f89512da60e9532344de5a5183bd65af.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
Building Phylogenies
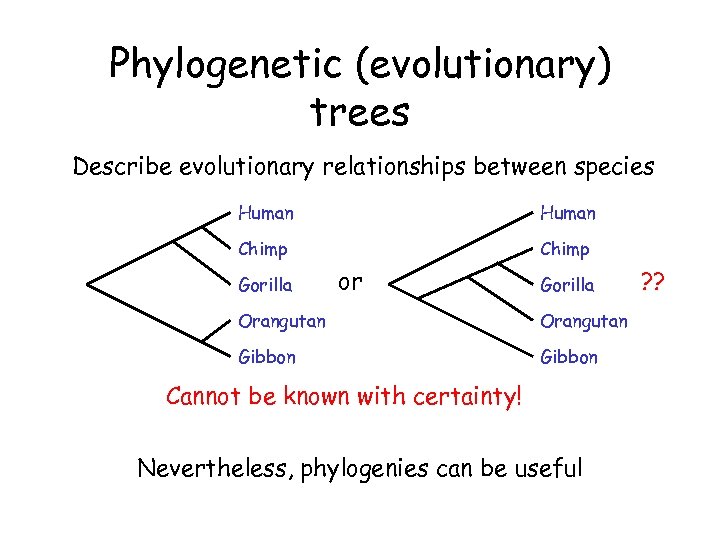
Phylogenetic (evolutionary) trees Describe evolutionary relationships between species Human Chimp Gorilla or Gorilla Orangutan Gibbon Cannot be known with certainty! Nevertheless, phylogenies can be useful ? ?
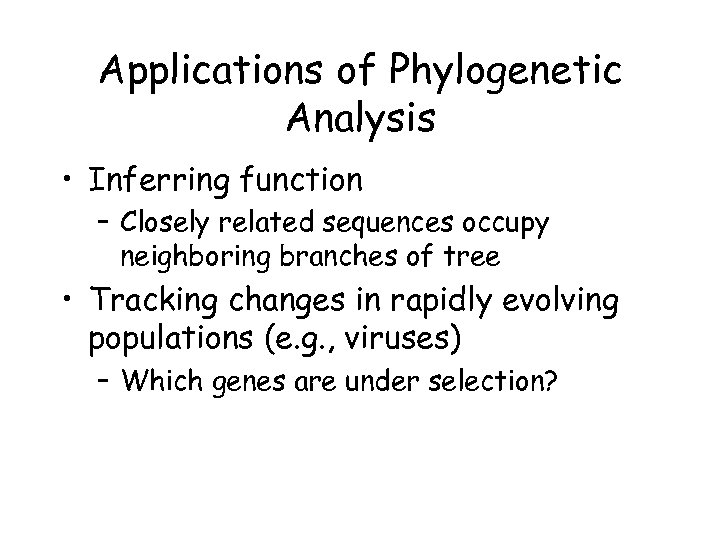
Applications of Phylogenetic Analysis • Inferring function – Closely related sequences occupy neighboring branches of tree • Tracking changes in rapidly evolving populations (e. g. , viruses) – Which genes are under selection?
