f02db60476a56778ae5ab4a77c4a5299.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Building Public Health / Clinical Health Information Exchanges: The Minnesota Experience Marty La. Venture, MPH, Ph. D Director, Center for Health Informatics Minnesota Department of Health
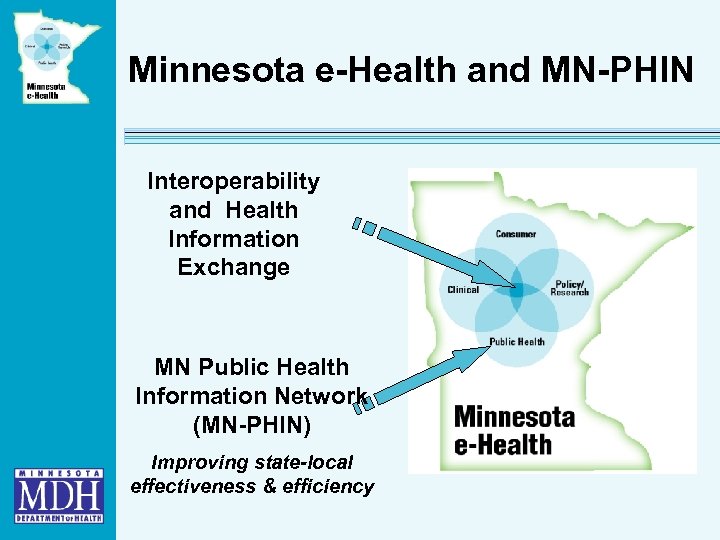
Minnesota e-Health and MN-PHIN Interoperability and Health Information Exchange MN Public Health Information Network (MN-PHIN) Improving state-local effectiveness & efficiency
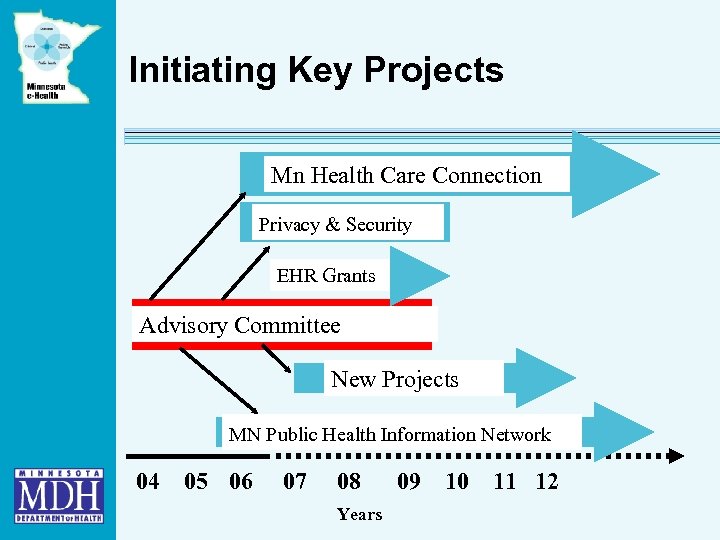
Initiating Key Projects Mn Health Care Connection Privacy & Security EHR Grants Advisory Committee New Projects MN Public Health Information Network 04 05 06 07 08 Years 09 10 11 12
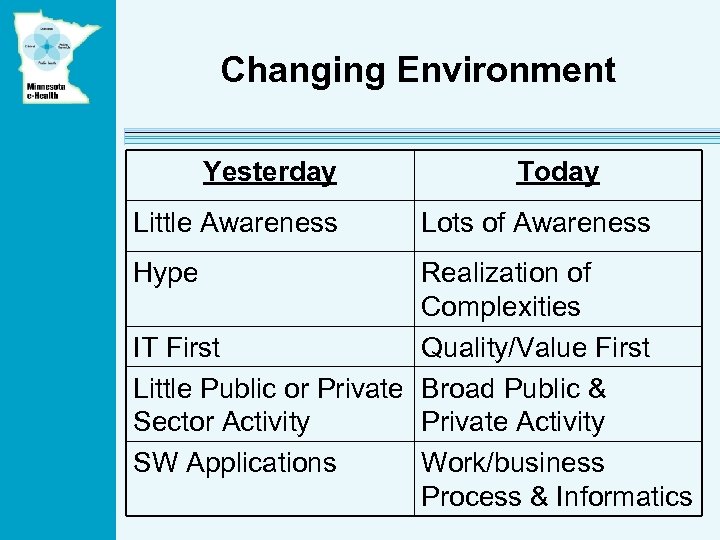
Changing Environment Yesterday Little Awareness Hype Today Lots of Awareness Realization of Complexities IT First Quality/Value First Little Public or Private Broad Public & Sector Activity Private Activity SW Applications Work/business Process & Informatics

The Purpose of MN-PHIN To create … ¬ the infrastructure, the policies and the skilled workforce To improve … ¬ the collection, management, uses, and exchange of timely and accurate data; and ¬ the design, functions and interoperability of public health information systems.

