535c2c5652bc502ce37095b6a07cb49a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS VIA E-MARKETING Dr Ilias Santouridis Assistant Professor of Applied IT TEI of Larissa Greece 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E -Marketing 1

WEAKNESSES OF TRADITIONAL MARKETING w Marketing theory: n n stuck in its ‘futile search for laws, regularities and predictability’, using approaches (e. g. the marketing mix) better suited to marketing’s ‘golden age’ proved very restrictive for industrial and services marketing w Customers are viewed as either: n n manipulation and exploitation targets and passive recipients of messages or one half of a controversial or adversarial relationship 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 2

DEFINING RELATIONSHIP MARKETING (1) w British CIM definition of marketing: n “The management process of identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably” w Early RM definition (Berry, 1983): n “The marketing approach aiming at attracting, maintaining and enhancing customer relationships” 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 3

DEFINING RELATIONSHIP MARKETING (2) w Nonetheless… n n n RM aims at profit and is not guided by altruistic sentiments NOT ALL RELATIONSHIPS ARE PROFITABLE (e. g. research shows that 50% of a retail bank’s customers are unprofitable) Unprofitable customers can be either: De-selected (i. e. dumped) or l Subsidised by profitable customers l 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 4

DEFINING RELATIONSHIP MARKETING (3) w Refined RM definition (Gronroos, 1994): n “The marketing approach aiming to identify and establish, maintain and enhance and, when necessary, terminate relationships with customers and other stakeholders, at a profit so that the objectives of all parties involved are met; and this is done by mutual exchange and fulfillment of promises” 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 5
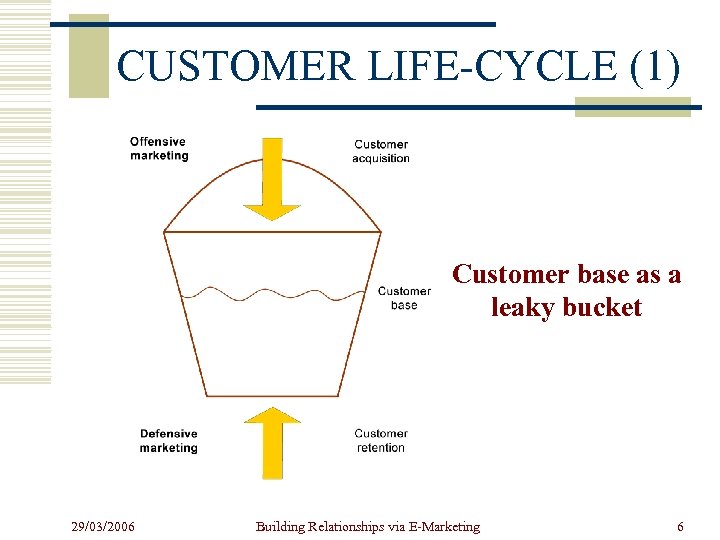
CUSTOMER LIFE-CYCLE (1) Customer base as a leaky bucket 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 6
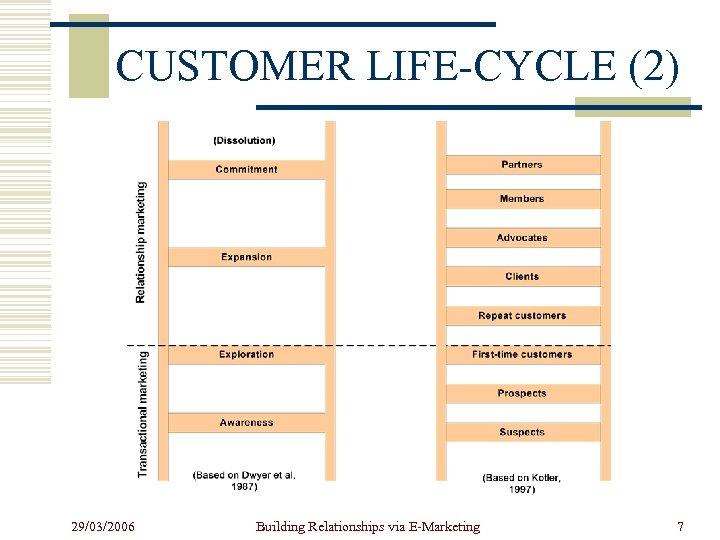
CUSTOMER LIFE-CYCLE (2) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 7
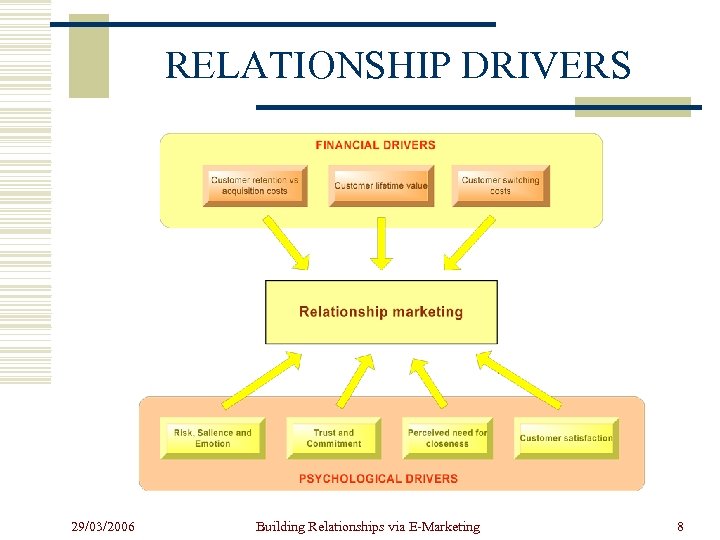
RELATIONSHIP DRIVERS 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 8

