, it is a legal requirement to keep minutes of meetings and generally the organisation's constitution will provide some instruction on this. In such circumstances, it is important for committee members to read minutes thoroughly and then confirm whether the minutes are a true record of what was said. Hence, in formal meetings, there is always an item on the agenda “Confirmation of minutes of previous meeting”.

The role of the Minutes is to: Provide an authoritative and permanent record of proceedings Provide formal evidence of decisions made and of expenditure and actions authorised Provide a record of policy decisions made Provide a starting point for action to be taken in the future Inform members not present at the meeting Assist the conduct of subsequent meetings If on reading the minutes, a member of the committee, disagrees with what was recorded in the minutes, then they should move to make an amendment. If the motion is agreed to by the majority of members present, the minutes may be altered.
Lesson 4: Chairing a Meeting

Opening the Meeting Good morning/afternoon, everyone. If we are all here, let's get started start the meeting start.

Welcoming and Introducing Participants Please join me in welcoming (name of participant) We're pleased to welcome (name of participant) It's a pleasure to welcome (name of participant) I'd like to introduce (name of participant) I don't think you've met (name of participant)

Stating the Principal Objectives of a Meeting We're here today to… Our aim is to. . . I've called this meeting in order to. . . By the end of this meeting, I'd like to have. . .

Giving Apologies for Someone Who is Absent I'm afraid. . , (name of participant) can't be with us today. She is in. . . I have received apologies for the absence of (name of participant), who is in (place).

Reading the Minutes (Notes) of the Last Meeting First let's go over the report from the last meeting, which was held on (date) Here are the minutes from our last meeting, which was on (date)

Dealing with Recent Developments Jack, can you tell us how the XYZ project is progressing? Jack, how is the XYZ project coming along? John, have you completed the report on the new accounting package? Has everyone received a copy of the Tate Foundation report on current marketing trends?

Moving Forward So, if there is nothing else we need to discuss, let's move on to today's agenda. Shall we get down to business? Is there any other business? If there are no further developments, I'd like to move on to today's topic.

Introducing the Agenda Have you all received a copy of the agenda? There are three items on the agenda. First, Shall we take the points in this order? If you don't mind, I'd like to go in order skip item 1 and move on to item 3 I suggest we take item 2 last.

Allocating Roles (secretary, participants) (name of participant) has agreed to take the minutes. (name of participant) has kindly agreed to give us a report on this matter. (name of participant) will lead point 1, (name of participant) point 2, and (name of participant) point 3. (name of participant), would you mind taking notes/minutes today?

Agreeing on the Ground Rules for the Meeting (contributions, timing, decision-making, etc. ) We will hear a short report on each point first, followed by a discussion round the table. I suggest we go round the table first. The meeting is due to finish at. . . We'll have to keep each item to ten minutes. Otherwise we'll never get through. We may need to vote on item 5, if we can't get a unanimous decision.

Introducing the First Item on the Agenda So, let's start with Shall we start with. . So, the first item on the agenda is Pete, would you like to kick off? Martin, would you like to introduce this item?

Closing an Item I think that covers the first item. Shall we leave that item? If nobody has anything else to add,

Next Item Let's move onto the next item The next item on the agenda is Now we come to the question of.

Giving Control to the Next Participant I'd like to hand over to Mark, who is going to lead the next point. Right, Dorothy, over to you.

Summarizing Before we close, let me just summarize the main points. To sum up, . . . In brief, Shall I go over the main points?

Finishing Up Right, it looks as though we've covered the main items Is there Any Other Business?

Suggesting and Agreeing on Time, Date and Place for the Next Meeting Can we fix the next meeting, please? So, the next meeting will be on. . . (day), the. . . (date) of. . . (month) at. . . What about the following Wednesday? How is that? So, see you all then.

Thanking Participants for Attending I'd like to thank Marianne and Jeremy for coming over from London. Thank you all for attending. Thanks for your participation.

Closing the Meeting The meeting is closed. I declare the meeting closed.

Meeting Terminology Agenda: The plan for a meeting, it lists the items to be discussed in the order in which they will be discussed. Amendment: Proposed modification to a motion which is not in conflict with the general thrust of that motion. If the amendment is adopted it becomes part of the original motion (now called ‘motion as amended’ or ‘substantive motion’) Apologies: Formal notifications of inability to attend a meeting Brainstorming: A technique used to gather ideas from a group, it involves the members of the group thinking of as many ideas as they can in a short period of time. Business Arising: Discussion on any matter recorded in the minutes of the previous meeting. Chair: The person who controls the conduct of the meeting, a sort of umpire. General Business: The body of the meeting where the main objectives of the meeting are discussed

Consensus: A type of group decision making. It involves coming to a decision acceptable to all members of the group without a vote being taken. Constitution: A document setting out the fundamental principles governing the running of an organisation. It normally includes such things as the goals of the organisation, membership requirements, rights and fees, meeting times, voting rights and standing orders for meetings. Minutes: The formal written record of a meeting. Copies are circulated to attendees and those who apologised (and sometimes to other interested parties), and formally confirmed at the next meeting as being a true record. Motion: A formal statement, usually involving some proposed action, put to a meeting for discussion and subsequent decision by vote. Mover: The proposer of a motion

