699262541495a01d6115558697f4e3fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
BUREAUCRACY Bureaucracy Staffing the Bureaucracy Modern Attempts at Bureaucratic Reform Iron Triangles

Article II, Section 2, Clause 1 The President. . . may require the Opinion, in writing, of the principle Officer in each of the executive Departments, upon any subject relating to the Duties of their respective Office.

What is a Bureaucracy? n Large, complex organization Appointed not elected directors n Hundreds government agencies n System of departments & divisions n Key factors n Hierarchy of command: top→bottom n Specialized division of labor n n. Expertise, experience Clear lines of authority, goals, rules n Merit based hiring and promotion n

Constitutionally, executive branch is responsible for enforcement of legislation n Congress controls overall organization n Can create n Can destroy n n Founding Fathers had little to say about executive branch agencies. Take direction from legislative n Directors appointed by executive. n

n Constitutional Convention Debates did not include references to an administrative system n Discussed the procedure for selecting heads of necessary departments n Constitution silent on subject of bureaucracy. n System functions independently of President – Congress controls overall organization n

Tradition of Bureaucratic Depts. n George Washington created cabinet 4 positions n State, war, treasury, Attorney General n Employees drawn from upper class, white male elite n n Andrew Jackson 1829 – Spoils system Reward for party loyalty n Provide participation for middle and lower classes n Allowed for little knowledge, background, merit n

HISTORY TRANSFORMED FROM SPOIL SYSTEM TO A MERIT SYSTEM – 1883 PENDLETON ACT n TENDENCY TO GROW DURING TIMES OF WAR / CRISIS n MARKED GROWTH DURING GREAT DEPRESSION (NEW DEAL) n REGULATION OF CIVIL SERVANTS HATCH ACT / PENDELTON ACTS n

Pendleton Act Civil Service Reform Act 1883 n 1881 Pres. Garfield assassinated by disgruntled office worker n Set up beginning of a merit system n Civil Service Commission n Supervises testing to evaluate candidates n 10% employment at beginning n 1950’s – 90% employment hired n

n 1978 – Civil Service Commission split n Office of Personnel Management • Administers exam, rules, regulations etc. • Sets up general schedule rating GS – salary • Senior Executive Service for top salaries and employees who can be moved between agencies n The Merit System Protection Board • Responsible for integrity of merit system
Public Perception of Bureaucracies Impersonal n Inclined to follow rigid or complex procedures n May stifle effectiveness and innovation n “red tape” – maze Of government regs n gridlock n

American Bureaucracy Own distinctive characteristics n 1. Divided supervision – 2 masters n Congress power to create, organize, destroy n President has constitutional authority to supervise / administer n Political authority is shared – encourages bureaucrats to play one against the other n n 2. Federalism: most agencies have counterparts at the state & local level

n 3. Close public scrutiny Transparency in US n ½ cases that go to federal court involve US government as either plaintiff or defendant n n 4. Regulation of enterprises rather than public ownership n Do not own large parts of the economy

What is the Federal Bureaucracy? http: //www. opm. gov/policy-data-oversight/data-analysis-documentation/federal-employment-reports/historical-tables/totalgovernment-employment-since-1962/ n 4. 2 million employees n n 2. 7 million - civilians or “civil servants” President only appoints ~ 3% 15 cabinet level departments n 200+ independent agencies n n Biggest / Smallest Department n Defense • 742, 000 civilian • 1. 3 military n Education – 5, 000

What are the functions of the Federal Bureaucracy? 1. Implementation Carry out laws of Congress, exective orders of the President 2. Administration routine administrative work; provide services Social Security Admin - sends checks 3. Regulation Munn v IL 1877 Issue rules and regulations that impact public EPA - sets clean air standards

How is the Federal Bureaucracy Organized? Consists of: 1. Cabinet Departments 2. Independent Executive Agencies 3. Independent Regulatory Commissions 4. Government Corporations
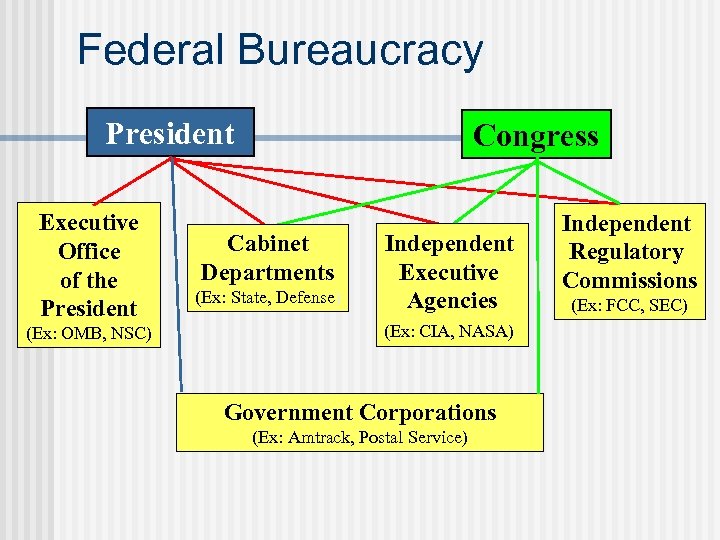
Federal Bureaucracy President Executive Office of the President (Ex: OMB, NSC) Congress Cabinet Departments (Ex: State, Defense) Independent Executive Agencies (Ex: CIA, NASA) Government Corporations (Ex: Amtrack, Postal Service) Independent Regulatory Commissions (Ex: FCC, SEC)