KNOWING YOUR CUSTOMER (1) w Not all customers contribute equally to the firm’s profit w The consequences of losing a profitable customer may be very significant, whereas the loss of a nonprofitable customer may be beneficial w Constant effort must be made to calculate: n n The customer’s contribution to the profitability of the relationship The costs of building and maintaining the relationship 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 9
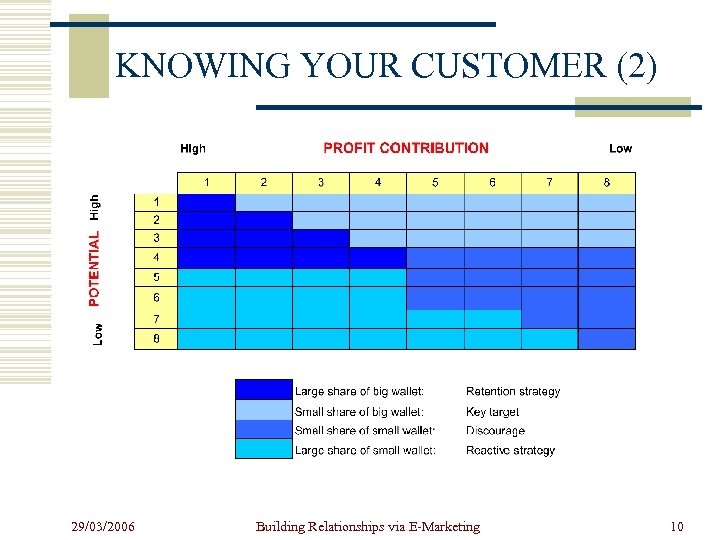
KNOWING YOUR CUSTOMER (2) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 10

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (1) w Firm relationship types: n n Customer partnerships Internal partnerships Supplier partnerships External partnerships 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 11

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (2) CUSTOMER PARTNERSHIPS w Customer – Supplier relationship remains the core issue of RM BUT IT DIFFERS SINCE… w The focus is not on what you can do to your customer but on what you can do for your customer and what you can do with your customer 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 12

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (3) CUSTOMER PARTNERSHIPS w Company prosperity remains the long-term aim of RM w RM strategies as an answer to the shift of balance of power from producer to consumer w Developing relationships with customers may be an effective way of building competitive advantage, since it is difficult to be replicated by competition 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 13

