edb1a735792bff6b978ab20c537e3db7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Business Combinations - IFRS Update Training Puts, Calls and Forwards Pricewaterhouse. Coopers LLP Pw. C

Puts, Calls and Forwards Refresher Puts Contracts giving one party the right to sell shares to the other party at a specified exercise price at a future date or during a specified future time period Calls Contracts giving one party the right to buy shares from the other party at a specified exercise price at a future date or during a specified future time period Forwards Binding contracts for one party to buy or sell shares from/to the other party at a specified exercise price at a future date or during a specified future time period Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 2

Puts, Calls and Forwards The issues • Contracts created at the time of acquisition or at a later date • Issues are: - Is the written put a liability? - Should MI continue to be recognised? - Where is the debit posted? - What about a forward purchase? - What about a call option? WARNING – Very Complex Issues! Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 3

Puts, Calls and Forwards The issues • This session covers: - Puts written in a business combination Puts written outside a business combination Policy choices Calls and forwards • Global ACS alert - Five minutes to read Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 4

Puts, Calls and Forwards Shake up ACCOUNTING FOR PUTS WRITTEN AS PART OF A BUSINESS COMBINATION FIXED PRICE Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 5

Puts, Calls and Forwards Recognition A written put is always a liability • Obligation to pay cash to holder [IAS 32. 23/IAS 32 AG. 29] • Can happen at any time during exercise period • Measured at present value of redemption amount [IAS 32. 23] Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 6

Puts, Calls and Forwards Recognition and Remeasurement Accounting depends on the substance of the transaction Transfer of Risks and Rewards MI purchased • Minority interest is NOT recognised [IAS 27 IG. 5] • Liability at present value of expected redemption amount • One credit approach – liability and no minority interest • Put is contingent consideration Liability is recognised as part of cost of acquisition (GW) Liability remeasurements adjust cost of acquisition Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 7
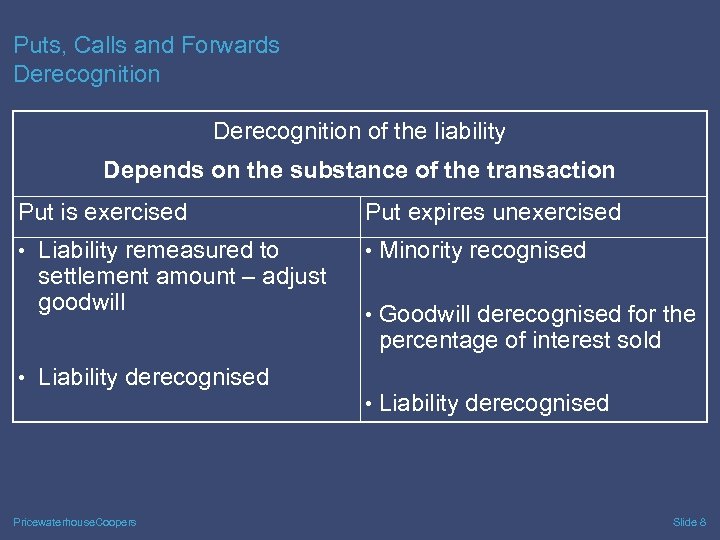
Puts, Calls and Forwards Derecognition of the liability Depends on the substance of the transaction Put is exercised Put expires unexercised • Liability remeasured to • Minority recognised settlement amount – adjust goodwill • Goodwill derecognised for the percentage of interest sold • Liability derecognised Pricewaterhouse. Coopers • Liability derecognised Slide 8

Puts, Calls and Forwards Shake up ACCOUNTING FOR PUTS WRITTEN AS PART OF A BUSINESS COMBINATION VARIABLE PRICE Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 9