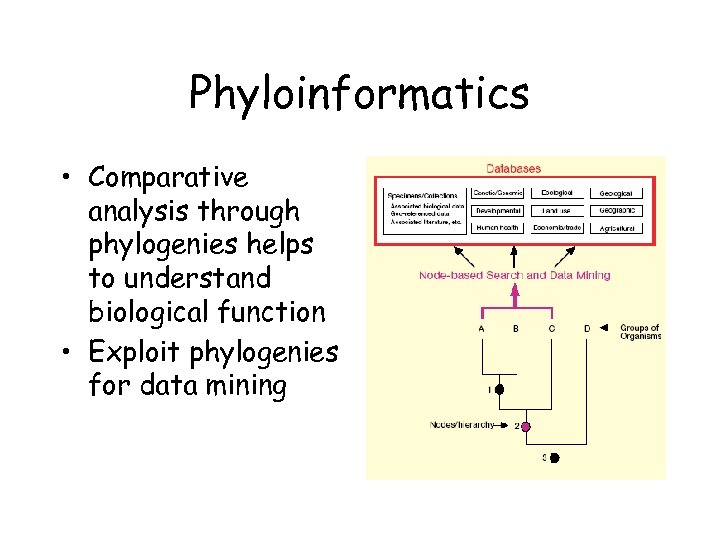
Phyloinformatics • Comparative analysis through phylogenies helps to understand biological function • Exploit phylogenies for data mining
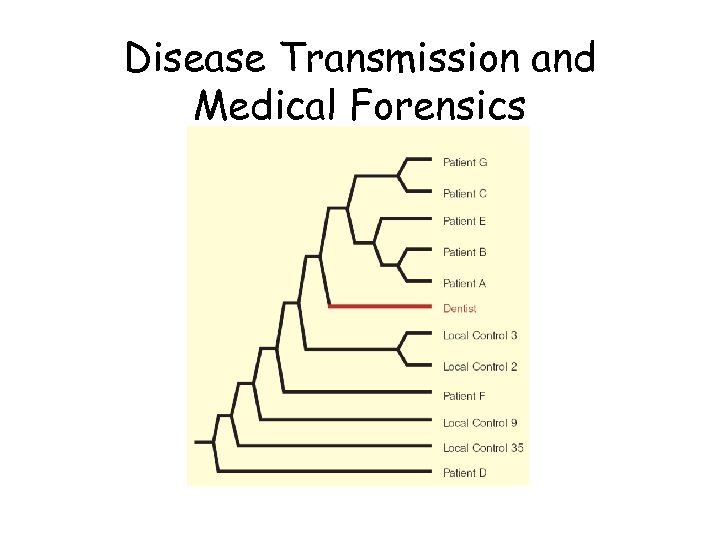
Disease Transmission and Medical Forensics
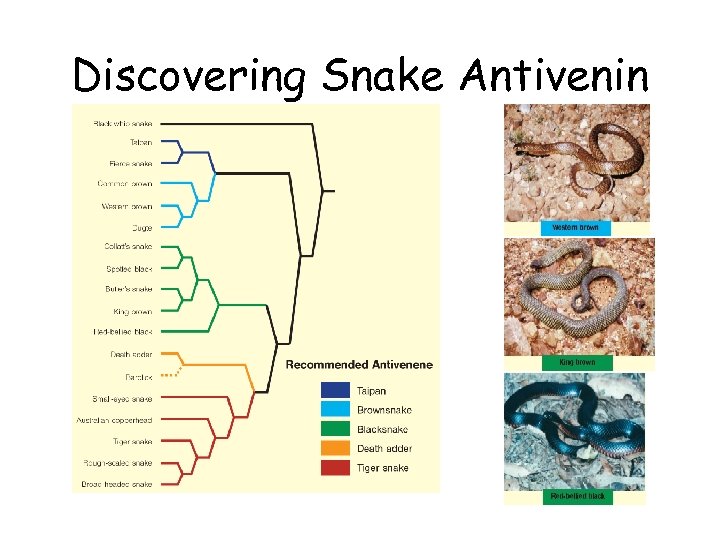
Discovering Snake Antivenin

Methods • Distance-based • Parsimony • Maximum likelihood
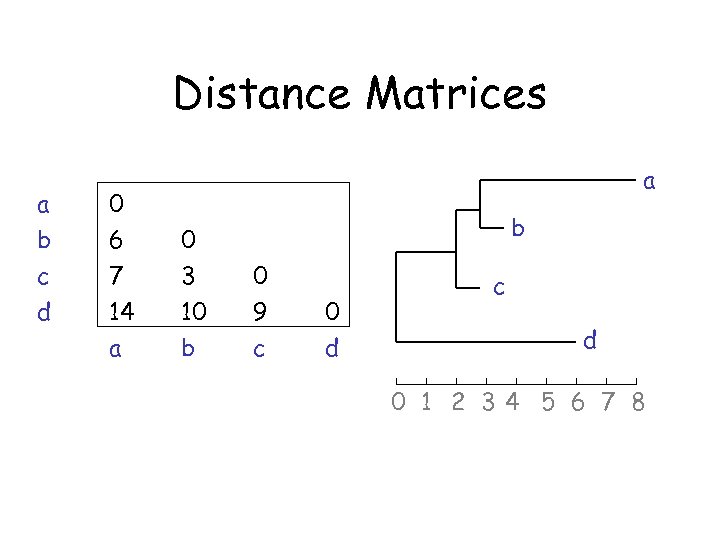
Distance Matrices a b c d 0 6 7 14 a a 0 3 10 b b 0 9 c 0 d c d 0 1 2 34 5 6 7 8
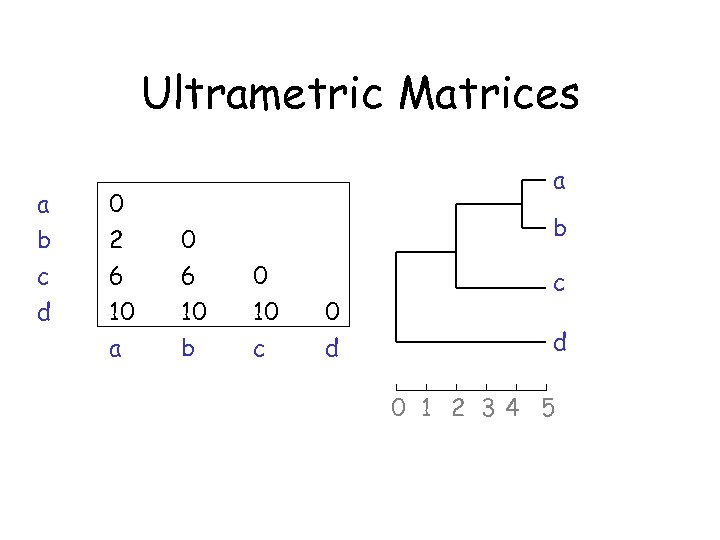
Ultrametric Matrices a b c d 0 2 6 10 a a 0 6 10 b b 0 10 c 0 d c d 0 1 2 34 5

Least Squares Dij = distance between i and j in matrix dij = distance between i and j in tree Objetive: Find tree that minimizes