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (4) INTERNAL PARTNERSHIPS w Internal marketing definition: n “A way of enabling an organisation to recruit, motivate and retain customer-conscious employees in order to boost employee retention and customer satisfaction levels” (Clark, 2000) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 14

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (5) INTERNAL PARTNERSHIPS w RM implies empowering the employees and breaking down the organisation’s functional barriers leading to: n n n The generation of organisation-wide market intelligence Dissemination of that intelligence across departments Organisation-wide responsiveness to it 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 15

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (6) SUPPLIER PARTNERSHIPS w Vertical relationships: all or part of the supply chain is integrated through component suppliers, manufacturers, and intermediaries w Horizontal relationships: organisations at the same point in the distribution channel (including competitors) cooperate for mutual benefit 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 16

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (7) SUPPLIER PARTNERSHIPS w Partnering foundation: Partners share proprietary data and processes used in decision making 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 17

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (8) EXTERNAL PARTNERSHIPS w Industry collaborations are formed by competitors from the same market sector w It should be a ‘win-win’ relationship if it is to succeed w The main objectives may include: n n Effectiveness and efficiency of distribution channels Servicing or other support facilities Market sector growth Market sector dominance 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 18

CORE FIRM RELATIONSHIPS (9) EXTERNAL PARTNERSHIPS w External collaborations are formed by firms from different market sectors, bringing different skills, competences and assets w The main objectives may include: n n n To take advantage of a new sector (e. g. web portals owned by media and retail stores) To improve the total package offering (e. g. airlines and car rental companies) To promote existing sector differentiation (e. g. TV companies and football teams) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 19

E-MARKETING SITUATION 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 20

E-MARKETING OBJECTIVES w Sell – using the internet as a sales tool w Serve- using the internet as a customer service tool w Speak – using the internet as a communications tool w Save – using the internet for cost reduction w Sizzle – using the internet as a brand-building tool 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 21
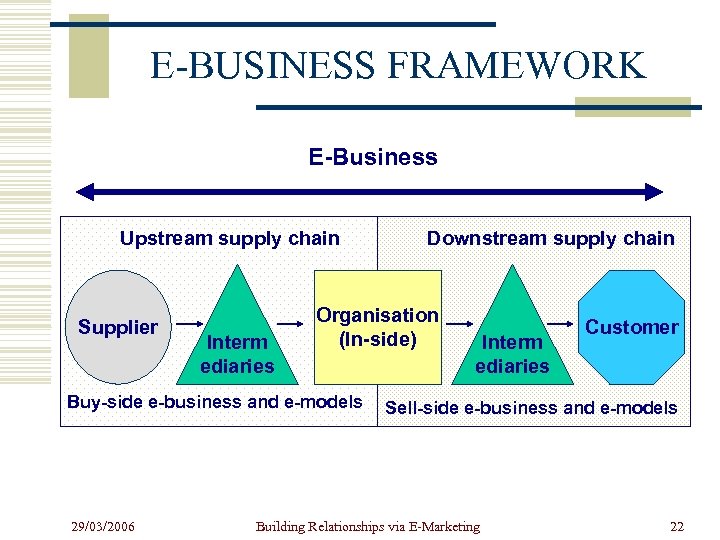
E-BUSINESS FRAMEWORK E-Business Upstream supply chain Supplier Interm ediaries Organisation (In-side) Buy-side e-business and e-models 29/03/2006 Downstream supply chain Interm ediaries Customer Sell-side e-business and e-models Building Relationships via E-Marketing 22

SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (1) w Internet technology can be used to facilitate an organisation in areas such as: n n Purchasing (E-Procurement) In-bound logistics Stock management Re-ordering 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 23

SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (2) w The organisation can create extranets to open up certain aspects of its business to selected suppliers to build an ‘extended enterprise’ w A great facilitator towards that direction is the integration of the partnering organisations IT systems w This sharing of information and goals move the partners from independence to interdependence 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 24
INTERNAL RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (1) w The organisation intranet can: n n Replace cumbersome paper-based systems Create ‘responsive knowledge workers’ Lead to better decisions Support employee ‘just-in-time learning’ processes 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 25
INTERNAL RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (2) w Examples of organisation intranet IT tools: n n n File management systems Document management systems Workflows Timesheet Message boards 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 26

CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (1) w Maintaining online customer relationships is not an easy task: n “That’s what’s so scary about customer retention in the online space. We’ve created this empowered, impatient customer who has a short attention span, a lot of choices, and a low barrier to switching” (Laurie Windham, 2001) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 27
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (2) w The IDIC approach for using the web to form and build relationships with customers (Pepper and Rogers, 1998): 1. 2. 3. 4. 29/03/2006 Customer Identification: identify each customer on their first and subsequent visits Customer Differentiation: build profiles to segment customers Customer Interaction: online interactions (e. g. customer enquiries, tailored product) Customer Communications: personalisation or masscustomization of content or emails according to segmentation Building Relationships via E-Marketing 28
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS E-MODELS (3) w The marketer must continuously measure the success of customer relationship drivers with metrics such as: n n n Order fulfilment: % that ship on time exactly as the customer specified Product performance: frequency of problems experienced by customers Post-sale service and support: % of problems solved on the first visit 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 29

CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (1) w Customer Relationship Management (CRM) definitions: n n n A continuous performance initiative to increase a company’s knowledge of its customers The capabilities of a company to build profitable relationships with loyal customers A system designed to impact your customers so they’ll be satisfied and maintain long relationships with you 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 30

CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (2) w CRM database: a database used to hold analyse customer information, thereby helping create strategies for marketing w A database stores: n n Historical data (e. g. names, addresses, responses to offers, recency, frequency, amount and category of purchases) Predictive data used to indicate customers’ future behaviour (e. g. type of house and business, past behaviour) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 31

CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (3) CAUTION! w Data captured for data’s sake does not make a good database w The important question is : what will you do with the data? w “Without a corresponding marketing programme, database marketing should not be introduced” (Rohner, 2001) 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 32

CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (4) w It is of utmost importance that the database is kept updated and maintains its integrity w Databases can become ‘dirty’ due to: n n n Incorrectly captured data Change of customer information Data duplication 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 33
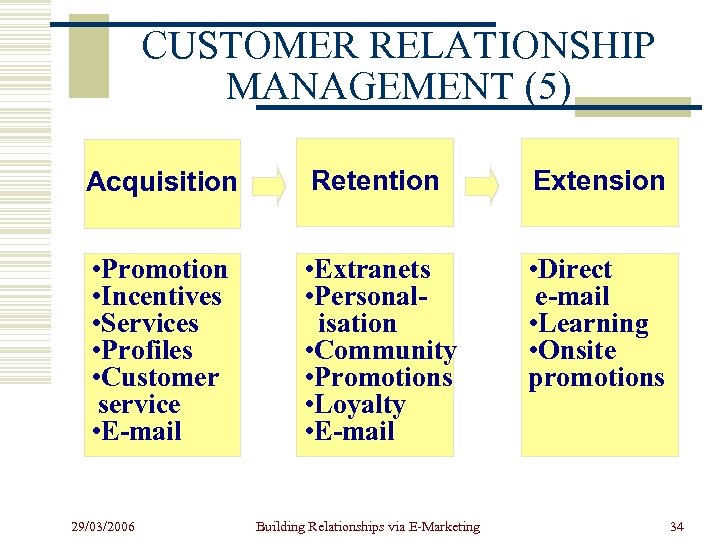
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (5) Acquisition Retention Extension • Promotion • Incentives • Services • Profiles • Customer service • E-mail • Extranets • Personalisation • Community • Promotions • Loyalty • E-mail • Direct e-mail • Learning • Onsite promotions 29/03/2006 Building Relationships via E-Marketing 34
535c2c5652bc502ce37095b6a07cb49a.ppt