Motion of Dissent: A formal statement involving some proposed action, put to a meeting for discussion and subsequent decision by vote. Other Business: An item on the agenda (usually the last) that provides an opportunity for those present to suggest additional matters for discussion. Point of Order: A formal complaint (to the chair person) at a meeting that a speaker is being irrelevant, unduly repetitive, exceeding prescribed time, speaking out of turn or in some way violating standing orders. Procedural motion: A motion aimed at changing the sequence or timing of events at a meeting, rather than one which addresses an agenda item. Quorum: Minimum number (or percentage of those invited) required to be at a meeting for it to proceed legitimately. Seconder: Someone who formally supports the mover of a motion Standing Orders: An organisation’s rules that govern how its meetings should be run.

Task: Call for meeting Organize a Formal Meeting to discuss: “The ways of improving sales in ABC Company”.

LESSON 5: Business Travel/Trip.

At the Airport (International/Domestic) Hello/ Hi! Good morning! Good afternoon! Good evening! Trolley? Check-in counter?

Check-in Counter Check-in Staff: Passport and ticket, please. You: Here you are. Check-in Staff: Can I see your hand luggage, please? You: I just have this bag and a laptop Check-in Staff: Thank you. Window or aisle? You: Window, please. Check-in Staff: Here's your boarding card. You: Thanks.

In the Transit Lounge You: Excuse me, where is gate 56? Airport Staff: That way. You: Thank you. Airport Staff: You're welcome

At the Boarding Gate Airline Staff: Can I see your passport and boarding card please? You: Sure. Here you are. Airline Staff: Thank you. Airline Staff: Ok, enjoy your flight. You: Thank you.

On the Plane Flight Attendant: What is your seat number? You: 35 -A. Flight Attendant: Down this way. You: Thank you.
![Instructions [Fasten your seat belt] Stewardess : Sir, your seat belt is unbuckled. Traveler Instructions [Fasten your seat belt] Stewardess : Sir, your seat belt is unbuckled. Traveler](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-93.jpg)
Instructions [Fasten your seat belt] Stewardess : Sir, your seat belt is unbuckled. Traveler : Pardon me? Stewardess : The plane is going to land [take off] soon. Please fasten your seat belt. Traveler : Oh, I see. I didn’t notice it.
![[Set your seat back] Stewardess : Excuse me, sir. Traveler : Yes? [What is [Set your seat back] Stewardess : Excuse me, sir. Traveler : Yes? [What is](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-94.jpg)
[Set your seat back] Stewardess : Excuse me, sir. Traveler : Yes? [What is it? ] Stewardess : Please return your seat and table in the upright position. [Please return your table to its original position. ] Traveler : Oh, I’m sorry.
![[Drinks] Stewardess : What would you like to drink? You : What do you [Drinks] Stewardess : What would you like to drink? You : What do you](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-95.jpg)
[Drinks] Stewardess : What would you like to drink? You : What do you have? Stewardess : (We have) Coke, Pepsi, seven-Up, orange juice. . . You : Orange juice, please.
![[Dinner] Stewardess : (Which would you like, ) Beef, chicken or fish? You : [Dinner] Stewardess : (Which would you like, ) Beef, chicken or fish? You :](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-96.jpg)
[Dinner] Stewardess : (Which would you like, ) Beef, chicken or fish? You : Beef, please. Stewardess : What kind of dressing would you like to have for your salad? You : I’ll have blue cheese.
![[Coffee or tea? ] Stewardess: Coffee or Tea? You: Is it green tea? Stewardess: [Coffee or tea? ] Stewardess: Coffee or Tea? You: Is it green tea? Stewardess:](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-97.jpg)
[Coffee or tea? ] Stewardess: Coffee or Tea? You: Is it green tea? Stewardess: No, it isn’t. But we have some green tea. Stewardess: Would you like some? You: Yes, please.

After the Meal Flight Attendant: Can I take your tray, sir? You: Thank you. Flight Attendant: Would you like another drink? You: A beer, please. Flight Attendant: Which one? You: That one. Flight Attendant: Here you are. You: Thanks very much.

Mid-flight Rest Flight Attendant: Pillow, sir? You: Sure. Thank you. Flight Attendant: Blanket? You: No, thanks.
![At the Immigration [May I see your passport? ] Officer : Hello. Traveler : At the Immigration [May I see your passport? ] Officer : Hello. Traveler :](https://present5.com/presentation/3029457_438654580/image-100.jpg)
At the Immigration [May I see your passport? ] Officer : Hello. Traveler : Hello. Officer : May I see your passport and immigration card? Traveler : (Yes. ) Here you are. [Period and purpose of the stay] Officer : What’s the purpose of your visit [trip] to…. ? Traveler : Work/Business. Officer : How long do you plan to stay (here) ? Traveler : Two weeks.

At Customs Officer: Passport, please. You: Here you are. Customs Officer: Do you have anything to declare? You: Yes/ No. Customs Officer: What is in this bag? You: Personal things/items. Customs Officer: Open it please. You: Sure.