Executive Office of the President (EOP) - 1939 White House Office - Chief of Staff n President’s closest advisors n Reorganized with each administration n Office of Mgt and Budget n National Security Advisors n Council of Eco Advisors n Office of National Drug Control n Faith Based Community Initiatives-Bush-expand private efforts to combat drugs, homelessness etc. n

n Office of Homeland Security n n Newest job - keep president informed of all efforts being made to protect the country from terrorism National Security Council n VP, Sec of State, Defense, Dir CIA, Joint Chiefs, - advises Pres on domestic, foreign & military matters related to national security n CIA does most of work at the discretion of NSC ex: sold arms to Iran, used $ to aid Contra rebels in Nicaragua despite Congressional prohibition - Iran/Contra Scandal

The Cabinet Departments 15 departments - Created by Congress n Headed by cabinet Secretary (except Justice - Attorney General) n Appointed by Pres. , confirmed by Senate n Department head n Advisor to President n In line for Pres. Succession n n 60% of the workforce

Independent Executive Agencies Established by Congress n Resemble cabinet dept n n Narrower area of responsibility Given a specific mandate and generally perform a service function n Not part of any cabinet department n Ex: CIA, NASA, EPA, Social Security Ad n n EPA – part of president’s formal cabinet.

Independent Regulatory Commissions Created by Congress n Exist to regulate a specific economic activity or interest n n FCC, Federal Reserve Board, SEC Operate independently from Congress and the Pres. n Once appointed and seated, cannot be removed without cause. n

Government Corporations Government owned businesses n Created by Congress n May or may not be profitable n Services a public need that could be provided by private business. n Ex: Postal Service, Amtrak, Tennessee Valley Authority, PBS n

Who are the “Bureaucrats? ” 97% are career government employees n Only 10% live in the D. C. area n 30% work for the D. O. D. n Less than 15% work for social welfare agencies n Most are white collar workers: secretaries, clerks, lawyers, inspectors & engineers n Civil employees more diverse demographically than Congress n

Appointees /Civil Servants n Appointed positions considered “political plums” Often go to politically well connected n Listed in the Policy and Supporting Positions or the Plum Book n n Rest of the employees belong to the civil service n Obtain jobs through a formal process

Appointees Suggestions solicited from politicians, businesspersons and other prominent individuals n Often a way for president to pay off outstanding political debts n Ambassadorships often used to reward individuals for their campaign contributions n All appointments have to be confirmed by the Senate n

Appointment errors n Michael Brown to head FEMA • No experience in emergency planning and relief efforts n George C. Deutsch to head NASA • Did not graduate from Texas A&M as he had indicated on his résumé

Political Appointees Average term of service is less than two years n Many appointees are figureheads n Civil servants who occupy permanent staff may not feel compelled to carry out their directives n • Know they will not be around long

Civil Servants 97% are career government employees who work in the executive branch n Most are white collar workers: secretaries, clerks, lawyers & engineers n Pendleton Act: employees are selected by merit standards n Tests n Educational criteria n Prevents employees from being fired for political reasons n

Merit System and the Hatch Act n Merit system n n Hatch Act - 1939 n n Best qualified hired Party politics involvement limited Government employees can’t wear campaign buttons At work n Wearing a uniform n Driving government vehicle n

Difficult to discharge n Fewer than. 01% of federal employees have been fired for incompetence n Prevents implementation of dramatic change n How to fire a bureaucrat p. 323 table 9. 2 • Easier to fire for misconduct than for incompetence

How Bureaucrats Work Not elected officials n Usually outlast the president who so heavily dictates public policy n Since their department, agency, commission etc. are created by Congress, their decisions have the authority of law n Discretionary power to make policies and choose actions that are not spelled out in advance by laws n

Accountability Criticism of merit-based – no accountability n Do not lose job with new president n Suggestions for accountability n Limiting appointment to 6 -12 years, need to be re-examined n Easier to fire n Rotate professionals between agencies n