Puts, Calls and Forwards Recognition and Remeasurement A written put is always a liability Accounting depends on the substance of the transaction No Transfer of Risks and Rewards MI recognised • Liability at present value of expected redemption amount • Liability recognised as a reclassification from equity [IAS 32. 23] • Two credits approach – MI and liability • Put is not contingent consideration MI not acquired Liability remeasurements go to income statement [IAS 39 AG. 8] Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 10
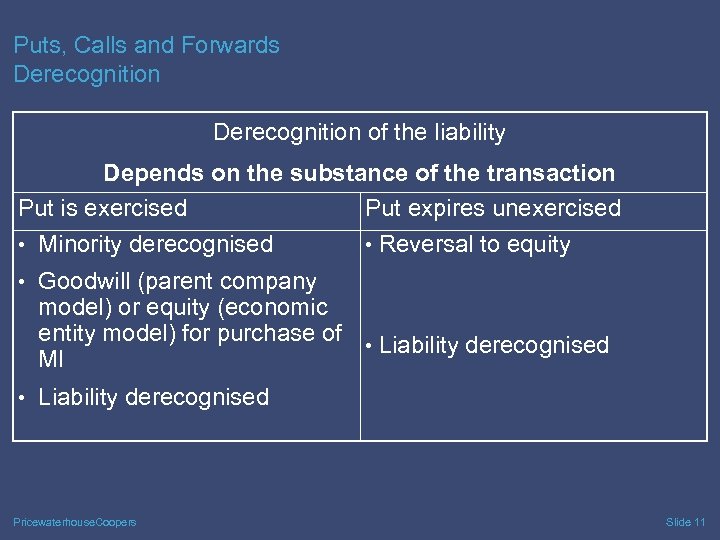
Puts, Calls and Forwards Derecognition of the liability Depends on the substance of the transaction Put is exercised Put expires unexercised • Minority derecognised • Reversal to equity • Goodwill (parent company model) or equity (economic entity model) for purchase of • Liability derecognised MI • Liability derecognised Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 11
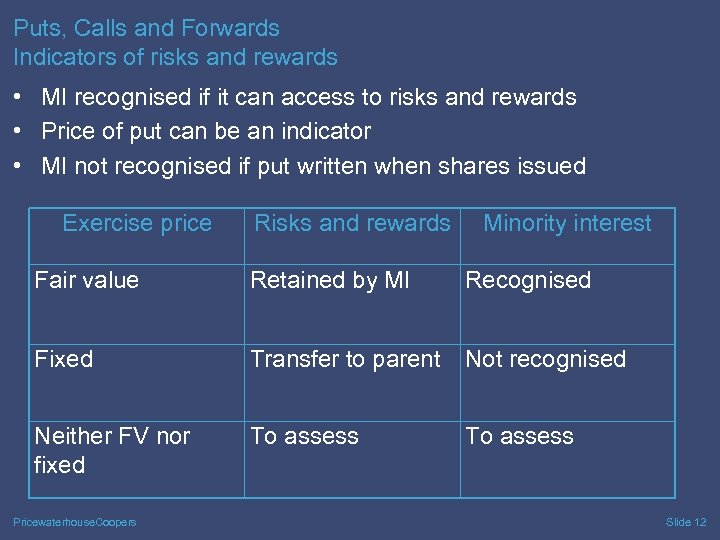
Puts, Calls and Forwards Indicators of risks and rewards • MI recognised if it can access to risks and rewards • Price of put can be an indicator • MI not recognised if put written when shares issued Exercise price Risks and rewards Minority interest Fair value Retained by MI Recognised Fixed Transfer to parent Not recognised Neither FV nor fixed To assess Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 12