At the baggage claim area - a damaged baggage Officer : Is there anything wrong? [How can we (I) help you? ] Traveler : Yes. My baggage [luggage] has been damaged. Officer : Sorry to hear that. Go to the baggage claim office, and they will help you. Traveler : Could you tell me where it is?

At the baggage claim area - a missing baggage Traveler : My baggage seems to be missing. [I can’t find my baggage. ][My baggage didn’t arrive. ] Officer : May I see your baggage claim tag? Traveler : Here it is. Officer : All right. What kind of suitcase is it?

Arriving at Your Destination Where is the currency exchange? Where is the bus stop? Where can I find a taxi/cab? I would like to go to _____. Do you know where this hotel is?

At the Hotel You: Hello, I have a reservation. Receptionist: What name, sir? You: Tanaka. Receptionist: Ok, here is your key. You: Thank you very much. ? ? How many beds are in the room? I would like one queen/king/double/single bed, please. What floor am I on? Where are the elevators? How do I access the Internet? Is there free breakfast? My room needs towels. My room is messy, and I would like it cleaned. How do I call for room service? How do I call down to the front desk?

A Wake-up call Traveler : Could you give me a wake-up call, please? [ I’d like to get a wake-up call, please ] Clerk : Sure. What time do you want it? Traveler : Seven fifteen, please. Clerk : OK. I’ll wake you up at 7: 15 tomorrow morning.

Check-out from the hotel Traveler : I’d like to check out. My room number is 205, and this is the room key. Clerk : There’s no extra charge listed, so that’ll be 152 dollars including tax. Traveler : (Paying the bill) I’ve enjoyed my stay here, thank you (for everything. ) Clerk : Thank you. Have a nice day [trip].

Keys Greetings and Introductions 1 a (i) How do you do? (Hello)! (ii) How are you? b (i) Excuse me, are you Mrs…. ? (We know the name) (ii) Sorry, I don’t know your name c(i) May I introduce myself? (Formal introduction) (ii) Hi, everybody. My name’s …. . (Informal) d (i) This is Mary. (Informal) (ii) Let me introduce you to Mary Higgins. (Formal) e (i) Goodbye. It’s been very interesting talking to you. (Formal) (ii) See you. I really had a good time. (Informal) f (i) I got to go now. (Informal) (ii) I’m afraid I must be going soon. (Formal)

2 a M = Martin, J = Jacqueline M Excuse me, are you Jacqueline Turner? J: Yes, that’s right. M: May I introduce myself? I’m Martin Young. How do you do? J: How do you do, Mr Young. b C = Chris, F = Frank C: Hello, Chris Evans. Mind if I join you? F: Oh, of course not. Frank Richards. C: Nice/ Pleased to meet you, Frank. So how are you finding the conference so far? F: Actually, I’ve only arrived this morning. C: All right. I … c L = Lin, D = Dan, P = Peter L: Dan! Good to see you again. How are things? D: Hello, Lin. Fine thanks. Pretty busy, as always, I suppose. Can I introduce you to a colleague of mine, Peter Winston? Peter, this is Lin Farrell. P: Nice to meet you, Ms Farrell. L: Nice to meet you, too. Please, call me Lin. P: Then you must call me Peter.

Socializing 1 a Hi, how are you? (i) Fine, thanks. And you? (iii) Not too bad. b Meet my friend Jack. (i) Nice to meet you. ((iii) How do you do? c How was your flight? (i) It was all right. (iii) The plane was a bit late but it didn’t matter. d Would you like to look around the company? (ii) That’d be lovely. (iii) Yes, I’d love to. e Would you prefer red or white wine? (iii) I don’t mind. f I’m terribly sorry about the delay. (i) Don’t worry about it. g Thank you very much. (ii) Don’t mention it. h My sister has had an accident. (ii) I’m sorry to hear that. Is she all right?

2 1 - j, 2 - i, 3 -g, 4 - c, 5 - f, 6 - d, 7 - a, 8 - h, 9 - e, 10 - b. 3 Mind if I join you? Please do. Are you giving a talk? No, I’m not. Actually, this is my first conference. So, what do you do? I work as a brand manager for Carsons.

What’s your line of business? Our company specialises in the production of lighting technologies. Can I get you a drink? That’d be nice, thank you. I’ll have a glass of white, please. So, where are you staying? In the Sheraton. Would you like me to get you anything from the buffet? Thank you. I’m fine. Do you know many people here? I’ve seen a couple of familiar faces. Is this your first visit to Denmark? Actually, I come here fairly often. My wife’s parents live here. Are you enjoying the conference? It’s been quite interesting so far. Will you excuse me a moment? Oh, of course. See you later.

Invitations 1 a. Why not come round for a drink? b. Would you like to join us for lunch? c. Fancy going out for a meal? d. I thought you would like to try some of our local cuisine. e. There’s a really nice place just round the corner. f. Shall we meet later to discuss it over dinner? g. What about going out for a meal? h. Why not join us for a drink? 2 Possible answers a. I was wondering if you would like to join us for a meal? b. Why not come round for a drink? c. I’d be delighted to come. d. That sounds fun. e. What time shall we meet and where? f. Say at nine. g. When shall I pick you up? h. Thank you very much, but I’m afraid I can’t come.

