59e97dc19c5eb972af36d2f050eda914.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31


Building J 2 EE Applications Based on Design Patterns with Business Components for Java Olivier LE DIOURIS Principal Product Manager Oracle Corporation

Agenda Ÿ J 2 EE Overview & Challenges Ÿ Design Patterns & Frameworks Ÿ BC 4 J Overview Ÿ Demo Ÿ Summary
What is J 2 EE? Ÿ Java 2 Enterprise Edition Ÿ “The J 2 EE application model defines an architecture for implementing services as multi -tier applications delivering scalability, portability, and manageability. ”
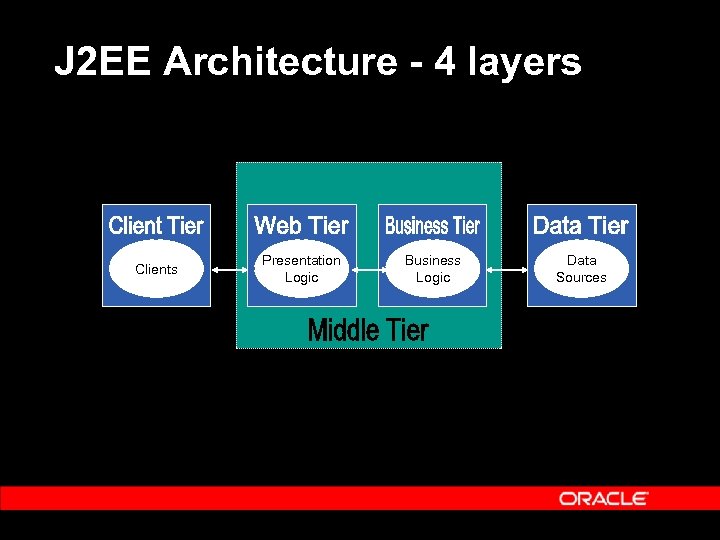
J 2 EE Architecture - 4 layers Clients Presentation Logic Business Logic Data Sources
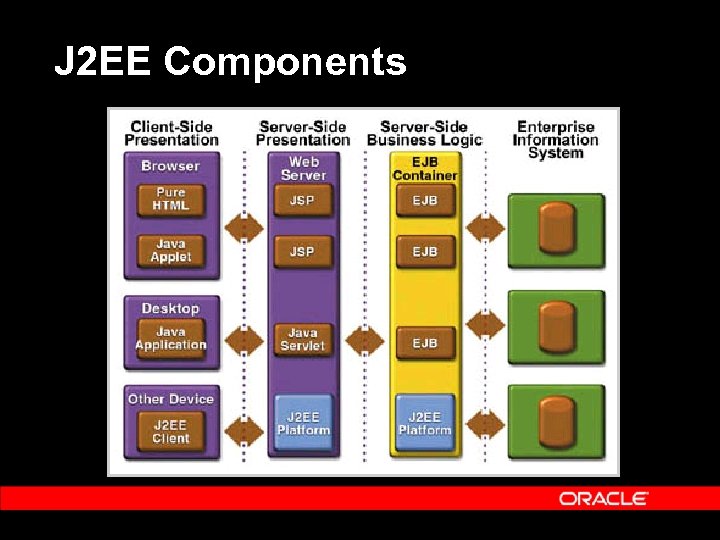
J 2 EE Components
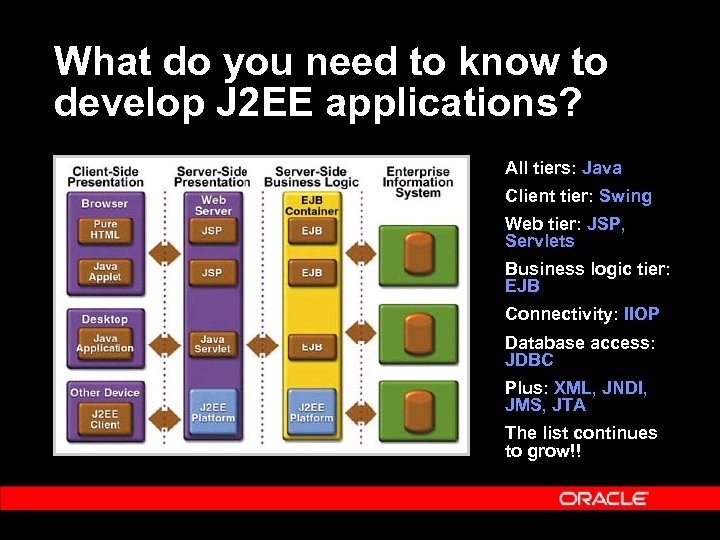
What do you need to know to develop J 2 EE applications? All tiers: Java Client tier: Swing Web tier: JSP, Servlets Business logic tier: EJB Connectivity: IIOP Database access: JDBC Plus: XML, JNDI, JMS, JTA The list continues to grow!!