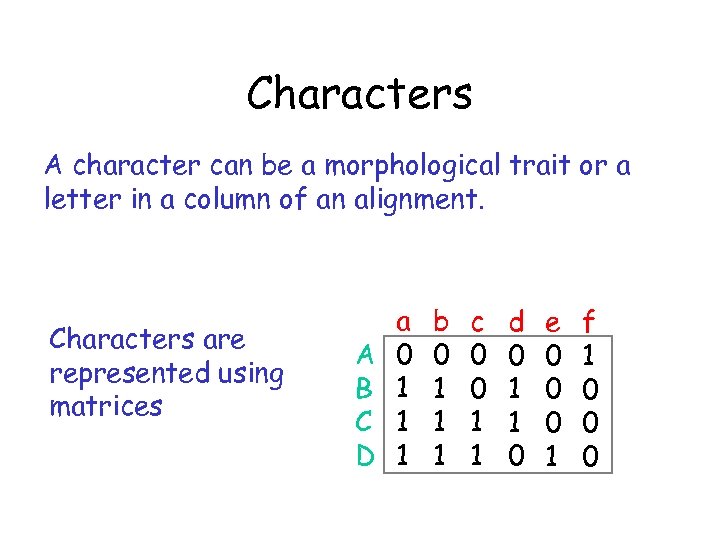
Characters A character can be a morphological trait or a letter in a column of an alignment. Characters are represented using matrices A B C D a 0 1 1 1 b 0 1 1 1 c 0 0 1 1 d 0 1 1 0 e 0 0 0 1 f 1 0 0 0
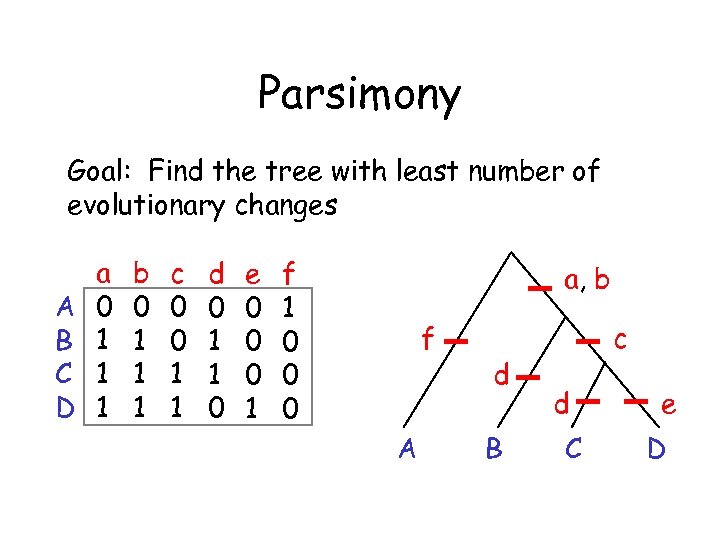
Parsimony Goal: Find the tree with least number of evolutionary changes A B C D a 0 1 1 1 b 0 1 1 1 c 0 0 1 1 d 0 1 1 0 e 0 0 0 1 f 1 0 0 0 a, b f A d B c d C e D

Markov models on trees • Observed: The species labeling the leaves • Hidden: The ancestral states • Transition probabilities: The mutation probabilities • Assumptions: – Only mutations are allowed – Sites are independent – Evolution at each site occurs according to a Markov process