Telephoning? ? 1 a. If you don’t know his number, why don’t you look it up in the phone book/ directory? b. The phone’s ringing. Would somebody answer it, please? c. I called you a while ago, but your line was busy/ engaged. d. The telephone charge has been increased. e. I left her a message on the answerphone/ answering machine, but she didn’t call me back. f. Our telephone bill was enormous last month. I had to call abroad several times, so it is not a big surprise. g. I’m sorry, it’s a bad line. I can’t hear you very well. h. Sorry, you have the wrong number.

2 a. The phone’s ringing. ’ – ‘I’ll pick it up. ’ b. Sorry, I’ve got to go now. I’ll call/ ring you back later. c. Could I speak to Mr Barring, please? ’ – ‘I’ll put you through. ’ d. I tried to call you several times last night, but I couldn’t get through. There must have been something wrong with the lines. e. I was going to explain the details when suddenly we were cut off. f. Could you hold on for a moment. I’ll check the figures for you. g. Why don’t you look up his number in the directory? h. I was waiting for a couple of minutes but there was no answer, so I hung up. i. Could you put Harry on? I’d like to talk to him as well. j. Sorry, I can’t hear you very well. Could you speak up?

On the phone 1 a. I’ll put you through. 3 I’ll connect you. b. Who’s calling please? 5 Could I have your name? c. Anything else? 1 Is that all? d. The line’s busy. 6 The line’s engaged. f. Go ahead. (taking a note)2 I’m ready. g. Hold on. 7 One moment. h. This is … 4 … speaking

Lesson 6: Job Interview

The Entrance (Greeting) I= Interviewer I: Please, come in and take a seat. You: Thank you, Sir/Madam. I: Hello. What is your name? You: Good morning, Mr/Mrs/Ms/Professor Smith. My name is John Doe. (NB: first name first, last name last!) It’s a pleasure/ Nice/Pleased to meet you. I: How do you do? You: How do you do. My name is….

Questions about you Sample questions: • Tell us something about yourself. • How would you describe yourself? • Can you talk to us about yourself?

Sample answer: My name is Jane Smith. I come from Moscow, but I live/am currently living in Ukraine. I have conferred a BSc in Geology and hold an MSc degree in Physics. I am currently working towards a Ph. D in Geophysics. (I graduated in Geology from the University of Texas, in 2010) My qualifications also include knowledge of petrol research and 3 years’ experience in geological surveying. I am single/married//separated/ divorced. I have one/two/three…. children.

Question about your strengths Sample questions: • What are/would you consider to be your greatest strengths? • What would you say your strongest assets are? • What are your most positive aspects?

Include 3 -4 positive character traits trustworthy honest persistent determined tolerant open-minded adaptable flexible hard-working reliable friendly loyal

Include 3 -4 proficiency traits expert detail-oriented team-player problem-solver competent multi-tasker achiever initiator mediator quick-learner Leader efficient

Sample Answers I would say I am an honest, reliable, hardworking person. I also possess a positive outlook towards my profession and life in general. People say I am friendly and good at giving advice. I have very good leadership qualities, as well as organizational and time management skills, but my greatest strengths are my flexibility and ability to effectively handle multiple projects and meet deadlines.

Useful patterns I am… • I have/possess • My greatest strengths are/include… • I would (I’d) say I am…. • I would (I’d) define/describe/depict myself as…. • I consider myself to be…. • I think/believe I am… • People say I am….

Useful grammar I am honest. (adjective) • I am a good listener. (noun) • I have/possess good managerial skills. (noun) • I am good at multitasking. (-ing form noun) • I know how/am able to adapt to new work situations. (verb)

Questions about your weaknesses Sample questions: • What are your greatest/strongest weaknesses? • Which aspects or areas of yourself are you improving or would like to improve?

Sample Answers I am always working on improving my communications skills to be a more effective presenter. I recently joined Toastmasters which I find very helpful. I'm too detail oriented. I never want to leave anything out and I want everything to be perfect. This is bad because it slows down my work. Initially, I tried to work faster to compensate, but that only made me sloppy. So I decided to put more emphasis on priority and planning. By doing so, I'm hoping that I can make the proper decisions on what to work on and what to intentionally leave out.

Short term goals "What are your short term goals? "My short term goal is to find a position where I can use the knowledge and strengths that I have. I want to partake in the growth and success of the company I work for. "I've learned the basics of marketing during my first two years. I want to take the next step by taking on challenging projects. My short term goal is to grow as a marketing analyst. "As a program manager, it's important to understand all areas of the project. Although I have the technical abilities to be successful in my job, I want to learn different software applications that might help in work efficiency. "My goal is to always perform at an exceptional level. But a short term goal I have set for myself is to implement a process that increases work efficiency.

"What are your long term goals? "I would like to become a director or higher. This might be a little ambitious, but I know I'm smart, and I'm willing to work hard. "After a successful career, I would love to write a book on office efficiency. I think working smart is important and I have many ideas. So after gaining more experience, I'm going to try to write a book. "I've always loved to teach. I like to grow newer employees and help co-workers where ever I can. So in the future, I would love to be an instructor. "I want to become a valued employee of a company. I want to make a difference and I'm willing to work hard to achieve this goal. I don't want a regular career, I want a special career that I can be proud of.