Who supervises the Federal bureaucracy? n President: Appoints and removes agency heads n Reorganize n Issue executive orders n Reduce an agency’s budget n

n Congress: Create or abolish agencies/departments n Cut or reduce funding n Investigate agency activities n Hold committee hearings n Pass legislation that alters agency functions n Influence or fail to confirm presidential appointments n

n Federal Courts: n Judicial review - rule whether the agency acted within the law n Provide due process for individual affected by a bureaucratic action
The real power in the Federal Government? - 4 th branch

Thinking Critically 1. Why is the federal bureaucracy often referred to as “the fourth branch? ” 2. Some critics believe that the real power in the federal government lies with the federal bureaucracy. To what extent do you believe this is true?

Modern Attempts at Bureaucratic Reform

Sunshine Laws before 9/11 n 1976 n All - Sunshine Act agencies headed by committee hold their meetings in public n Exception: court proceedings personnel problems n Sunshine laws exist at all levels of govt.

Sunshine Laws after 9/11 Since 9/11 trend towards less information disclosed n Within weeks of 9/11 thousands of documents were removed from Internet by federal agencies n Diagrams of power plants n Structural details on dams n Safety plans for chemical plants n

n Military, FBI restricted info. regarding current and planned activities n Once people begin to feel safe, will take agencies to court demanding access to the information - re-impose the Sunshine Laws

Sunset Laws requiring that existing programs be reviewed regularly for their effectiveness and be terminated unless specifically extended as a result of these reviews. n Congress must reauthorize the program or it would be terminated - its sun would set n Most laws do not have sunset clauses; in such cases, the law goes on indefinitely. n

National Performance Review n Al Gore 1994 Horrors of red tape n Called for less centralized management n More employee initiative n Fewer rules n Emphasis on customer satisfaction n n As of 2008 Few recommendations have been followed n Change is difficult – two masters n

Benefits of a Bureaucracy Effective for large groups of people n Reduction of conflicts over who makes decisions n Job specialization: promotes focus on one job n n Gain mastery of specialized skill

Downside of a Bureaucracy n Red tape: procedures or outcomes? ? Complex rules and procedures n All parts of organization must work together n Result of bigness n n Conflict Agencies that work at cross purposes n Agriculture research service tells farmers how to grow crops more efficiently n Agricultural stabilization & Conservation service pays framers to grow fewer crops n

n Duplication n n Custom Service & DEA both attempt to intercept illegally smuggled drugs Imperialism – unchecked growth Tendency of agency to grow without regard to benefits provided or cost incurred n Seek vague goals, receive vague mandates, n • Take the broadest possible view of their power • Dept. Trans. Required wheelchair lifts on all buses

n Waste n Agency spends more than is necessary to buy some product or service • $300. 00 hammer purchased by the military n n What is the motivation to keep the costs down? Accountability Difficulty in firing or demoting incompetent workers p. 323 n Oversight difficulty – size, structure, complexity n

Privatization Replacement of government services by private sector n Successful on local level n Trash collection n Snow removal n n US Defense Dept contracted out many services in Iraq and Afghanistan

Cost savings through E-government Improved efficiency with which government agencies deliver services to public n Web-sites to deliver information to public n 2003: federal agencies are required by the Government Paperwork Elimination Act to use electronic commerce whenever it is practical n

Whistleblowers Someone who brings to public attention gross governmental inefficiency or an illegal action n 1978 Civil Service Reform Act n n n Prohibits reprisals 1989 Whistle-Blower Protection Act n Established commission responsible for investigating complains and reprisals
Iron Triangles n When competing interests are in agreement, Political Scientists call this an IRON TRIANGLE n Bureaucratic Agency forms ties with Interest Groups who form ties with Legislative Committees n EXAMPLE: Tennessee Valley Authority n n Created in 1933 GOAL: Cheap electric power for economic development in Tennessee
Ex: Defense Policy n 1. Department of Defense - Bureaucratic agency n 2. Defense Contractors - Interest Groups n 3. House & Senate Armed Services Committees

Ex: Transportation Policy n Congress: Transportation Committee n Bureaucracy: Department of Transportation n Interest Groups: Truckers Union, AAA
EXCHANGES n Bureaucratic Agency Interest Groups n n n Information regarding enforcement of laws Share research process, findings Access Enforcement support Bureaucratic Agency Congress Comm. n n Budgetary support Informed about issues being discussed Access to leg process Enforcement support

n Congress Comm. Interest Groups Tailoring legislation n Access to legislative arena n Keeping each other informed n Electoral support n Campaign contributions n

n Create your own Iron Triangle n Follow instructions on work sheet n Use pages 328, 251, 585 to help you get started.
699262541495a01d6115558697f4e3fa.ppt