6b6e415b2a7eaac4725c8638a8d04c52.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
BUS 1 MIS Management Information Systems Semester 1, 2012 Week 4 Lecture 1

Administration Online Quiz – Tutorial 2 (theory), Week 4 • • 25 multiple choice and true/false questions Conducted during tutorial time or at home Becomes available on Thursday 22 th March at 9 am Remains available for a week BUT – you only get one chance 50 minute time limit Tests Chapter 1, Section 1. 1 p. 3 – 13 and Section 1. 2 Textbook can be used

Essentials of IS: Hardware and Software Why should a business manager take any interest in hardware and software? At some stage an investment in hardware and software will be required. The investment may be a significant one. There are better and worse times to make the investment. The investment needs to be protected. Why not just call in an IT consultant? Why not indeed. However, a business manager with no knowledge of hardware and software requirements, and current trends and prices, cannot effectively oversee the consulting process. Ref: Appendix B, on-line website for the text

Essentials of IS: Hardware and Software Learning Objectives • Describe the six major categories of hardware and provide an example of each. • Identify the different computer categories and explain their potential business uses. • Explain the difference between primary and secondary storage. • List the common input, output, storage and communication devices • Describe the eight categories of computers by size • Define the relationship between operating system software and utility software
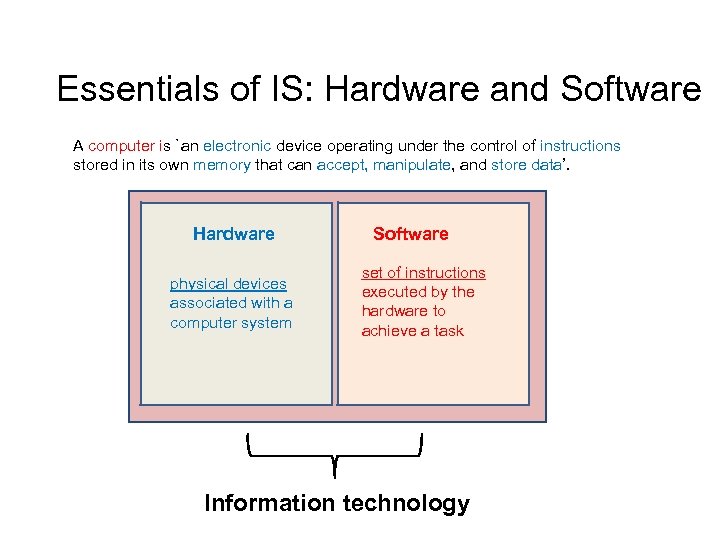
Essentials of IS: Hardware and Software A computer is `an electronic device operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept, manipulate, and store data’. Hardware physical devices associated with a computer system Software set of instructions executed by the hardware to achieve a task Information technology
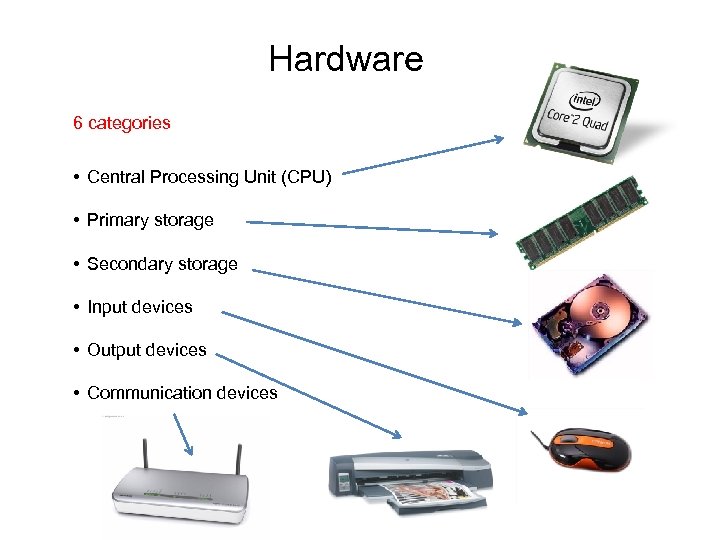
Hardware 6 categories • Central Processing Unit (CPU) • Primary storage • Secondary storage • Input devices • Output devices • Communication devices
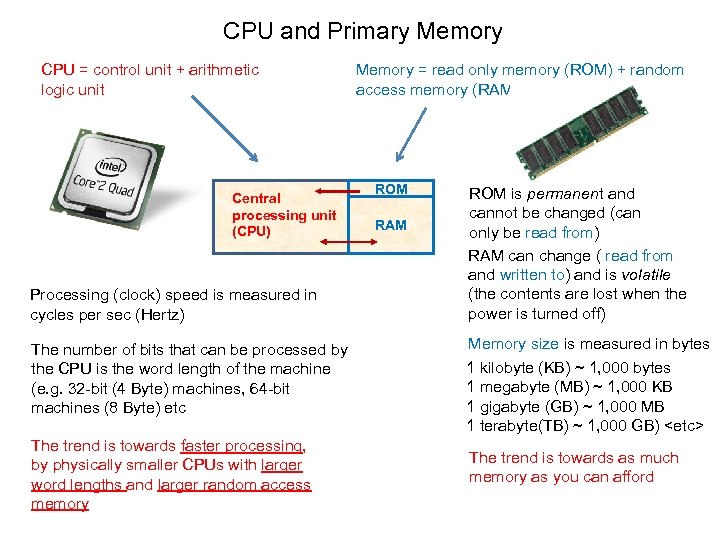
CPU and Primary Memory CPU = control unit + arithmetic logic unit Central processing unit (CPU) Processing (clock) speed is measured in cycles per sec (Hertz) Memory = read only memory (ROM) + random access memory (RAM) ROM RAM ROM is permanent and cannot be changed (can only be read from) RAM can change ( read from and written to) and is volatile (the contents are lost when the power is turned off) The number of bits that can be processed by the CPU is the word length of the machine (e. g. 32 -bit (4 Byte) machines, 64 -bit machines (8 Byte) etc Memory size is measured in bytes 1 