Questions about hobbies/interests Sample questions: • What are your hobbies/interests? • Do you practice any sports? • What do your free/leisure time? • Do you belong to any clubs or associations? • Do you do any volunteer work?

Sample Answers Well, I really enjoy travelling because it gives me an opportunity to appreciate new cultures. In the evenings, I unwind by playing the piano. I am also keen on speed-walking and playing volleyball with friends. I’m a member of the Rotary Club International where I put forth my professional aptitudes to serve others. At weekends, I volunteer with the Save Child Society where I spend time with children.

Useful grammar Verbs to express: • interests: like, love, enjoy, be fond of, be passionate about, be keen on, be interested in, be active in • sports: practice/do/play • musical instruments: play Nouns to express activities: • -ing form: swimming, cycling, cooking…

Questions about the job you are applying for Sample questions: • Why are you interested in working here? • Why have you applied for this post? • What do you expect from this job?

Sample Answer It would be a privilege to work in a reputable company such as yours. When I read about the opening, I found that my skills and qualifications matched the requirements, and I could make use of the experience gained in the past 5 years. Furthermore, I believe your company will allow me to grow both professionally and as a person.

Question about hiring you Sample questions: • Why should we hire you? • Give us a good reason for taking you on. • Why do you think you are the best person/fit/candidate for this position?

Sample Answers I think I am a great match for this position. My degree in Maths coupled with 3 years of experience working in the field of computational analysis helped me to improve productivity by 30%. I believe I can do the same for your organization and would be a great addition to your team. • As I am a fresher, I have theoretical knowledge, but I can work hard and learn the practical aspects quickly. Moreover, I will make a great effort to fulfill my duties and responsibilities and contribute to the good progress of the organization.

Useful Grammar: Conditional form and sentences to express: • the likelihood of your working for them If I am hired, I can/could/will contribute significantly to the progress of your company. • the possibility of your working for them If I were hired, I would make a great effort to learn quickly. Linking forms to state opinions: • I believe/think that I…. • In my opinion, … • According to me, …. . • In my experience, …. • I’d say that… • I have no doubt that… • I am sure/confident that…

Questions about what YOU know about the company Sample questions: • What do you know about our company? • Are you familiar with our company’s current projects and future prospects?

Sample Answers I know it is one of the fastest growing companies in Europe and has many branches in different countries. The work environment is pleasant and people feel proud to be a part of the company. I have read it provides full support to its employees on a professional front and offers many career growing opportunities. I know it is currently working on a largescale project in Italy and that its major competitor is SA Geo. Sci.

Questions about current and past work experience Sample questions (current employment): • Who is your current employer? • What are your duties and responsibilities? • Why are you leaving your current job?

Sample Answer I am currently employed at SA Geo. Sci and have been working for them for the last four years. I have received great training and education there. I have been entrusted with international job assignments and a 10 member team staff. However, I feel that the time is right for me to transit the outstanding skills and experience I have obtained there to a different job market, and I am confident I can bring these same skills to your organisation.

Sample questions (past employment): • Have you worked for a similar company before? • Tell us something about your previous employer(s)? • What were your duties and responsibilities? • How long did you work for them? • What major challenges did you face? • Why did you leave your last job? • What did you like and dislike about your former employment?

Sample Answers I (have) worked for 3 years with the Saudi Arabia Gas Company where I am/was Surveying Director and am/was responsible for/in charge of conducting research on potential petrol reservoirs. The average work-week consists(ed) of 38 hours, but I often put in extra hours to complete assignments and meet deadlines. I enjoy(ed) this job quite a lot and my employer treats/ed staff with respect and always rewards/ed accomplishments. However, I now feel it is time for me to move on and acquire further work experience in different fields ( or: I was laid off/ made redundant because the company relocated/ downsized/ needed to cut costs.

Questions about career goals Sample questions: • Where do you see yourself five years from now/in five years’ time? • What are your career goals? • How do plan to achieve your career goals?

Sample Answers "In five years, I see myself as a valued employee of a company. I want to be an expert at my position and start training to be a manager. "In five years, I want to be a senior analyst. I want my expertise to directly impact the company in a positive way. "My goal is to become a lead in five years. Although not everyone gets promoted to this level, I believe I can achieve this goal through hard work. "Although I really enjoy working hands on as a mechanical engineer, I want to eventually become a manager. I want to continue gaining experience, and after learning many different aspects, I see myself in management.

Patterns: • • • In the future, I would like to… Hopefully, I will… I hope to… My dream is to… My aspirations are/include….

If you could change one thing about your personality, what would it be and why? "I get easily frustrated at people who don't work very hard. But I know people have different work styles and different work habits. So if I could change something, I would like to be more understanding. "I have high expectations and I have these expectations on others. I think if I was more understanding, I could help other workers improve instead of being disappointed. "I would like to be more of a risk taker. I always do my work and complete it at an exceptional level, but sometimes taking a risk can make the work even better. I'm working on this by thinking the issue through and weighing the pros and cons. "I would like to be more of an extrovert. I'm a little quiet and a little closer to the introvert side. I would like to change this because I would appear more friendly.

