613eff15c8e1185bbadea72a94b9e620.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64

Building Retirement for Business Owners and Their Key Employees Brought to you by the Advanced Consulting Group of Nationwide® A 2 hr Continuing Education (C. E. ) presentation Nationwide, the Nationwide N and Eagle, Nationwide is on your side and other marks displayed in this presentation are service marks of Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company or its affiliates, unless otherwise disclosed. © 2016 Nationwide

Some things you need to know • • 2 The information contained herein was prepared to support the promotion, marketing and/or sale of life insurance contract, annuity contracts and/or other products and services provided by Nationwide life Insurance Company. Federal tax laws are complex and subject to change. Neither the company nor its representatives give legal or tax advice. Please talk with your attorney or tax advisor for answers to your specific questions. Life insurance is issued by Nationwide Life Insurance Company or Nationwide Life and Annuity Insurance Company, Columbus, Ohio, member of Nationwide®. The general distributor for variable insurance products is Nationwide Investment Services Corporation, member FINRA. © 2016 Nationwide NFM-9447 AO. 5 (10/16) APPROVED FOR PUBLIC USE 2

Agenda • Qualified plans • Nonqualified Deferred Compensation • Insurance Based Income Solution • IBIS for the Business Owner • IBIS for Key Non Owner Employees 3 3

Qualified plans • The first alternative • Advantages o Current tax deduction o Tax deferred growth • Disadvantages o Broad participation o Administrative expenses o Benefits taxable 4 4

Qualified Plan Excuses & Complaints • • 5 Cost Insufficient participation Contribution limits Business owner wants to cover only self 5

Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plans Advantages • • • 6 Flexible design Discriminatory No contribution limits Effective golden handcuff Pre-tax investing for nonowner Funded with COLI 6

Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan Drawbacks • • 7 Unsecured promise to pay Creditors’ claims In line with general creditors No current tax deduction 7

Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plan- for the Business Owner • • • Vesting schedules unnecessary Double taxation Business owner taxed on contributions Retirement triggers buy out Taxed again o C or S Corp – when benefits received o LLC/Partnership – included with final capital distribution 8 8

Conclusion • For the Business Owner, Qualified & Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plans Have Serious Limitations 9 9

Other Ways to Build for Retirement • Stocks & Bonds o Dividends & appreciation but current taxation • Mutual Funds & ETFs o Dividends & appreciation but current taxation • Annuities o Tax deferred growth but all ordinary income o Income in respect of a decedent 10 *Investing involves risk, including possible loss of principal. 10

Other Ways to Build for Retirement • IRAs o May be tax deductible but ordinary income o Contribution limits • Roth IRAs o Tax free income but contribution limits 11 11

Another Solution Insurance Based Income Solution 12 12

What is an Insurance Based Income Solution? • A combination of: o the death benefit of life insurance to protect the client’s family o with the tax preferences of life insurance to potentially invest and supplement retirement income in a tax efficient manner • Based on a life insurance policy o Personally owned – owned outside the business o Not a Modified Endowment Contract (non MEC) o Not a kind of a life insurance policy – a way to use one 13 13

What is an Insurance Based Income Solution? • Designed around cash accumulation life insurance • Provides supplemental retirement income • Universal life effective vehicle o o Non MEC Withdrawals to recover cost basis Borrow thereafter Cash flow is tax-free as long as policy in force • Income tax-free death benefit o Repays loans – converting loans to tax free income o Balance to personal beneficiaries (estate taxes may apply if estate and trust planning has not been done) 14 14

Client Profile for Universal Life • Needs life insurance • Would be interested in o Flexible death benefit o Lack of contribution limitations • Can overfund policy but avoid MEC status • Consistent with underwriting offer o Investing tax-preferred o Tax-deferred accumulation o Tax-preferred access to policy values 15 15

Maximum Funding • An IBIS is based on a dual need o Life insurance for the family o Vehicle for tax-preferred investing • IBISs work best when maximum funded o Provides more funds for highs and lows of market o Minimizes mortality costs • Two ways to plan maximum funding o Choose a death benefit, pay maximum premium o Choose a premium, solve for minimum death benefit that meets client’s needs 16 16