More Challenges Ÿ Where do I start ? Ÿ Application design complexity – – – How do I represent business entities in the middle -tier? How do I enforce business logic? How do I bind and interface client code? Ÿ How do I keep efficiency

Agenda Ÿ J 2 EE Overview & Challenges Ÿ Design Patterns & Frameworks Ÿ BC 4 J Overview Ÿ Demo Ÿ Summary

Design Patterns Ÿ A design pattern describes a proven solution to a recurring design problem Ÿ Reasons to use Design Patterns: Ÿ They are proven Ÿ They are reusable Source: http: //java. sun. com/j 2 ee/blueprints/design_patterns/index. html
Why Framework? “Large scale development of objectoriented software requires frameworks. It is important to have a framework, so that every time the design requires two objects to interact, a developer does not have to come up with a whole new notion of how the interaction works out. ” Section 10. 2. 2. 2, Page 253
Benefits of Framework Ÿ Better code Ÿ Simpler code Ÿ Better performing Ÿ Less complex
Business Component for Java (BC 4 J) Ÿ BC 4 J – A J 2 EE Framework that simplifies Development, Customization and Deployment of J 2 EE Applications Ÿ Implements SUN’s Design Patterns Ÿ Standard – Java and XML Ÿ Server Side Framework with Client Binding Ÿ Based on Oracle’s Developers experience
Major Benefits of BC 4 J Ÿ Simplifying Server Coding Ÿ Simplifying Client Binding Ÿ Simplifies O/R Mapping Ÿ Improve Network using Caching Ÿ Hides Complex Infrastructure
J 2 EE Framework – BC 4 J Simplifies and optimizes O/R mapping Simplifies and optimizes binding of GUI to logic Flexible Deployment