What does success mean to you? "To me, success means to have a goal, plan the steps to achieve the goal, implement the plan, and finally achieve the goal. "Success means to achieve a goal I have set for myself. "Success means to produce high quality work before the deadline. "Success to me is knowing that my contributions positively impacted my company.

What does failure mean to you? "Failure is when I do not reach my goal. "I think to fail at something is making a mistake and not learning anything from it. "To me, failure means to have a goal and not do anything about it. "I think failure is not reaching your potential. If you do not use the resources you have and the resources around you, that's failure because the work or goal could have been done better.

Are you organized person? "I'm a very organized person. I like to know exactly what I'm going to do for the day and the week. So I outline my tasks and organize my work load. By doing so, I can organize my time and work better. "I believe I'm very organized. I like to organize my work by priority and deadlines. I do this so I can produce the highest quality work in the amount of time I have. "I think I'm quite organized. I like my documents and papers in a way where I can retrieve them quickly. I also organize my work in a way where it's easy to see exactly what I'm doing. "Organization has always come easy to me. I naturally organize things like my desk, time, assignments, and work without thinking about them. This helps me tremendously during times when I'm approaching a deadline.

In what ways are you organized and disorganized? "I'm very organized with my time and work, but my desk is a little disorganized. "Since I work with many files, I like to keep my desk organized. I always have everything in a certain place so I can find things easier. The area I'm disorganized is probably my computer desktop. I usually have so many icons everywhere. I should organize it a little, but I've never needed to. "I organize my schedule the best. I'm used to many meetings so it's important for me to be organized with my schedule and time. The area I need to improve is probably my file cabinet. I started to sort things alphabetically, but when I'm busy, I start putting things in there. It started getting hard to find things, but this is something I'm going to fix.

Do you manage your time well? "I'm good at managing my time. I stay busy both at home and at work and being able to manage my time is necessary for me to do everything that I want to do. "I manage my time well by planning out what I have to do for the whole week. It keeps me on track and evens helps me to be more efficient. "Managing my time is one of my strong traits. I prioritize my tasks and this allows me to stay ahead of schedule. Each day I manage my time so I can achieve more than I set out to do. So managing my time in a goal oriented way is what I feel very comfortable doing.

"How do you handle change? "I'm good at dealing with change because I'm a quick thinker. If new information makes us change our marketing strategy for example, I'll be quick to analyze the information and create a plan to make the changes. "I've experienced many changes previously. I handle the situation by quickly coming up to speed on the changes and applying myself to make them a success. "I'm good at dealing with change because I'm flexible with my work and abilities. I'm not afraid of learning new and difficult things. Whenever I'm faced with a change, I'll put in extra effort to make the change a smooth transition.

How do you make important decisions? "I make important decisions by examining all the details and then weighing the pro's and con's for each decision. "I believe all decisions should be made by having all the information. If you are missing an important detail, it's easy to make a bad decision. So I make important decisions by having all of the information. "Important decisions are made by knowledge through information and wisdom through experience. I'll gather all the information I can find and then apply my experience while analyzing the information. With this combination, I'm confident I'll make the correct important decisions.

Do you work well under pressure? "I work well under pressure because I use the pressure to help me work more efficiently. "I enjoy working under pressure because I believe it helps me grow. In my previous experience, I always worked well during deadlines, and I always learned how to work more efficiently afterwards. "I work well under pressure because I don't panic. I maintain self control and work as efficiently as possible. In all my experiences, I did well and I always enjoyed the experience.

Exit: Your questions about the job and company Sample questions: • Do you have any questions for us? • Is there anything you’d like to know about us?

Candidate (prepare 4/5 questions): • How would you describe the company’s management style? • Is this a new position? • What would my duties include? • Is travel expected in this job position? • What are the prospects for growth and advancement?

Thanking and asking about the next steps At the end of the interview • Thank the interviewers for their time. • Ask about the next steps and when you can expect a response from them.

Sample Answers I would like to thank you for having given me the opportunity to participate in this job interview and for making me feel at ease. I have found the experience constructive and very interesting. When do you expect you will notify selected candidates? If I am/were offered the job, when will/would I start?

Post Interview • analyse the answers you gave in the interview and improve any weak language areas • Mail a thank-you note

Avoid: Showing up late Keeping phone ON Limp hand shake Chat up the storm Interviewer – Best friend/Girl friend Over dressed/Under dressed Not thanking

Remember manners and respect, and always use the magic words: Please and Thank you!

LESSON Writing 7: Formal

Formal letter Purpose: What do I want the reader to know? What kind of business letter am I writing? -Letter of inquiry -Letter of application -Letter of complaint -Letter of regret -Thank you letter

Audience How well do I know them? How much do they know about my subject? How will they feel about my message? What vocabulary will set the tone?