Typical IBIS Scenario • Policy owned by insured • Maximum non-MEC premium o 15 – 20 years • In retirement o Recover cost basis through policy withdrawals o Switch to loans o Keep policy in force until death • Death benefit repays loans o Balance to beneficiaries 17 17
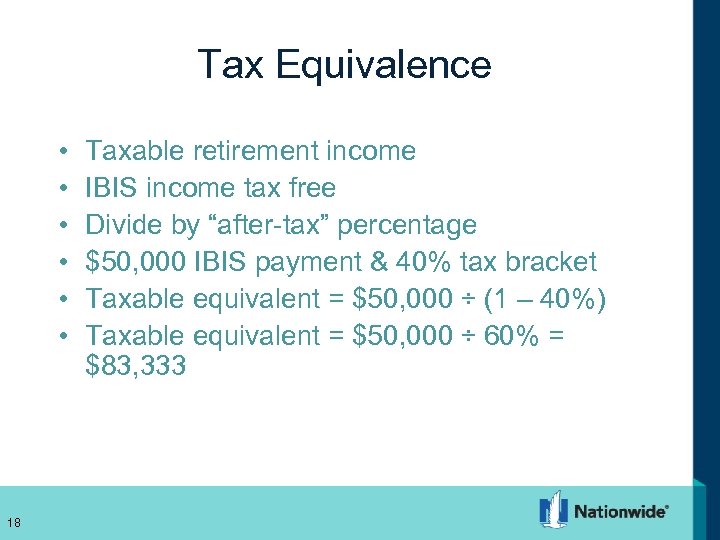
Tax Equivalence • • • 18 Taxable retirement income IBIS income tax free Divide by “after-tax” percentage $50, 000 IBIS payment & 40% tax bracket Taxable equivalent = $50, 000 ÷ (1 – 40%) Taxable equivalent = $50, 000 ÷ 60% = $83, 333 18
Universal Life Variations • Cash accumulation/Current assumption • Indexed • Variable 19 19
Cash Accumulation / Current Assumption UL • Guaranteed minimum crediting rate • Premiums invested o High grade bonds o Mortgages • Interest crediting rate adjusted for changes in investment portfolio yield, etc. • Surrender value enhancement • Conservative people • Overloan protection rider 20 20
Indexed Universal Life • Not a security • Crediting rates adjusted for increases in stock market indexes • Choose the index • No risk of loss of principal • Participation rate • Cap rate • Wash loan provisions • Overloan protection riders 21 21
Variable Universal Life Features • Permits investment in equity-based subaccounts • No tax due when switching sub-accounts • No tax due on dividends, interest, or trading gains • No tax due on annual cash value growth • Sub-account reallocations without charge o Subject to limitations in prospectus 22 22

Variable Universal Life Features • Cash value not subject to creditors of insurance company • Wash loans • Overloan protection riders* • Buy term and invest the difference 23 *Riders are offered at an additional cost and may not be available in all states. A life insurance or annuity purchase should be based on the life insurance or annuity contract, and not optional riders or features. The cost of an option may exceed the actual benefit paid under the option. 23

Variable Universal Life Suitability • Willing to invest for the long haul 15 – 20 years • Wants market opportunity through investment in fixed and variable subaccounts • Accepts risk of loss of principal • Understands market volatility of subaccount investments 24 24

Limitations of using Universal Life • Insurable with reasonable health • Variable UL – Loss of principal • Additional funds may be required when not properly funded • Income may be higher or lower than illustrated, depending on market performance • Loans taken from the policy, when policy lapses before death, will be taxable o Overloan Protection Rider 25 25

Nine Layers of Tax Insulation Income from IBIS is free from • • • 26 Federal Income Tax State Income Tax Local Income Tax Capital Gains Tax FICA/Social Security Tax Supplemental Medicare Tax No effect on Alternative Minimum Tax No effect on taxation of Soc Sec benefits No Net Investment Income Tax(Medicare) 26