Puts, Calls and Forwards Recap • Two models based on substance: - One credit minority not recognised - Two credits minority recognised • Key difference is treatment of remeasurements • Consider employee/management compensation Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 13
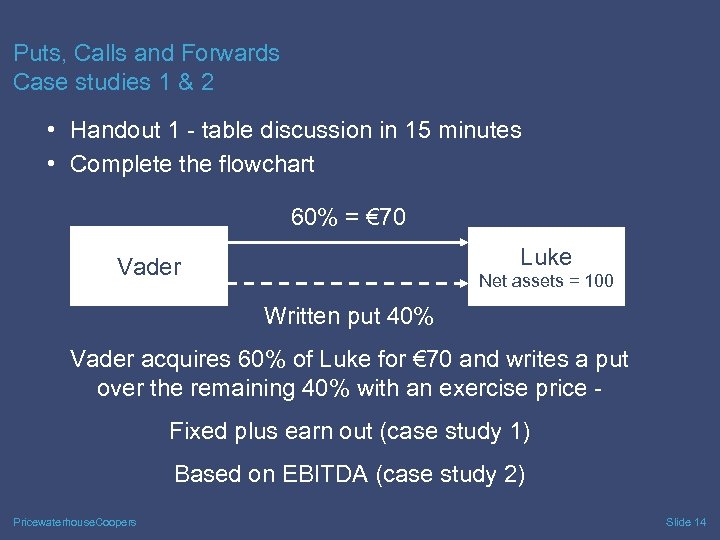
Puts, Calls and Forwards Case studies 1 & 2 • Handout 1 - table discussion in 15 minutes • Complete the flowchart 60% = € 70 Luke Vader Net assets = 100 Written put 40% Vader acquires 60% of Luke for € 70 and writes a put over the remaining 40% with an exercise price Fixed plus earn out (case study 1) Based on EBITDA (case study 2) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 14

Puts, Calls and Forwards Principles ACCOUNTING FOR PUTS WRITTEN OUTSIDE OF A BUSINESS COMBINATION Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 15

Puts, Calls and Forwards Principles A written put is always a liability Accounting depends on the substance of the transaction Transfer of Risks and Rewards MI purchased • Minority interest is derecognised - One credit approach – liability and no minority interest • Financial liability at present value of expected redemption amount [IAS 32. 23] No business combination, so cannot be contingent consideration Liability remeasurements go to income statement [IAS 39 AG. 8] Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 16

Puts, Calls and Forwards Principles A written put is always a liability Accounting depends on the substance of the transaction No Transfer of Risks and Rewards MI unchanged Two credits approach – MI and liability • Financial liability at present value of expected redemption amount [IAS 32. 23] • Financial liability is recognised as a reclassification from equity • Liability remeasurements go to income statement Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 17
Puts, Calls and Forwards Case studies 3 & 4 • Handout 2 - table discussion in 15 minutes • Complete the flowchart MI CV = 40 40% 60% Vader Luke Net assets = 100 Vader has owned 60% of Luke for many years and written a put over 40% with an exercise price – Fixed plus earn out (case study 3) Based on EBITDA (case study 4) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 18

Puts, Calls and Forwards Accounting policy choices • Based on substance as above - One credit - Two credits Or • Always use one credit approach and derecognise minority interest [IAS 32 AG. 29] Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 19

Puts, Calls and Forwards Forward contracts • • • Binding contracts Parent access to economic benefits of the shares No minority interest one credit approach Treat as contingent consideration in a business combination Overlapped puts and calls – treated as forwards, as always in the money for one of the parties Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 20

Puts, Calls and Forwards Call only • Purchased call option - If fixed number of shares exchanged for fixed amount of cash equity instrument • Premium paid to equity - Other cases: • Derivative, unless • Exercise price is based on non-financial variable that is specific to a party to the contract Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 21

Puts, Calls and Forwards Summary • Written put is complex • Written put is always a liability • Part of a business combination • Accounting depends on substance • Assessment for transfer of risks and rewards • Recognition of MI two credits approach • Derecognition of MI one credit approach • Policy choice • Forward contracts – binding contract • Call only – equity, derivative or disclosure only Consult! Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 22

Thank you Pricewaterhouse. Coopers Slide 23
edb1a735792bff6b978ab20c537e3db7.ppt