e9ff7958824580c2ec3505ae2c8617d6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Building success into a hightech start-up Feature by J T Preston -who has helped start nearly 100 companies as an enterprenuer, venture investor, and director of technology development and licensing at the MIT

Brief introduction • Technology based entrepreneur needs more 1. 2. than an innovative product, typically requires Right attitude , people and actions make a bigger contribution than a novel idea Series of actions from securing patents to moving high quality product to market quickly

ATTITUDES • MIT’s Hoo-min Toong helped pioneer the personal • • computers and on advisory board of IBM and his student Mitch Kapor was on developing 1 -2 -3 IBM refused to take exclusive license after repetitive suggestions and had to purchase Lotus company for $3. 5 billion Its because of old way of thinking, IBM missed an opportunity to take advantage of a radical innovation that was offered to it

Cont… • Other famous example was of short sightedness of • Goliath Corporation president who refused to buy telephone patent for $100, 000 and describing it as a “scientific curiosity” that would never has practical use Many examples of market leaders trying to sabotage the radical innovations. Eg: safety of alternating current, an innovation of George Westinghouse was discredited by Edison, who used alternating current for electric chair

Management teams • Too many innovators underestimate the need for • • excellent management team and acc. to author firstrate management team with average technology is better than first-rate technology with second rate management team Entrepreneurial behavior succeeds more often when performed in teams and it is not an individual behavior Success increases dramatically with team size until you get up to four or five entrepreneurs with complementary skills to perform better

Passionate behavior • • i. iii. iv. People who lack passion often use the first barrier they encounter as an excuse for failure and high passion people will do whatever it takes to overcome those barriers What we achieve in life depends on a number of things how hard we work How smart we work How much leverage we have on the work How much courage we have in pursuing goals

Cont… • How hard we work is tied to how passionate we are • Wide shareholder ownership is one of the best ways • • to stimulate passionate behavior because they no longer behave like employees but like owners Eg: pilot, co-pilot and flight attendant of southwest airlines which has high percentage of employee ownership, clean up trash to save money on cleaning crew Share credit for success also improves passion

Investors • Quality of investors and the pace at which money • • • flows into the company are keys to determining its success Besides cash investors can also provide significant leverage in success Companies that have investors with “deep pockets” will succeed more often Eg: Venrock which invests Rockefeller family money is most successful vanture capital firm, in part because it has incredibly deep pockets and has staying power to help ensure the success of companies in which it invests

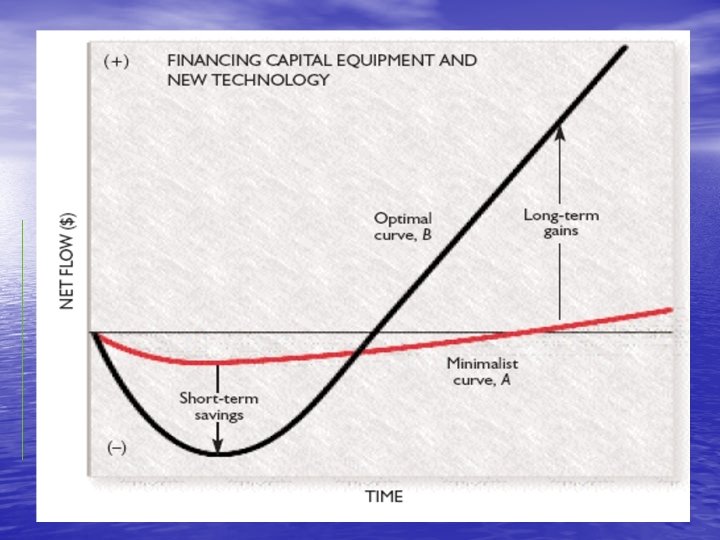
Investment timing • There are two different investment scenarios, with a net flow of money as a function of time i. Putting small amounts of money over long period of time ii. Aggressive entering and capturing the market in small time Cons of first strategy a. Management often spends toomuch time raising money instead of building business b. Wide window of opportunity for competitor

Cont… • The second one is optimal curve to make more • • money in the short term using fewer assets and for share holders point of view The entrepreneurs with too much money might end up with ‘taj mahal syndrome’, fancy tomb of their business The extravagant spending often increases overhead costs and makes the company less competitive

Series of actions • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Once company is organized and financed, it must also pursue a course of action Intellectual property Speed of innovation Time to market Flexibilty Location and clusters Risk tolerance

Intellectual property • It is important to consider intellectual property • • protection at the founding of the company If you do not have strong intellectual property position, others might simply appropriate your technology Strong patent position will solve potential partner and financial problems

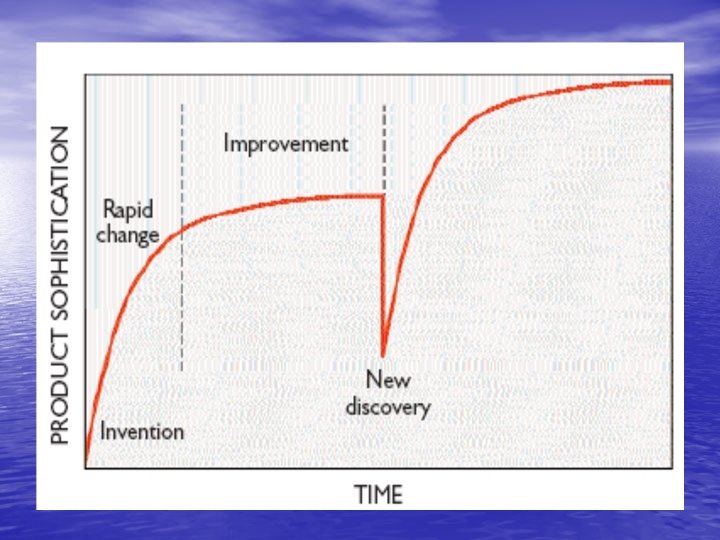
Speed of innovation • Innovations go through cycles in which there is • • • typically period of rapid discovery followed by incremental improvement This cyclical trend repeats itself improvements should be built in to manufacturing effectively Eg: invention of transistor by willium shackley in bell lab till invention of integrated circuits Competition between US and Japan

Time to market • The time at which your product reaches the • • • marketplace may determine its success and failure Clearly speed to market is major factor in determining product profitability & success Reaching the market either six months earlier or six months later increased or decreased, respectively, a products lifetime profits by one third Eg: intel chips in series released in 2 years gap

Flexibility • Managers must create rules with caution • • because they might inhibit innovation and old rules should be reviewed periodically to make sure they are still constructive Lack flexibility inhibits developing innovative technologies Eg: early and wide adoption of internet in US and late adoption in japan

Clusters give an edge • A business should be located close to your • • fierce competitor or close to your most demanding customer That way gain from advantages created by the cluster of companies that have complementary and competitive skill set would be high eg: labour pool, vendors, investors, customers, etc Eg: cut flower business in Netherlands

Risk tolerance • The only people who never experience failure are • • those who never push the envelop of what mankind is capable of doing. The risk tolerance among individuals should be encouraged Many cultures which have stigma for success, conceals success from public eye and fails to create role models for young would-be entrepreneurs Eg: stigma for failure is less in US and result is best and brightest gravitate towards start-ups
e9ff7958824580c2ec3505ae2c8617d6.ppt