Current MN-PHIN Priorities ¬ Support information system projects of state and local importance ¬ Promote adoption of standards for interoperability and exchange ¬ Communicate knowledge, information and best practices; assess and build informatics capacity ¬ Engage key partners in advancing the strategic application and management of public health information systems.
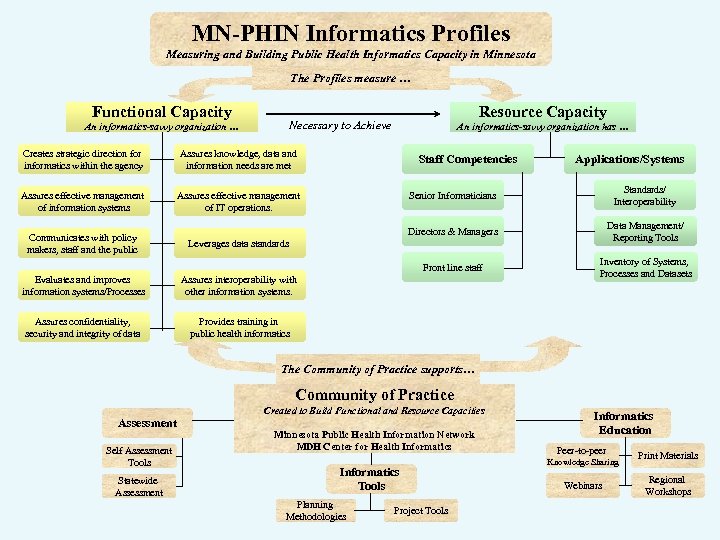
MN-PHIN Informatics Profiles Measuring and Building Public Health Informatics Capacity in Minnesota The Profiles measure … Functional Capacity Resource Capacity Necessary to Achieve An informatics-savvy organization … Creates strategic direction for informatics within the agency Assures knowledge, data and information needs are met Assures effective management of information systems An informatics-savvy organization has … Assures effective management of IT operations. Staff Competencies Applications/Systems Standards/ Interoperability Directors & Managers Data Management/ Reporting Tools Front line staff Communicates with policy makers, staff and the public Senior Informaticians Inventory of Systems, Processes and Datasets Leverages data standards Evaluates and improves information systems/Processes Assures interoperability with other information systems. Assures confidentiality, security and integrity of data Provides training in public health informatics The Community of Practice supports… Community of Practice Created to Build Functional and Resource Capacities Assessment Self Assessment Tools Statewide Assessment Minnesota Public Health Information Network MDH Center for Health Informatics Tools Planning Methodologies Project Tools Informatics Education Peer-to-peer Knowledge Sharing Webinars Print Materials Regional Workshops
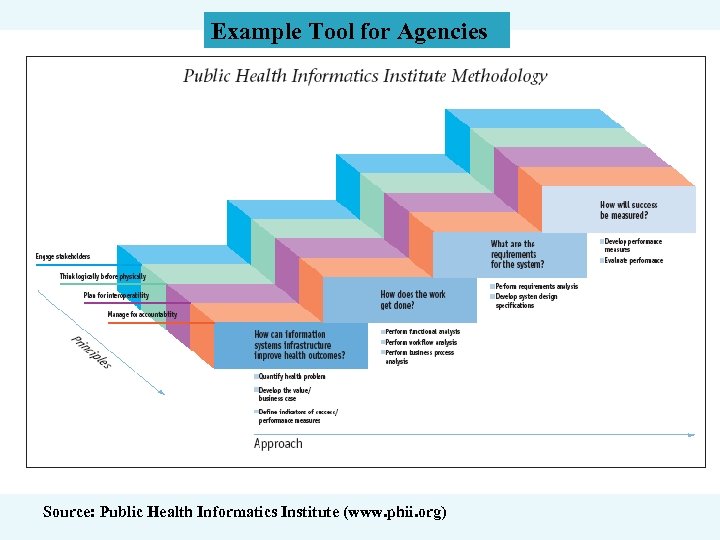
Example Tool for Agencies Source: Public Health Informatics Institute (www. phii. org)

Examples of supporting the Community of Practice “Public Health Data Standards 101”

1. Value Proposition 3. Key Barriers and Challenges • “What are the achieved or anticipated benefits of HIE” • “What are some of the key challenges and barriers? ¬Empower citizens as health/care consumers ¬Ensure all relevant medical information on an individual is securely available to their current physician or to an emergency room ¬Reduce costly inefficiencies within and across health care settings ¬Use health care and public health data to better protect communities against health risks or threats. ¬Improve the safety and quality of health care ¬Data (e-mail) overload / knowledge deficit ¬Assuring rural / underserved needs are met ¬Addressing population health issues ¬Use opportunities for federal/private funding ¬Model for sustainable funding for projects ¬Utilizing expertise state wide 2. Securing “Buy-In” From Stakeholders 4. Key Lessons Learned • “How did you secure buy-in from stakeholders? ” • “ What would you recommend others do? ” ¬Be inclusive of private and public healthcare and public health settings, including LTC ¬Build on a “culture of collaboration” ¬Create broad statewide vision ¬Focus action on visible steps ¬Guide by broad public – private advisory Committee ¬Use a neutral convening body ¬Be consumer focused ¬Establish communities of practice ¬Use endorsing Legislation ¬Gov/t role: neutral convening body, facilitation, assist in measurement, assessment and communications ¬You don’t need “all” the answers today ¬Leading from the “backseat” is OK ¬Plan Broadly, Implement Incrementally ¬Include Public Health from the beginning

Thank You Web Resources ¬ Reports and policy ¬ Directory of projects ¬ Shared tools and templates Minnesota e-Health Initiative www. health. state. mn. us/e-health Martin. laventure@state. mn. us
f02db60476a56778ae5ab4a77c4a5299.ppt