Formatting Business Letters Choose a font that is easy to read. - Use 10 -12 point font - Use a simple font (Times New Roman or Arial) - Use the right ragged formatting - Single space within paragraphs - Double space between paragraphs - Leave 3 -5 lines for signature - Use comma after salutation - Double space between last sentence and closing (Sincerely, Regards) Present information: -completely -concisely -professionally

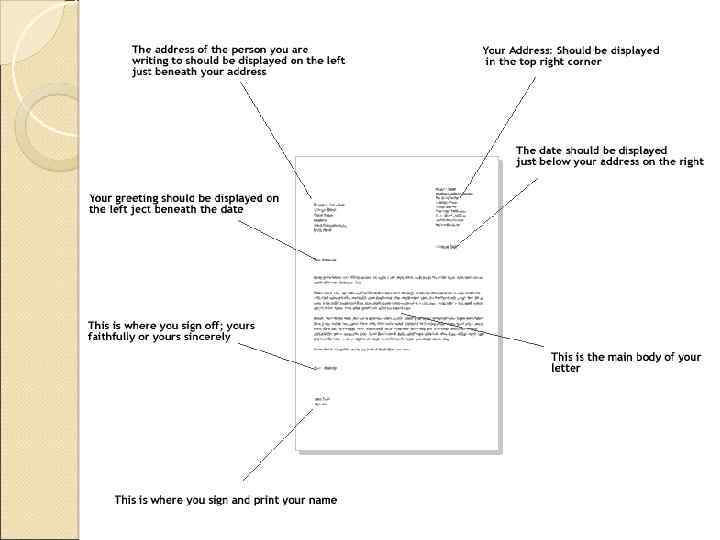
Parts of a Business Letter Heading Writer’s complete address (Return Address) -Current date Inside Address: -Receiver’s complete name, title, company and address (Letter Address) However, if you have a letterhead, you don’t need the Return Address

Example: Your address Place your address in the upper left-hand/right-hand corner. It is common practice not to give the name of the sender above the address. Instead, the name is typed below the signature. Academika Volgina 13 Moscow Russia Tel. : ………. E-mail: …… Date: ……. .

Example: The address of the recipient includes his/her full name and title(s). Professor John A. Smith BSc(Eng) MSc Ph. D Head of Department of Electrical Engineering Faculty of Engineering The University of Nottingham 34 University Park Nottingham NG 7 2 RD United Kingdom

Salutation If you know the name of the recipient: Dear Ms/Mr/Dr + the last name: Dear Dr Smith, Dear Ms Brown, Dear Professor Stubbs, NOT: Dear Mr Professor White If you know the position of the recipient but not the name: Dear Admissions Officer, Dear Personnel Manager, If you know neither the name nor the position: Dear Sir, Dear Madam, Dear Sir or Madam, Dear Sir/Madam, Dear Sirs or Madams, Dear Sirs/Madams, To Whom It May Concern Skip a line between the salutation and the subject line or body.

Body The body of the letter is where you present yourself and explain the reason for writing the letter. Single-space paragraphs Double-space between paragraphs. 3 -4 paragraphs. (keep it short) Avoid long phrases. Avoid making business letters longer than one page. Avoid using big words Be concise

Complimentary close The complimentary close is typed one line below the body of the letter. If you used the recipient’s name, end with Yours sincerely/Sincerely yours. If you did not use the recipient’s name, end with Yours faithfully/Faithfully yours. Put a comma after the end of the closing. Skip 3 -4 lines between the closing and your typed name so that there is room for your signature. Capitalize only the first word.

Signature lines Leave four lines for your handwritten signature Type your name and title below the signature line. Type the words Enclosure(s) (if any) two lines below the typed signature.

Enclosure(s)/Encl(s) Do not put a colon (: ) after these words. Example: Enclosure/Encl CV If there are several documents enclosed, you can type their number in brackets; it is not necessary to list them. Enclosures (3) If you are submitting your cover letter by e-mail, use the word Attachment instead of Enclosure. Sending a copy of the letter elsewhere? -cc: PLUS the person or department name. This line goes beneath the enclosure line.

Cover letter A cover letter, is primarily a document of transmittal. It identifies an item being sent, the person to whom it is being sent, and the reason for its being sent, and provides a permanent record of the transmittal for both the writer and the reader.

Types of cover letters A short letter sent together with something to explain what you are sending. A job application letter sent together with a CV. An academic cover letter, i. e. an application for a university position/scholarship/ fellowship/admission to a course of study, also sent with a CV. The academic cover letter is usually longer than a job application letter and emphasis is on academic achievements. A grant application cover letter is similar to a statement of proposed activity. Completion of a detailed application form provided by the relevant grant agency/institution together with the statement of proposed activity is, at present, the most common way of applying for a grant.