Agenda Ÿ J 2 EE Overview & Challenges Ÿ Design Patterns & Frameworks Ÿ BC 4 J Overview Ÿ Demo Ÿ Summary
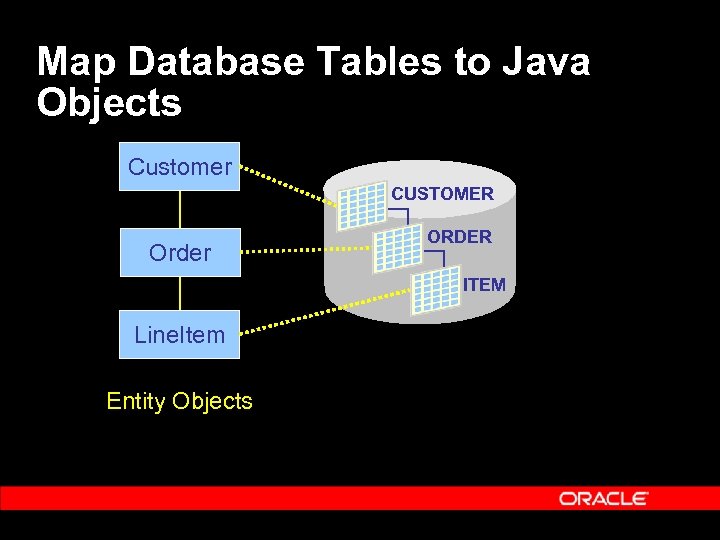
Map Database Tables to Java Objects Customer CUSTOMER Order ORDER ITEM Line. Item Entity Objects
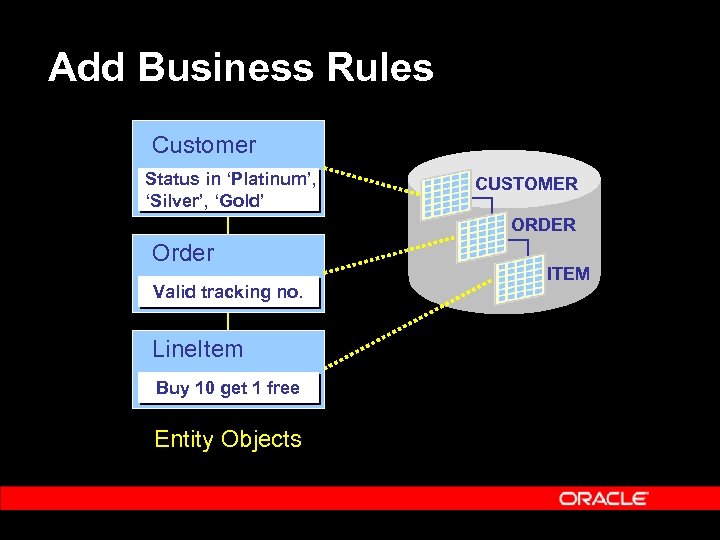
Add Business Rules Customer Status in ‘Platinum’, ‘Silver’, ‘Gold’ CUSTOMER ORDER Order Valid tracking no. Line. Item Buy 10 get 1 free Entity Objects ITEM
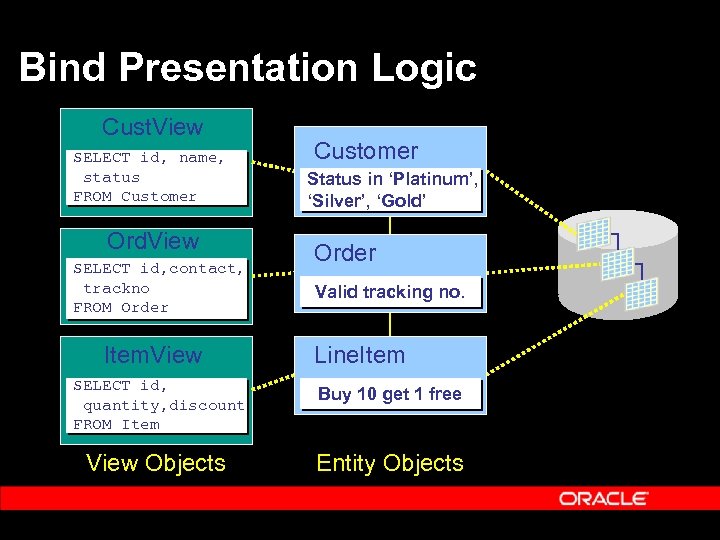
Bind Presentation Logic Cust. View SELECT id, name, status FROM Customer Ord. View SELECT id, contact, trackno FROM Order Item. View Customer Status in ‘Platinum’, ‘Silver’, ‘Gold’ Order Valid tracking no. Line. Item SELECT id, quantity, discount FROM Item Buy 10 get 1 free View Objects Entity Objects
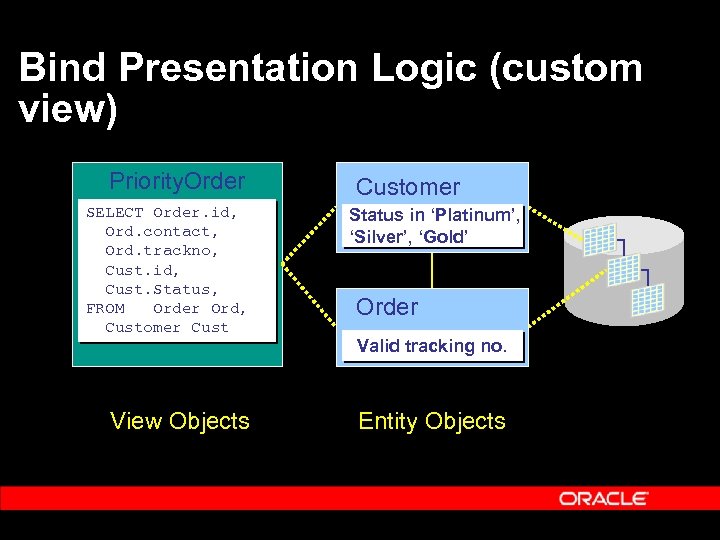
Bind Presentation Logic (custom view) Priority. Order SELECT Order. id, Ord. contact, Ord. trackno, Cust. id, Cust. Status, FROM Order Ord, Customer Cust View Objects Customer Status in ‘Platinum’, ‘Silver’, ‘Gold’ Order Valid tracking no. Entity Objects
Middle Tier Caching Ÿ Pulls data from database into middle tier and preserves relationships between data Ÿ Cache synchronizes data from different view objects that reference that same entity object. Ÿ Reduces round trips to database Ÿ Control synchronization and locking modes
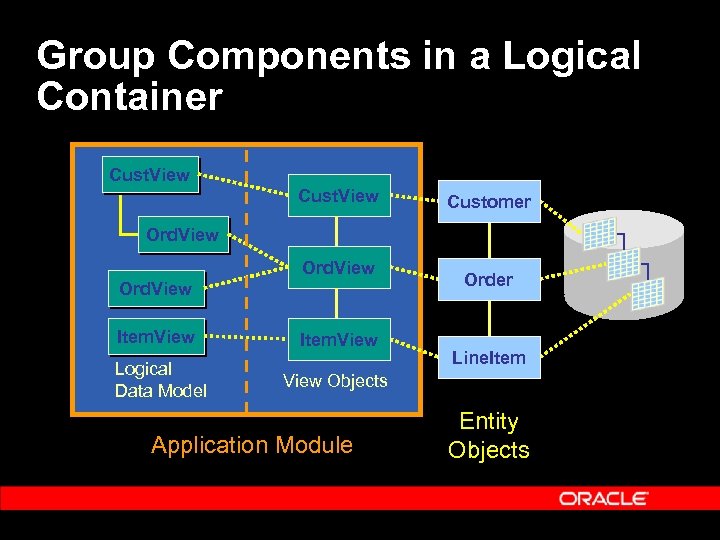
Group Components in a Logical Container Cust. View Customer Ord. View Item. View Logical Data Model Item. View Order Line. Item View Objects Application Module Entity Objects
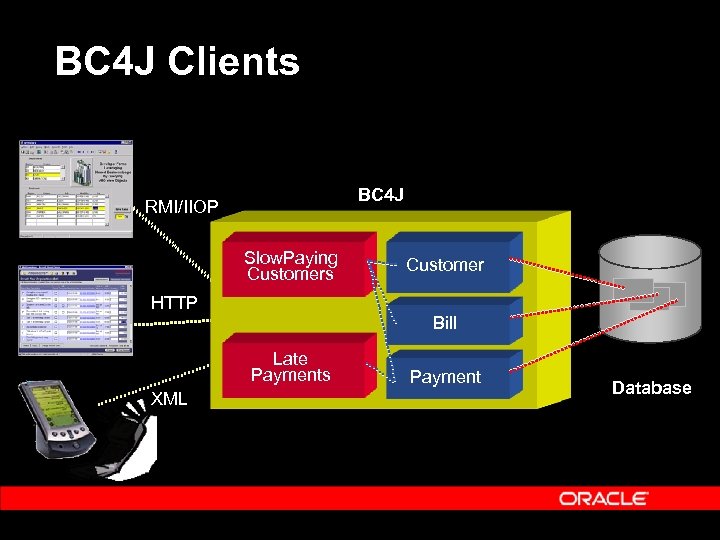
BC 4 J Clients BC 4 J RMI/IIOP Slow. Paying Customers HTTP Bill Late Payments XML Customer Payment Database