kilobyte (KB) ~ 1, 000 bytes 1 megabyte (MB) ~ 1, 000 KB 1 gigabyte (GB) ~ 1, 000 MB 1 terabyte(TB) ~ 1, 000 GB) <etc> The trend is towards faster processing, by physically smaller CPUs with larger word lengths and larger random access memory The trend is towards as much memory as you can afford

CPU and Primary Memory Check out the CPU and Primary Memory at: http: //dicksmith. com. au/product/XC 7831/hp-pavilion-dv 6 -6027 tx-notebook
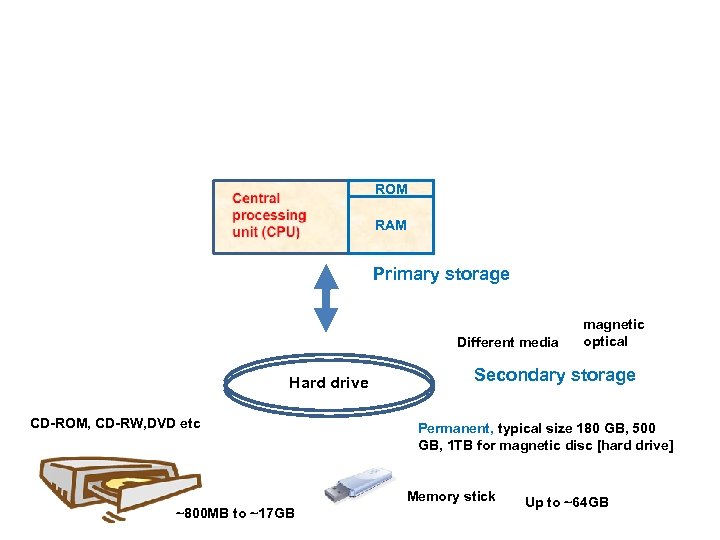
ROM RAM Primary storage Different media Hard drive CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD etc Secondary storage Permanent, typical size 180 GB, 500 GB, 1 TB for magnetic disc [hard drive] Memory stick ~800 MB to ~17 GB magnetic optical Up to ~64 GB
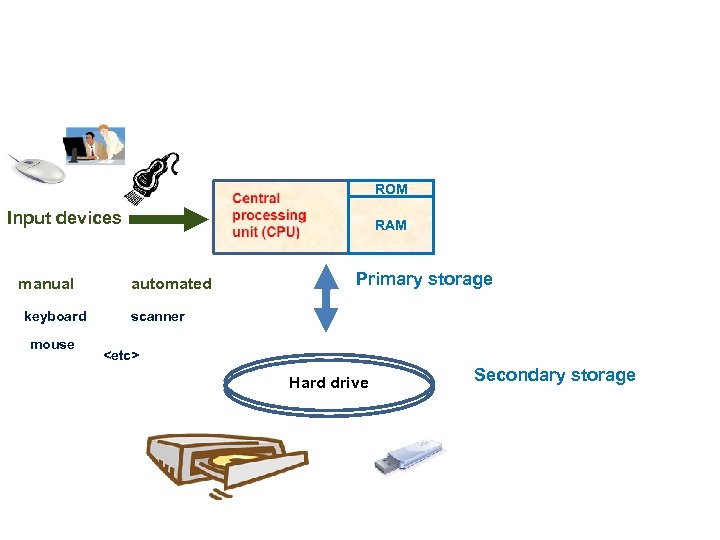
ROM Input devices manual keyboard mouse RAM automated Primary storage scanner <etc> Hard drive Secondary storage
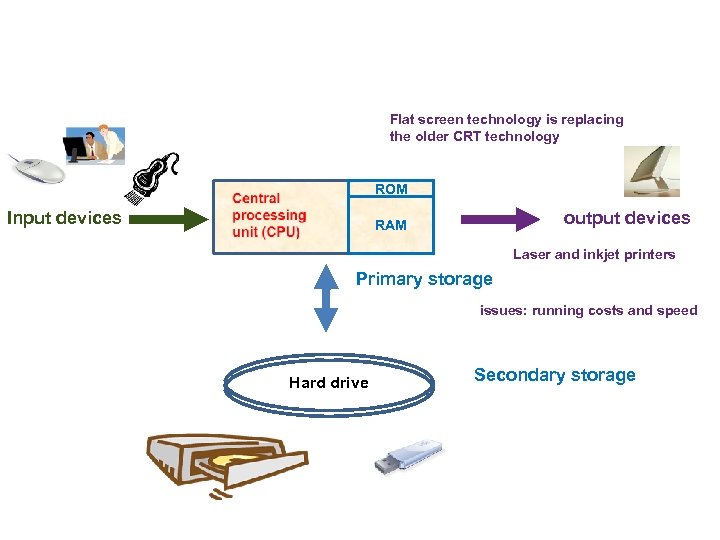
Flat screen technology is replacing the older CRT technology ROM Input devices output devices RAM Laser and inkjet printers Primary storage issues: running costs and speed Hard drive Secondary storage
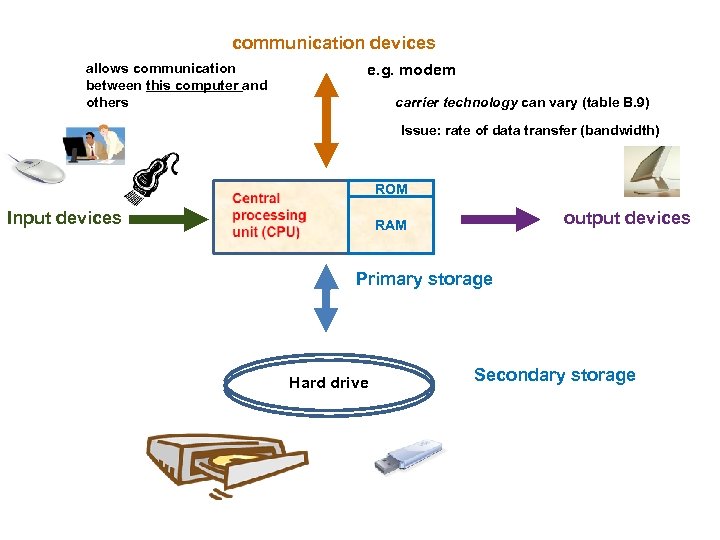
communication devices allows communication between this computer and others e. g. modem carrier technology can vary (table B. 9) Issue: rate of data transfer (bandwidth) ROM Input devices output devices RAM Primary storage Hard drive Secondary storage