Client Profile for IBIS • • • Who is a Potential Client for an IBIS? Age 35 -55 High income individuals with cash flow Comfortable with equity or market exposure Believe in long-term investing Executives who have maximized qualified plans but wish to invest more • Clients who want tax preferences without the restrictions of qualified plans • Business owners without access to qualified plans (plan for self) • Business owners wanting to provide additional benefits to executives 27 27

This concludes IBISs Questions? 28 28

Funding the IBIS for the Business Owner • Individually owned policy • Goal o Get the money out of the business o For the benefit of the business owner o In the most tax efficient manner 29 29

Depends on the Form of Business Organization • • • C Corporation S Corporation Partnership Sole proprietorship Limited Liability Companies o Elect taxation o C Corp, S Corp, Partnership or Sole Proprietorship 30 30

C Corporation Owner Planning: Executive Bonus • • A raise in pay Income tax withholding Payroll taxes Simplicity o Usually double bonus o Additional comp = premium / (1 – max tax rate) • Favorable tax leverage • Avoids double taxation o Reasonable compensation • 1099 not available 31 31

C Corporation Owner Planning: Dividends • • Double taxation may work Pay corporate income tax @ 15% Pay dividend from after-tax profits Taxed like Long Term Capital Gain – up to 20% No Social Security Tax Maybe Medicare Tax on NII Requires 15% bracket for C Corp and at least 35% bracket for owner • May not work for multiple owners 32 32

C Corporation Review • Probably Executive Bonus – additional compensation • Maybe a dividend 33 33

S Corporation Owner Executive Bonus? • Raise in pay • IT’S DEDUCTIBLE!! • Probably doesn’t work o No income tax advantage o Additional payroll taxes 34 34
Hypothetical The following case studies are hypothetical and are not meant to portray a particular client or client situation. All references to rates of return are provided in order to demonstrate mathematical concepts and are not a projection or prediction of future returns, nor do they represent the returns of any specific investment. Life insurance death benefits used in these hypothetical situations are subject to the claims paying ability of the issuing company. 35 35

S Corporation Owner Executive Bonus Example No Bonus With Bonus Taxable Income before owner’s compensation 500, 000 Less owner’s wages 200, 000 400, 000 Taxable income of S Corp 300, 000 100, 000 Wages 200, 000 400, 000 Profit from S Corp 300, 000 100, 000 Owner’s taxable income 500, 000 Owner’s income tax return Additional Medicare Tax = $200, 000 X 3. 8% = $7600 36 36

S Corporation Distributions • • • The solution Profits taxed when earned Not taxed when actually withdrawn No payroll tax on distributions Owners do it all the time o To pay tax on S Corp profits o Limit Social Security Tax • Multiple owners – may force combination 37 37

Partnerships • Partners cannot be employees • No Executive Bonus • What to do? 38 38

Partnerships – The Solution • Withdraw from Capital Account • Comparable to S Corp Distributions – Not deductible – Taxable income unaffected – Not deductible, but – Generally no additional income tax 39 39

Sole Proprietorships • Single owner • Owner not an employee – No Executive Bonus • Draws – Withdrawals of owner’s capital – Not taxable, not deductible 40 40

Funding the IBIS for Business Owners • C Corporation owners – Executive bonus → likely – Dividends → maybe – run the numbers • S Corporation owners – Executive bonus → unlikely – S Corp dist. → probable 41 41

Funding the IBIS for Business Owners • Partnerships o Capital withdrawals • Sole proprietorships o Draws 42 42

This concludes Business Owners Questions? 43 43

Key Non-Owner Executives Different Considerations Golden Handcuffs 44 44

NQDC Plan Candidate • Stable Business o Profits o Cash flow • • • 45 Executives/HCEs Willing to take longer view Retention more important than taxes Effective plan for right employer Supplement qualified plan contributions 45

NQDC Plan Difficulties • Employer not a candidate o o Business too young Business too small Unstable profit & cash flow Candidates not comfortable • Unsecured promise to pay o Expensive documentation and administration o Wants income tax deduction 46 46