Building UI for BC 4 J Ÿ HTML UI – JSP Tag library for BC 4 J Ÿ Java UI – JClient – Swing components with BC 4 J connectivity Ÿ XML UI – JSP – – XML messaging from/to BC 4 J XSQL Servlet interface to BC 4 J
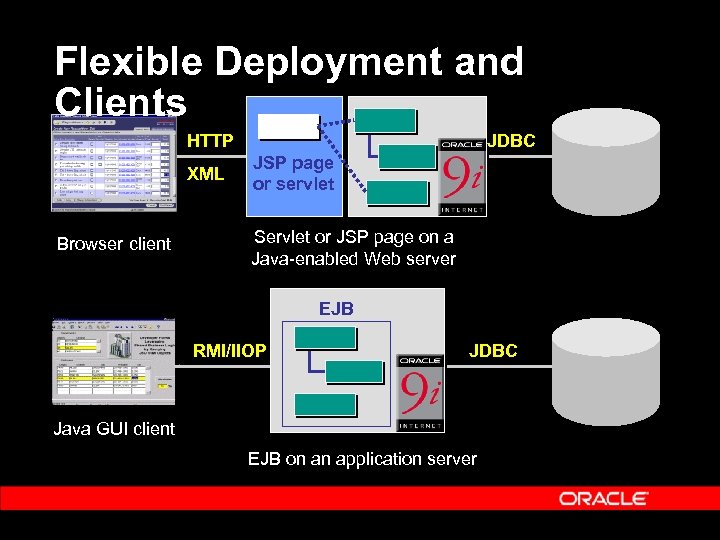
Flexible Deployment and Clients HTTP XML Browser client JDBC JSP page or servlet Servlet or JSP page on a Java-enabled Web server EJB RMI/IIOP JDBC Java GUI client EJB on an application server