![Models of evolution at a site • Transition probability matrix: M = [mij], i, Models of evolution at a site • Transition probability matrix: M = [mij], i,](https://present5.com/presentation/f89512da60e9532344de5a5183bd65af/image-14.jpg)
Models of evolution at a site • Transition probability matrix: M = [mij], i, j {A, C, T, G} where mij = Prob(i j mutation in 1 time unit) • Different branches of tree may have different lengths
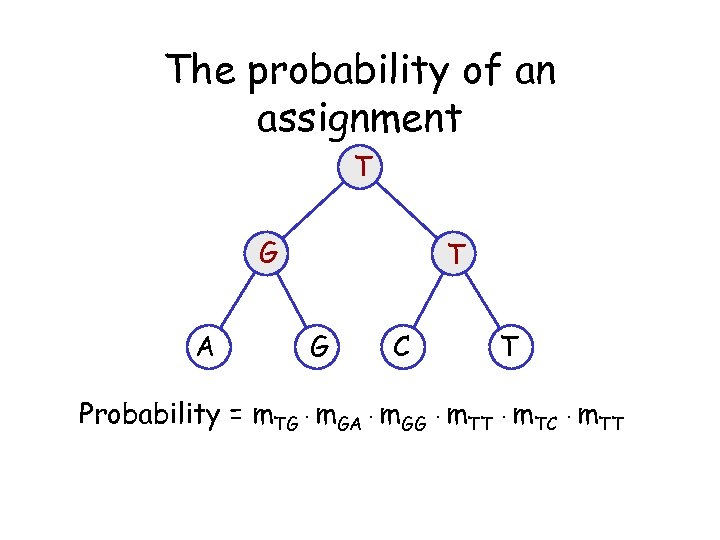
The probability of an assignment T G A T G C T Probability = m. TG · m. GA · m. GG · m. TT · m. TC · m. TT
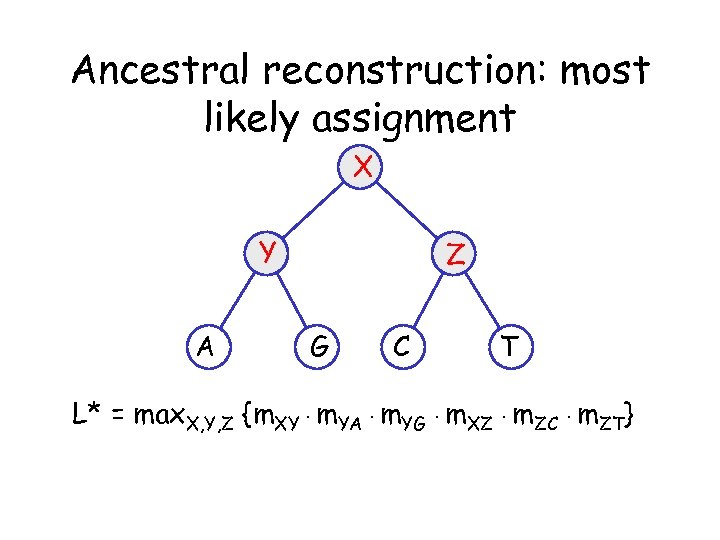
Ancestral reconstruction: most likely assignment X Y A Z G C T L* = max. X, Y, Z {m. XY · m. YA · m. YG · m. XZ · m. ZC · m. ZT}
f89512da60e9532344de5a5183bd65af.ppt