Tips for Writing Cover Letters In a cover letter, keep your remarks brief. Your opening should explain what you are sending and why. In an optional second paragraph, you might include a summary of the information you are sending. A letter accompanying a proposal, for example, might point out sections in the proposal that might be of particular interest to the reader. The letter could then go on to present a key point or two explaining why the writer’s firm is the best one for the job. The closing paragraph should contain acknowledgements, offer additional assistance, or express the hope that the material will fulfill its purpose.
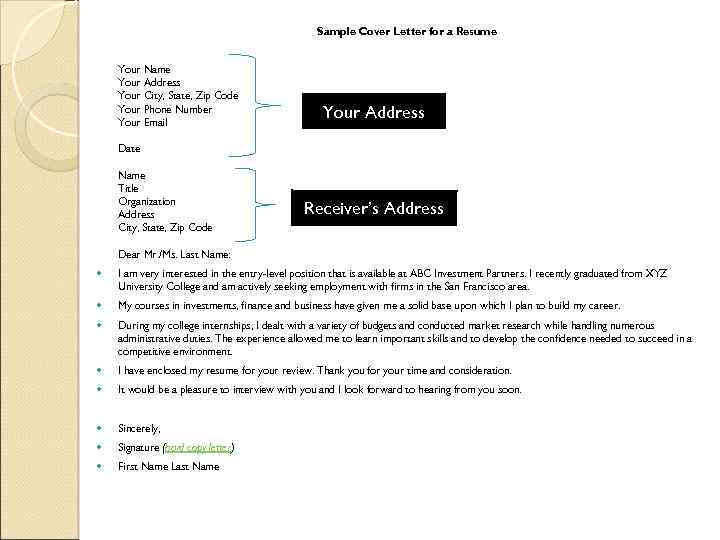
Sample Cover Letter for a Resume Your Name Your Address Your City, State, Zip Code Your Phone Number Your Email Your Address Date Name Title Organization Address City, State, Zip Code Receiver’s Address Dear Mr. /Ms. Last Name: I am very interested in the entry-level position that is available at ABC Investment Partners. I recently graduated from XYZ University College and am actively seeking employment with firms in the San Francisco area. My courses in investments, finance and business have given me a solid base upon which I plan to build my career. During my college internships, I dealt with a variety of budgets and conducted market research while handling numerous administrative duties. The experience allowed me to learn important skills and to develop the confidence needed to succeed in a competitive environment. I have enclosed my resume for your review. Thank you for your time and consideration. It would be a pleasure to interview with you and I look forward to hearing from you soon. Sincerely, Signature (hard copy letter) First Name Last Name

Writing Email How to write a formal email Follow these five simple steps to make sure your English emails are perfectly professional. Begin with a greeting Thank the recipient State your purpose Add your closing remarks End with a closing

Begin with a greeting Always open your email with a greeting, such as “Dear Lillian”. If your relationship with the reader is formal, use their family name (eg. “Dear Mrs. Price”). If the relationship is more casual, you can simply say, “Hi Kelly”. If you don’t know the name of the person you are writing to, use: “To whom it may concern” or “Dear Sir/Madam”.

Thank the recipient If you are replying to a client’s inquiry, you should begin with a line of thanks. For example, if someone has a question about your company, you can say, “Thank you for contacting ABC Company”. If someone has replied to one of your emails, be sure to say, “Thank you for your prompt reply” or “Thanks for getting back to me”. Thanking the reader puts him or her at ease, and it will make you appear more polite.

State your purpose If you are starting the email communication, it may be impossible to include a line of thanks. Instead, begin by stating your purpose. For example, “I am writing to enquire about …” or “I am writing in reference to …”. Make your purpose clear early on in the email, and then move into the main text of your email. Remember, people want to read emails quickly, so keep your sentences short and clear. You’ll also need to pay careful attention to grammar, spelling and punctuation so that you present a professional image of yourself and your company.

Add your closing remarks Before you end your email, it’s polite to thank your reader one more time and add some polite closing remarks. You might start with “Thank you for your patience and cooperation” or “Thank you for your consideration” and then follow up with, “If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to let me know” and “I look forward to hearing from you”.

End with a closing The last step is to include an appropriate closing with your name. “Best regards”, “Sincerely”, and “Thank you” are all professional. Avoid closings such as “Best wishes” or “Cheers” unless you are good friends with the reader. Finally, before you hit the send button, review and spell check your email one more time to make sure it’s truly perfect!


Curriculum Vitae/ Resume The purpose of a resume Your resume is a marketing tool. It needs to demonstrate: That you are employable How you meet the job and the organisation's requirements That you have the right qualifications and education That you have the right experience and skills That you have the right level of professionalism for the job

How long should my resume be? There is no set length for a resume. A resume varies in length depending on your experience and education. If you haven't worked much before, one or two pages is best, but three pages is okay if you've got a lot of study and work behind you. Make sure you don't pad out your resume. If your resume is only one page, as long as it's well-presented it might get better results than a two-page resume full of unnecessary information.

How should I order my resume? Generally it's always good to present the information on your resume in this order: Contact details Opening statement List of key skills List of technical/software skills Personal attributes/career overview Educational qualifications Employment history/volunteering/work placements References/referees Not everything in this list must appear on your resume every time, and the order can change from application to application.

Do I need to change my resume for each application? You need to tailor your resume to every job application so that it responds to the specific requirements of the job you're applying for. You might not need to change much, but you do need to make sure your opening statement, your key skills and your personal attributes all respond to the needs of the role, based on the job ad (if there was one) and the research you've done into the job. You should also tailor your resume to show your work experience specifically meets the needs of the job you're applying for.

How to tailor your resume Ways that you can tailor your resume include: Using your opening statement to link your experience and education to the organisation and the requirements of the job Listing your most relevant key skills first Including examples of achievements that meet the advertised requirements of the job Including specifically relevant key words and phrases throughout your resume.

Example Resume

Fax


Writing memorandum

Business Etiquettes

Business contracts

Business lexicon
B.Eng1.ppt