Best Practice Steps Our Apps Teams Follow Ÿ Design Application Business Model – Using UML Class Diagrams Ÿ Implement Application Business Model – Using of BC 4 J Framework Ÿ Identify Application Task – Using UML Use Cases Ÿ Implement Application Data Model for the Task – Using BC 4 J Framework Ÿ Bind Interfaces to Application Data Model – Swing, JSP, or XML Ÿ Test Interface and Select Deployment Target – Decide to Target Web Tier or EJB Tier

D E M O N S T R A T I O N BC 4 J

Agenda Ÿ J 2 EE Overview & Challenges Ÿ Design Patterns & Frameworks Ÿ BC 4 J Overview Ÿ Demo Ÿ Summary

BC 4 J = Easier J 2 EE Ÿ J 2 EE Can be complex Ÿ BC 4 J Makes J 2 EE Simple Ÿ BC 4 J Is standard based Java+XML Ÿ BC 4 J is part of JDeveloper

Where to get more Information http: //otn. oracle. com http: //technet. oracle. com Ÿ Complete technical resource for developers Ÿ Software, samples, & code downloads Ÿ Discussion forums Ÿ Whitepapers, technical information, documentation http: //www. oracle. com Product news, Press Release, customer stories

59e97dc19c5eb972af36d2f050eda914.ppt