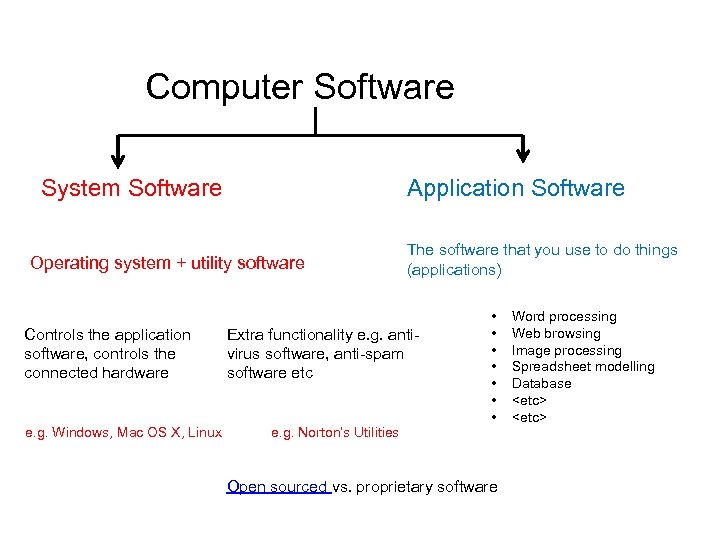
Computer Software System Software Application Software Operating system + utility software Controls the application software, controls the connected hardware e. g. Windows, Mac OS X, Linux The software that you use to do things (applications) Extra functionality e. g. antivirus software, anti-spam software etc e. g. Norton’s Utilities • • Open sourced vs. proprietary software Word processing Web browsing Image processing Spreadsheet modelling Database <etc>
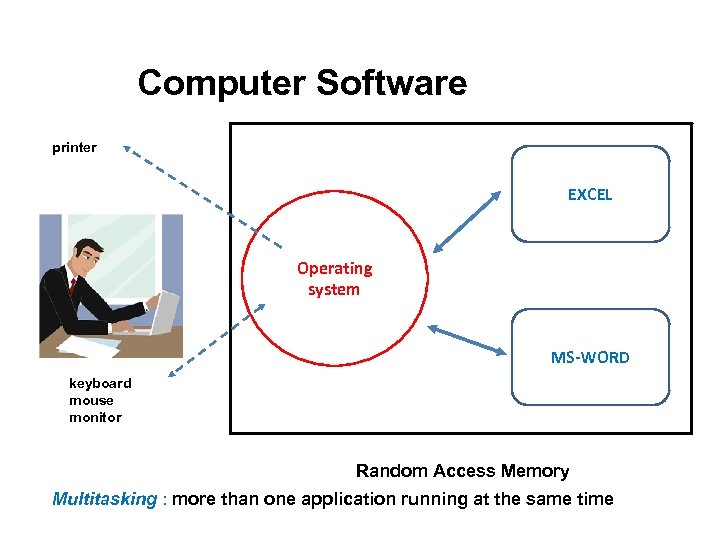
Computer Software printer EXCEL Operating system MS-WORD keyboard mouse monitor Random Access Memory Multitasking : more than one application running at the same time
![Computer types [categories] Most relevant to small business … …and larger organisations • • Computer types [categories] Most relevant to small business … …and larger organisations • •](https://present5.com/presentation/6b6e415b2a7eaac4725c8638a8d04c52/image-15.jpg)
Computer types [categories] Most relevant to small business … …and larger organisations • • PDA [personal digital assistant] Laptop In general … increasing physical size • Tablet • Desktop • Minicomputer • Mainframe • Supercomputer See fig B. 11 increasing cost [although laptops tend to be a little more expensive that a corresponding desktop] increasing processing power
