0aa3e69b4aca6f983671dba7bccc979e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

Business and Climate Change Efforts: A Supply Chain Perspective Mansour Hajbagheri Erasmus Mundus Conference: Higher Education and Climate Change Central European University, Budapest 26 -27 Feb. 2009

Agenda § Introduction § Why Supply Chain? § What is a Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM)? § Green Sourcing Principles and Values § Corporate Practices for Green Sourcing § Conclusion § Discussion 2

Drivers of Going Green § Legislations, regulations and standards for going Green § Ethical obligations and social responsibility § Financial incentives 3

Impediments to Going Green § Lowers economic profits § Imposes unequal costs among competitors § Costs of going green will eventually be shifted to the stakeholders § Social issues are best solved by government. “Business of business is business”. 4
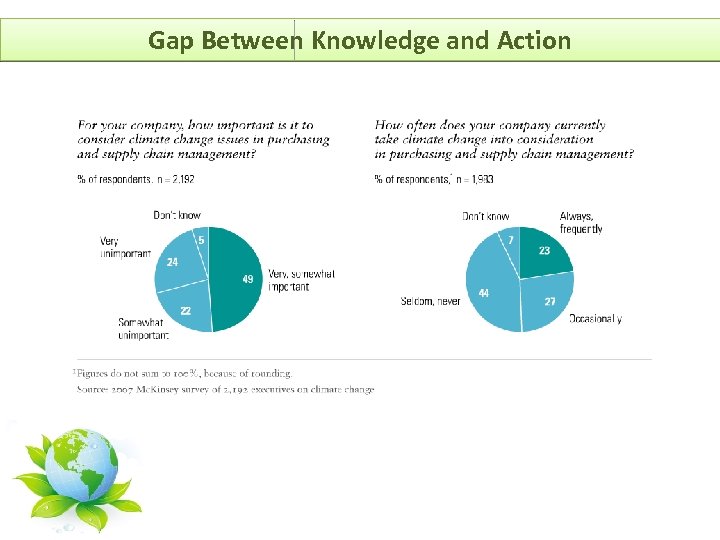
Gap Between Knowledge and Action

Why Supply Chain? § Profitability: It has the potential to create value (profit) for the business. Is this a Green car? § Criticality: Firms cannot be sustainable unless their supply chains become sustainable first. 6

Why Supply Chain? (Cont. ) § Synergic nature: “Networked” vs. Individual effort 7
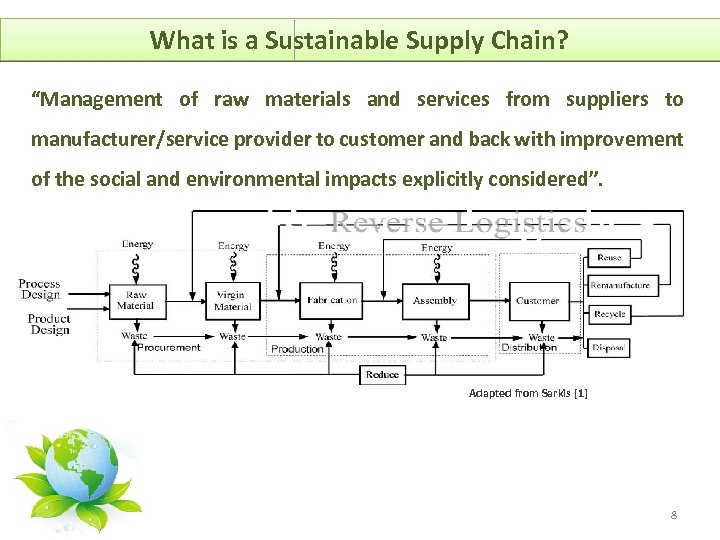
What is a Sustainable Supply Chain? “Management of raw materials and services from suppliers to manufacturer/service provider to customer and back with improvement of the social and environmental impacts explicitly considered”. Adapted from Sarkis [1] 8

Green Sourcing Principles & Values § Best efforts to mitigate all kinds of pollution: § Air, water, land, noise, etc. § Avoid creating waste whenever possible: § Packaging – inbound and outbound § Environmentally friendly chemicals § Reduced disposal costs: § Recycling waste § Reusable packaging § Lower operational costs § Energy conservation § High density lighting 9

Corporate Practices for Green Sourcing § Make Green part of the RFI/RFP process and filter out non-green suppliers – What % of their waste stream is recycled? – What % of their raw materials are from recycling? – What $’s have they invested in Green initiatives? § Require or encourage suppliers to undertake independent environmental certification , e. g. ISO 14000 § Build environmental criteria into supplier contract conditions § Supply base environmental performance management § Conduct life cycle analysis in cooperation with suppliers § Coordinate minimization of environmental impact in the extended supply chain 10

Corporate Practices for Green Sourcing (Cont. ) § Cooperate with suppliers to deal with end-of-pipe environmental issues: § Reduce packaging waste at the customer/supplier interface § Reuse/recycle materials in cooperation with the supplier § Launch reuse initiatives (including buy backs and leasing) § Reverse logistics: § Give supplier an incentive to reduce the customer’s environmental load § Waste by-products reused by the raw material suppliers § Material ‘Life Cycle Management’ 11

Conclusion § Supply Chain is the most important issue that a green business should address in its environmental efforts. § Greening the supply chain can potentially reduce costs and provide profit opportunities. § Bringing sustainable practices into supply chain is a certain trend in the future. Thus, those who start from now gain a competitive advantage. 12


References 1. Sarkis J. , Manufacturing strategy and environmental consciousness, Technovation 1995, 15(2), 79– 97. 2. Sarkis J. , A strategic decision framework for green supply chain management, Journal of Cleaner Production, 2003, 11, 397 -409. 3. Institute for Supply Management (ISM) website: www. ism. ws 4. 2007 Mc. Kinsey survey of 2, 192 executives on climate change: http: //www. mckinseyquarterly. com/Operations/Supply_Chain_Logistics/How _companies_think_about_climate_change_A_Mc. Kinsey_Global_Survey_2099 14
0aa3e69b4aca6f983671dba7bccc979e.ppt