Which brings us back to Insurance Based Income Solution 47 47

Funding the IBIS for Key Non Owner Employees • Split Dollar o Collateral Assignment/Loan Regime o Endorsement/Economic Benefit Regime • Executive Bonus • Restrictive Executive Bonus Arrangement (REBA) 48 48

Split Dollar: Collateral Assignment/Loan Regime • Effective fringe benefit • • o Low cost life insurance o Golden handcuff Employer loans premiums Employee owns policy/collateral assignment Employee taxed on interest free element of loan Employee taxation & employer deduction if loans forgiven • Documentation & significant administration • Covered by 409 A if employer promises to forgive loan 49 49

Split Dollar: Endorsement/ Economic Benefit Regime • Effective fringe benefit • • • o Low cost life insurance o Golden handcuff Employer owns policy Employee names beneficiary Employee taxed on value of insurance coverage Employee taxation for FMV if policy transferred Employer deduction for premiums if policy transferred • Documentation & significant administration • 101(j) & possible 409 A 50 50

Executive Bonus • • • 51 Effective fringe benefit Section 162 Plan A raise in pay Payroll and income tax withholding Employee owns policy Current tax deduction 51

Executive Bonus • Pro o Very simple o Minimal documentation o Current tax deduction • Con o Little “retain” incentive o Little golden handcuff • Loyal employee 52 52

Restrictive Executive Bonus Arrangement The simple Golden Handcuff • • • A raise in pay – additional compensation Payroll and income tax withholding Employee owns policy Current tax deduction Reasonable compensation Some written documentation o o 53 Repayment obligation Restrictive endorsement 53

Repayment Obligation • First element of Golden Handcuff • Repayment obligation o Employee repays some or all of the additional compensation o Time bound – expires at a future date o No collateral assignment • Design flexibility o Employer & Employee can negotiate 54 54

Restrictive Endorsement • Second element of Golden Handcuff • Employee can change beneficiary • Access to policy values requires employer’s signature • Time bound o Expires at a future date o Usually coordinated w/expiration of repayment obligation 55 55

Flexibility in Designing Repayment Obligation • • • 56 5 year graded or cliff 10 year graded or cliff Graded to retirement Cliff at retirement Whatever ER and EE negotiate Can be modified 56

Tax Considerations • • 57 IRC § 162(a)(1) - Compensation IRC § 264(a)(1) - Indirect beneficiary IRC § 61 – Income IRC § 83 - Risk of forfeiture 57

If Employee Leaves Before Obligation Satisfied? • IRC § 1341, Claim of Right Doctrine o Deductible for employee • IRC § 61 o Taxable income to employer 58 58

Advantages of REBA • • • 59 Current income tax deduction Significant incentive to stay Minimal documentation Employee feels more confident No 409 A issue No 101(j) issue 59

REBA Drawbacks • • No policy ownership for employer No security interest Lack of control – subjective All covered by written agreements o o 60 Nonqualified deferred compensation Collateral assignment split dollar Endorsement Split Dollar Restrictive Executive Bonus Arrangement 60

Conclusion: Funding the IBIS for the Key Non-Owner Employee • Split dollar o Low cost life insurance o Documentation & administration o No current tax deduction for premiums • Executive Bonus o Little incentive to stay o Loyal employee • Restrictive Executive Bonus Arrangement o Tax deductible o Golden handcuff o Employee comfort – employee owns life insurance 61 61

Funding the IBIS for Business Owners • LLCs o Find out how it is taxed • C Corp owners o Executive bonus → likely o Dividends → maybe • S Corporation owners o Executive bonus unlikely o S-Corp distributions (probable) 62 62

Funding the IBIS for Business Owners • Partnerships o Capital withdrawals 63 63

Here when you need us National Sales Desk: ® Nationwide Financial Network : Brokerage General Agents (BGAs): 1 -800 -321 -6064 1 -877 -223 -0795 1 -888 -767 -7373 Option 9, extension: 677 -6500 64 NFM-9447 AO. 5 (10/16) APPROVED FOR USE WITH THE PUBLIC 64
613eff15c8e1185bbadea72a94b9e620.ppt