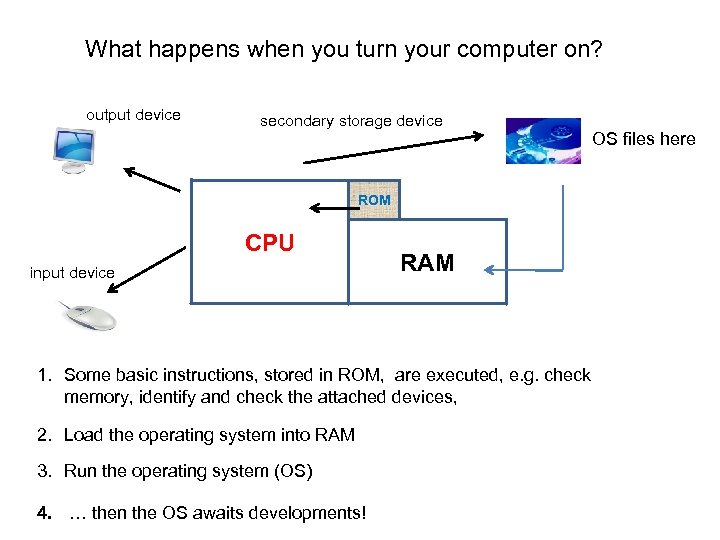
What happens when you turn your computer on? output device secondary storage device ROM CPU input device RAM 1. Some basic instructions, stored in ROM, are executed, e. g. check memory, identify and check the attached devices, 2. Load the operating system into RAM 3. Run the operating system (OS) 4. … then the OS awaits developments! OS files here
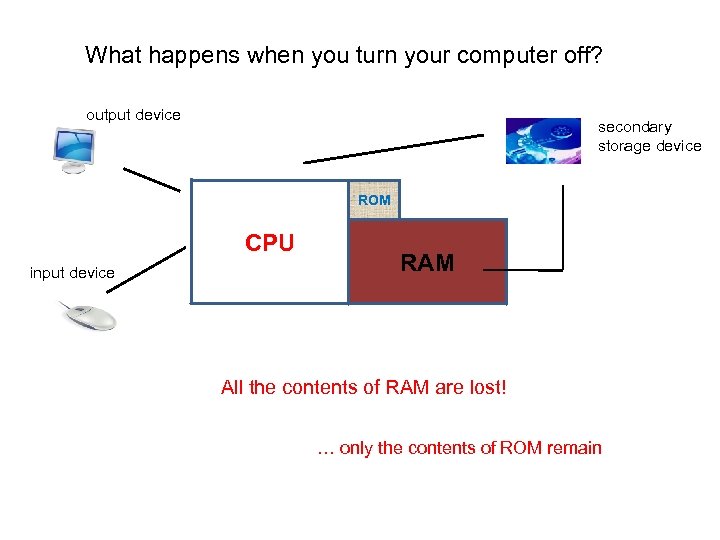
What happens when you turn your computer off? output device secondary storage device ROM CPU input device RAM All the contents of RAM are lost! … only the contents of ROM remain

Hardware and Software: Issues When acquiring a computer system you should consider … your requirements … compatibility with your existing systems … your budget … off the shelf vs a customised solution When dealing with an IT consultant you need to have some understanding of technical issues such as … operating and application software … processing speed and memory size …storage media and storage capacity … automated and manual input … softcopy and hardcopy output The three exercises described at the end of Appendix B, Hardware & Software Basics, illustrate some of these issues

Hardware and Software: Humour Blackberry – PDA Orange – phone company in the UK http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k. AG 39 j. Ki 0 l. I
6b6e415b2a7eaac4725c8638a8d04c52.ppt